Quantifying method for oligonucleotide microarray
A technology of nucleic acid and target nucleic acid, which is applied in the system field of various nucleic acids, and can solve the problem of limited number of fluorescent dyes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
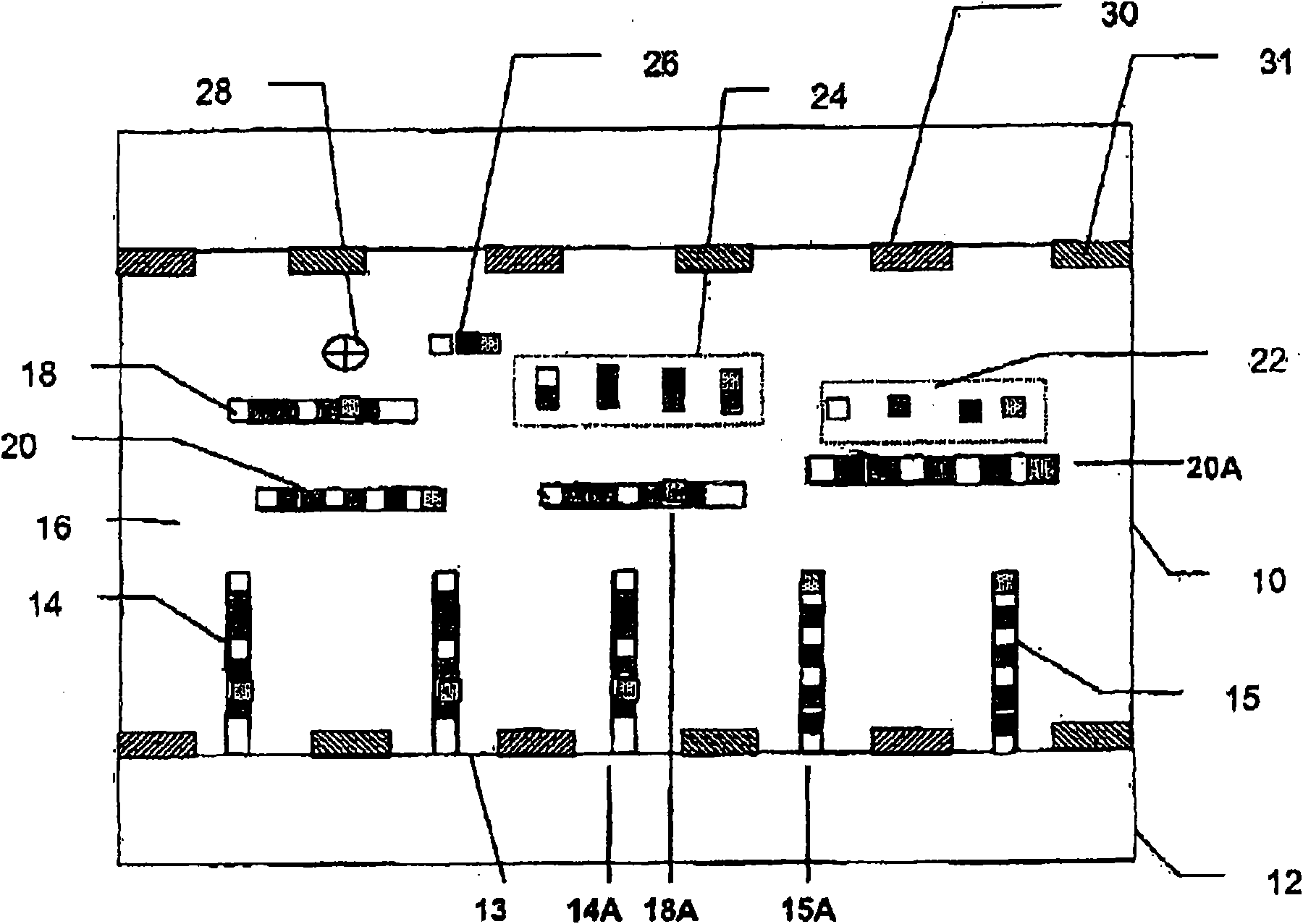
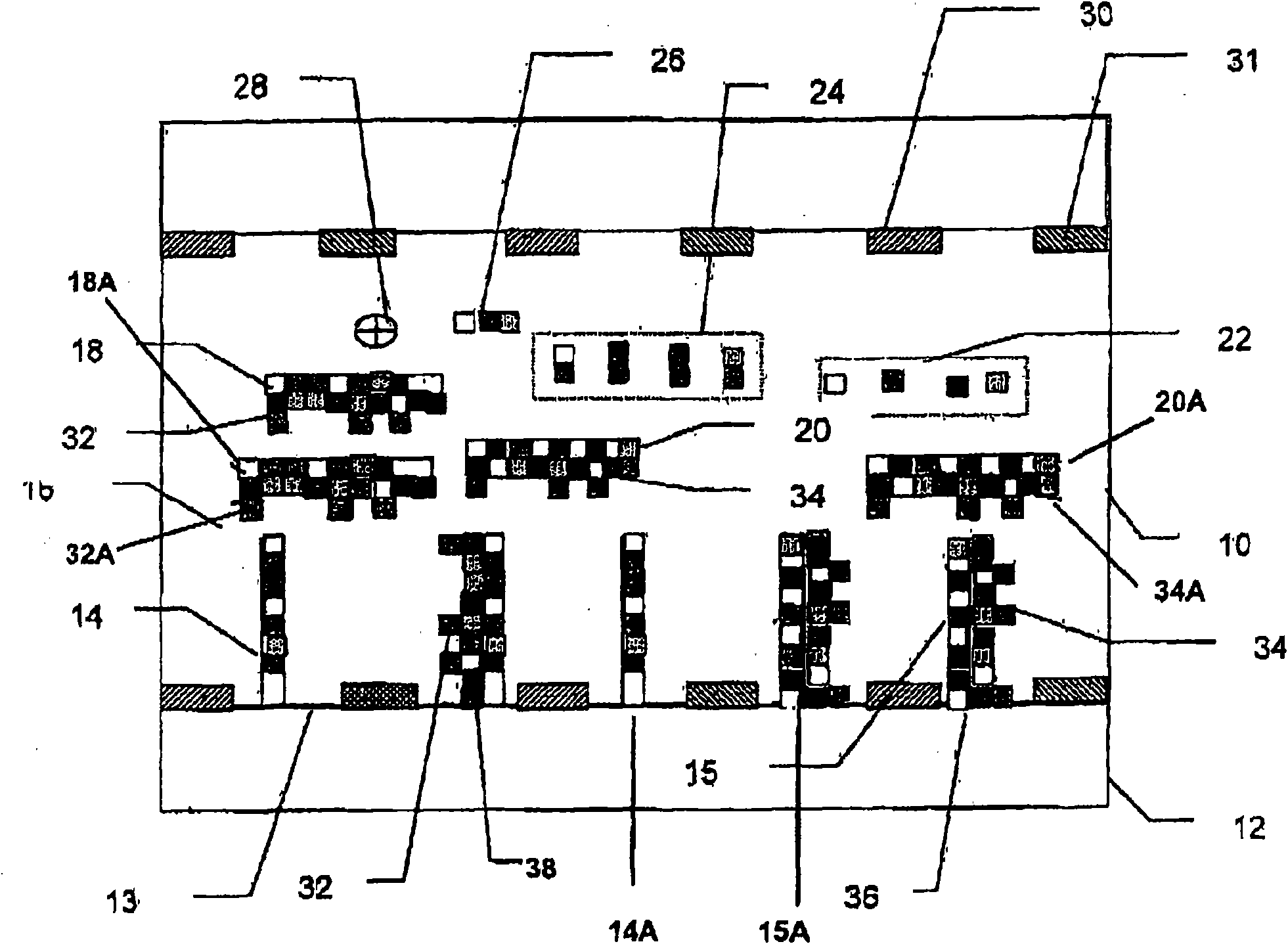
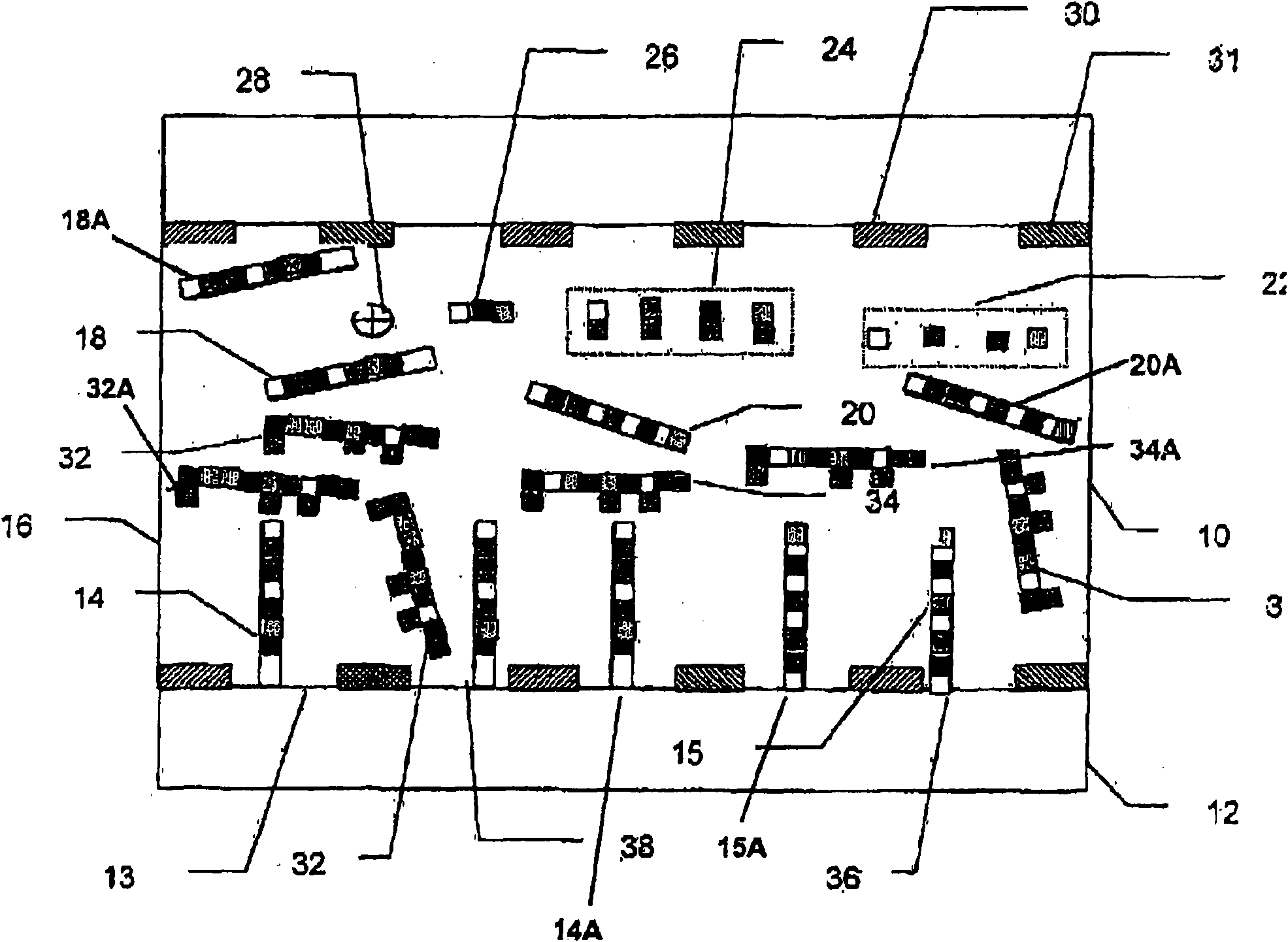
[0147] Quantified Microarray of Twelve Bacteria
[0148] The target panel included twelve different types of cells and two internal nucleic acid controls. Internal nucleic acid control A will be a known low concentration and internal nucleic acid control B will be a known high concentration. Primer sets included forward and reverse primers for all twelve bacterial species as well as internal nucleic acid controls A and B. The probe set will include probes for all twelve bacterial species as well as internal nucleic acid controls A and B. For example, target probe A is specific for target nucleic acid A, and target probe B is specific for target nucleic acid B.
[0149] Typically, there should be no cross-reactivity between probes for all twelve bacterial species and probes for internal nucleic acid controls A and B. Furthermore, typically there should be no cross-reactivity between the internal nucleic acid control probes A and B and the twelve target nucleic acids. Intern...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com