Methods of cutting or forming cavities in a substrate for use in making optical films, components or wave guides
a technology of optical film and substrate, applied in the field of cutting or forming cavities in the substrate for use in making optical films, components or wave guides, can solve the problems of short useful life, high cost and expense of cutting or forming cavities of certain types of optical elements, and the difficulty of spinning tools needed to make geometric shapes such as these, so as to achieve the effect of substantially reducing the length and width of the optical substra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
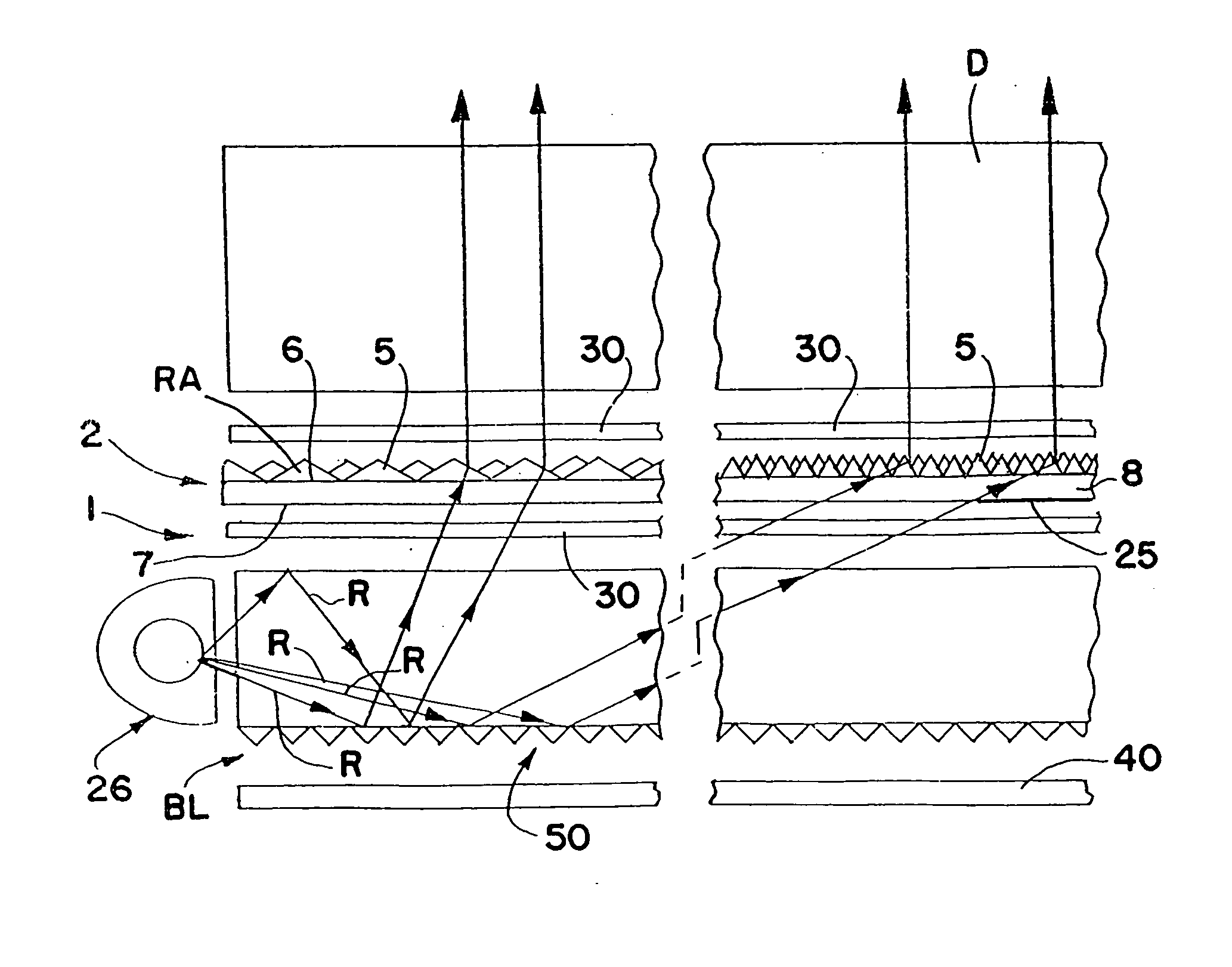
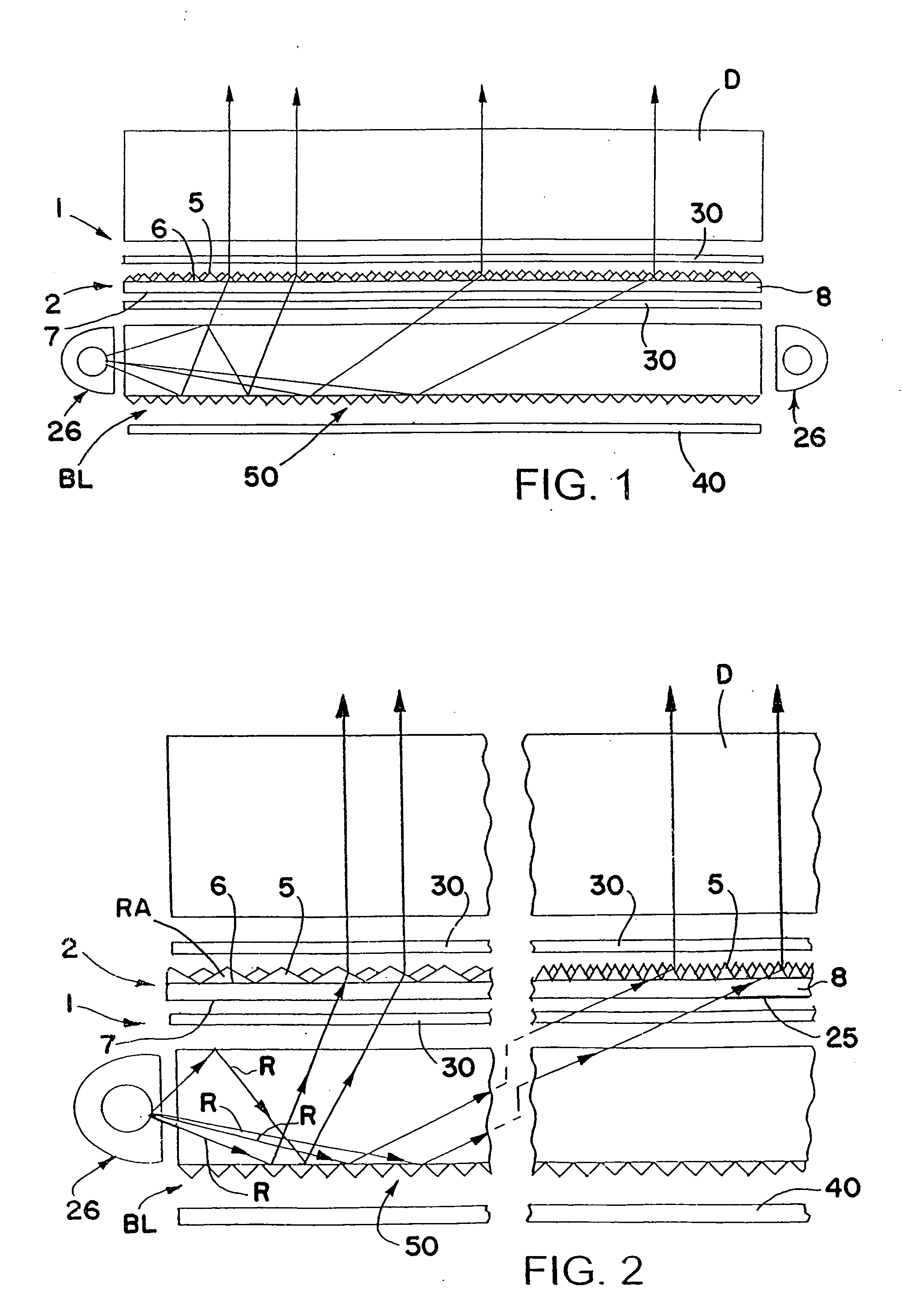
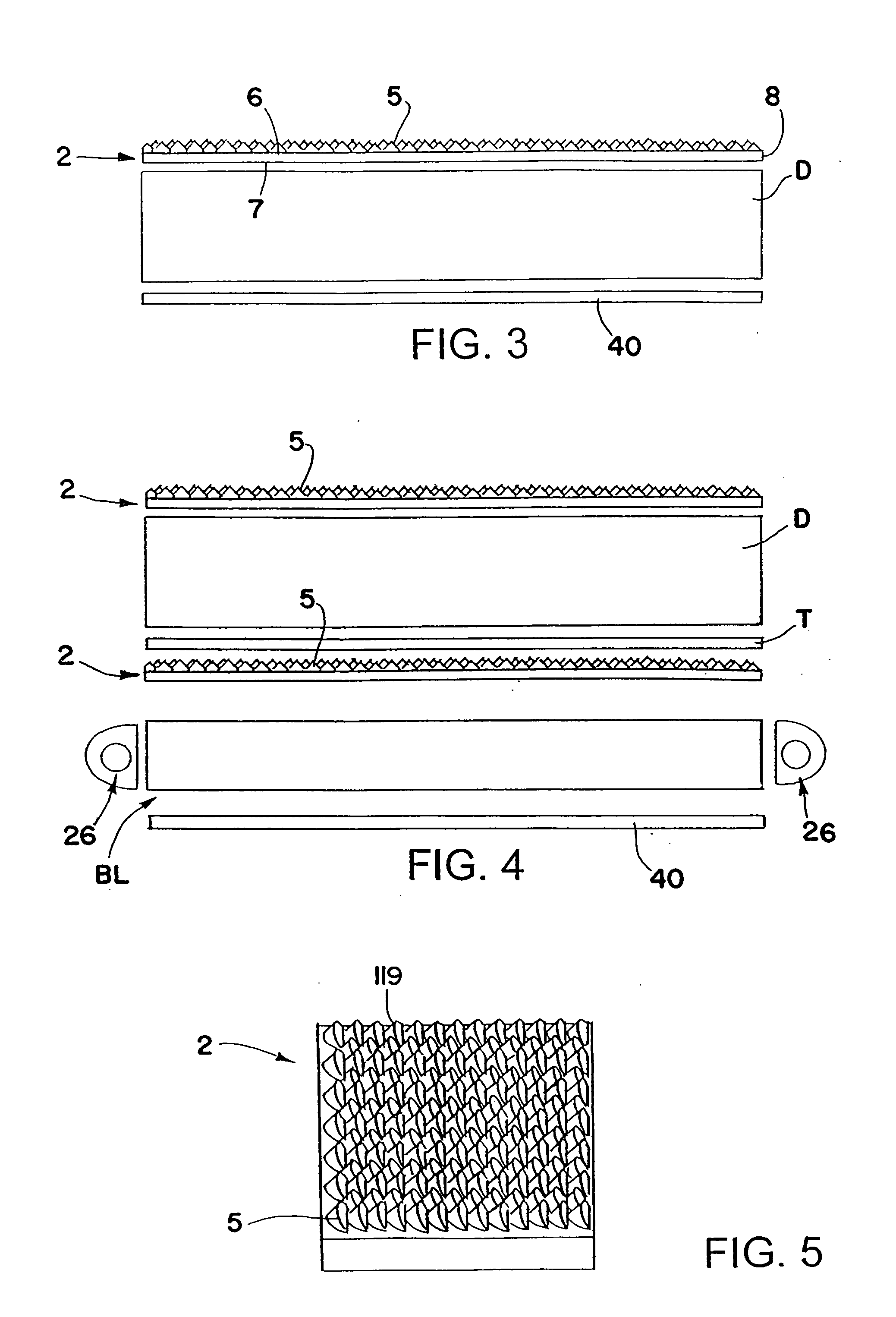
[0041]FIGS. 1 and 2 schematically show one form of light redirecting film system 1 in accordance with this invention including a light redirecting film 2 that redistributes more of the light emitted by a backlight BL or other light source toward a direction more normal to the surface of the film. Film 2 may be used to redistribute light within a desired viewing angle from almost any light source for lighting, for example, a display D such as a liquid crystal display, used in laptop computers, word processors, avionic displays, cell phones, PDAs and the like, to make the displays brighter. The liquid crystal display can be any type including a transmissive liquid crystal display as schematically shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, a reflective liquid crystal display as schematically shown in FIG. 3 and a transflective liquid crystal display as schematically shown in FIG. 4.
[0042] The reflective liquid crystal display D shown in FIG. 3 includes a back reflector 40 adjacent the back side for refl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com