Database system and a method of data retrieval from the system
a database and system technology, applied in the field of database systems and data retrieval methods, can solve the problems of difficult for users to recognize all these facts and retrieve accurate information, and it is difficult for users to search the db system. to achieve the effect of easy search of the db system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
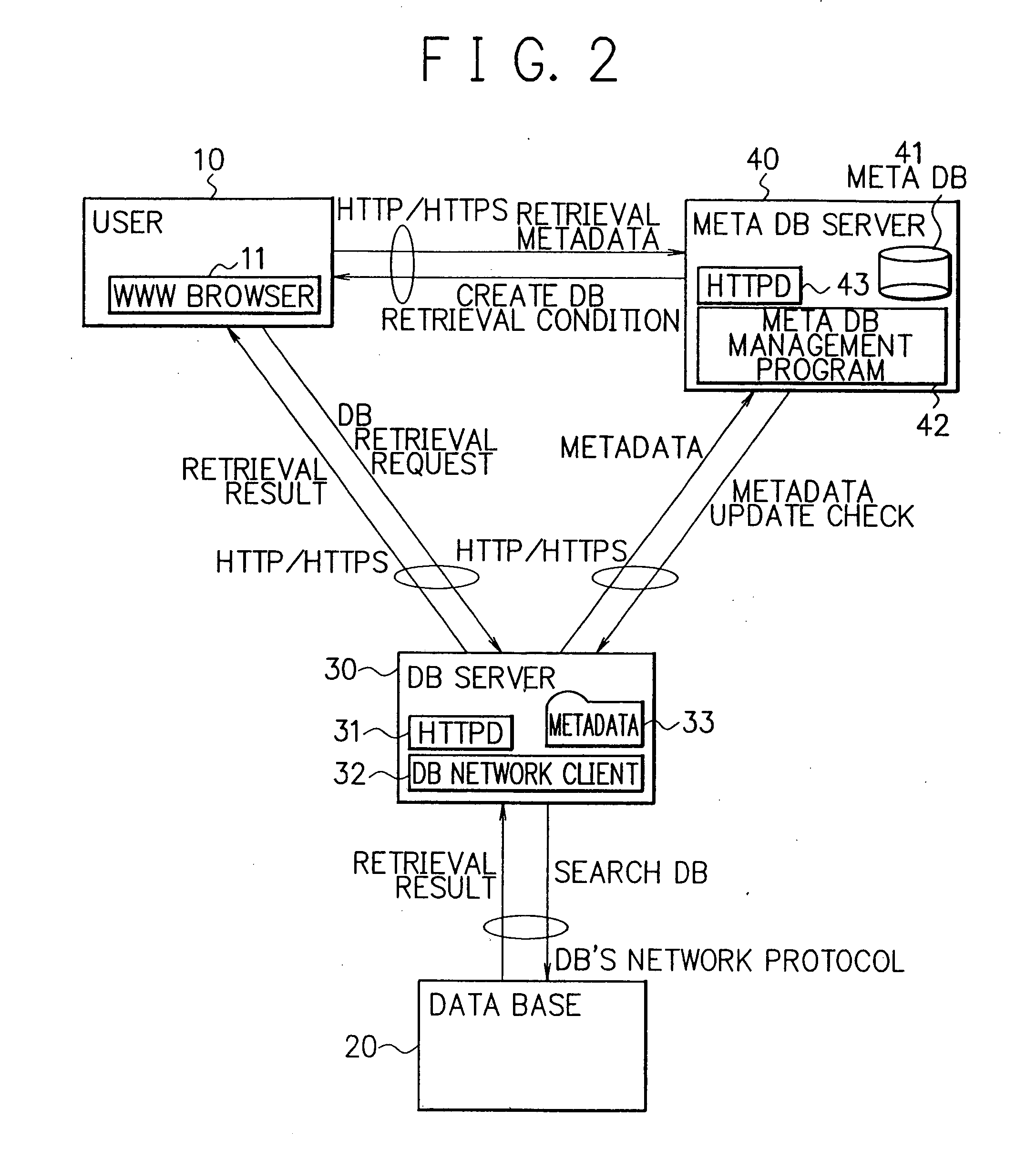
[0065]FIG. 2 is a schematic block diagram showing the arrangement of a database system according to the first embodiment, and FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing software and hardware images of the database search system.
[0066] Referring to FIG. 2, reference numeral 10 denotes a user terminal which is installed with a WWW (World Wide Web) browser 11, and which inputs a keyword for search, issues a retrieval request, displays a retrieval result, and so forth on the WWW browser 11. A search for a meta DB (to be described later) or for real data is designated on this WWW browser 11. The WWW browser 11 comprises a GUI module 11a and retrieval request transfer module 11b, as shown in FIG. 3, allows the user to make various operations for search using the GUI module 11a, and transfers a retrieval request signal using the retrieval request transfer module 11b.
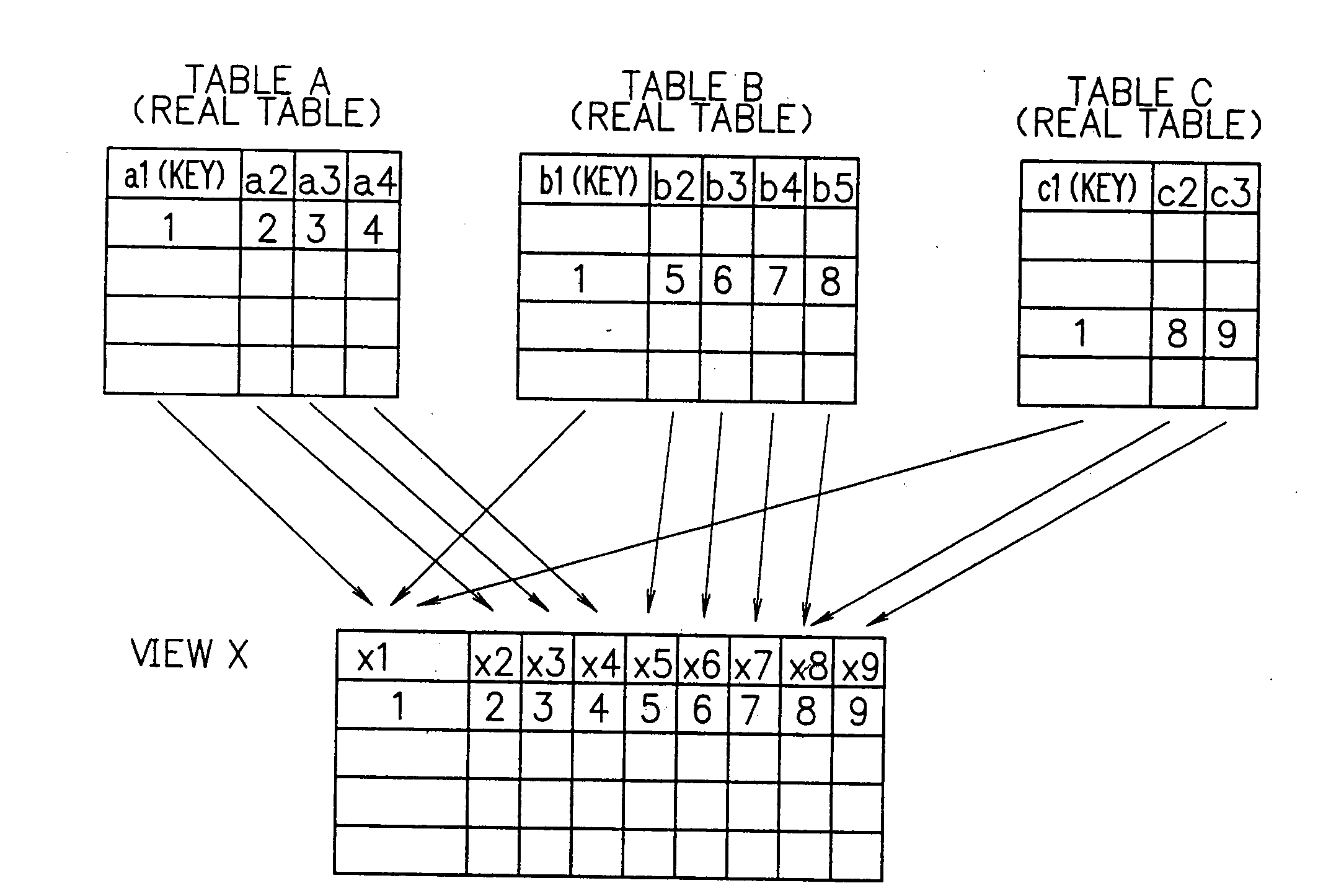
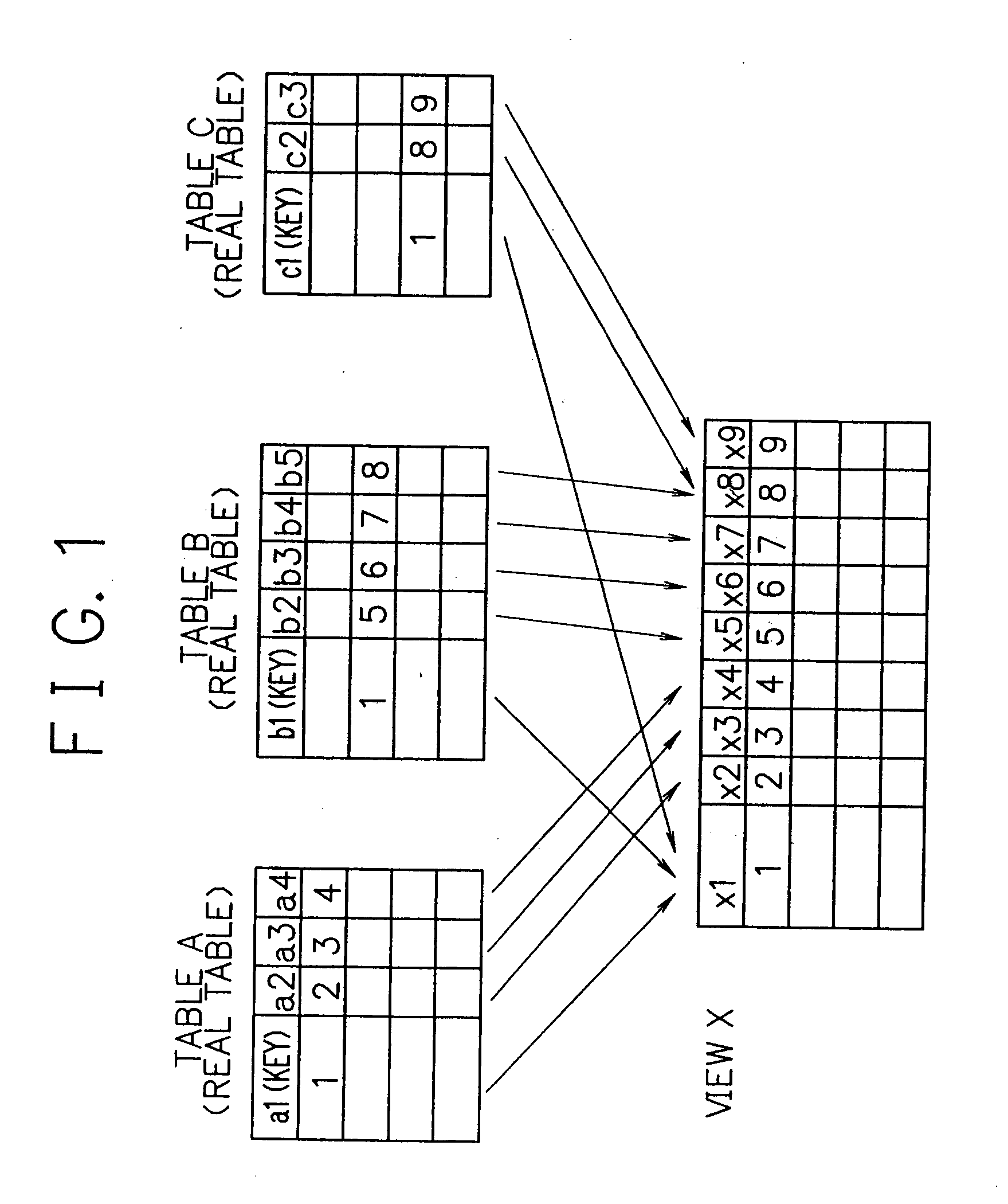
[0067] Reference numeral 20 denotes a database (DB) which stores actual data. At least one DB 20 is present on the network. A platfo...
second embodiment
[0127] The second embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0128]FIG. 9 is a block diagram showing an example of the arrangement of a database system according to this embodiment. The database system of this embodiment shown in FIG. 9 can be used alone or may be combined with the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2.
[0129] The combination with the first embodiment can be implemented when the DB server 30 shown in FIG. 2 comprises functional blocks bounded by the one-dashed chain line in FIG. 9 other than the database 20. On the other hand, the DB server 30 in FIG. 2 may comprise only a search engine 60 and joined table generation means 65 shown in FIG. 9, and the meta DB server 40 may comprise a metadata management means 69 and metadata storage means 70 shown in FIG. 9.
[0130] When the database system of this embodiment is combined with the first embodiment, in metadata to be used, other joinable DB names (JOINABLE) are ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com