Taggant fibers
a technology of taggant fibers and fibers, applied in the field of taggant fibers, can solve the problems of limited number of polymer domains available for arrangement, combination, and/or modification to make different patterns, and achieve the effects of less noticeable use, less likely to degrade or interfere with performance, and low cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
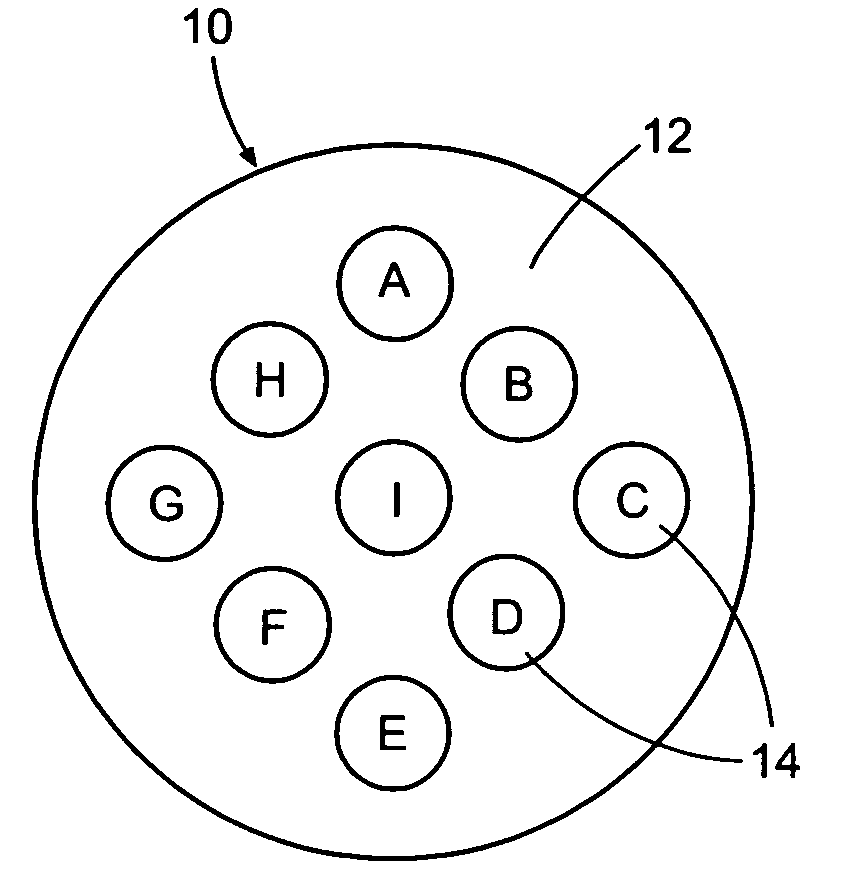
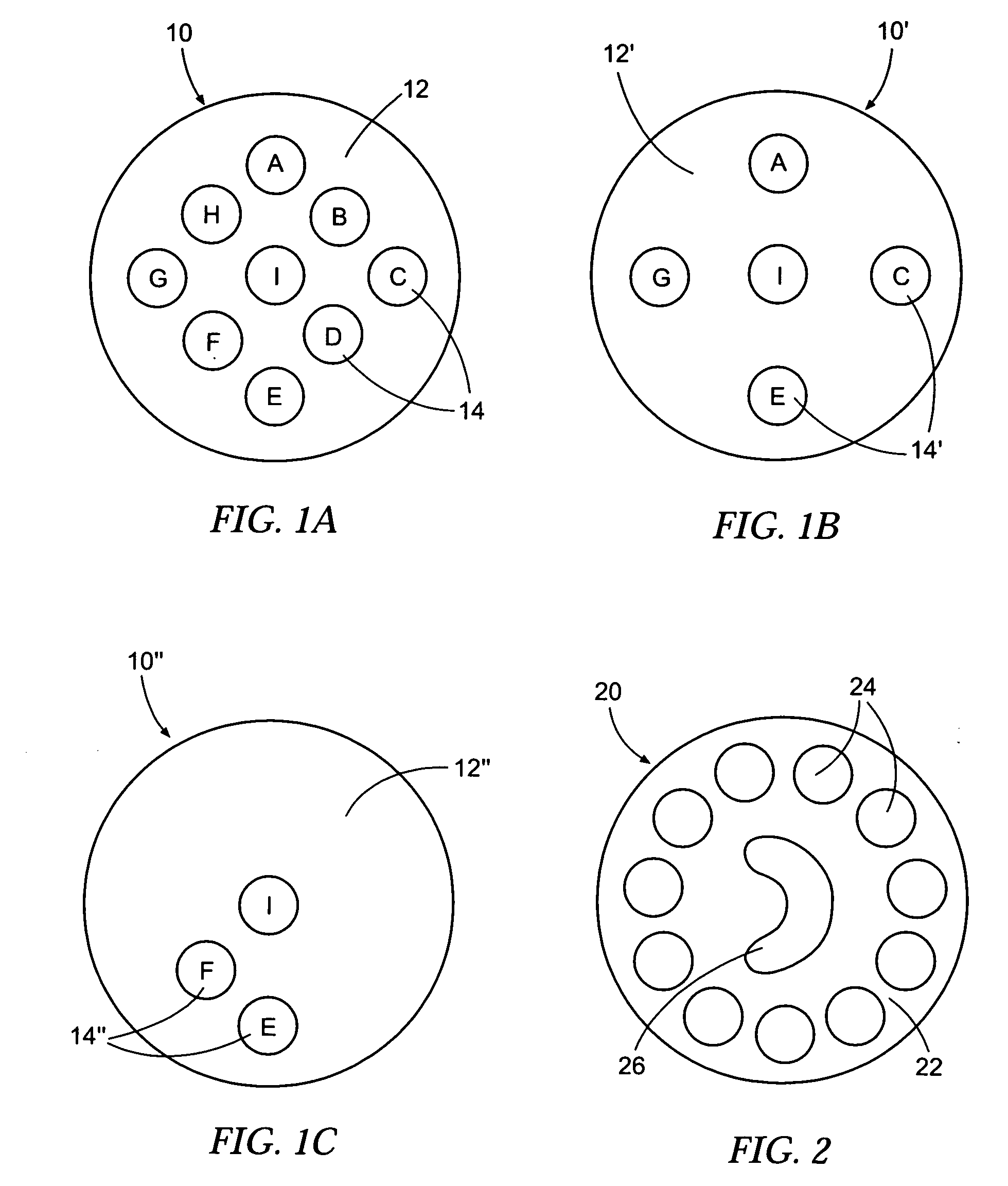
[0063] In a multicomponent fiber spinning apparatus as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,361,736, which is incorporated by reference in its entirety, distribution plates and metering plates were formed so as to produce a round cross section fiber with twelve round “island” polymer domains in a “sea” polymer domain, said twelve island domains positioned around the perimeter of the fiber and surrounding a central core comprising an additional domain of the “island” polymer, said core being predominantly circular but having a substantial indentation as well as a fully-enclosed domain comprising the “sea” polymer, such that the shaped core resembled a “Pac-Man” shape similar to that of the computer game character. Plasticized polyvinyl alcohol was extruded through the distribution plate channels to form the “sea” polymer domains, and polylactic acid was extruded through the distribution plates to form the “island” polymer domains. The fiber was melt extruded through 175 round-hole spinneret ...
example 2
[0064] In the same spinning apparatus as used in Example 1, a single distribution plate was replaced by a new distribution plate that prevented the “island” polymer from flowing into position for three of the twelve circumferential islands formed in the fiber of Example 1. In all other respects, the production of the fiber was identical to that of the fiber of Example 1. The resulting fiber's cross section had the same shaped core domain, and had “island” polymer domains in the same positions as in Example 1, in the case of only nine of the twelve “islands,” whereas only “sea” polymer was present where the missing three “islands” appeared in the fiber of Example 1. This fiber was also subsequently cut into short lengths and adhered to products, where they were analyzed by the same machine vision system, which was able to distinguish the cross section of these fibers from those of Example 1 by virtue of the number and position of the missing islands.
example 3
[0065] The fibers of Examples 1 and 2 were alternately processed with a step that exposed the fibers to water, which dissolved and removed the polyvinyl alcohol “sea” component. As a result, the twelve and nine (respectively) “islands” were dissociated from the shaped core, and the “eye” of the shaped core was made hollow. Without the association of the twelve or nine (respectively) islands with the core, the fibers lost their ability to be distinguished by the machine vision system.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| physical characteristic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com