Cooling of extruded and compression molded materials
a technology of applied in the field of cooling extruded and molded materials, can solve the problems of reducing the supply of wood in the world's forests for construction and other purposes, increasing the cost of wood, and retaining moisture, so as to improve the structural, physical and aesthetic characteristics, the effect of efficient cooling of the manufactured product or articl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
)
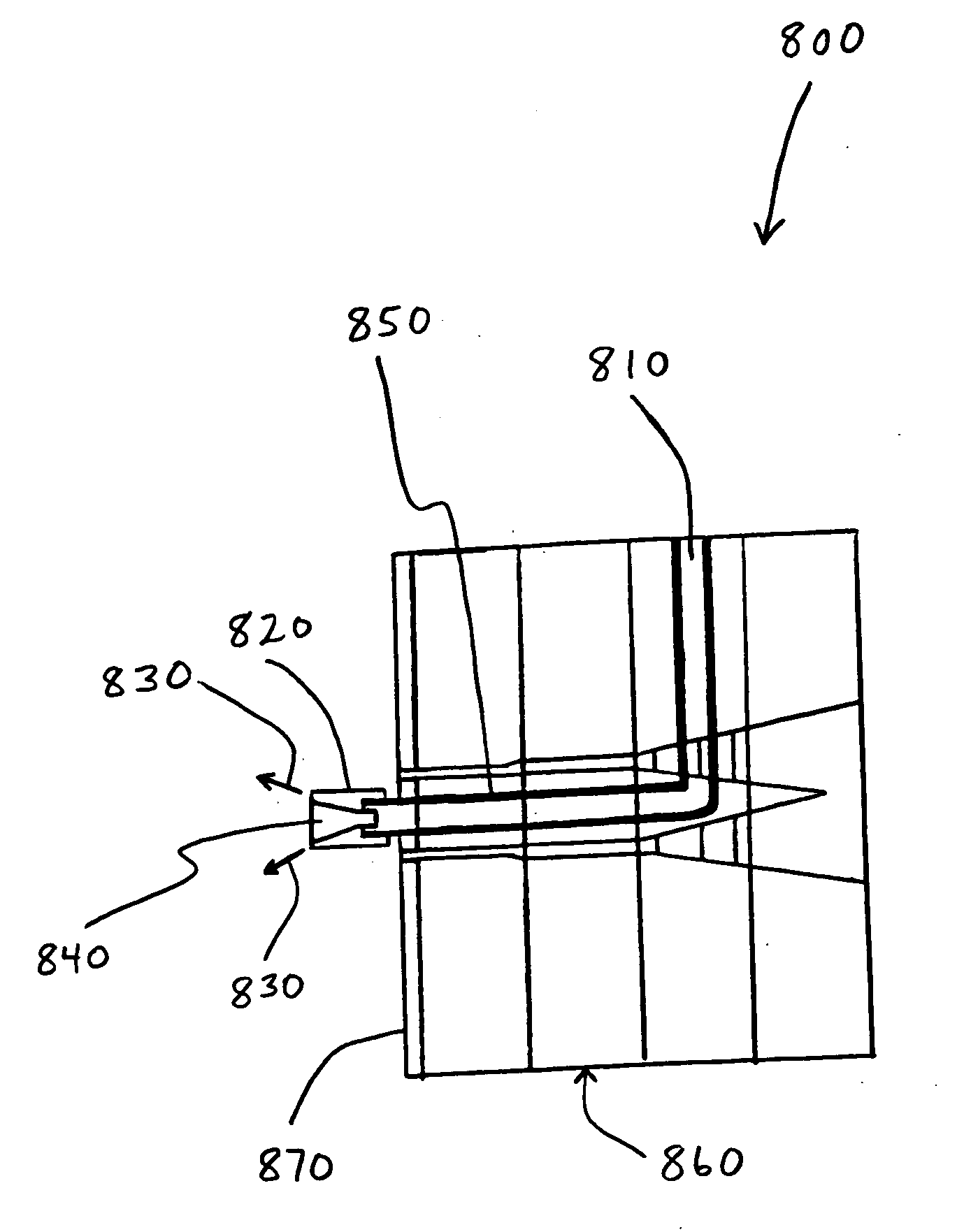
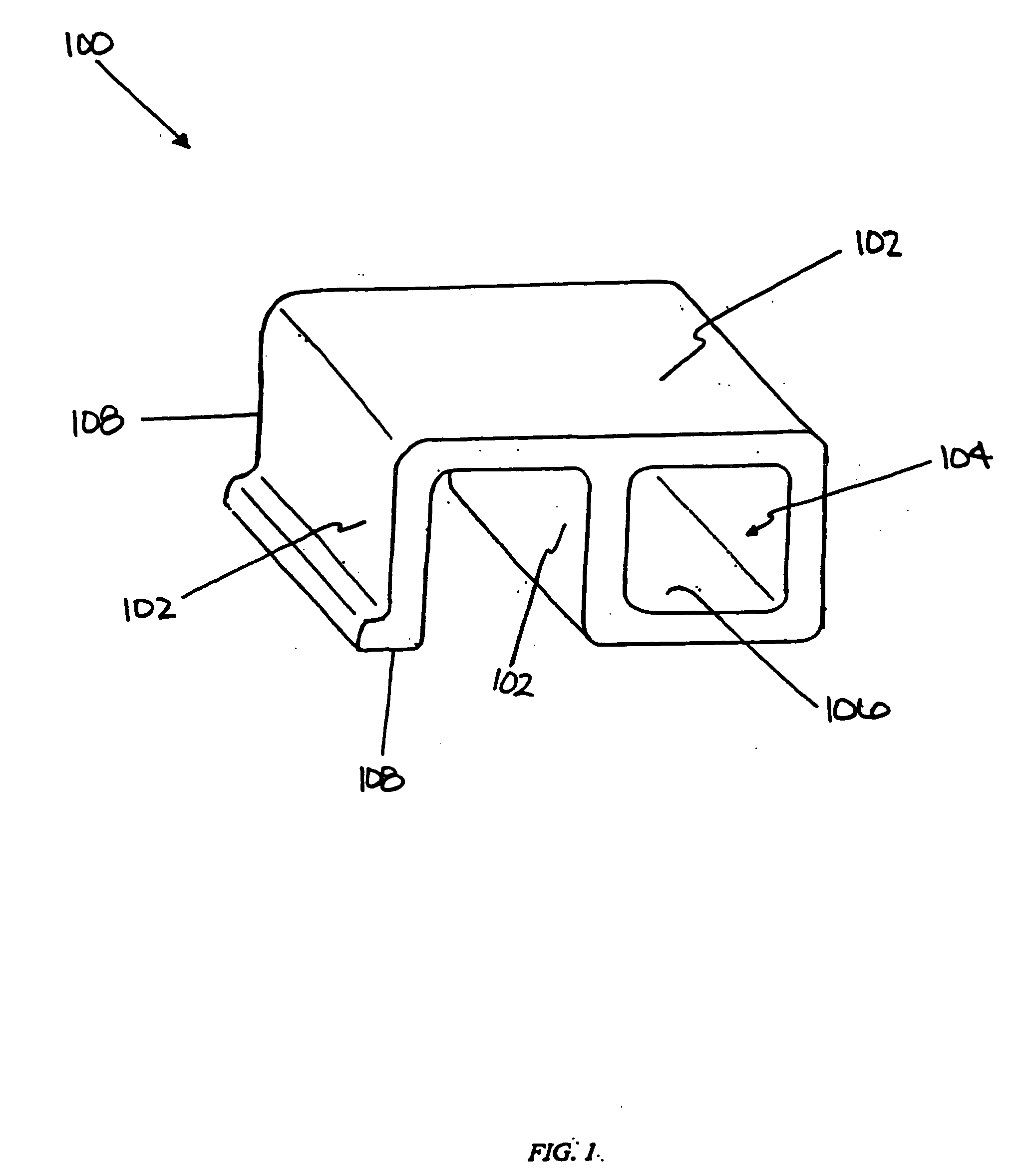
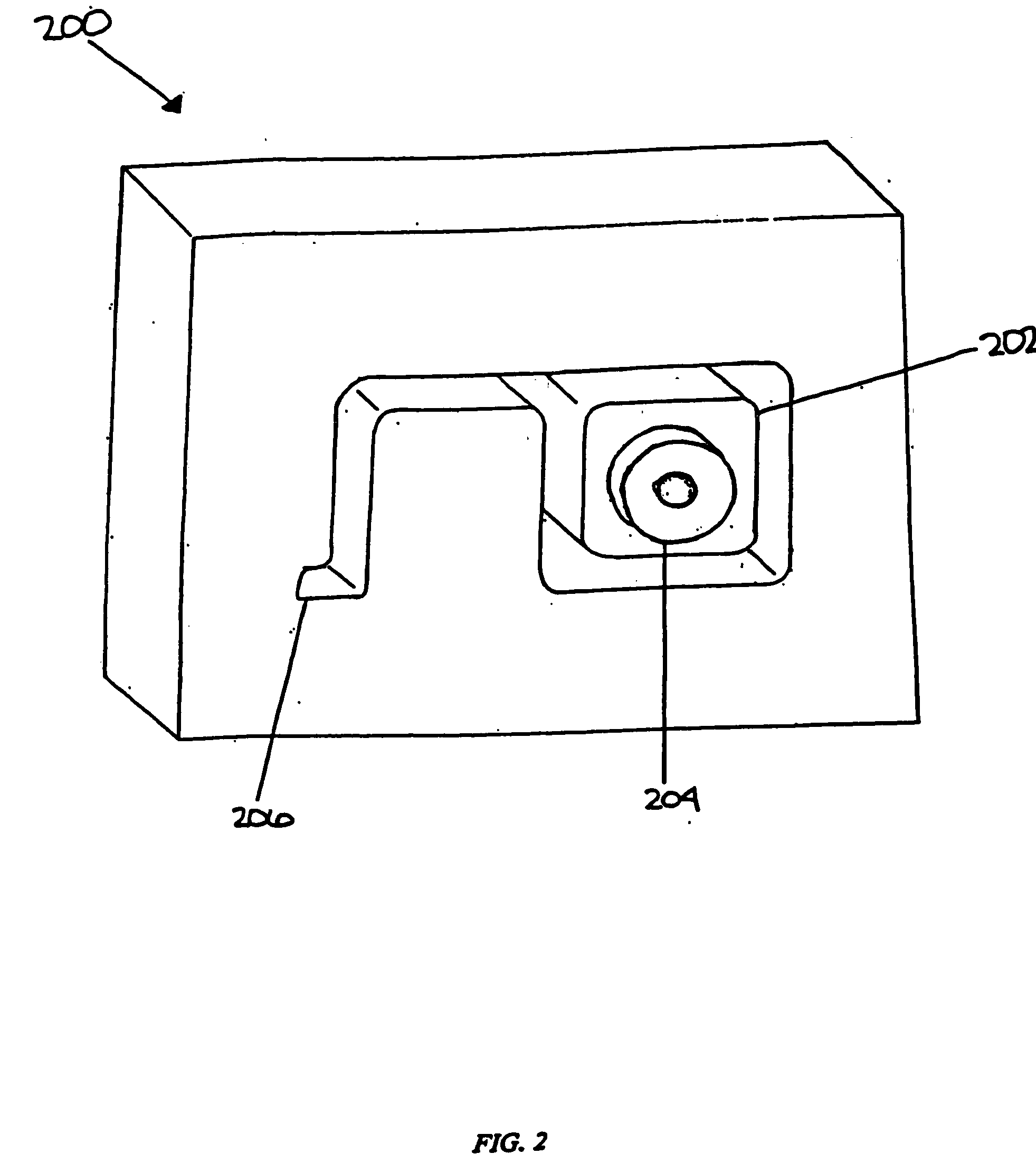
[0019] The present invention is directed to a system and method for cooling manufactured articles or products. It is not intended to limit the present invention to particular manufacturing techniques or particular materials. The present invention may be used to cool articles or products made by variety of different manufacturing techniques. Examples of manufacturing techniques that may utilize the present invention include, but are not limited to, extrusion (including co-extrusion), compression molding, injection molding, and other known, similar, or conventional techniques for manufacturing products or articles from plastic, wood, metal, mixtures of these materials, or other materials used to make products.
[0020] The present invention is particularly useful for cooling plastics, polymers, and cellulosic / polymer composite materials that have been extruded or molded. The materials that may be used to make cellulosic / polymer composites include, but are not limited to, cellulosic fil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com