VEGF-conjugate combined methods for tumor vasculature targeting and tumor treatment
a combined method and tumor vasculature technology, applied in the direction of immunoglobulins, peptides, drugs against animals/humans, etc., can solve the problems of cell death and tumor necrosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
A Murine Model for Antibody-Directed Targeting of Vascular Endothelial Cells in Solid Tumors
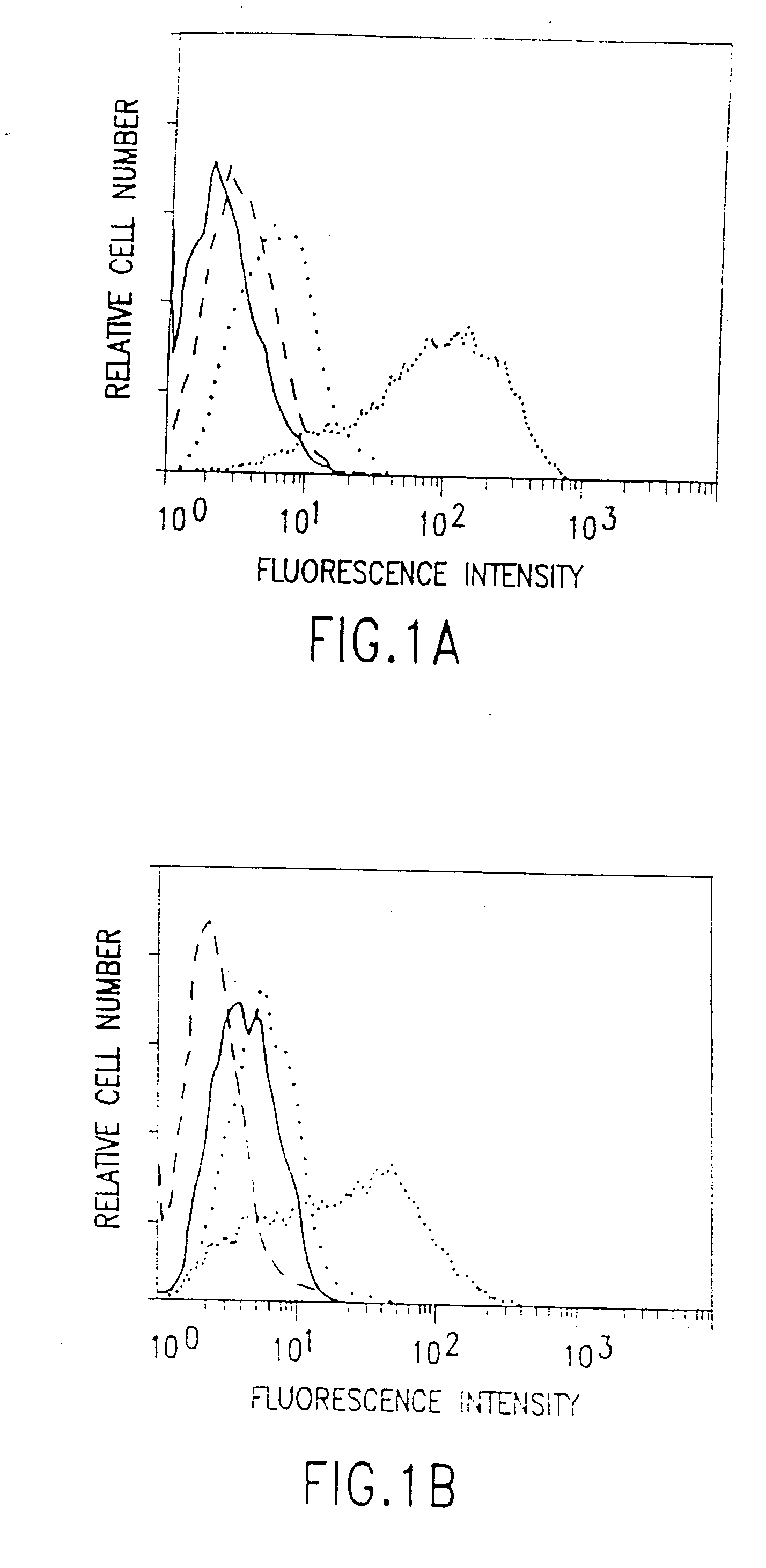
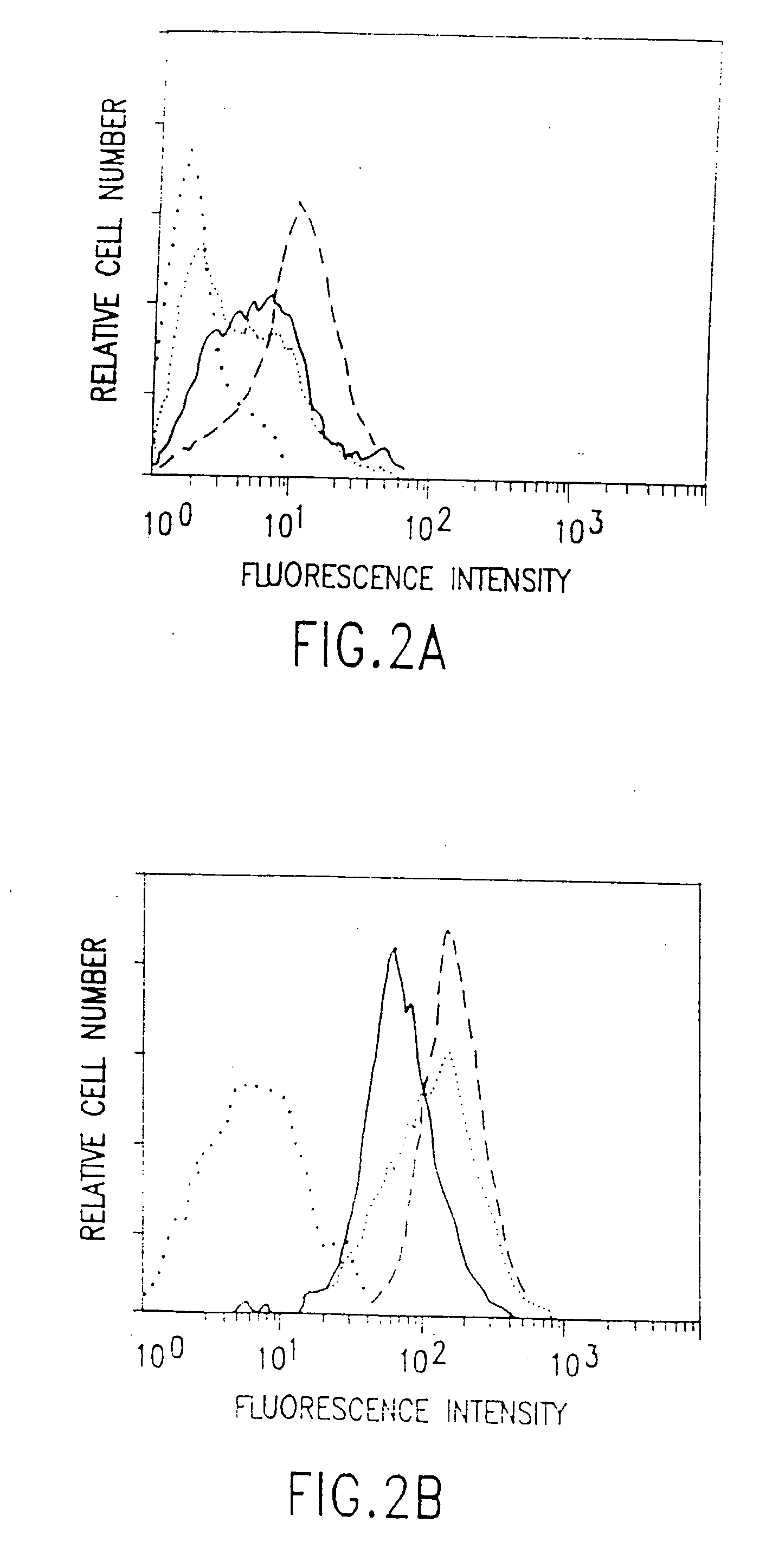
[0185] This example describes the development of a model system in which to investigate the antibody-directed targeting of vascular endothelial cells in solid tumors in mice. A neuroblastoma transfected with the mouse interferon-γ (IFN-γ) gene, C1300(Muγ), was grown in SCID and antibiotic-treated BALB / c nude mice. The INF-γ secreted by the tumor induces the expression of MHC Class II antigens on the tumor vascular endothelium. Class II antigens are absent from the vasculature of normal tissues, although they are present on B-lymphocytes, cells of monocyte / macrophage lineage and some epithelial cells. Intravenously-administered anti-Class II antibody strongly stains the tumor vasculature whereas an anti-tumor antibody, directed against a MHC Class I antigen of the tumor allograft, produces classical perivascular tumor cell staining.
A. Materials and Methods
[0186] 1. Animals
[0187] BALB / c nu...
example ii
Solid Tumor Therapy Using A Vascular Targeted Immunotoxin
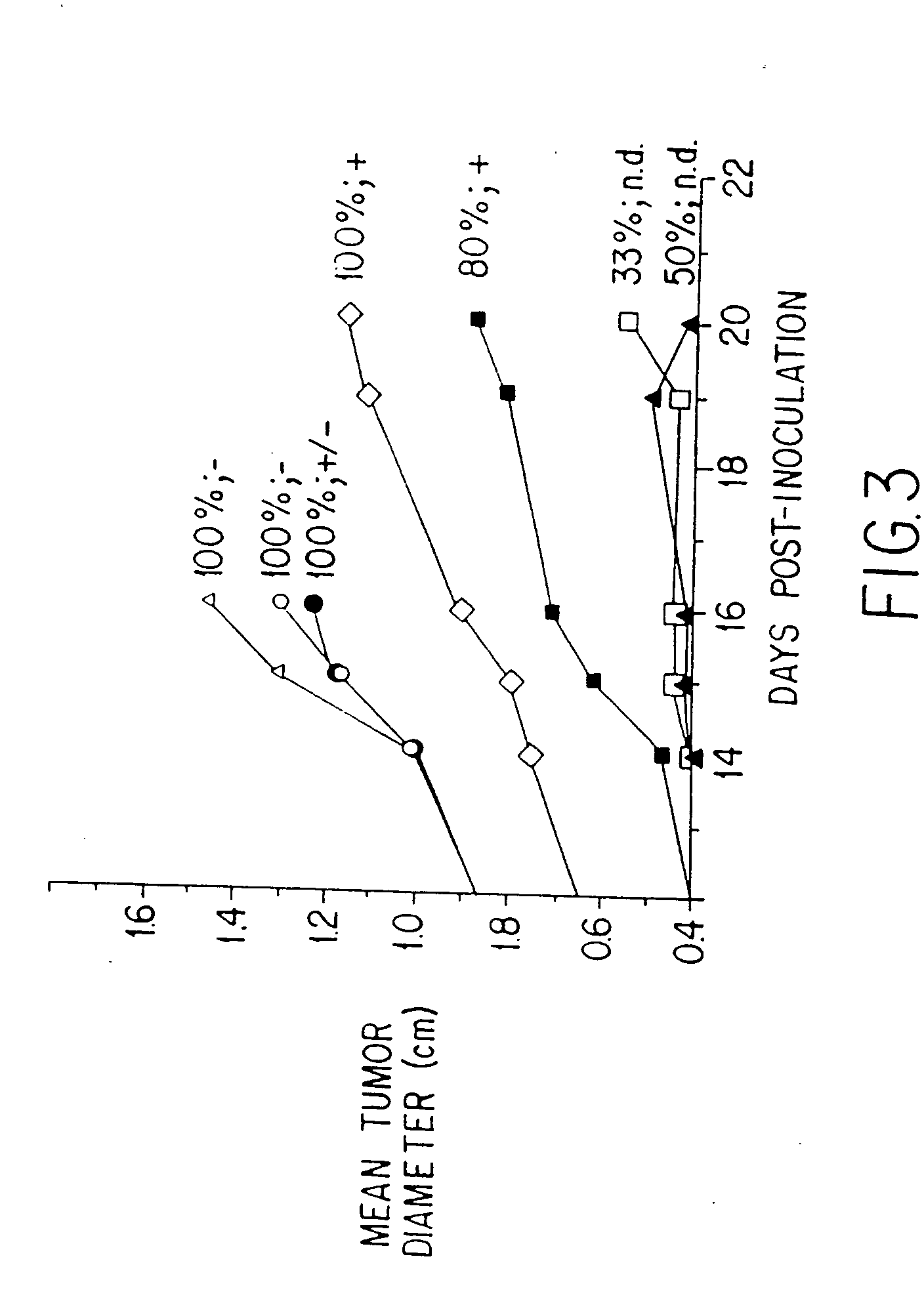
[0236] This example describes the successful therapy of the solid tumor model described in Example I, using the anti-tumor endothelial cell immunotoxin, MS / 114dgA, and the anti-tumor cell immunotoxin, 11-4.1dgA, alone as well as in combination therapy.
A. Materials and Methods
[0237] 1. Animals
[0238] BALB / c nu / nu mice were purchased from Simonsen (Gilroy, Calif.). SCID mice were from the National Cancer Institute (Bethesda, Md.). Germ-free SCID mice were from the University of Wisconsin (Madison, Wis.). All animals were maintained in microisolation units on sterilized food and water.
[0239] 2. Cells and Culture Conditions
[0240] All cell lines used in this study were cultured in modified Eagle's medium (MEM) supplemented with 10% (v / v) fetal calf serum, 2.4 mM L-glutamine, 200 units / ml penicillin and 100 μg / ml streptomycin. Cultures were maintained at 37° C. in a humidified atmosphere of 90% air / 10% CO2. The C1300 neuroblas...
example iii
Targeting the Vasculature of Breast Tumors
[0270] This example describes an approach for targeting the vasculature of breast cancer and other solid tumors in humans. This approach is exemplified through the use of bispecific antibodies to selectively induce the activation antigens, Class II and ELAM-1, on the vascular endothelial cells of syngeneic breast tumors in mice and then targeting these antigens with immunotoxins.
[0271] Murine models may first be employed. The results from such studies will be understood to parallel the situation in humans, as mouse models are well accepted and routinely employed for such purposes. Following successful vascular targeting in the mouse, success in man is likely as highly specific anti-breast cancer antibodies are available (Denekamp, 1984; Girling et al., 1989; Griffin et al., 1989; Lan et al., 1987; Boyer et al., 1989).
[0272] In the case of clinical (as opposed to diagnostic applications), the central issue is to confine the expression of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com