Virtual forward lean snowboard binding
a technology of snowboard bindings and forward leaning, which is applied in snowboard bindings, skis, skiing, etc., can solve the problems of not optimally positioning the highback with respect to the rider's ankle, and achieve the effect of facilitating the movement of the board
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
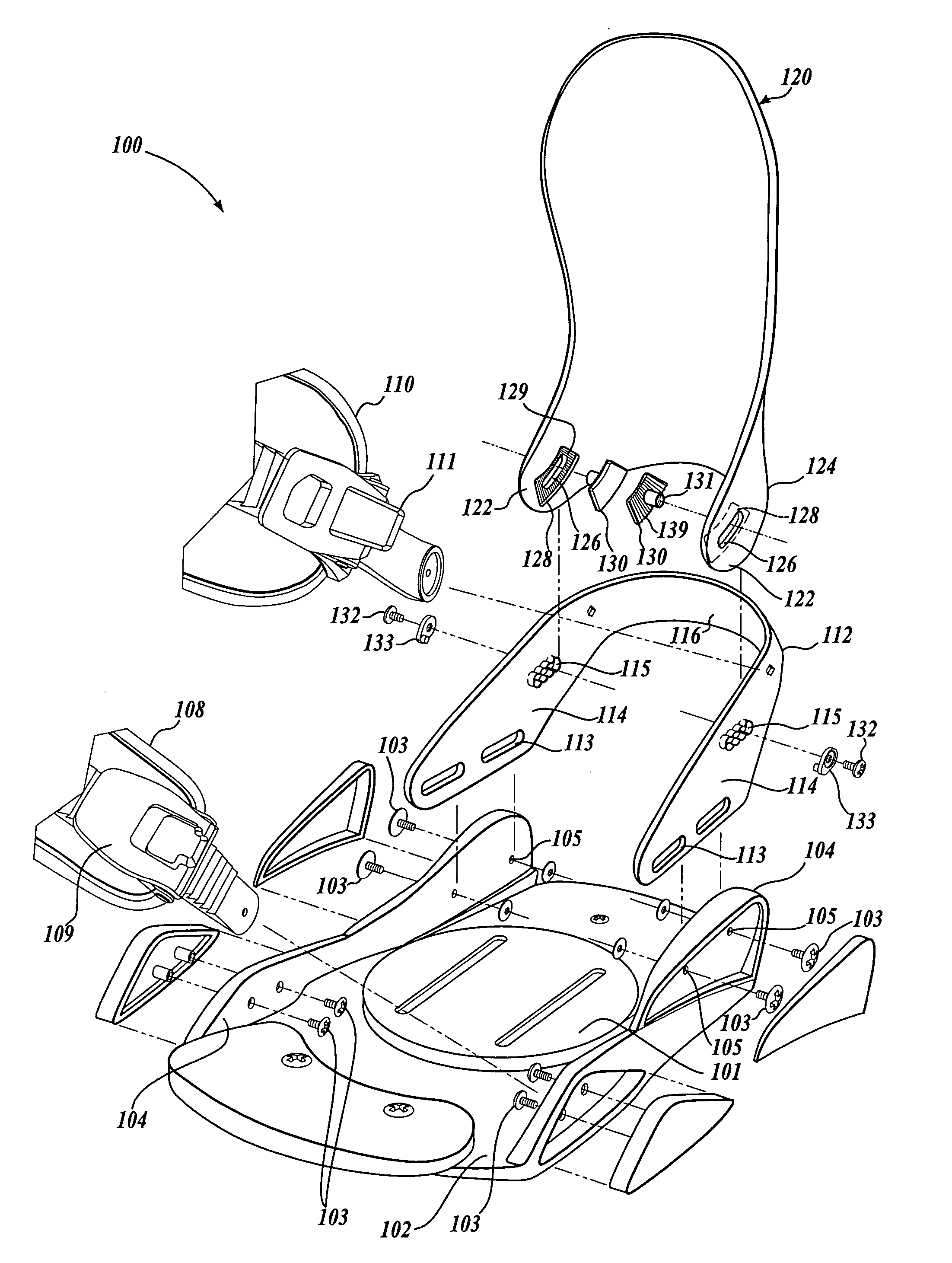
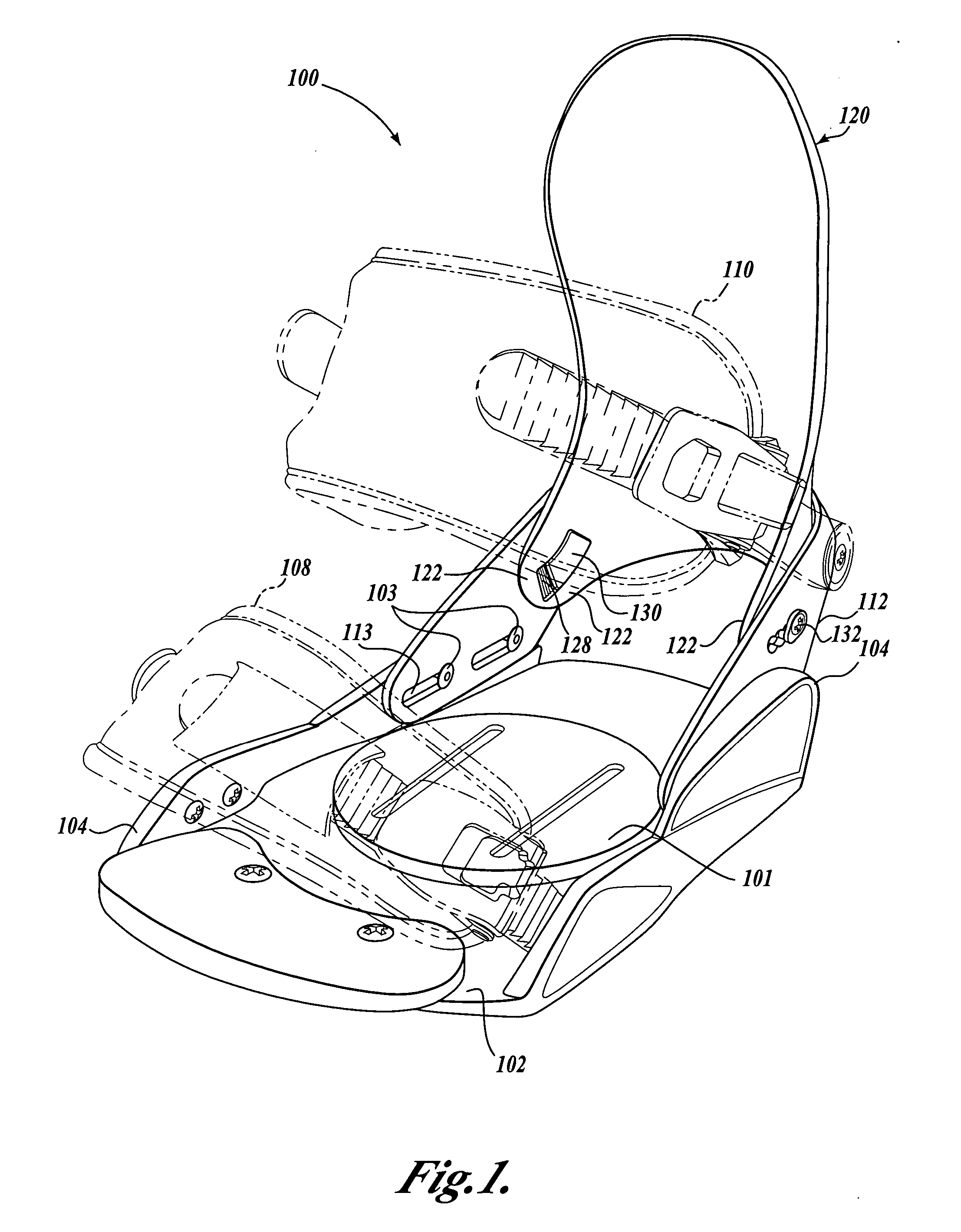
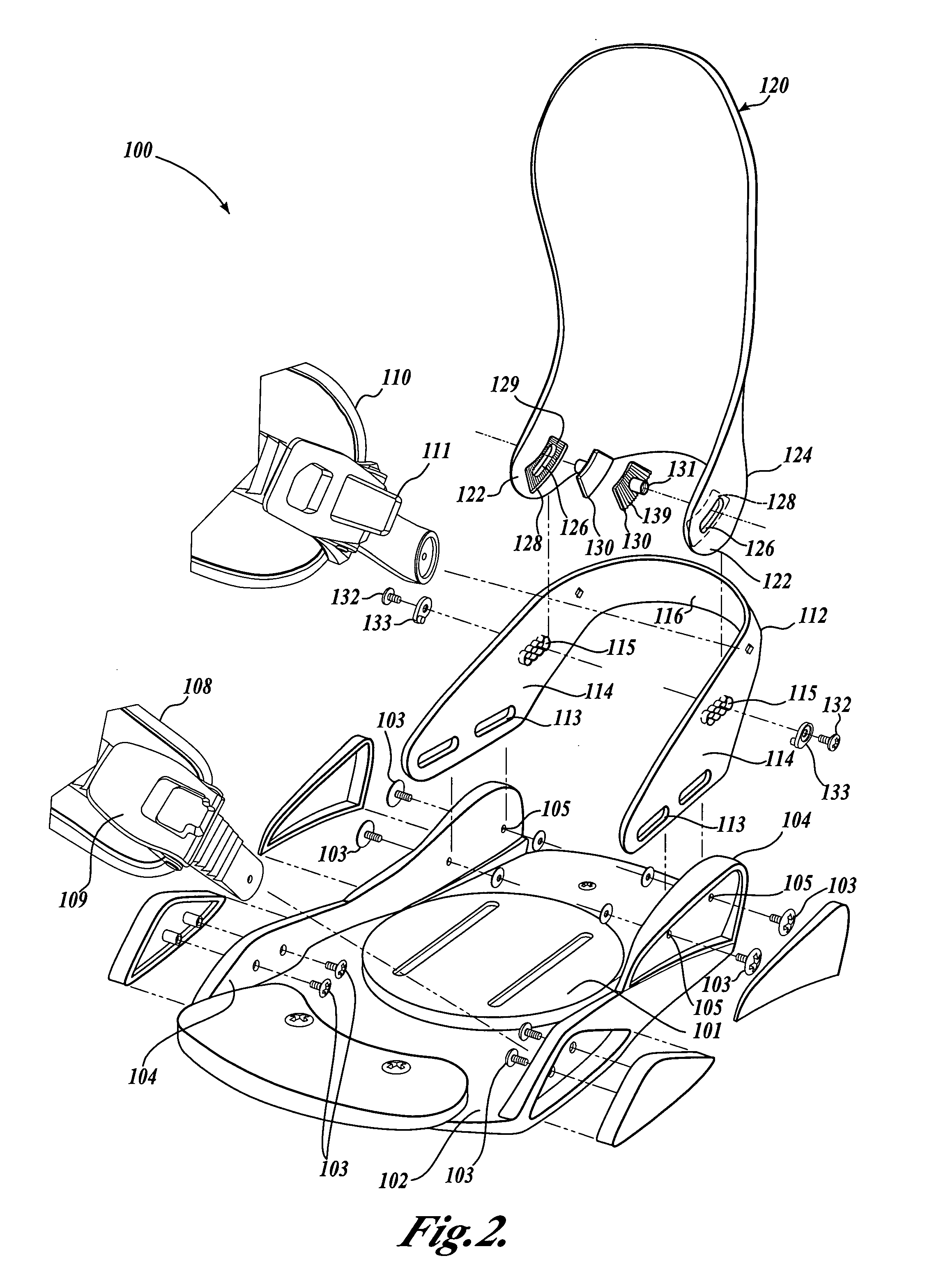
[0018] Refer now to the figures, wherein like numbers indicate like parts. FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a snowboard binding 100 illustrating a currently preferred embodiment to the present invention and FIG. 2 shows an exploded view of the snowboard binding 100. It should be appreciated that the binding 100 includes certain general aspects in common with the commonly-owned U.S. Pat. No.5,727,797, to Bowles, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
[0019] The binding 100 includes a base plate 102 that is adapted to be selectively attached to a snowboard (not shown) by conventional attachment mechanisms as are well known in the art—for example, with fastening hardware extending through apertures in an adjustment disk 101. The base plate 102 provides a platform for receiving the snowboard boot (not shown) of a rider and includes a pair of oppositely disposed sidewalls 104. A generally U-shaped heel loop 112 is attached to the base plate 102 with attachment hardware...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com