Dynamic application placement under service and memory constraints
a dynamic placement and memory constraint technology, applied in the direction of multi-programming arrangements, program control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of cluster directly affecting the amount of load that the cluster can sustain without performance degradation, and the size and complexity of computing service centers have increased, so as to achieve the effect of fine granularity of resource allocation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
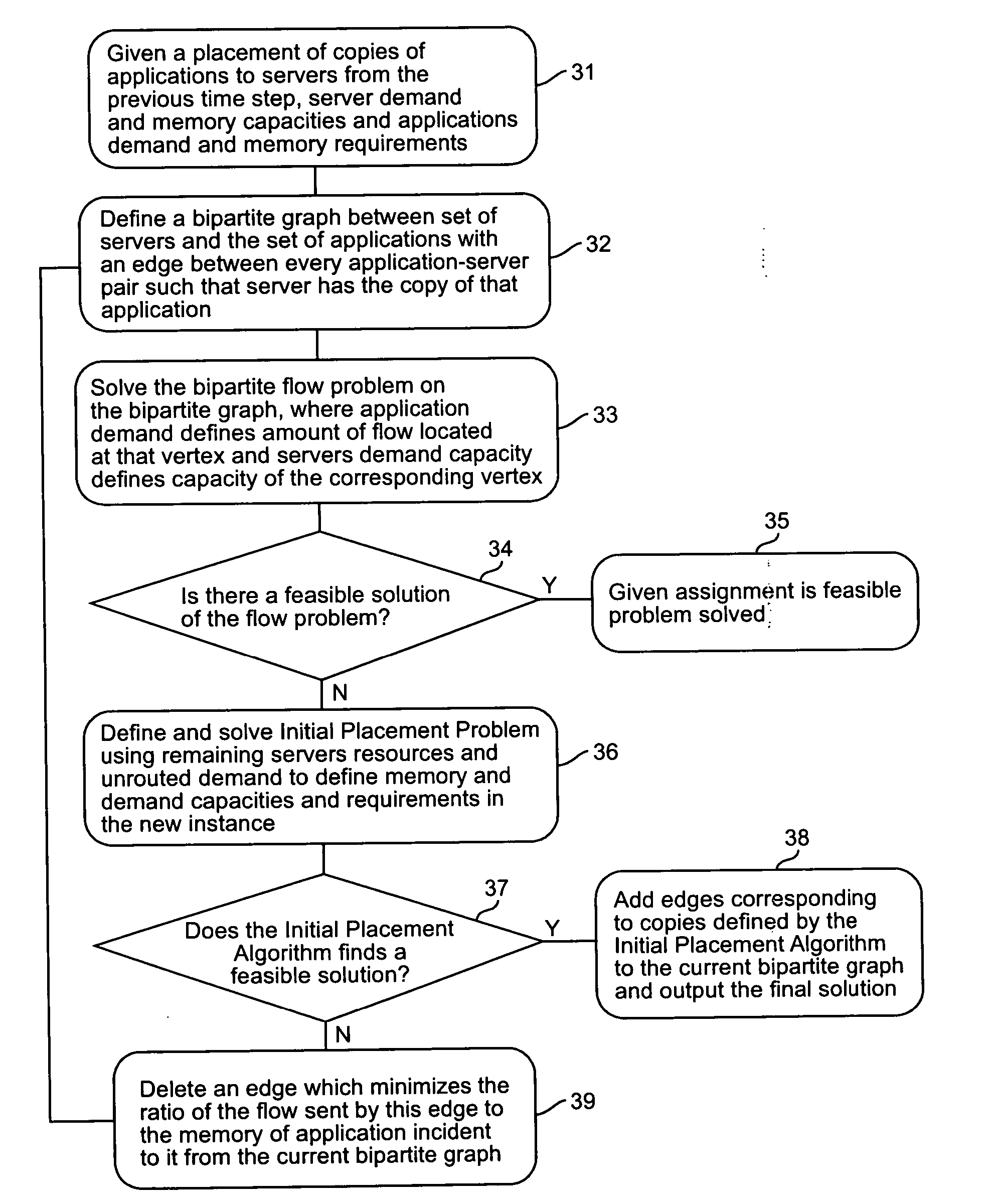
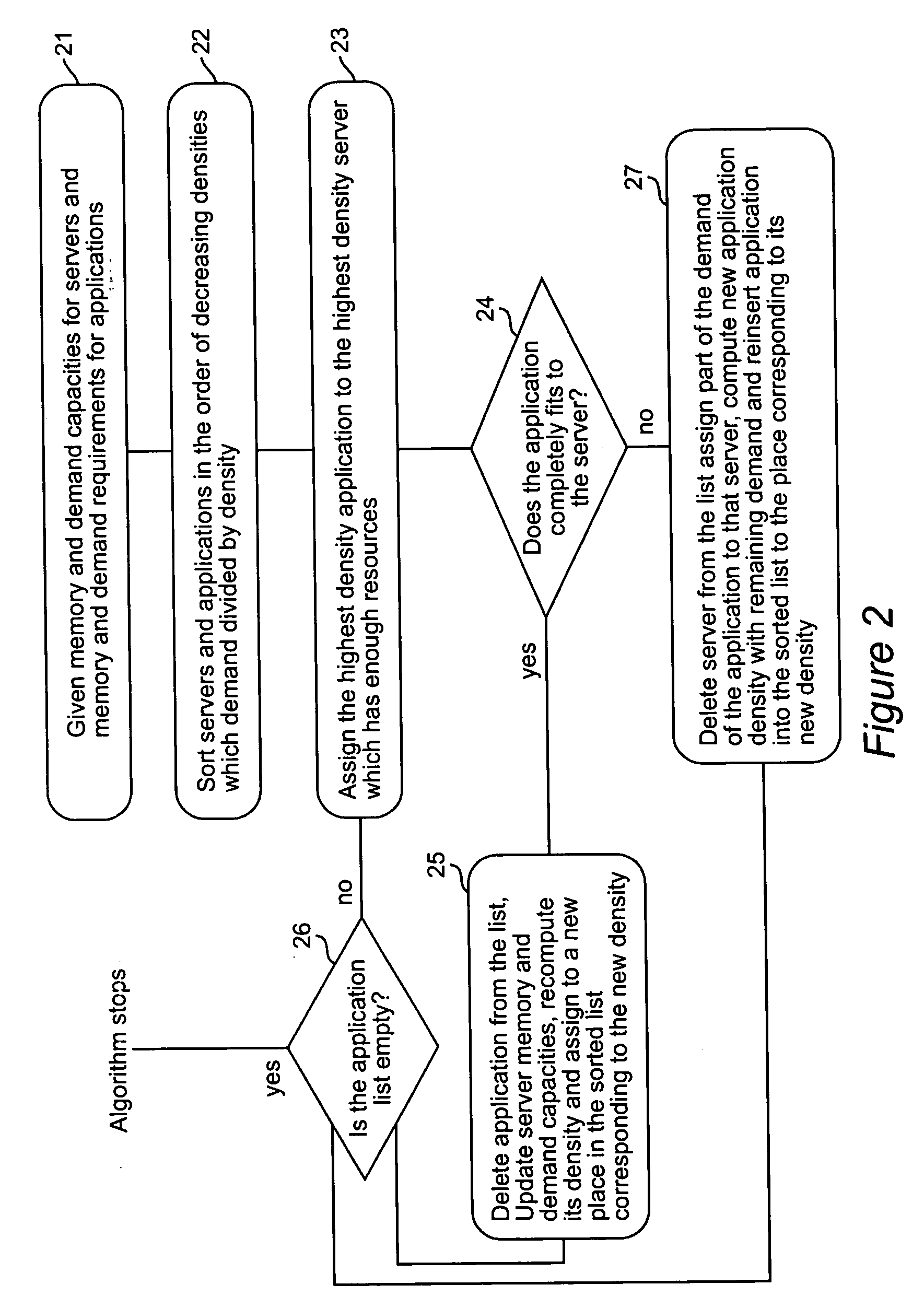
Problem Formulation
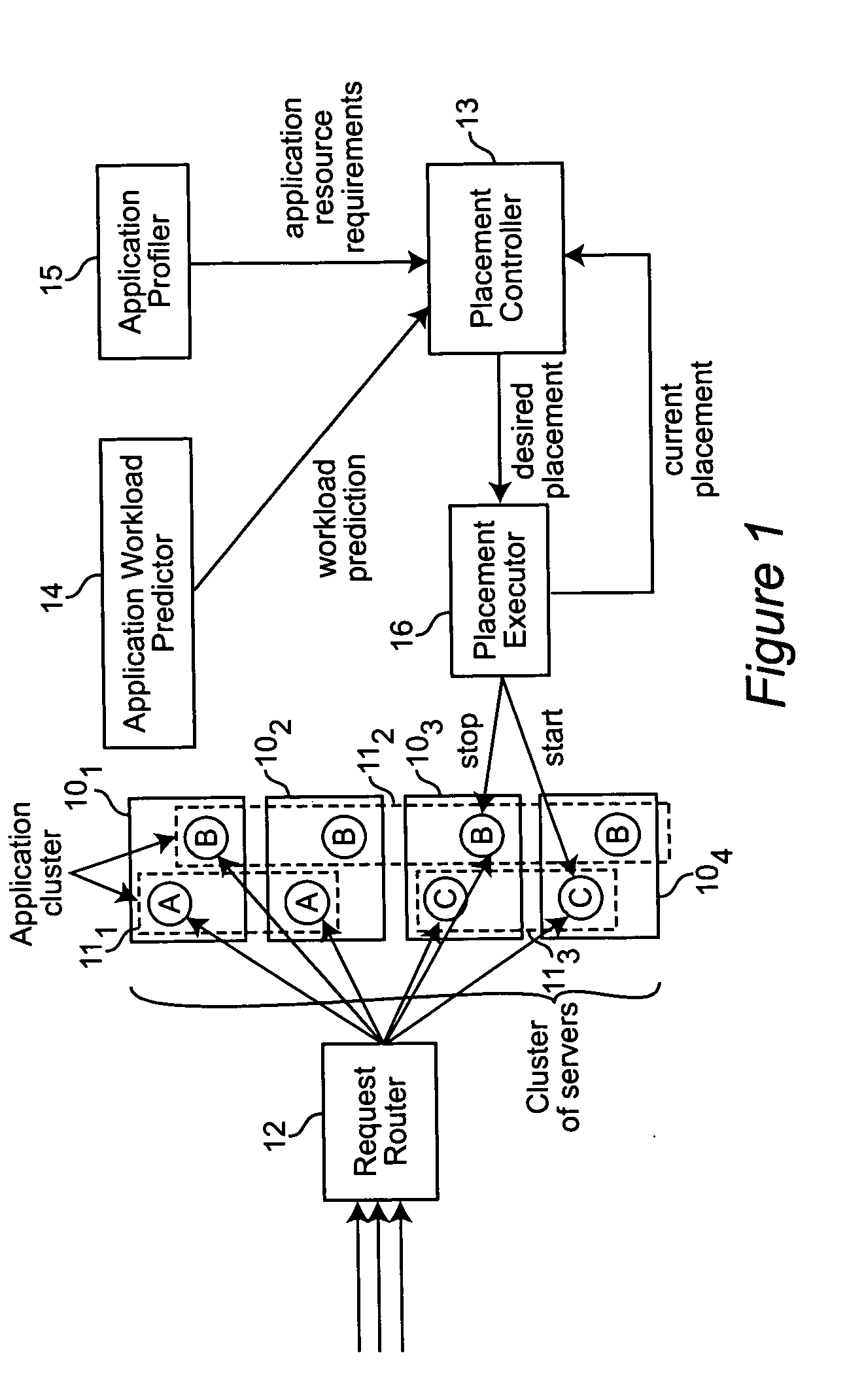
[0022] The invention is implemented in a system as generally illustrated in FIG. 1. This system comprises a cluster of servers 101, 102, 103 and 104 across which application clusters 111, 112 and 113 are distributed. These application clusters are designated by the letters “A”, “B” and “C” running on the several servers. Thus, application cluster “A” is running on servers 101 and 102 and application cluster “C” is running on servers 103 and 104, while application cluster “B” is running on all four servers. It will of course be understood by those skilled in the art that four servers and three application clusters are used here for illustrative purposes only and that, in practice, there may be any number of servers and any number of application clusters. Requests for specific ones of the application clusters from various clients (not shown) are received by a request router 12 and directed to the appropriate application cluster, as shown in FIG. 1.
[0023] As will b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com