Call-stack pattern matching for problem resolution within software
a software and problem resolution technology, applied in the field of software-based system fault detection and resolution, can solve the problems of increasing complexity of software-based system, increasing the difficulty of identifying the source of faults, and affecting the ability of users to experience the same fault within the software application by more than one user
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
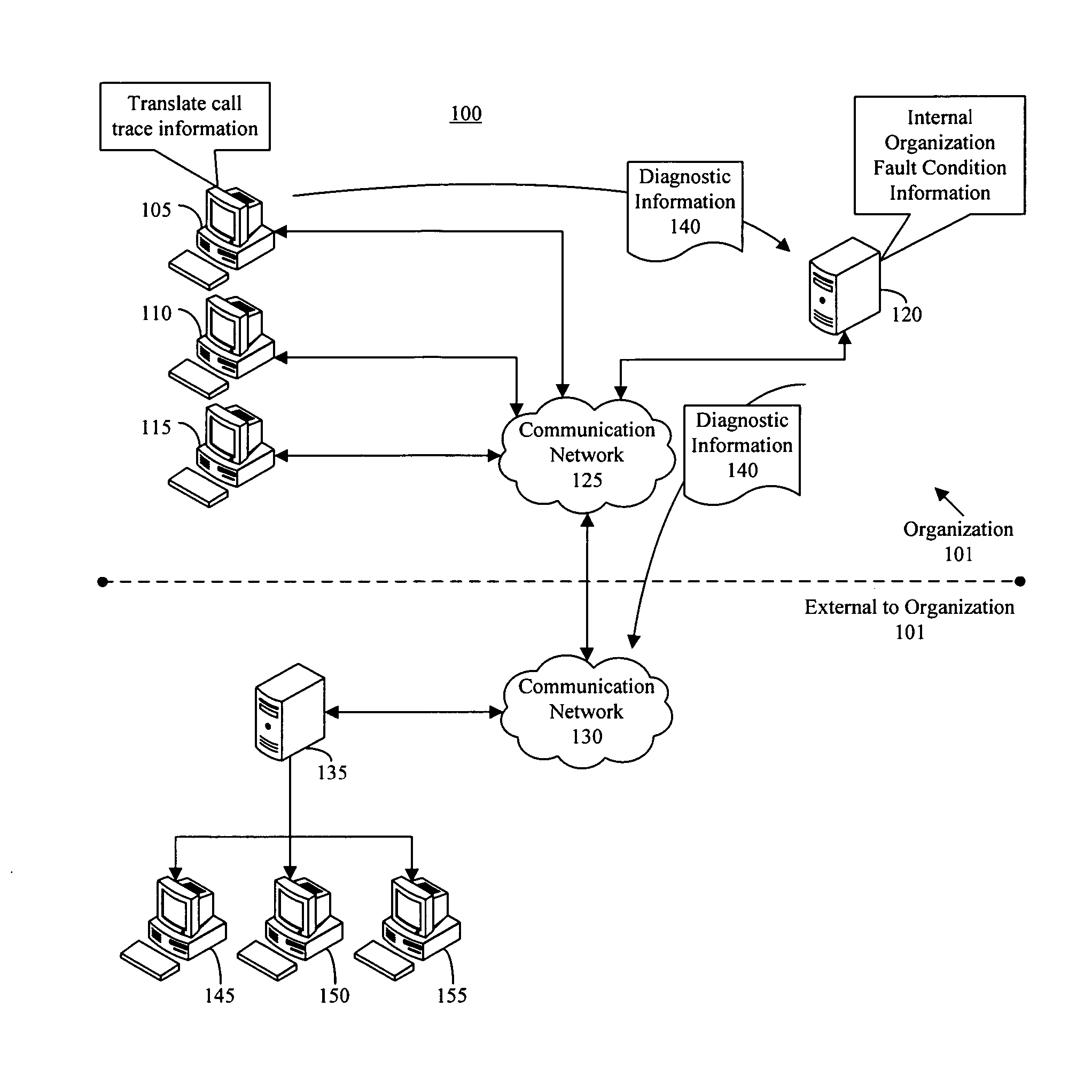
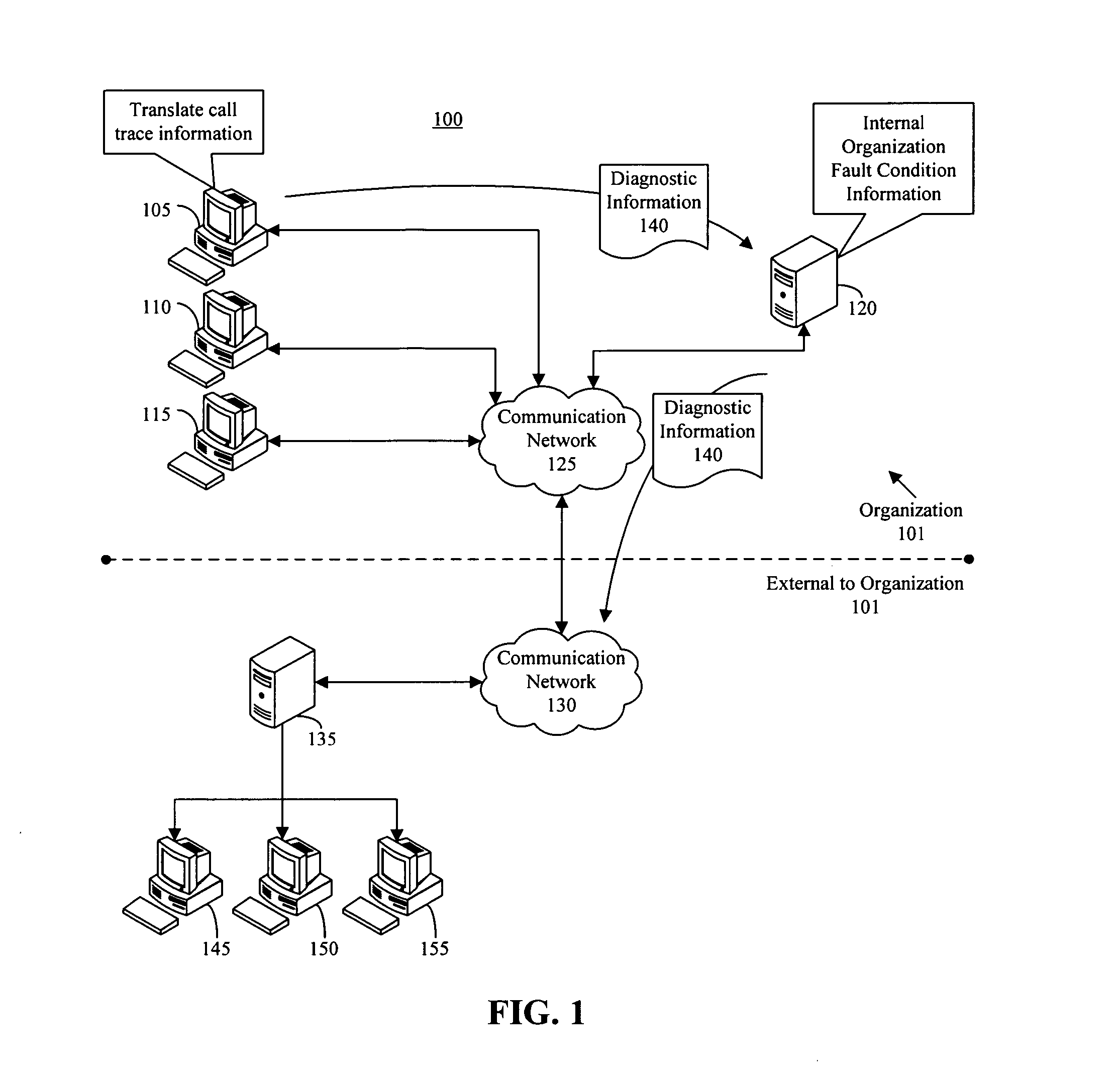
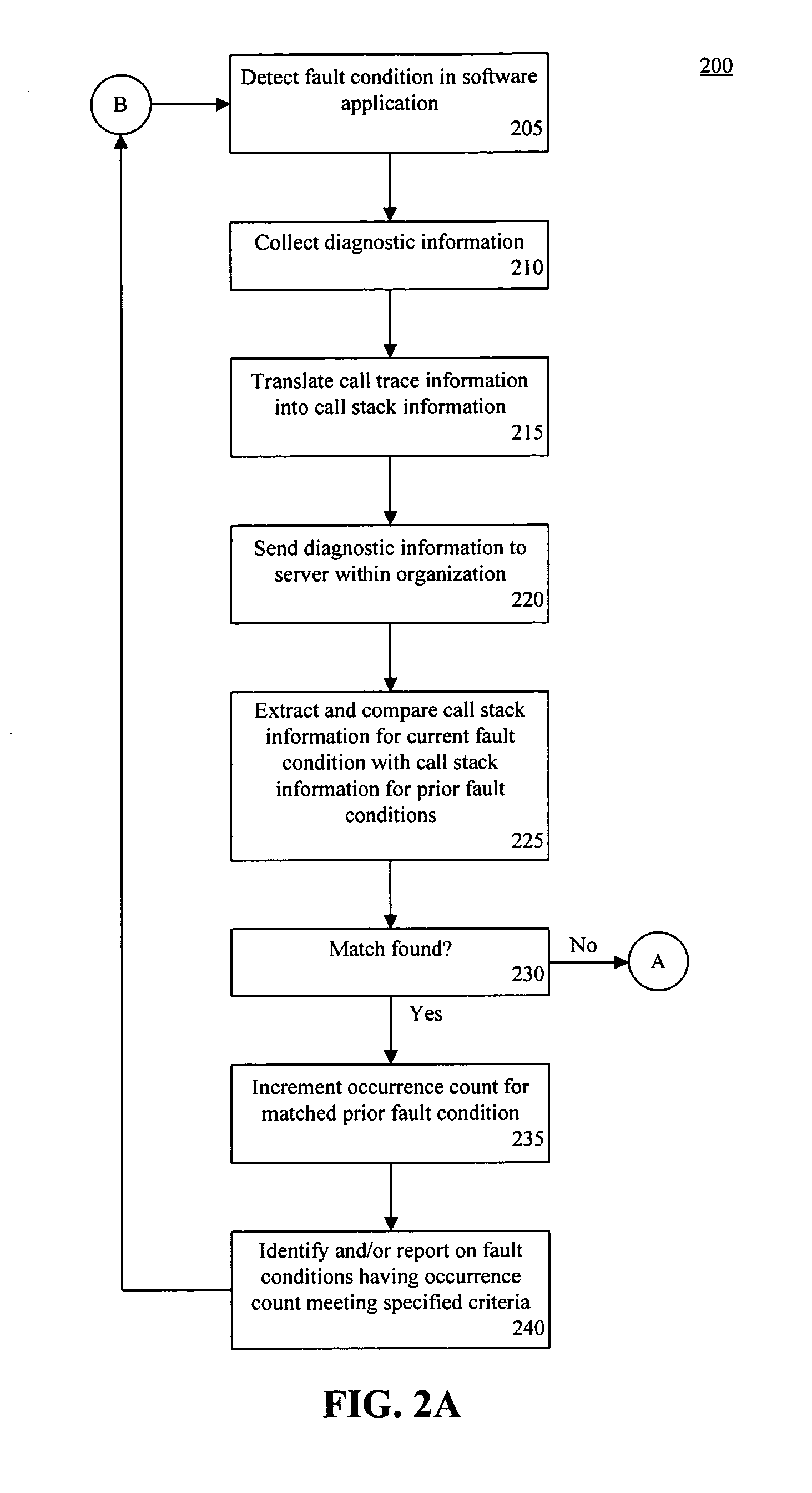
[0015] The present invention provides a method, system, and apparatus for fault detection and resolution for use with software-based systems. In accordance with the inventive arrangements disclosed herein, a two tiered approach is presented where fault conditions are first matched with prior software faults that have occurred within an organization. In the event that the fault condition does not match prior software faults, the fault condition information is sent to an evaluation system which is not part of the organization. Typically, the outside evaluation system is associated with the developer and / or entity charged with administering the software system that experienced the fault condition. In any case, the outside evaluation system can compare the fault condition information with faults that have occurred across one or more different organizations to determine whether a solution exists.
[0016] While the specification concludes with claims defining the features of the invention ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com