Method and apparatus for plasma processing
a plasma processing and plasma technology, applied in the field of semiconductor semiconductor fabrication, can solve the problems of non-uniform electric field at the circumference, increase of fabrication cost, non-uniform wafer process, etc., and achieve the effect of maximizing the uniformity of process rate and processed structure shape, and significantly prolonging the life of the focus ring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
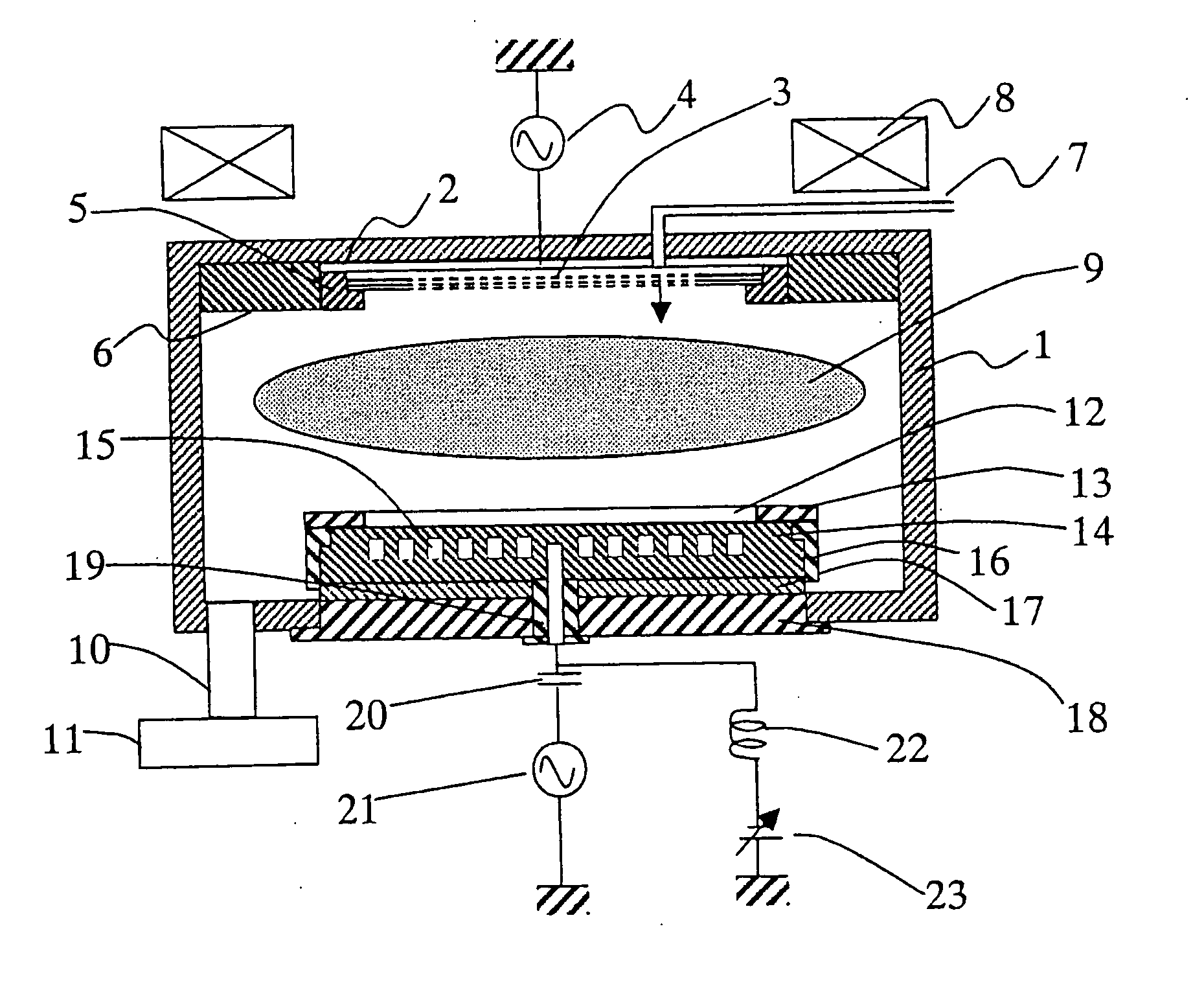
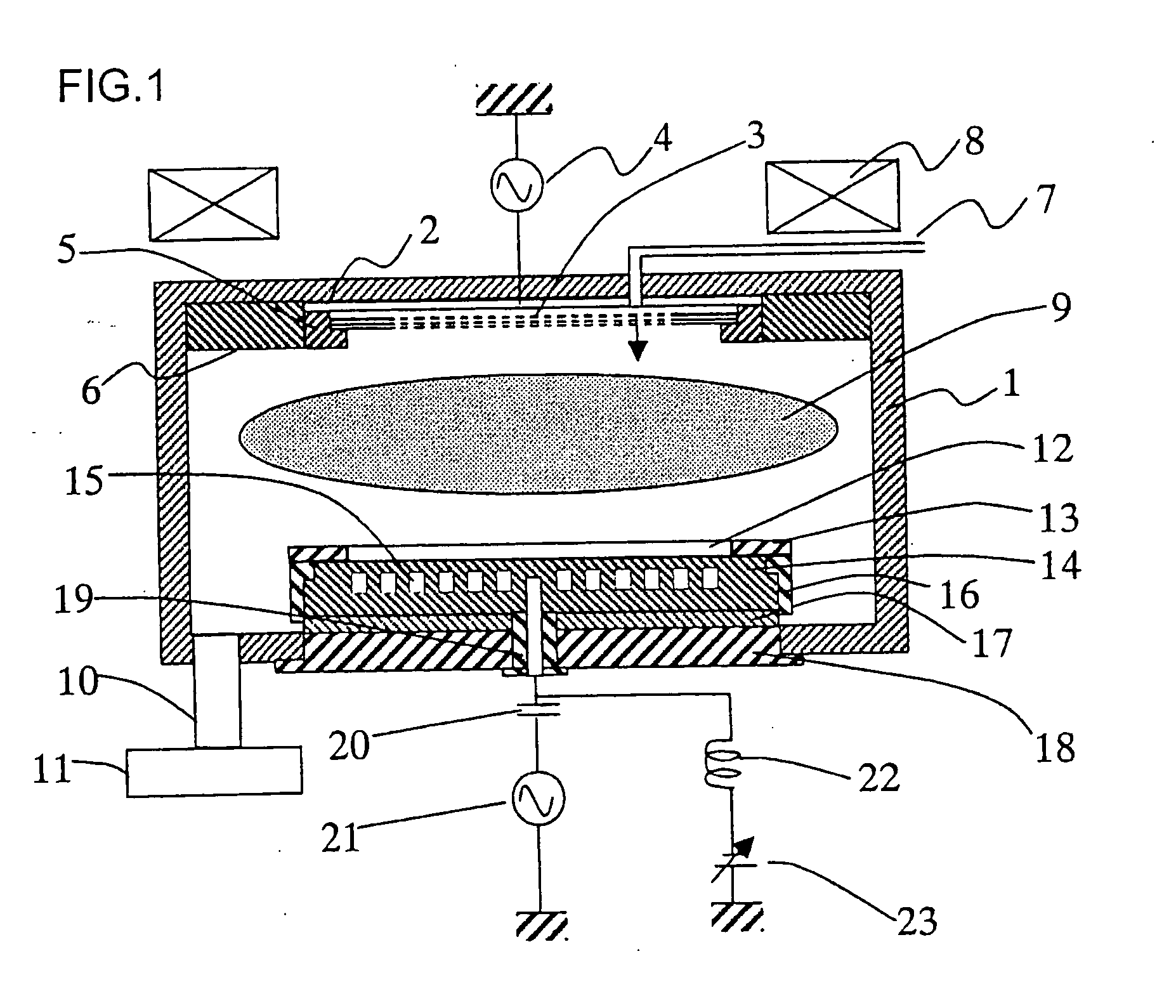
[0068] We will now describe the method of replacing the above-mentioned theory with a specific equivalent circuit model. For simplicity, a structure illustrated in FIG. 3 showing the present invention will be considered. On the surface of an electrode 33, a dielectric film 34 for electrostatic chucking is formed via thermal spray coating of alumina or the like. A wafer 30 and a focus ring 31 are mounted thereon, and a susceptor 32 for protecting the electrode 33 and dielectric film 34 is disposed. Although not shown, an RF power supply and a DC power supply for electrostatic chucking are connected to the electrode 33, by which the wafer 30 is chucked to the dielectric film 34, and the wafer 30 and focus ring 31 are subjected to RF bias.
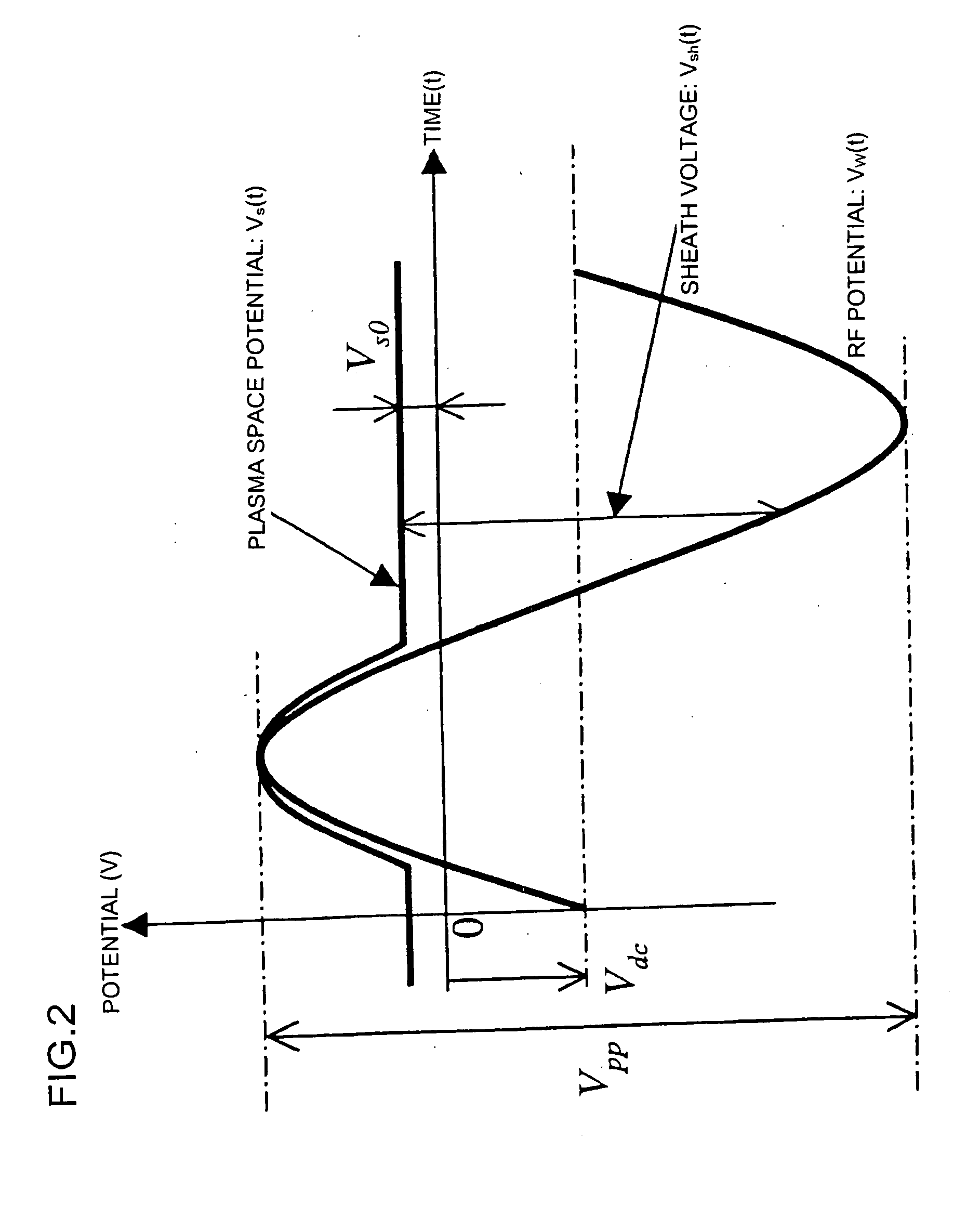
[0069] Plasma region 37 is formed above the wafer 30 and focus ring 31, and an ions heath region 36 is formed below a plasma-sheath interface 35. Now, the sheath thickness dsh given in formula 2 is the distance between the surface of wafer 30 (or focu...
second embodiment
[0089]FIG. 9 illustrates the present invention, in which a wafer 72 and a focus ring 73 are mounted on an electrode 70 having a dielectric film 71 for electrostatic chuck. A flat plasma-sheath interface 74 is formed above the wafer 72 and focus ring 73. The height of surfaces of the wafer 72 and the focus ring 73 are the same. In order to fulfill this condition, according to formula 8, HW=HFR and dW=dFR. In other words, V0−VW1=V0−VF1. From these equations, the following formula is obtained.
[Formula 9]ZW 1ZW 1+ZW 2+ZW 3=ZF 1ZF 1+ZF 2+ZF 3(9)
[0090] By forming simultaneous equations of formulas 7 and 9, the following formula 10 is obtained. This is the plasma-sheath interface flattening condition of FIG. 9.
[Formula 10]
ZW1:ZW2:ZW3=ZF1:ZF2:ZF3 (10)
[0091] By assigning individual conditions into formulas 7 and 8, the plasma-sheath interface flattening conditions corresponding to those specific conditions can be obtained. At this time, a gap (GWF) exists between the waf...
third embodiment
[0094] Regardless of the material of the focus ring, when a new focus ring is disposed, the thickness of the focus ring is determined so that the plasma-sheath interface above the focus ring is higher than the plasma-sheath interface above the wafer for a height corresponding to the tolerance of the sheath height difference, as illustrated in FIG. 11(a) showing the present invention. At this time, as shown in the circled portion of the drawing, the height difference of the plasma-sheath interface acts as a spherical lens for diverging ions with respect to the wafer. When the height of the plasma-sheath interface above the focus ring is reduced to the lowest tolerance from the plasma-sheath interface above the wafer due to consumption, the focus ring reaches its application limit, and will have to be replaced. At this time, as shown in the circled portion of the drawing, the height difference of the plasma-sheath interface acts as a spherical lens focusing the ions with respect to th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| relative dielectric constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| capacitance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com