Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Uniformity is maximised" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
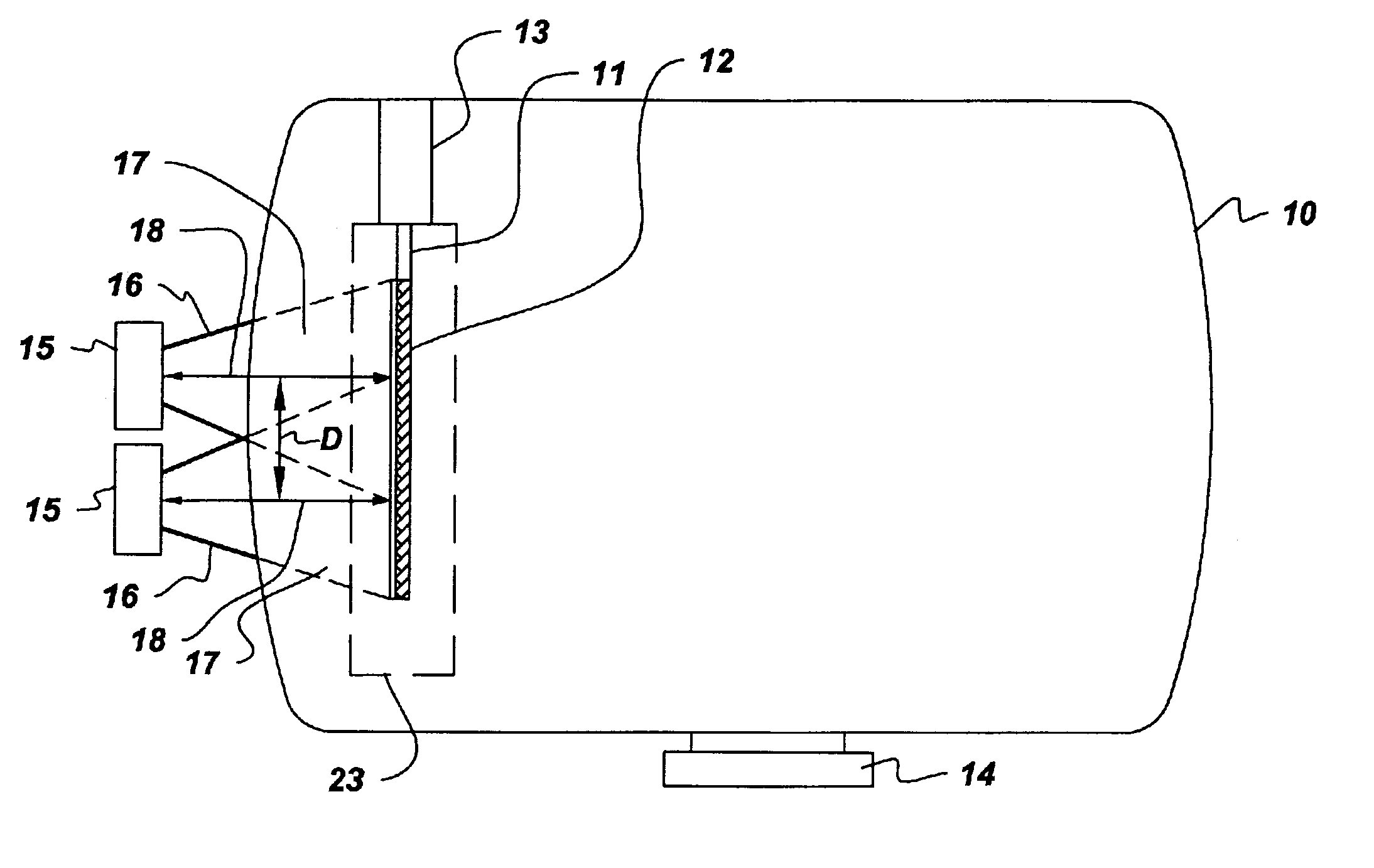
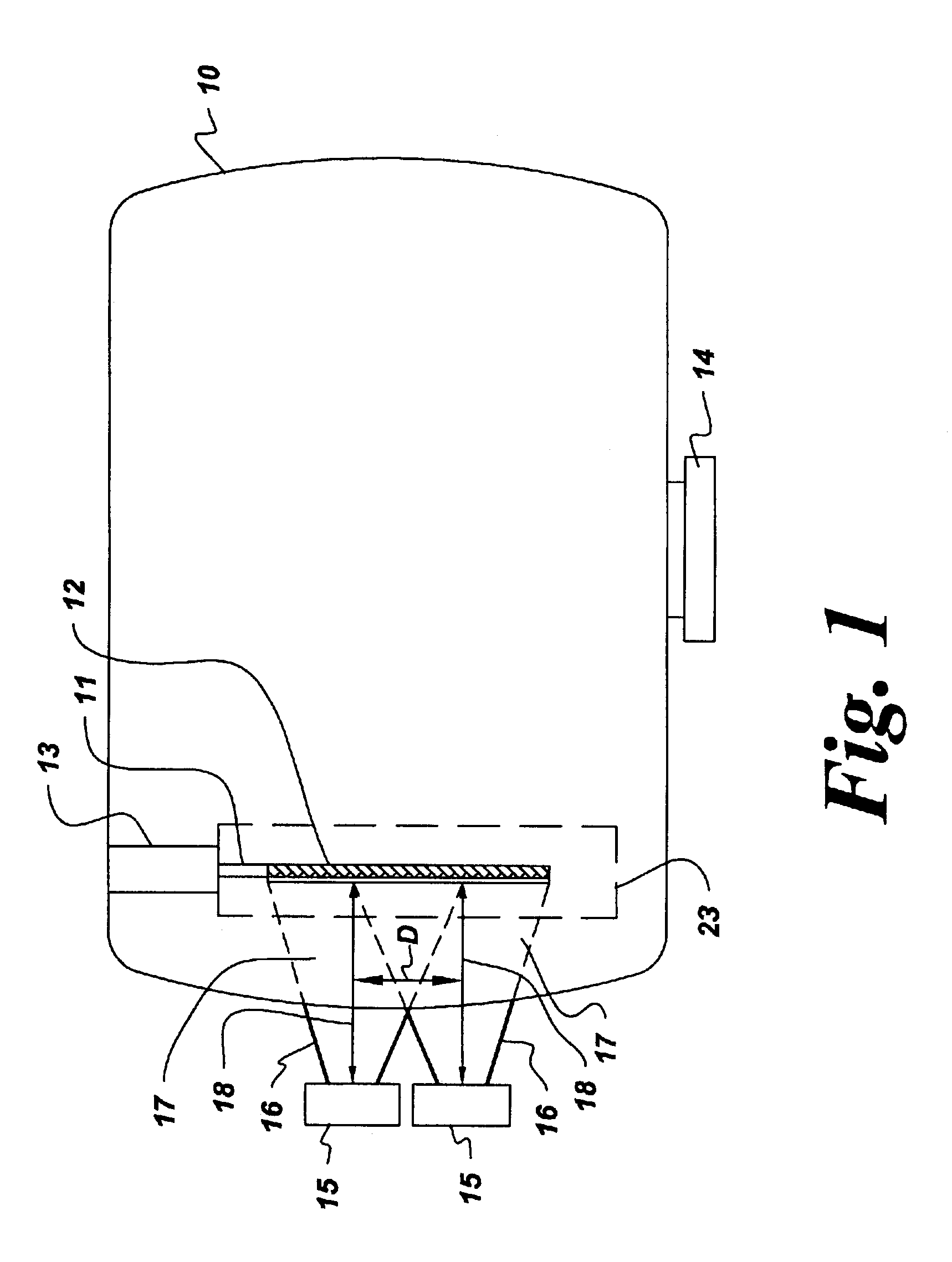
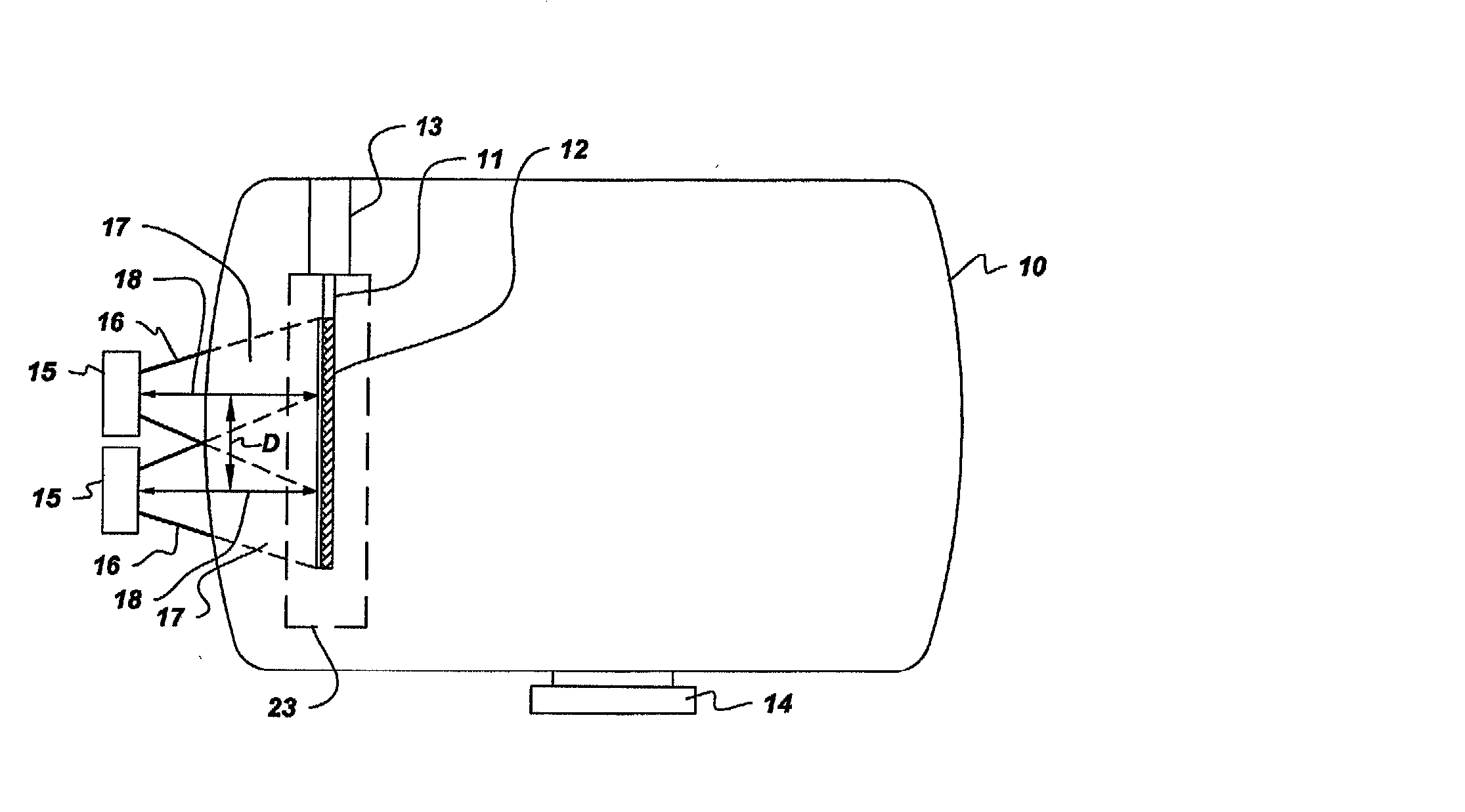
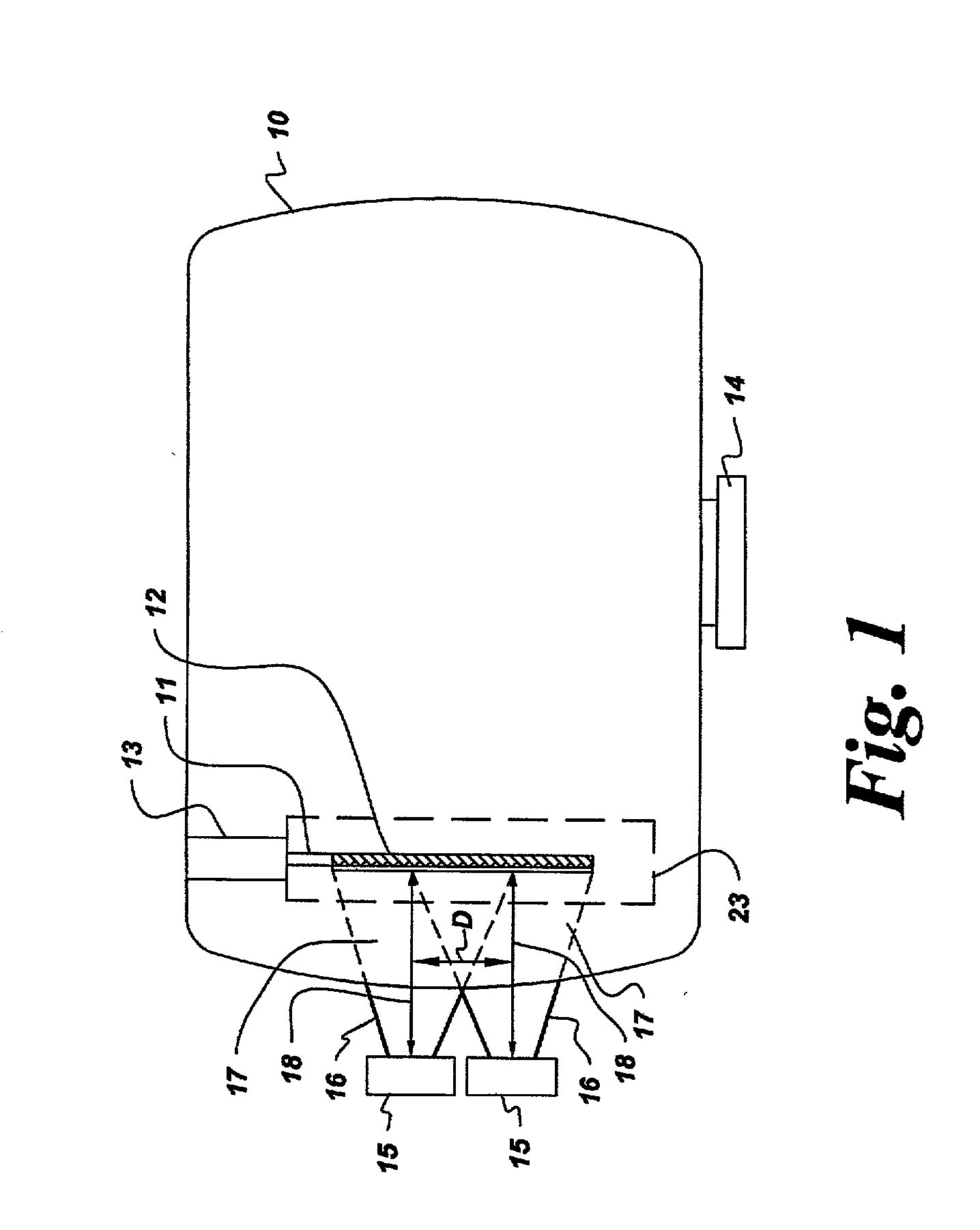
Apparatus for large area chemical vapor deposition using multiple expanding thermal plasma generators
InactiveUS6397776B1Efficient coatingDesirable propertyElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingThermoplasticGas phase
Chemical vapor deposition is performed using a plurality of expanding thermal plasma generating means to produce a coating on a substrate, such as a thermoplastic and especially a polycarbonate substrate. The substrate is preferably moved past the generating means. Included are methods which coat both sides of the substrate or which employ multiple sets of generating means, either in a single deposition chamber or in a plurality of chambers for deposition of successive coatings. The substrate surfaces spaced from the axes of the generating means are preferably heated to promote coating uniformity.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Apparatus and method for large area chemical vapor deposition using multiple expanding thermal plasma generators
InactiveUS20030072881A1Efficient coatingDesirable propertySpark gapsElectric discharge tubesThermoplasticGas phase
Chemical vapor deposition is performed using a plurality of expanding thermal plasma generating means to produce a coating on a substrate, such as a thermoplastic and especially a polycarbonate substrate. The substrate is preferably moved past the generating means. Included are methods which coat both sides of the substrate or which employ multiple sets of generating means, either in a single deposition chamber or in a plurality of chambers for deposition of successive coatings. The substrate surfaces spaced from the axes of the generating means are preferably heated to promote coating uniformity.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
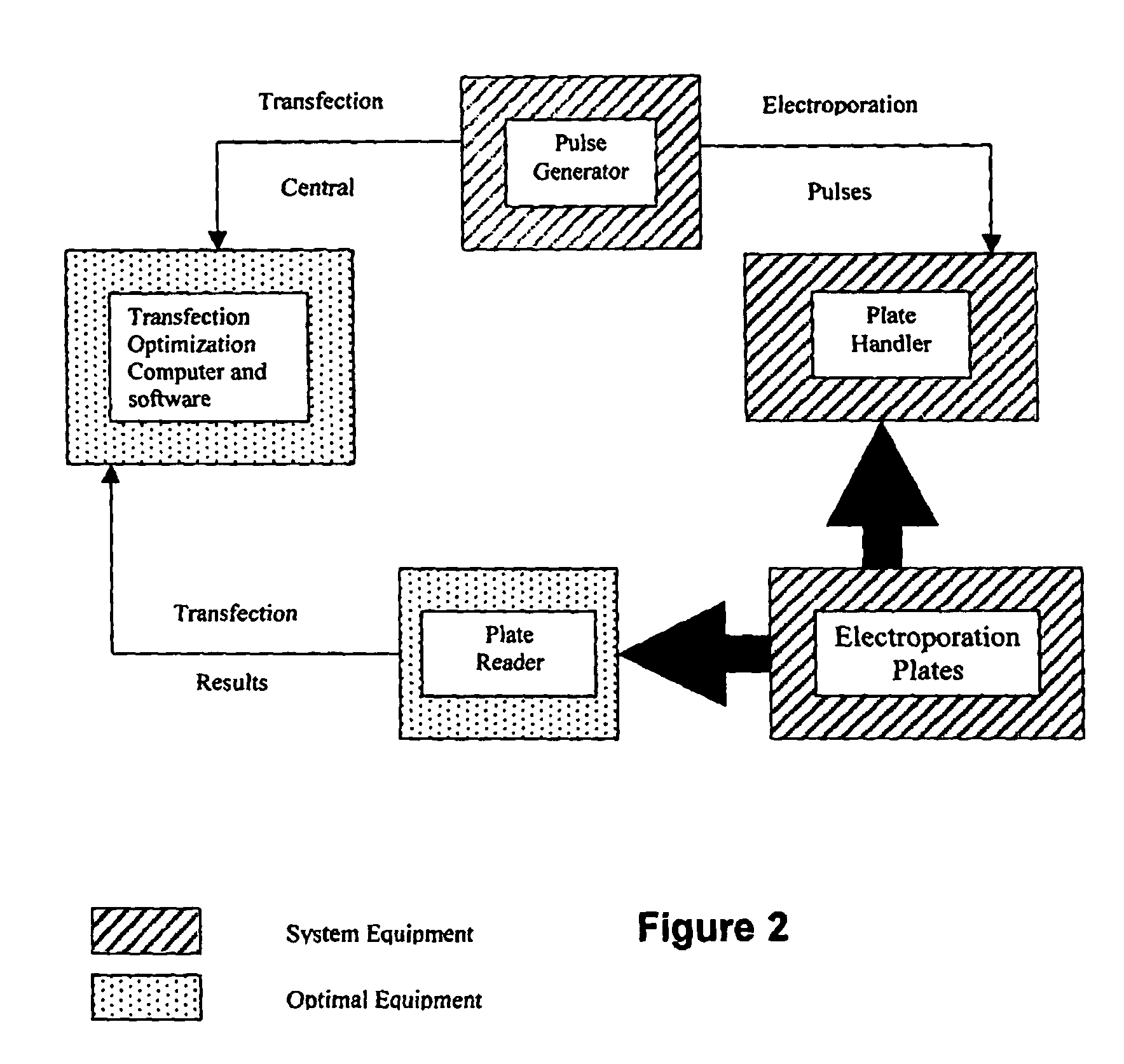
Large-scale electroporation plates, systems and methods of use
InactiveUS20060115888A1Different overall resultGood compatibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricitySolid substrate
Owner:GENETRONICS INC
Aim-enhancing, swing-stabilizing, resonant golf putter head
InactiveUS20030144077A1Good effectMaximize ease of assemblingGolf clubsRacket sportsSingle elementResonance
An aim-enhancing, swing-stabilizing, resonant golf putter head with central striking element, torque-resisting stabilizer, focusing element, and resonance-enhancing structure. A preferred embodiment includes the torque-resisting side stabilizer comprised as a single element, curved behind the central striking element and connecting to both the left and right side thereof, differentially massed with the majority of the mass being divided equally between the right and left sides beyond the center of balance of the central striking element. A preferred embodiment includes the torque-resisting side stabilizer which does not stay within the horizontal plane of the central striking element.
Owner:CULLEN H LEO
AlInGaN LIGHT-EMITTING DEVICE
InactiveUS20090179191A1Easy injectionHigh outputSolid-state devicesNanoopticsQuantum dotLight emitting device
A semiconductor light-emitting device fabricated in the (Al,Ga,In)N materials system has an active region for light emission (3) comprising InGaN quantum dots or InGaN quantum wires. An AlGaN layer (6) is provided on a substrate side of the active region. This increases the optical output of the light-emitting device. This increased optical output is believed to result from the AlxGa1-xN layer serving, in use, to promote the injection of carriers into the active region.
Owner:SHARP KK
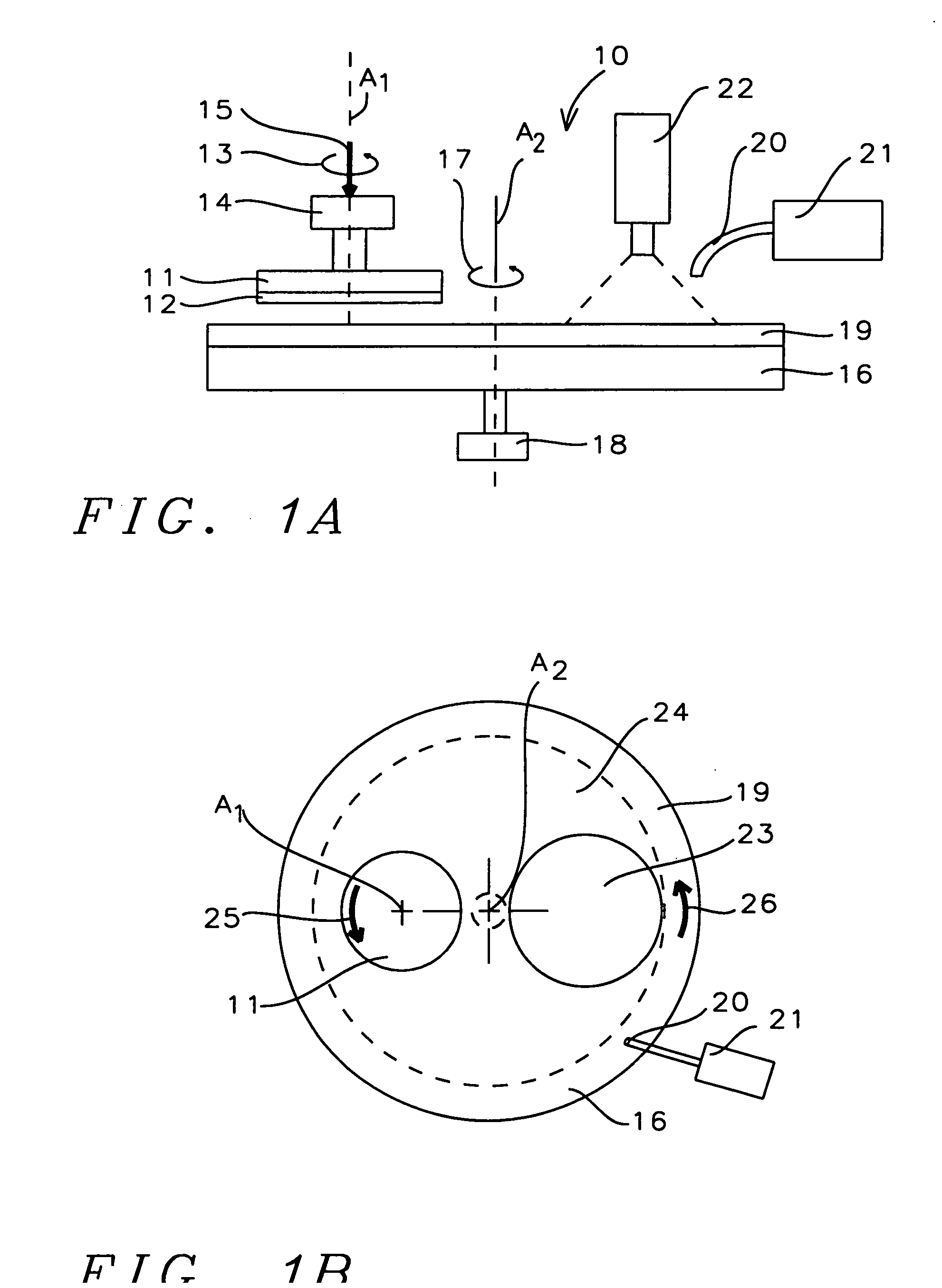
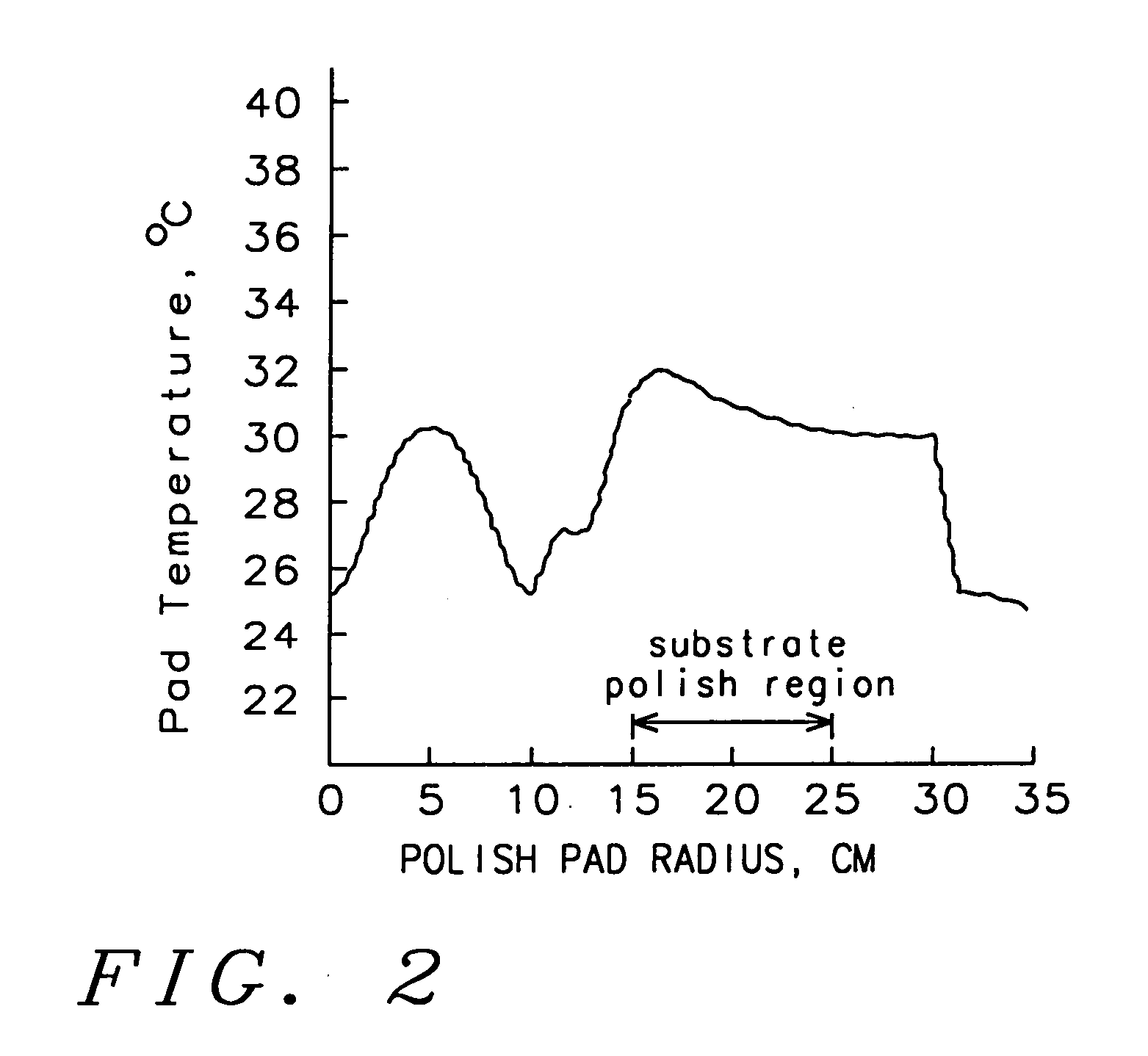
Chemical mechanical polish process control method using thermal imaging of polishing pad
InactiveUS20050118839A1Simple methodImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesMaterial removalCompound (substance)
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
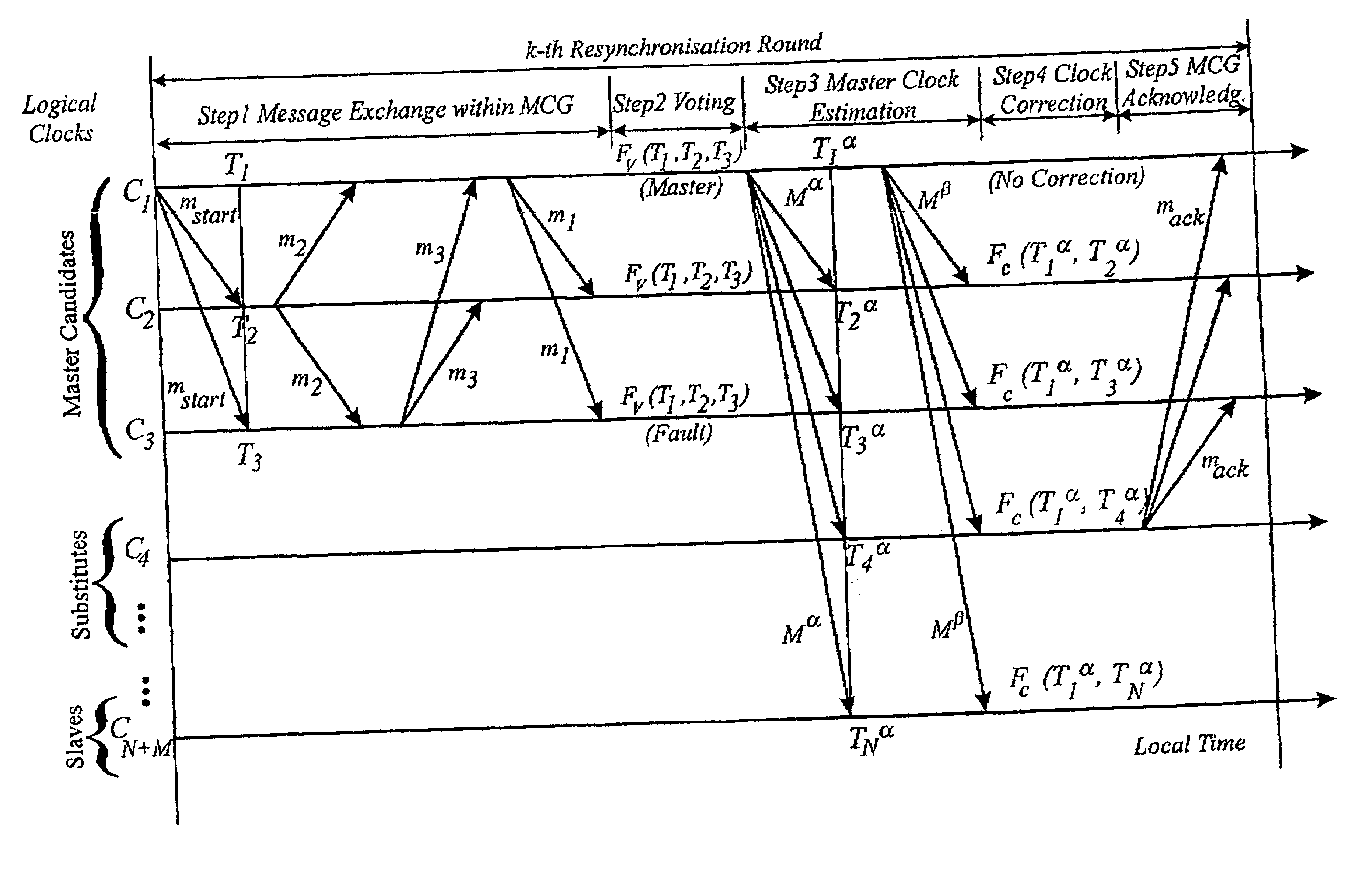
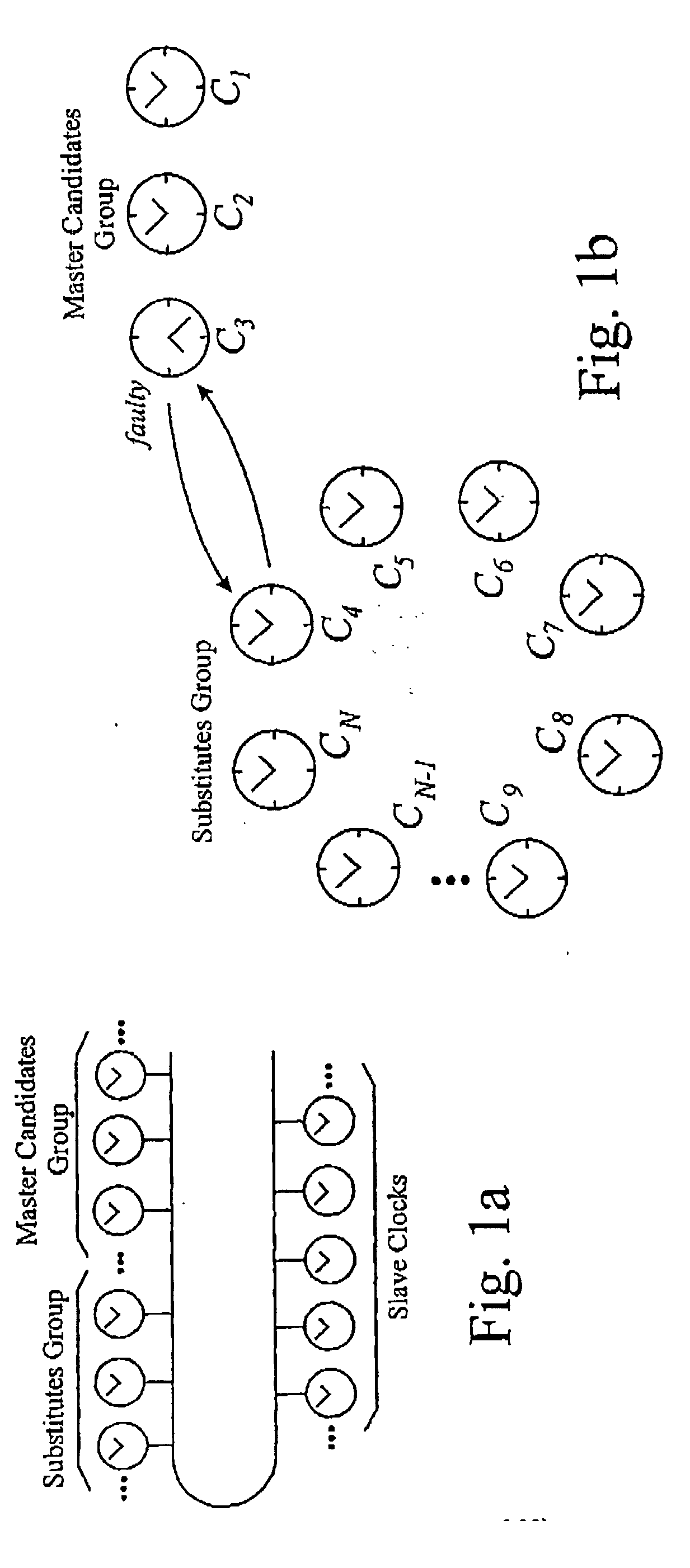
Fault-tolerant clock synchronisation
InactiveUS20050071703A1Improved real-time clock uniformityImprove uniformityTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlBroadcastingClock synchronization
A clock synchronization method is described for a system including N clocks, at least three and at most N−1 of which are master candidate clocks. A start message is broadcast from the fastest master candidate clock. From each of the master candidate clocks, a response message including the local time of receipt of the start message according to the clock in question is broadcast. Using the information representing the times of receipt of the start message, the median master candidate clock is selected and becomes the master clock. The master clock determines the clock synchronisation error for each master candidate clock, using the information representing the times of receipt of the start message. If any such clock synchronisation error is excessive the master clock declassifies the clock in question as a master candidate clock and classifies another clock as a master candidate clock. This is achieved by broadcasting a classification message identifying which of the N clocks are to be classified as master candidate clocks. Next, the master clock broadcasts a synchronisation message including the local time of receipt of the classification message according to the master clock. Each of the other N−1 clocks is then synchronised with the master clock using that information and the local time of receipt of the classification message according to the clock in question.
Owner:DEPENDABLE REAL TIME SYST
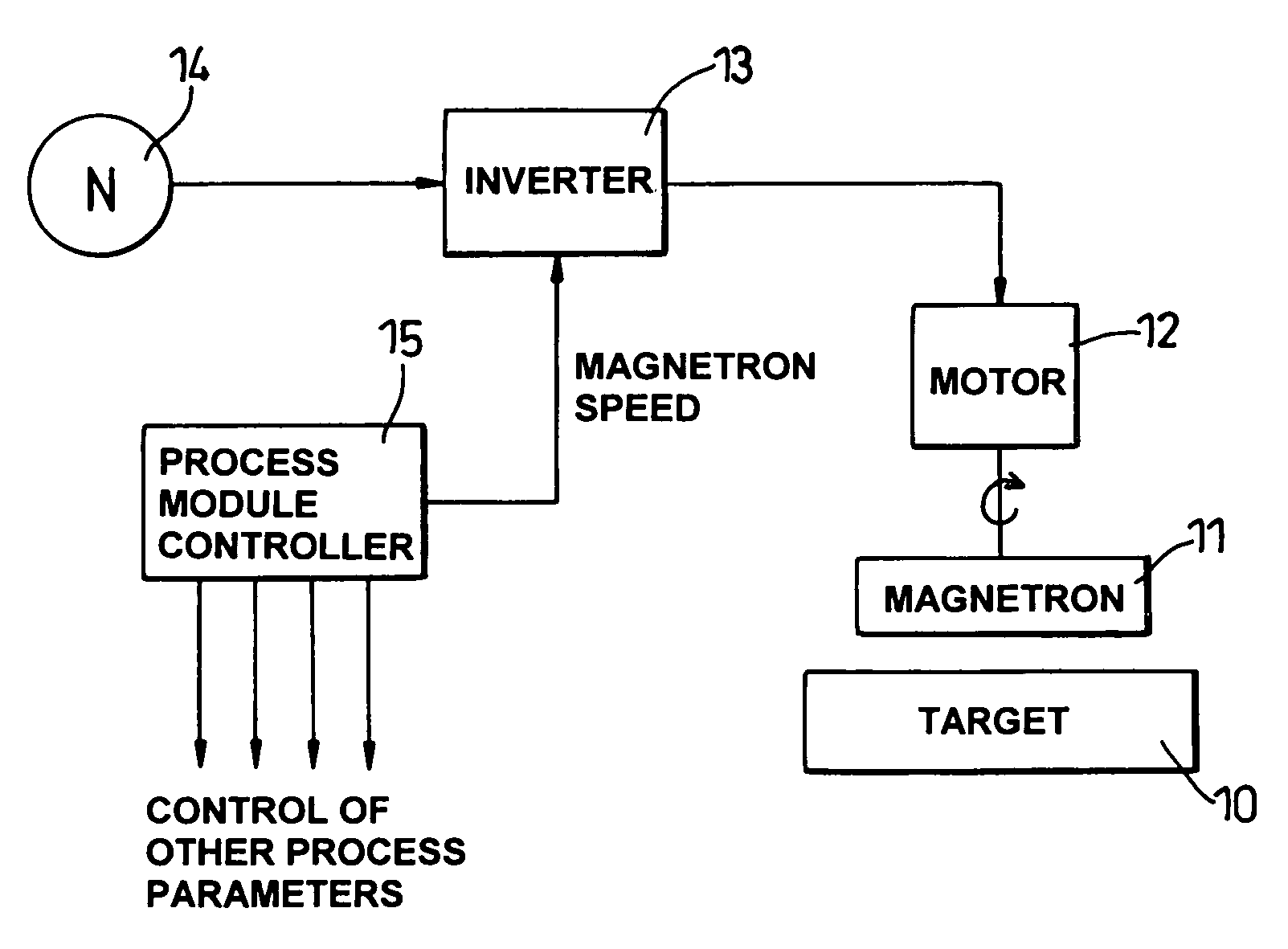
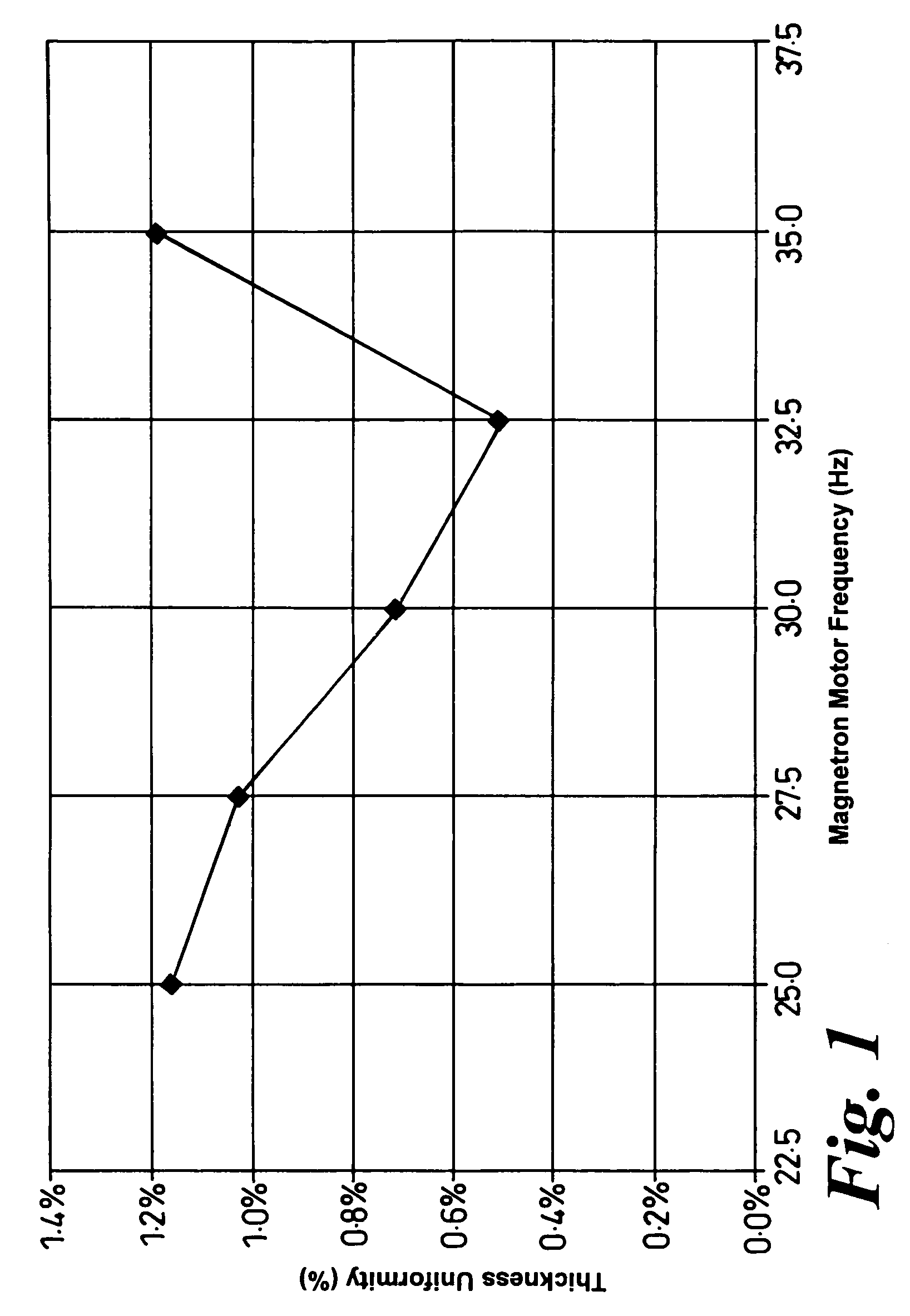
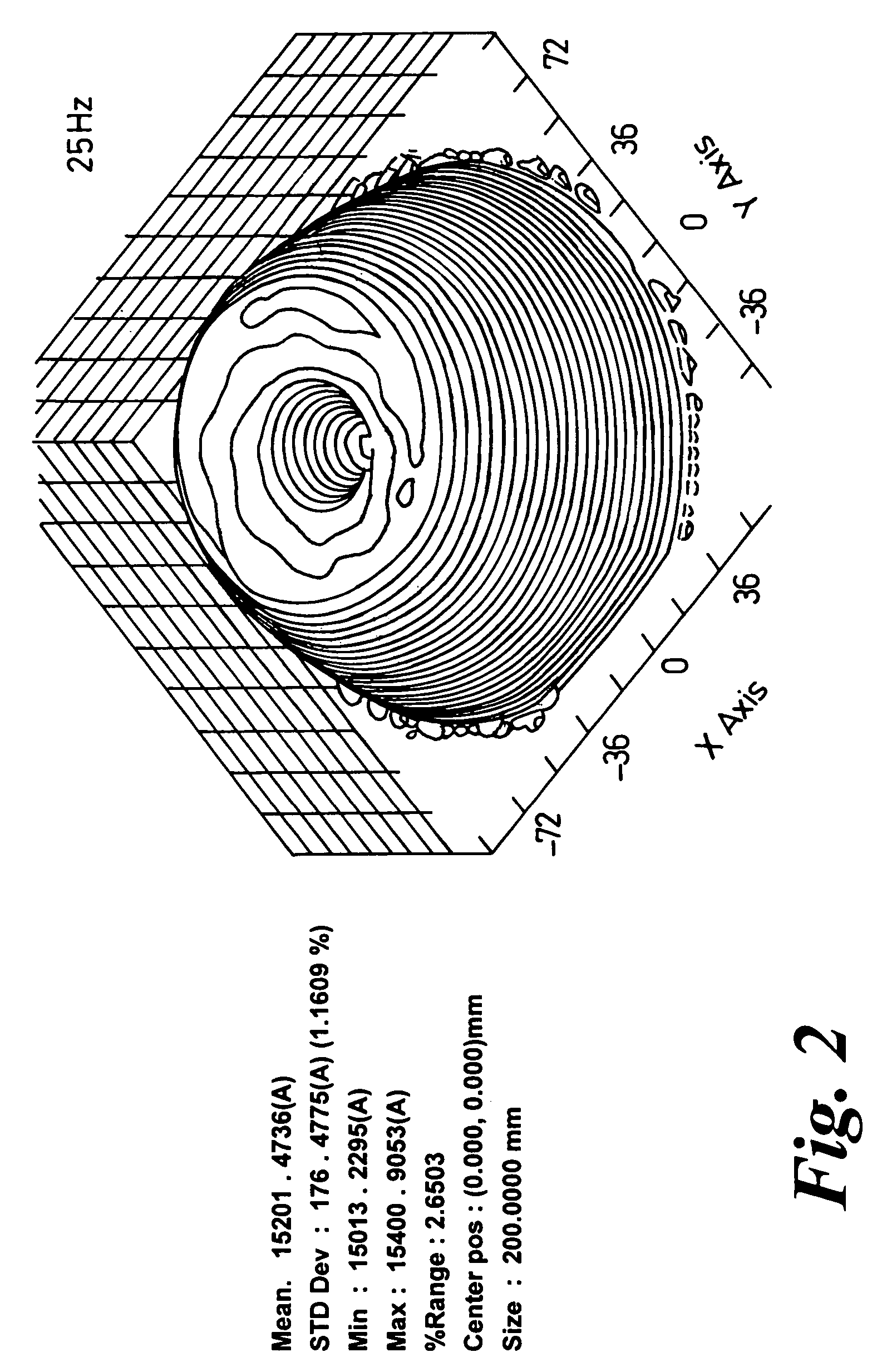
Methods and apparatus for sputtering
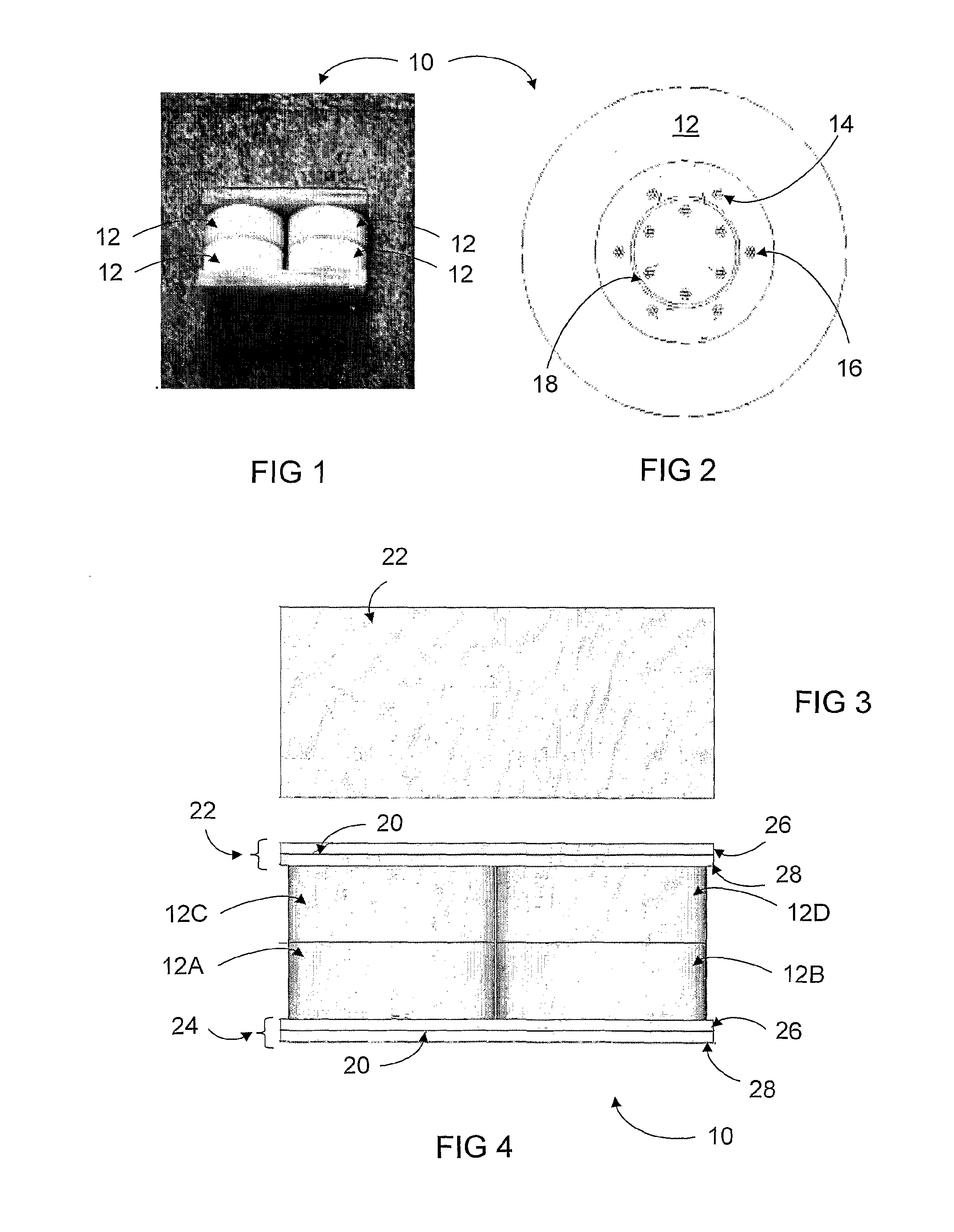
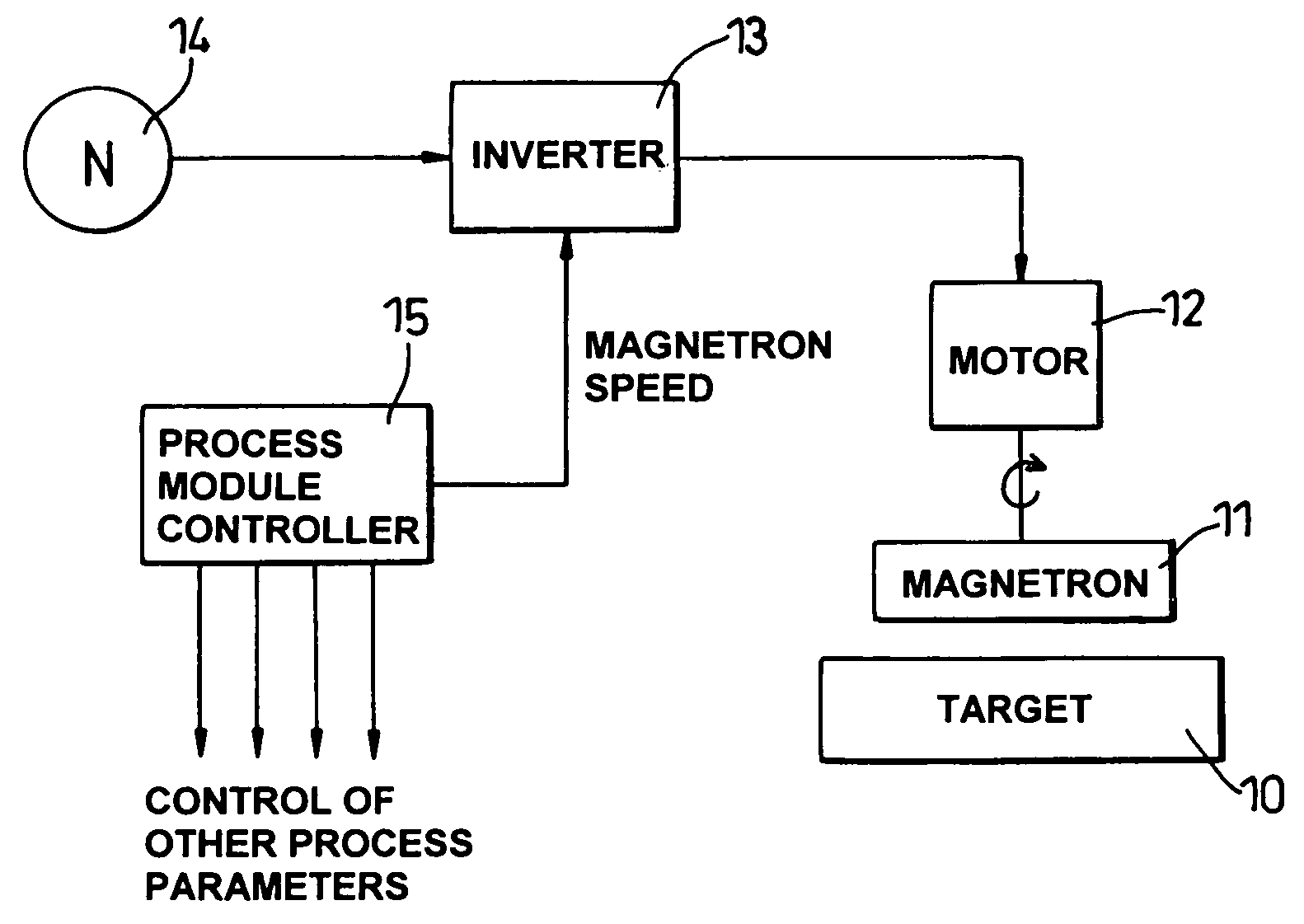
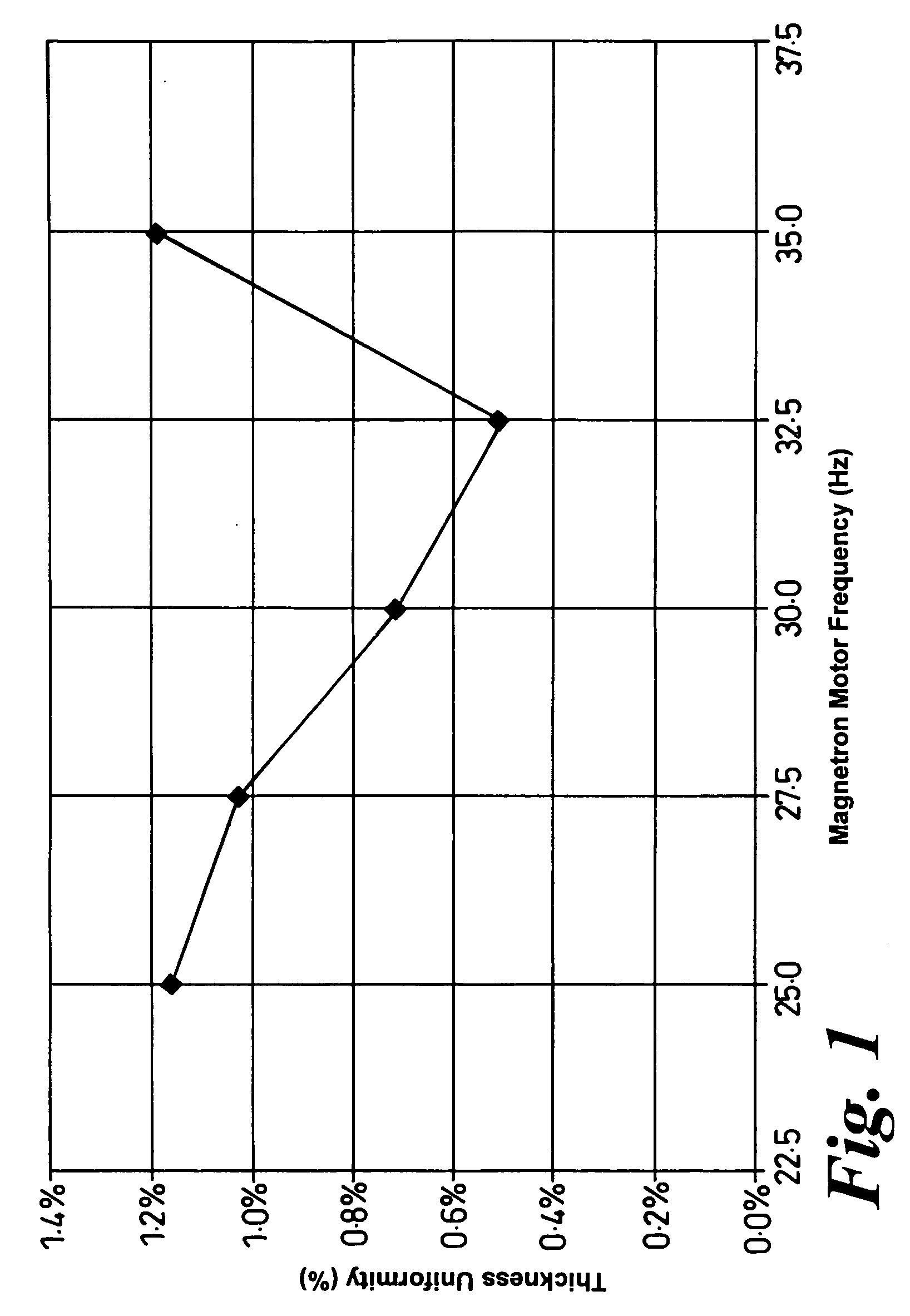
ActiveUS8585873B2Improve uniformityUniformity is maximisedCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringEngineering
A method of sputtering with sputtering apparatus is for depositing a layer upon a substrate. The apparatus includes a sputter target with a face exposed to the substrate and a magnetron providing a magnetic field that moves relative to the target face. The speed of movement of the field is controlled such that the uniformity of the deposition on the substrate is enhanced. A particular method includes monitoring uniformity verses speed, selecting the speed that gives the preferred uniformity and controlling the field to the selected speed. The selected speed may vary over the life of the target, with increased speeds becoming desirable as the target thins.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
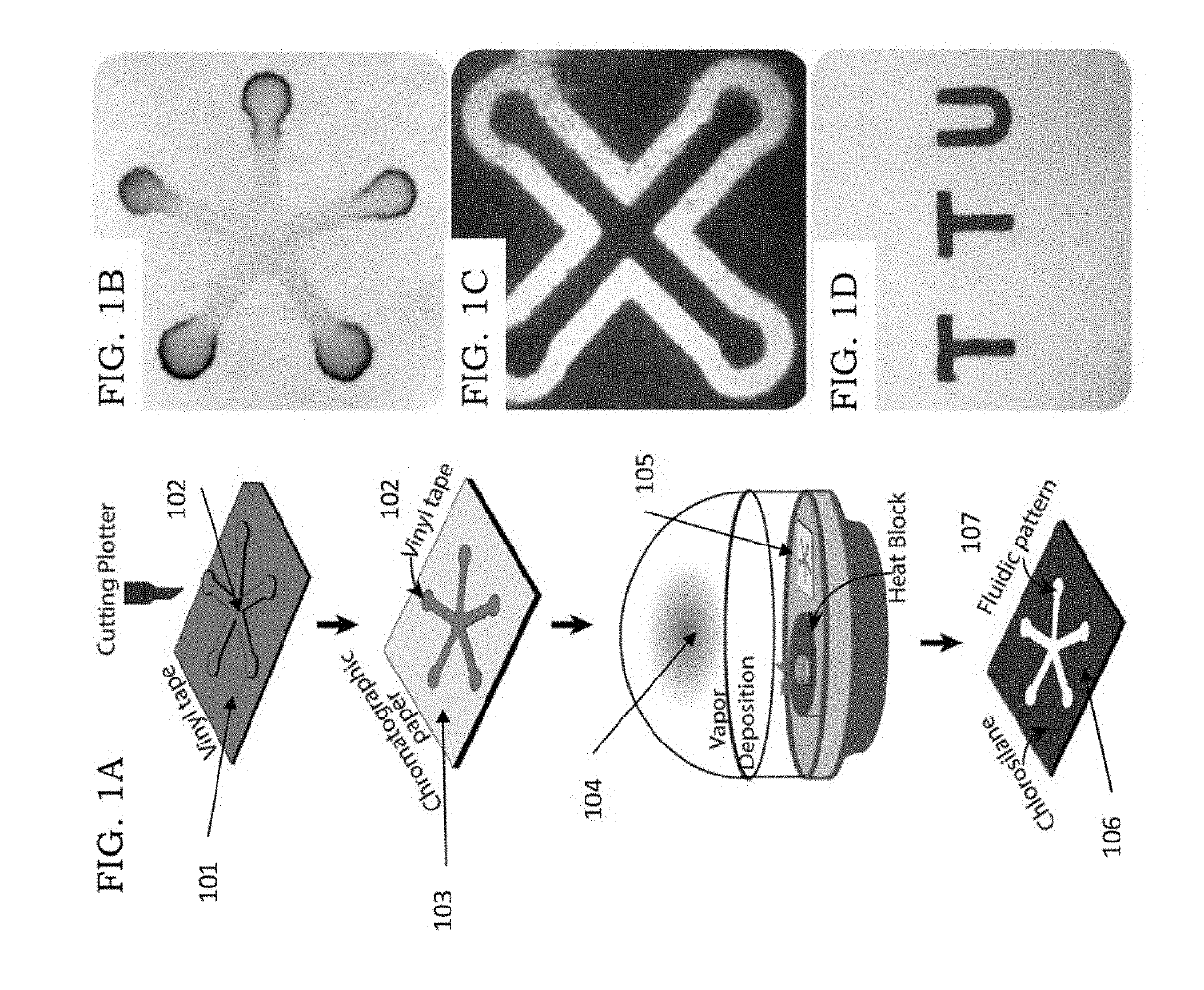
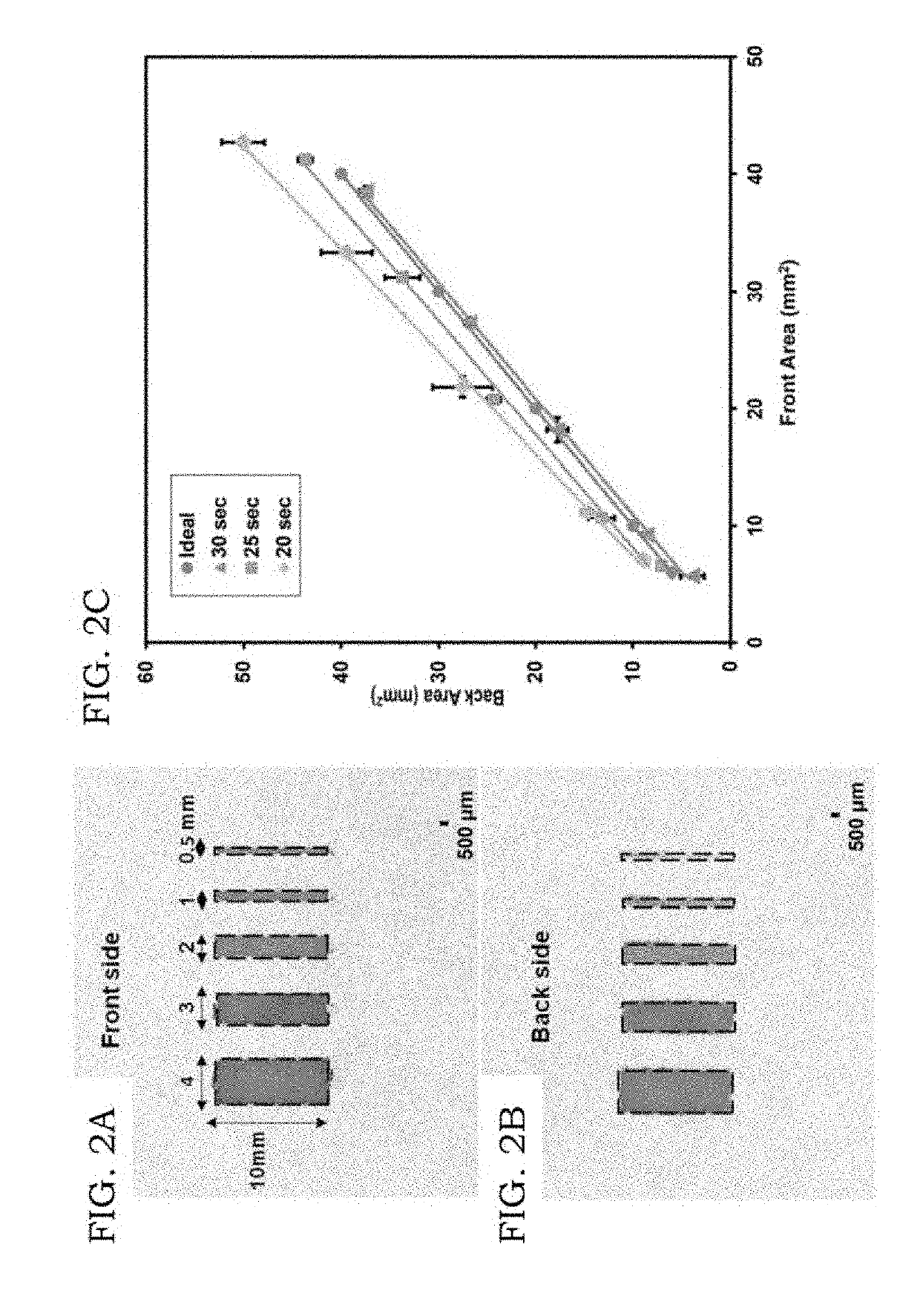
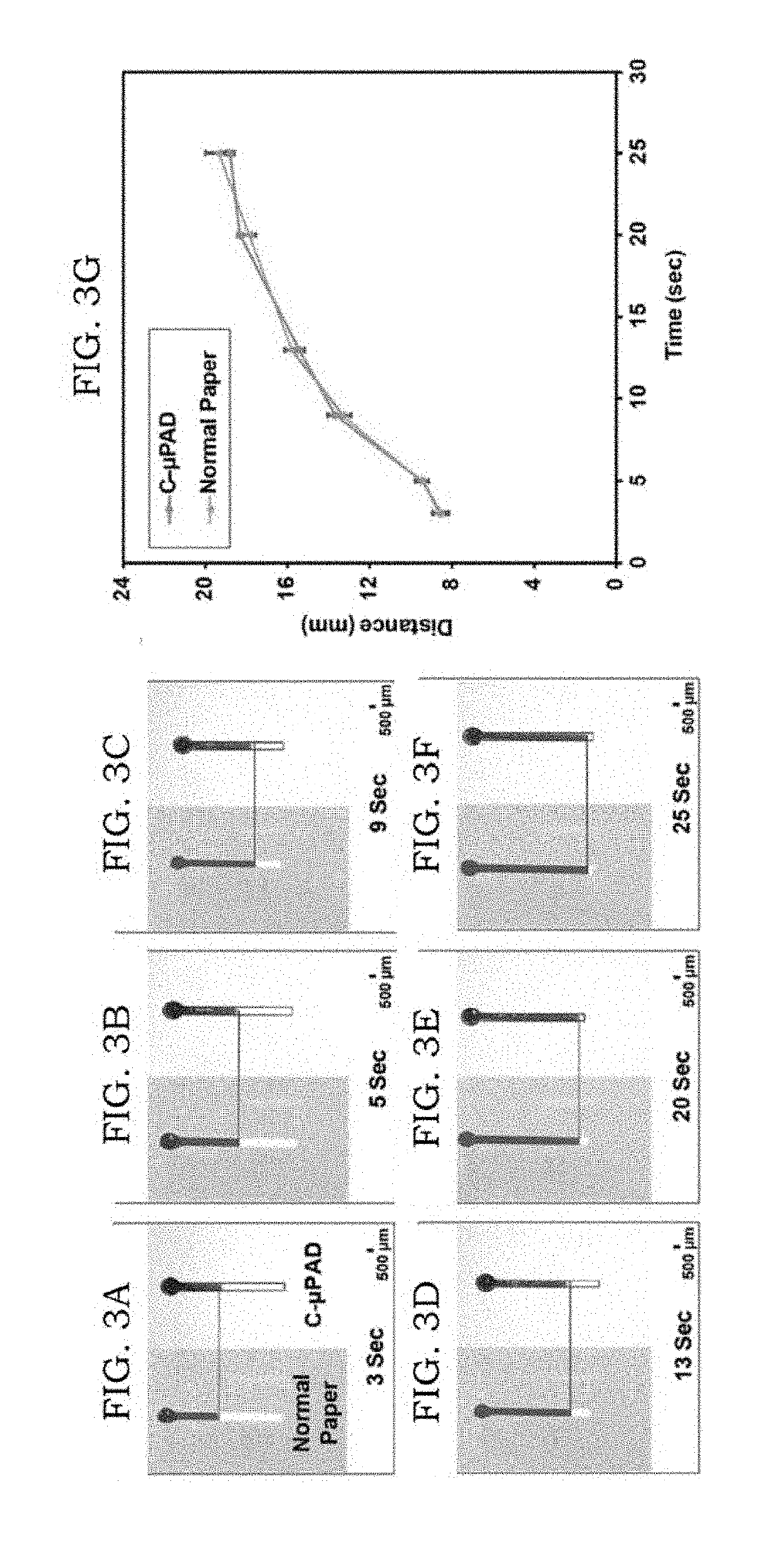
Chemically patterned microfluidic paper-based analytical device (c-µpad) for multiplex analyte detection
ActiveUS20190118175A1Simple and fast and sensitive methodMinimizing cross-reaction with chelating agentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careGas phase
Disclosed is a device and method for a microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD), for low-cost and user-friendly analytical devices capable of use for disease screening, point-of-care pathogen and biomarker detection, food and water quality testing. A microfluidic paper-based analytical device is further produced by chemical vapor deposition for multiplex heavy metal detection in water. Assay demonstrations proved that the immobilization of functional groups and multiplex heavy metal detection is suitable for real-world applications and established the approach for DNA analysis. The disclosed invention comprises multilayer capability, including the ability for various biomolecules to be immobilized with charge interaction.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
In-ear device
InactiveUS7804975B2Increase physical strengthIncreasing the thicknessPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesHearing apparatusEngineering
Owner:SONOVA AG
AlInGaN light-emitting device
A semiconductor light-emitting device fabricated in the (Al,Ga,In)N materials system has an active region for light emission (3) comprising InGaN quantum dots or InGaN quantum wires. An AlGaN layer (6) is provided on a substrate side of the active region. This increases the optical output of the light-emitting device. This increased optical output is believed to result from the AlxGa1-xN layer serving, in use, to promote the injection of carriers into the active region.
Owner:SHARP KK
In-ear device
InactiveUS20070003085A1Increase physical strengthIncreasing the thicknessPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesEngineeringCommunication device
A housing inserted in to the ear of a user is disclosed, said housing comprising a lateral end defined by being a part of the housing which is directed towards surroundings if the housing is inserted into the ear, a medial end defined by being a part of the housing which is directed towards the inner ear of the user if the housing is inserted into the ear, said medial end comprising at least a medial opening, wherein at least the lateral end of the housing is covered by a cover element. The cover element is acoustically transparent and made of open porous foam. The inventive in-ear device can be used as hearing device to improve the hearing of a hearing impaired person or as a communication device for natural as well as for remote communication.
Owner:SONOVA AG
High frequency transformers
ActiveUS20110291792A1Increase vortexReduce decreaseTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsUnwanted magnetic/electric effect reduction/preventionThree-phaseEngineering
High frequency, high power density coaxial, planar and three-phase transformers for converters and inverters are disclosed. One of the coaxial transformers comprises at least one primary winding and at least one secondary winding associated with at least one magnetic core, at least one coaxial Faraday shield between and substantially coaxial with the at least one primary winding and the at least one secondary winding and a substantially planar Faraday shield at one or more ends of the at least one magnetic core.
Owner:HBCC
Methods and apparatus for sputtering
ActiveUS20060081458A1Improve uniformityUniformity is maximisedCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of sputtering with sputtering apparatus is for depositing a layer upon a substrate. The apparatus includes a sputter target with a face exposed to the substrate and a magnetron providing a magnetic field that moves relative to the target face. The speed of movement of the field is controlled such that the uniformity of the deposition on the substrate is enhanced. A particular method includes monitoring uniformity verses speed, selecting the speed that gives the preferred uniformity and controlling the field to the selected speed. The selected speed may vary over the life of the target, with increased speeds becoming desirable as the target thins.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
Switching lens for display apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20150077670A1Desired optical propertyDeviation in thicknessStatic indicating devicesOptical articlesLenticular lensEngineering
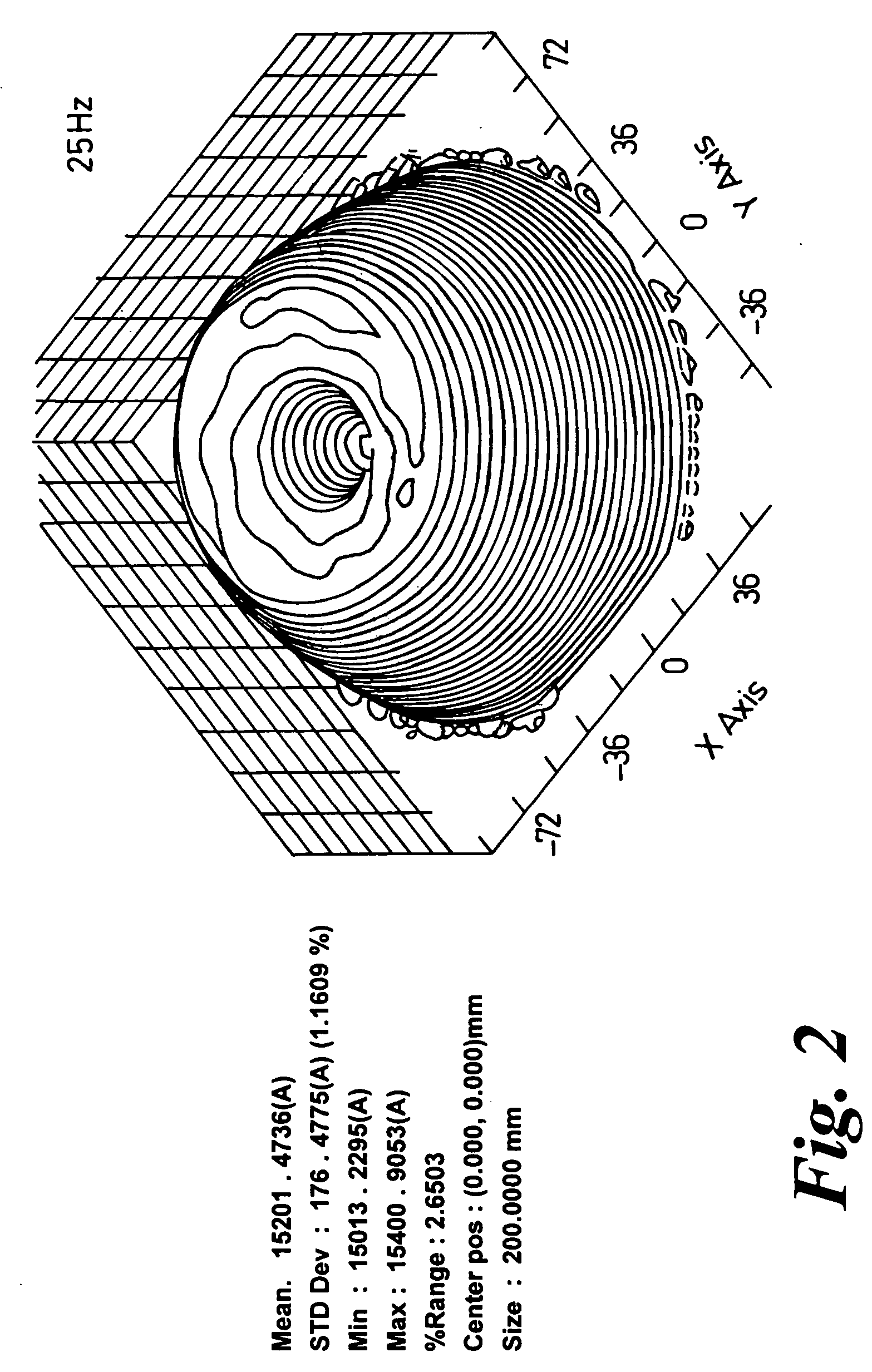
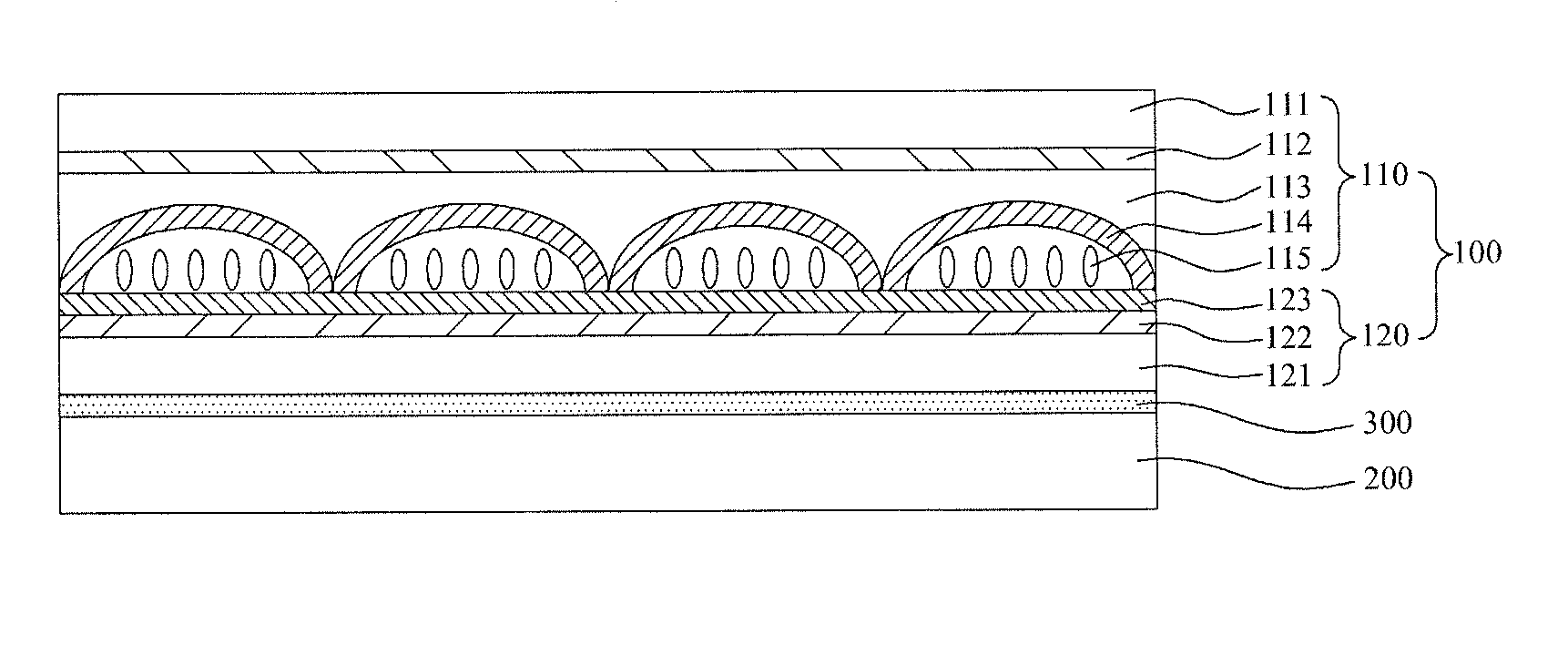
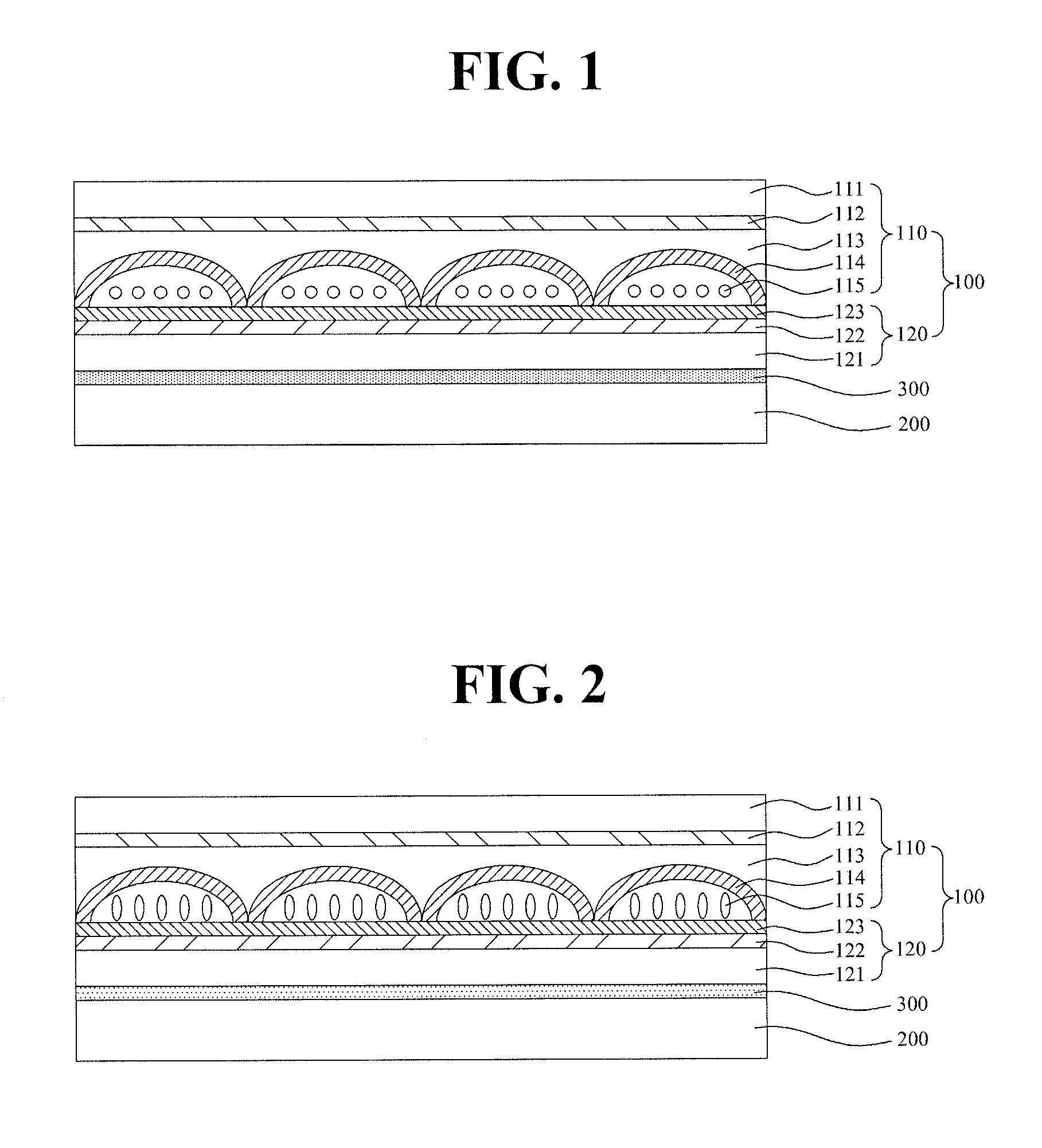
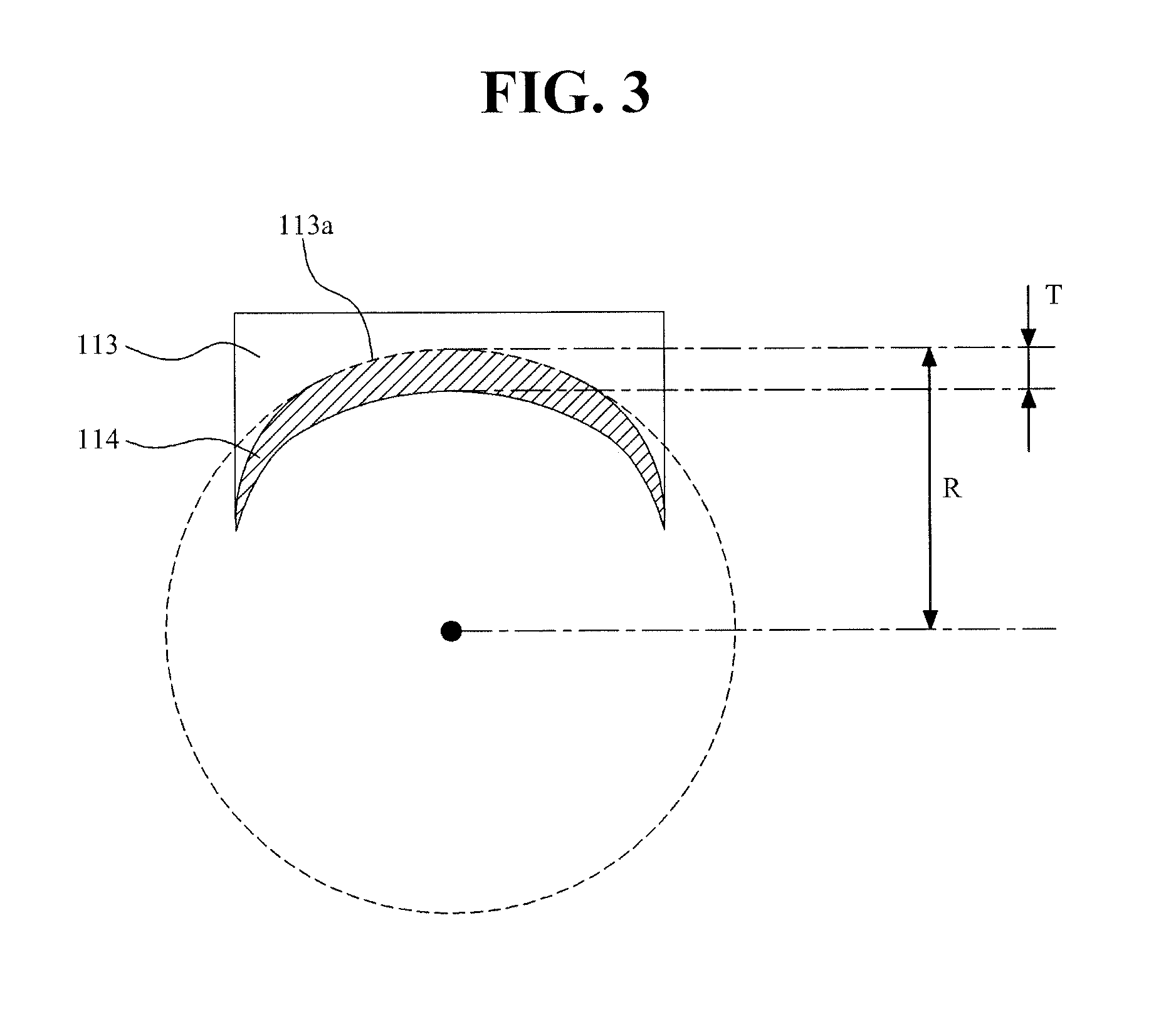
Disclosed are a switching lens and a method for manufacturing the same. The switching lens having liquid crystals of highly uniform orientation can be obtained by minimizing the thickness deviation of an alignment film formed on the whole curvature surface of a lenticular pattern. The switching lens of the present invention comprises a resin layer having a lenticular pattern and an alignment film on the resin layer. The alignment film covers the whole curvature surface of the lenticular pattern and has the maximum thickness equal to or less than 0.01 times the maximum radius of curvature of the lenticular pattern.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Precise fabrication of polymer microlens arrays
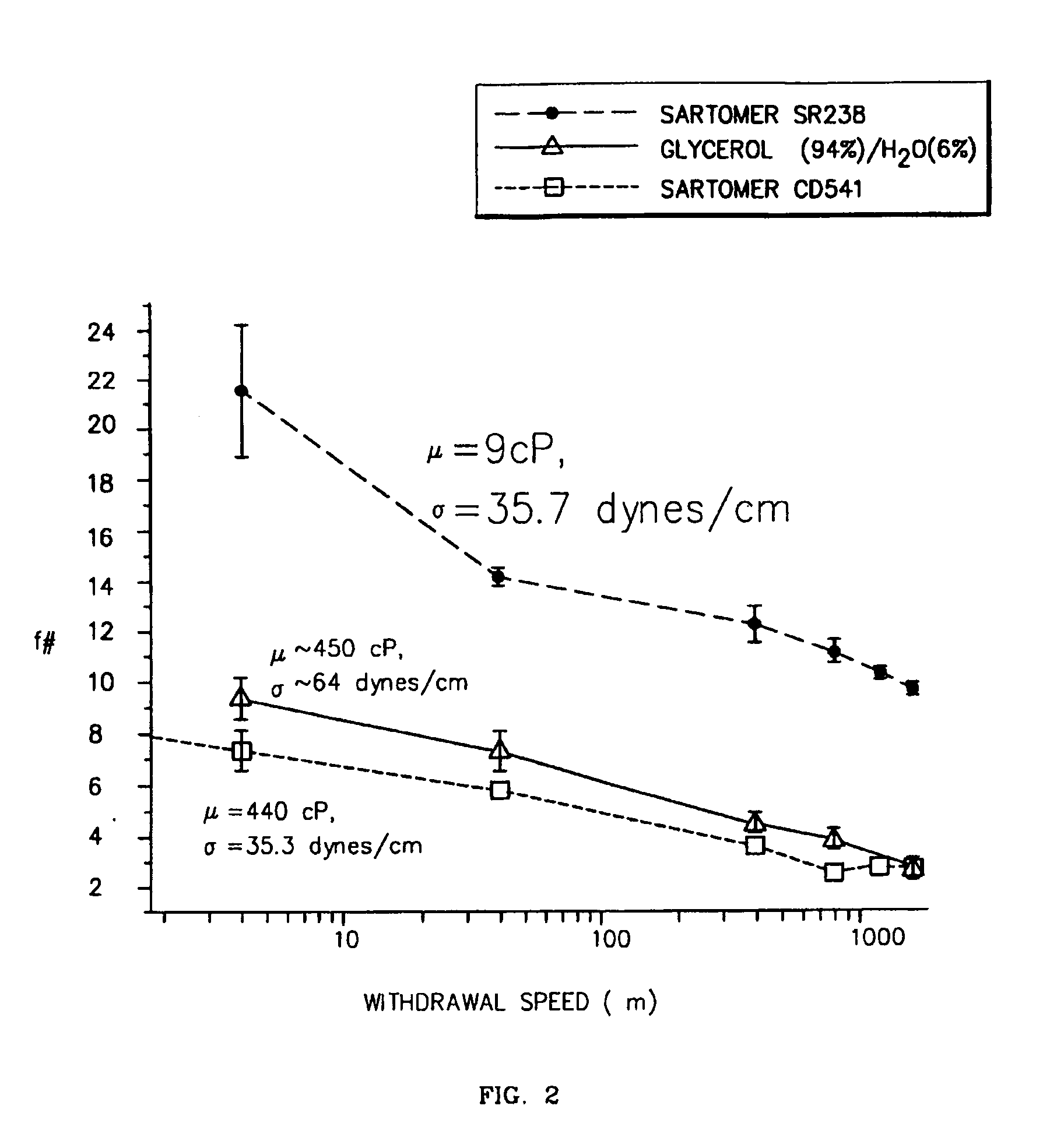
InactiveUS7771630B2Improve performanceUniformity is maximisedNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusLiquid viscosityRefractive index
High performance microlens arrays are fabricated by (i) depositing liquid on the hydrophilic domains of substrates of patterned wettability by either (a) condensing liquid on the domains or (b) withdrawing the substrate from a liquid solution and (ii) optionally curing the liquid to form solid microlenses. The f-number (f#) of formed microlenses is controlled by adjusting liquid viscosity, surface tension, density, and index of refraction, as well as the surface free energies of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic areas. The f-number of formed microlenses is also adjustable by controlling substrate dipping angle and withdrawal speed, the array fill factor and the number of dip coats used. At an optimum withdrawal speed f# is minimized and array uniformity is maximized. At this optimum, arrays of f / 3.48 microlenses were fabricated using one dip-coat with uniformity better than Δf / f˜±3.8% while multiple dip-coats permit production of f / 1.38 microlens arrays and uniformity better than Δf / f˜±5.9%. Average f#s are reproducible to within 3.5%. The method is adaptable and extendible to precision parallel fabrication of (i) microlenses precisely sized, aligned and spatially positioned to various small light sources and optical fiber ends, (ii) conductive bump bonds on substrate pads, and (iii) conductive bonds between corresponding domains on separate perpendicular substrates, all of which are self-aligned.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
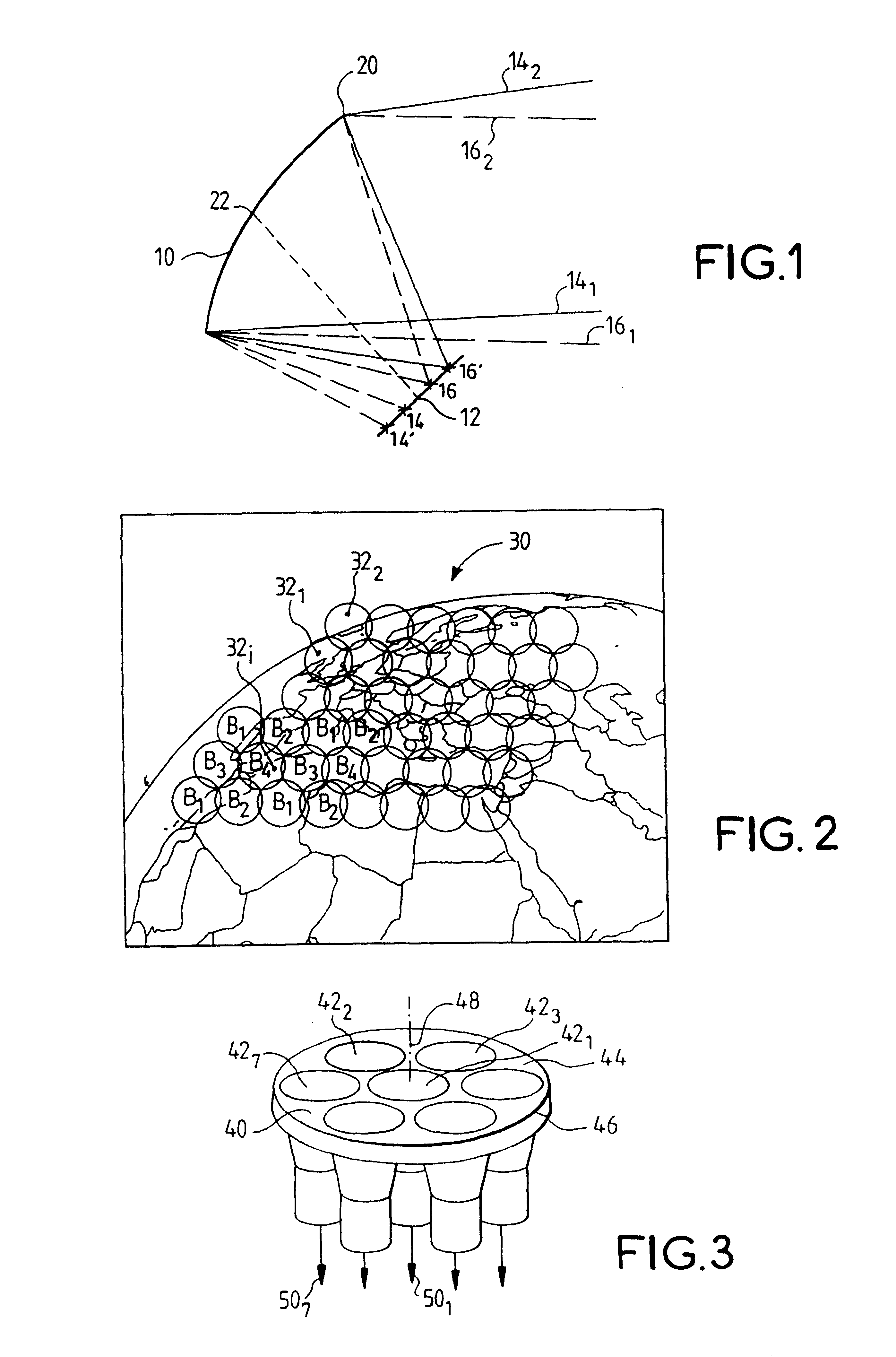
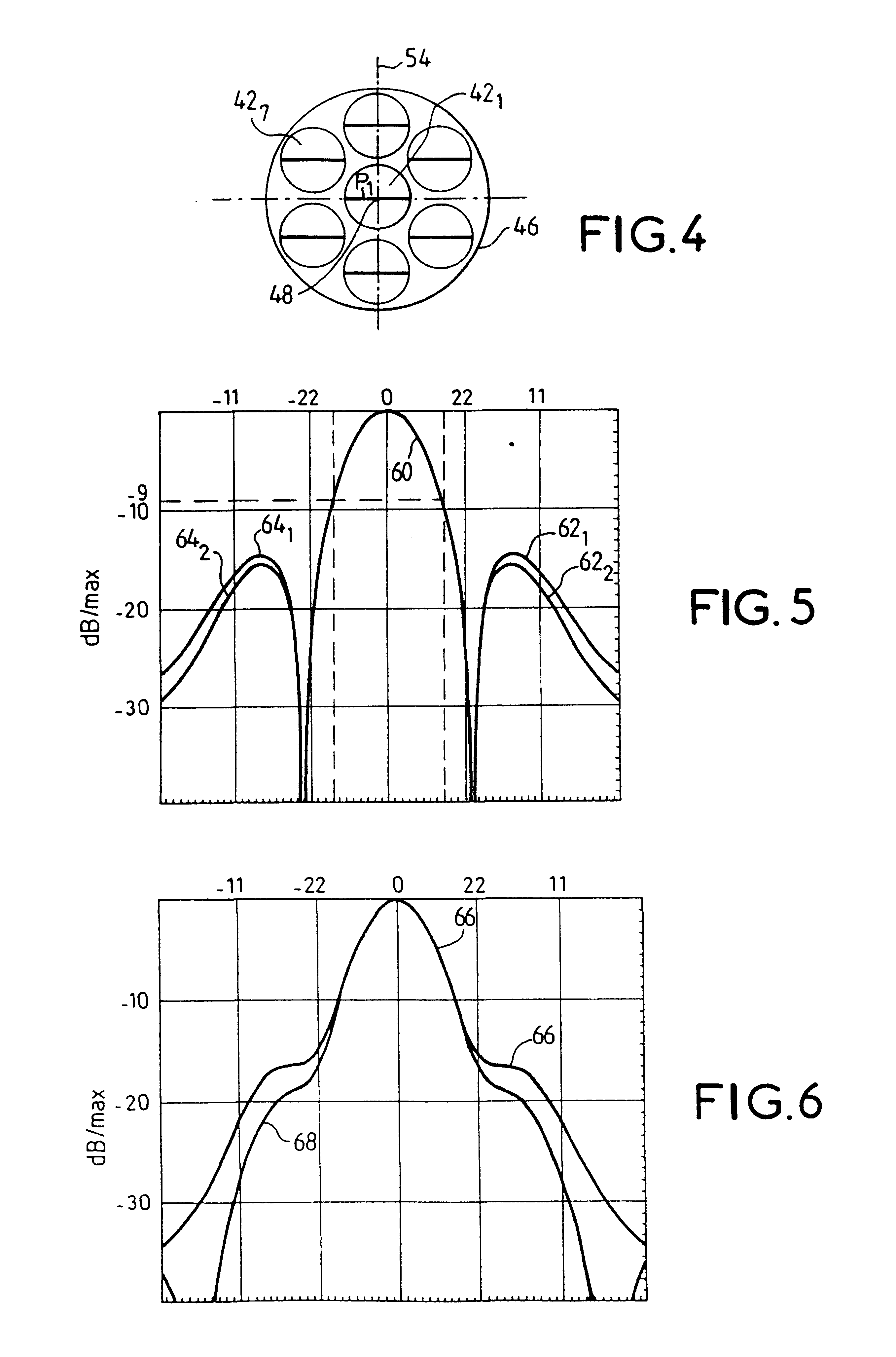
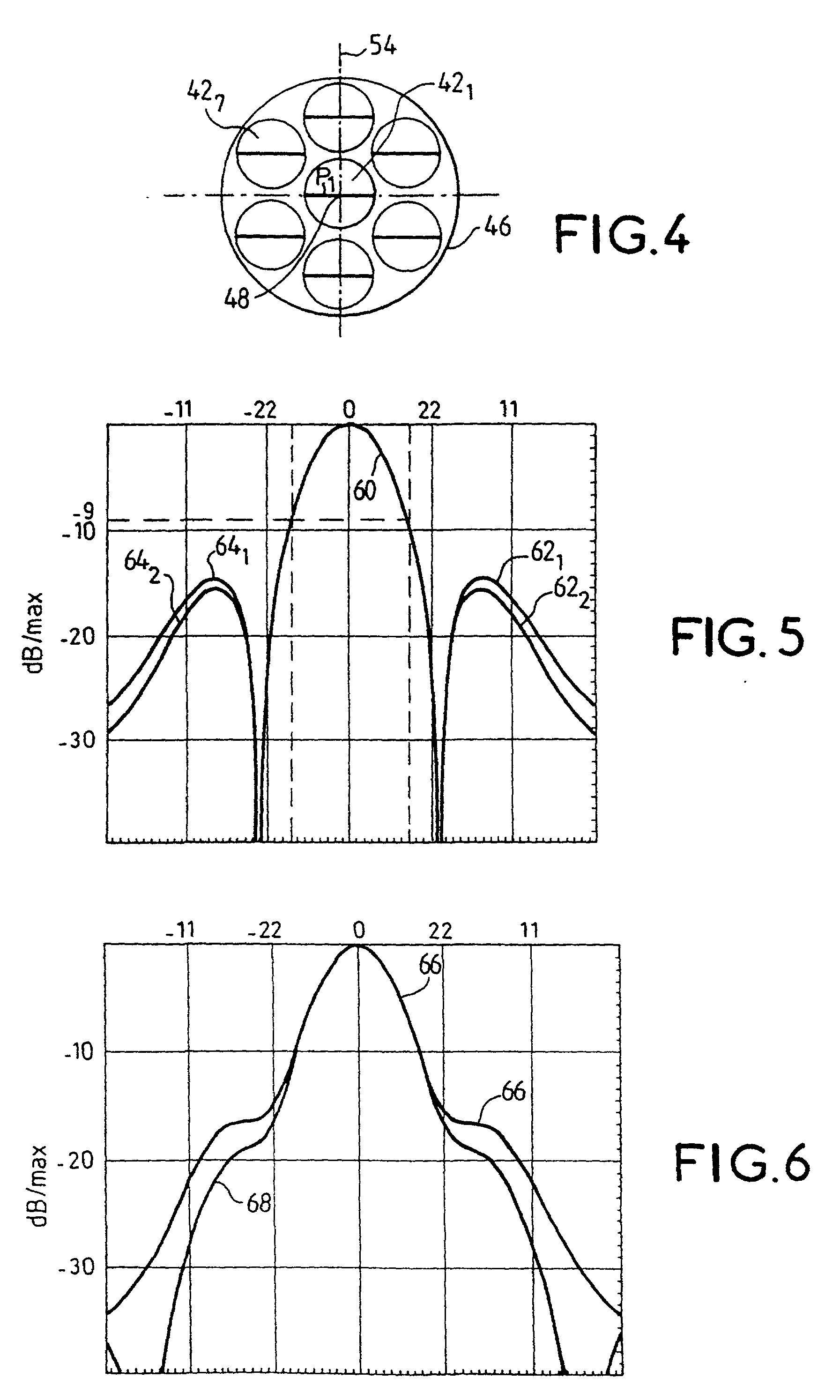
Radiating source for a transmit and receive antenna intended to be installed on board a satellite
InactiveUS6424312B2Lower levelWeaken energyCosmonautic vehiclesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesOn boardRadiation pattern
The invention relates to a radiating source for transmitting and receiving, intended to be installed on board a satellite to define a radiation pattern in a terrestrial zone, said source being intended to be disposed in or near the focal plane of a reflector associated with other sources corresponding to other terrestrial zones. The source includes a plurality of radiating apertures, each of which has an efficiency at least equal to 70%, and feed means for feeding said radiating apertures. The radiating apertures and their feed means are such that the energy radiated by all of the radiating apertures is practically limited to the corresponding reflector, at least for transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
High frequency transformers
ActiveUS8629746B2Increase vortexReduce decreaseTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresThree-phaseEngineering
High frequency, high power density coaxial, planar and three-phase transformers for converters and inverters are disclosed. One of the coaxial transformers comprises at least one primary winding and at least one secondary winding associated with at least one magnetic core, at least one coaxial Faraday shield between and substantially coaxial with the at least one primary winding and the at least one secondary winding and a substantially planar Faraday shield at one or more ends of the at least one magnetic core.
Owner:HBCC
Microwave furnace and a method of sintering
ActiveUS11435142B2Minimize timeGood translucency and material strengthBracketsFurnace typesSusceptorMicrowave oven
A microwave furnace has a furnace chamber formed between a chamber housing and a sintering platform for an object to be sintered. A microwave source is arranged for emitting microwaves into the furnace chamber. The microwave furnace further has a susceptor that comprises a material which over a temperature range of the material of at least 23 C to 700 C couples into microwaves. The susceptor and the furnace chamber are movable relative to each other between a first position, in which the susceptor is positioned relative to the furnace chamber, and a second position in which the susceptor is positioned further retracted from the furnace chamber relative to the first position. The invention helps providing a zirconia material with a relative homogeneous material structure.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Optical fiber processing system using a co2 laser
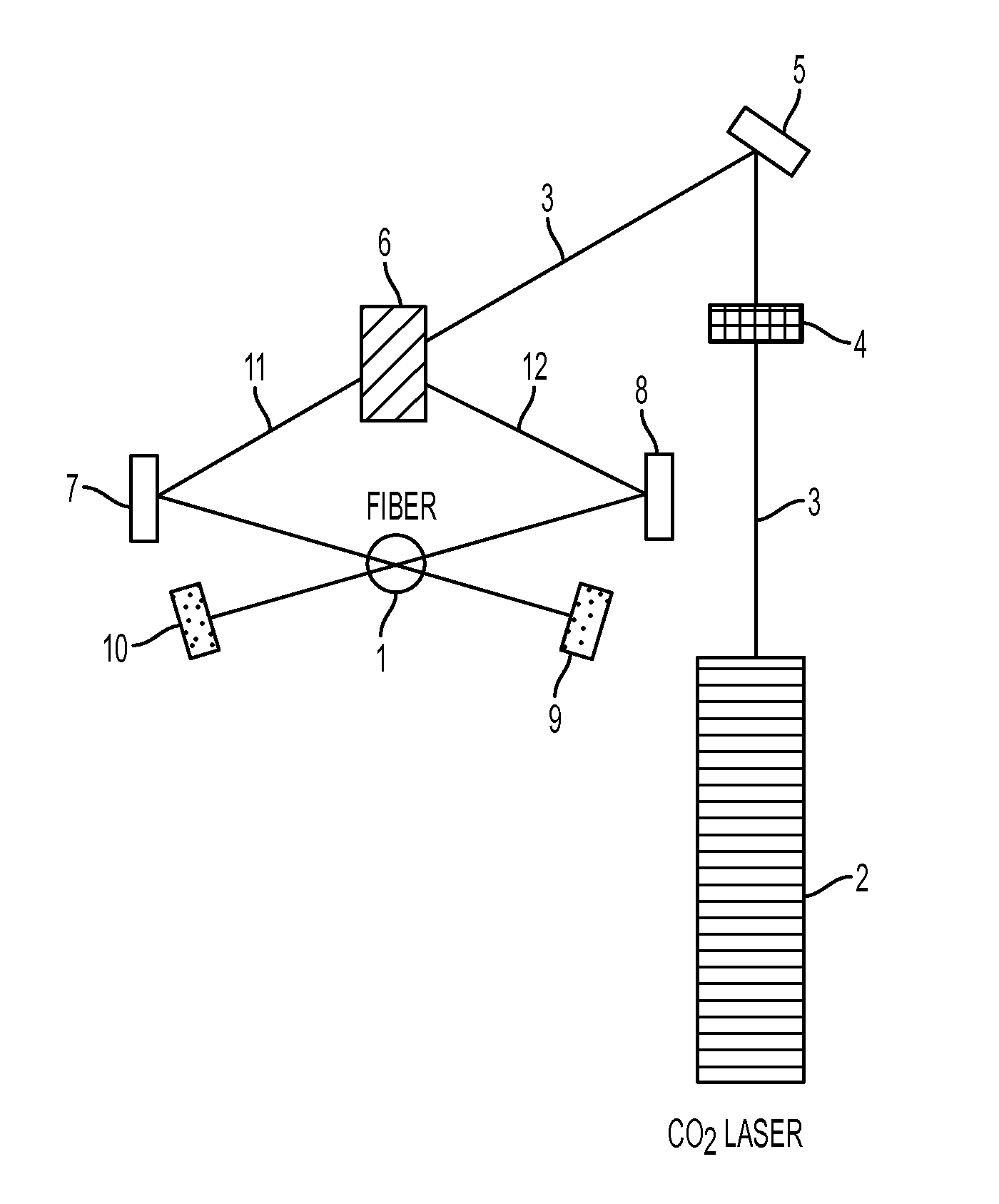
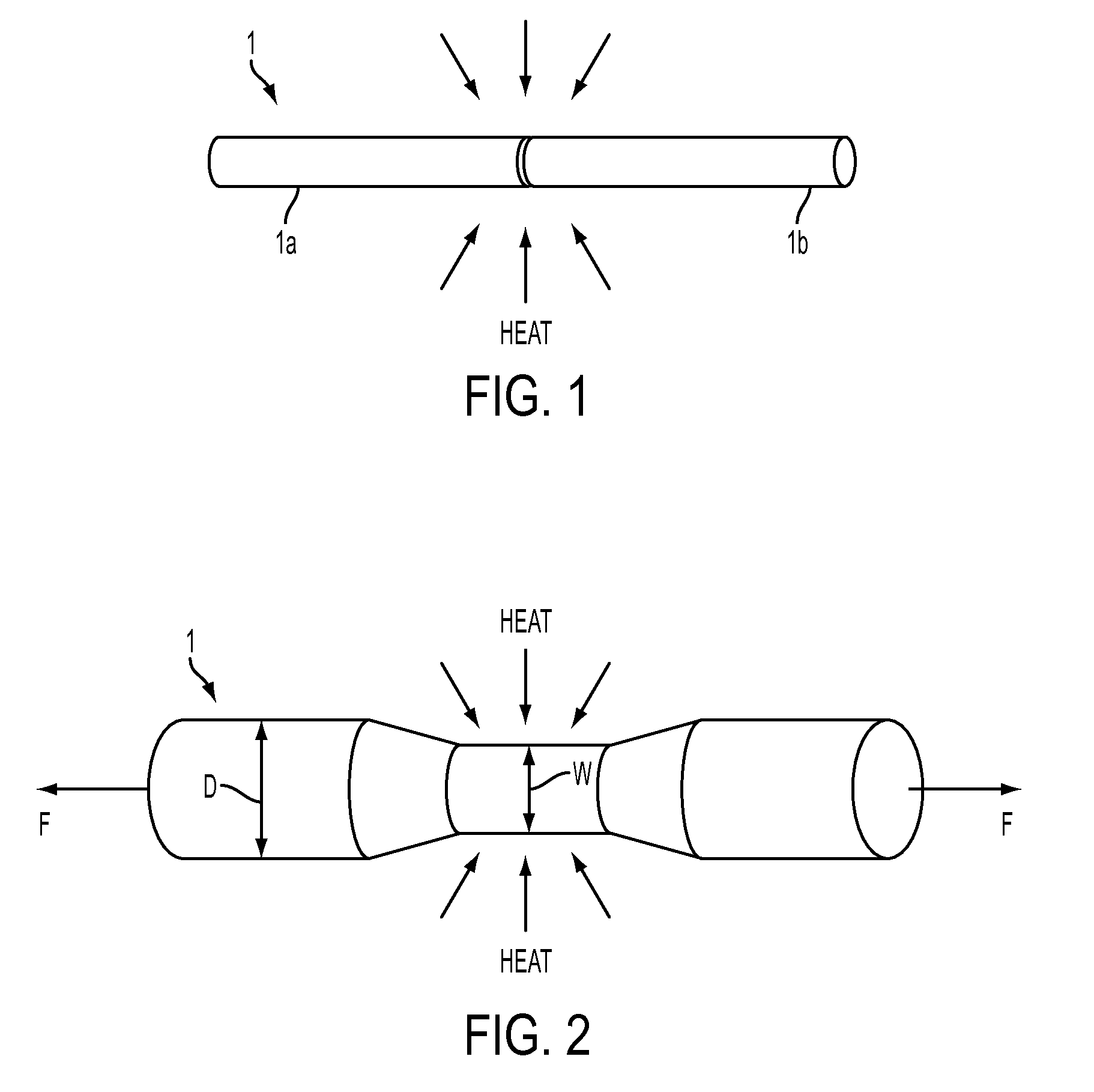
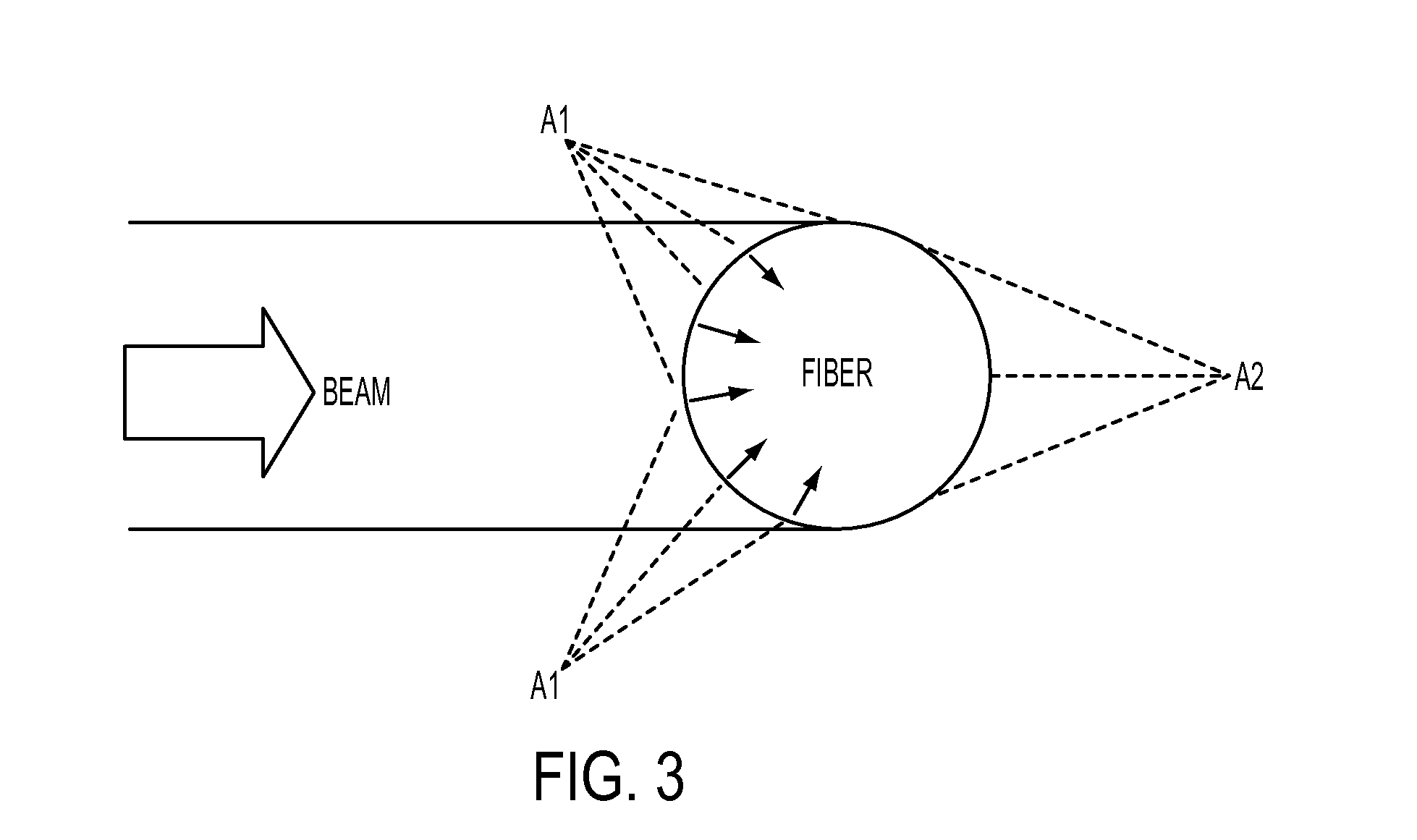
InactiveUS20150192738A1Avoid couplingUniform surfaceGlass making apparatusPhase-affecting property measurementsFiberLight beam
An apparatus for splicing, tapering and heat processing optical fibers is disclosed. The apparatus may include a laser configured to irradiate a portion of one or more optical fibers by at least two laser beams. The beams may be configured to irradiate different areas of the exterior surface of the fiber portion such as to increase the uniformity of heating distribution over the exterior surface of a portion of the optical fiber. In a configuration using two beams to irradiate the fiber portion the angle between the beams may be the closest angle to 180 degrees for which coupling between the first beam and the second beam is avoided. The apparatus may include three or more beams distributed around the optical fiber such as to irradiate the fiber portion uniformly and provide uniform heating of the fiber.
Owner:AFL COMM LLC
Radiating source for a transmit and receive antenna intended to be installed on board a satellite
InactiveUS20010003444A1Low level of illuminationLower levelCosmonautic vehiclesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesPhysicsSatellite
The invention relates to a radiating source for transmitting and receiving, intended to be installed on board a satellite to define a radiation pattern in a terrestrial zone, said source being intended to be disposed in or near the focal plane of a reflector associated with other sources corresponding to other terrestrial zones. The source includes a plurality of radiating apertures, each of which has an efficiency at least equal to 70%, and feed means for feeding said radiating apertures. The radiating apertures and their feed means are such that the energy radiated by all of the radiating apertures is practically limited to the corresponding reflector, at least for transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
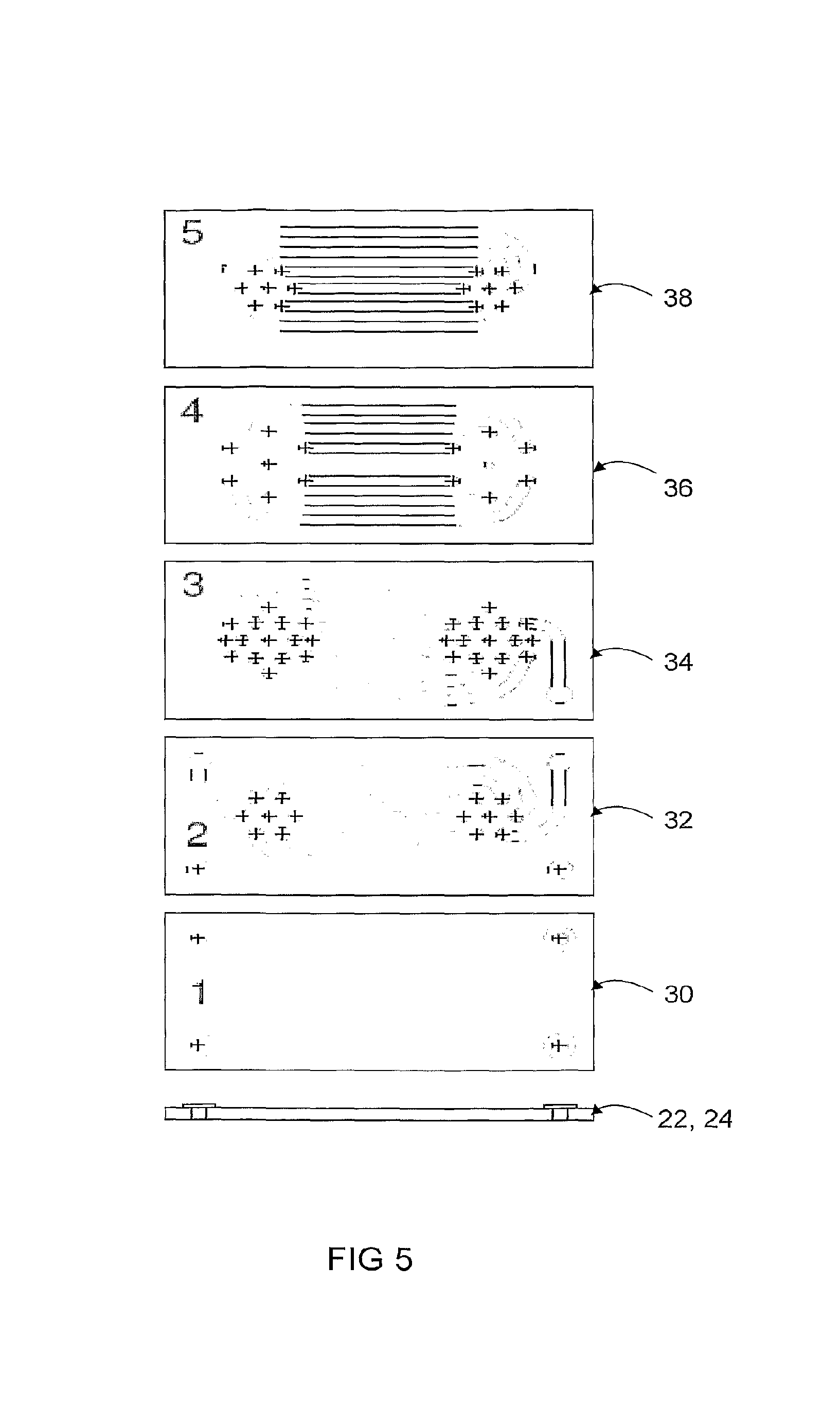
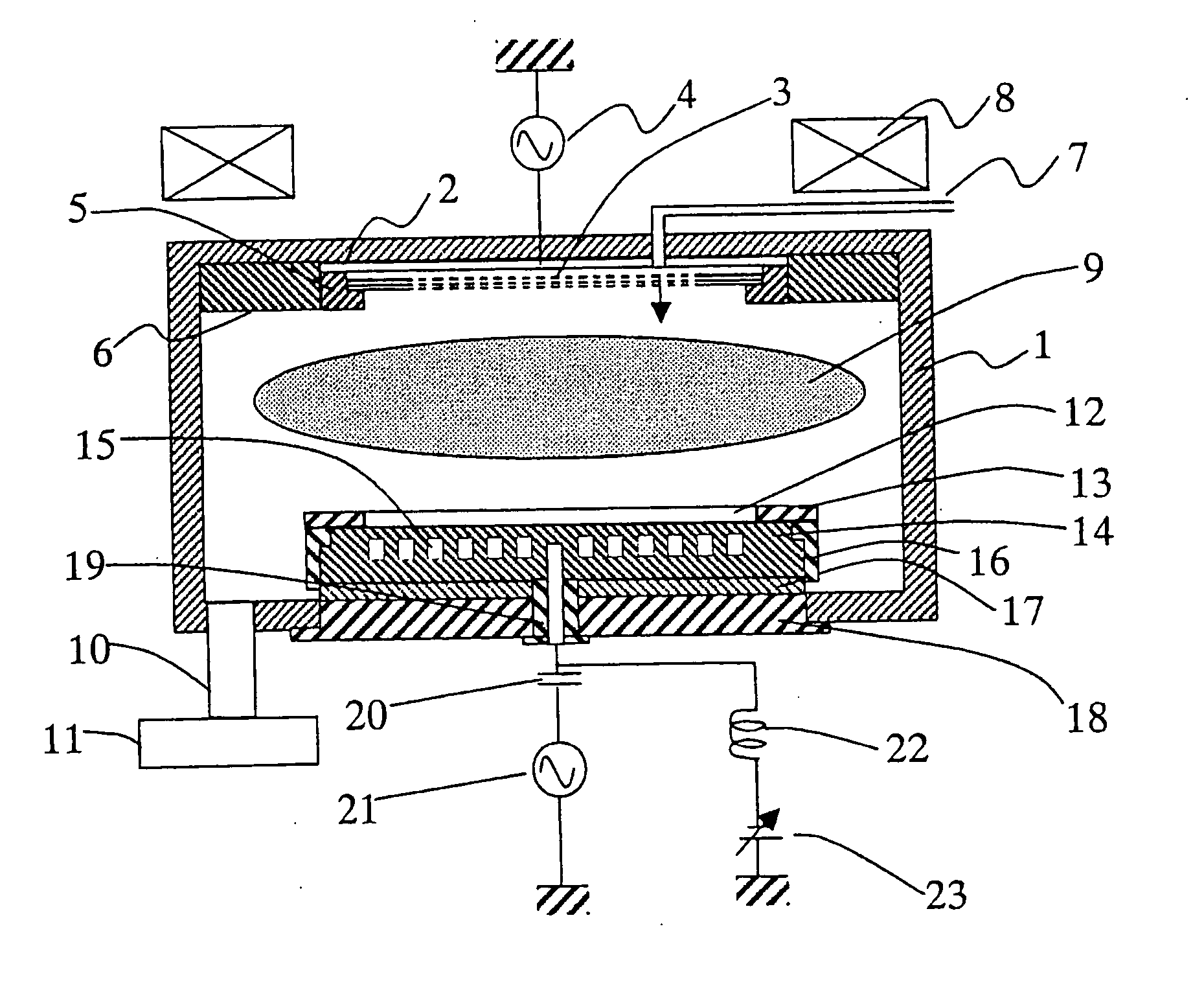
Device and method to control the uniformity of a gas flow in a CVD or an ald reactor or of a layer grown therein
InactiveUS20180128647A1Improve uniformityEfficient executionChemical vapor deposition coatingConverting sensor output mechanicallySusceptorProcess engineering
A measuring device is provided for determining the position of a susceptor in a reactor housing. The measuring device includes a central element, which can be fastened on the susceptor at a predefined location, and a plurality of sensing arms, which protrude from the central element beyond an outer periphery of the susceptor. The sensing arms respectively include a sensing section that can be brought in touching contact with a contact zone. The contact zone is formed by an inner periphery of the reactor housing or a component arranged in the reactor housing. Using the measuring device, the position of a susceptor of a CVD reactor is determined relative to the reactor housing or a component arranged in the reactor housing.
Owner:EUGENUS INC
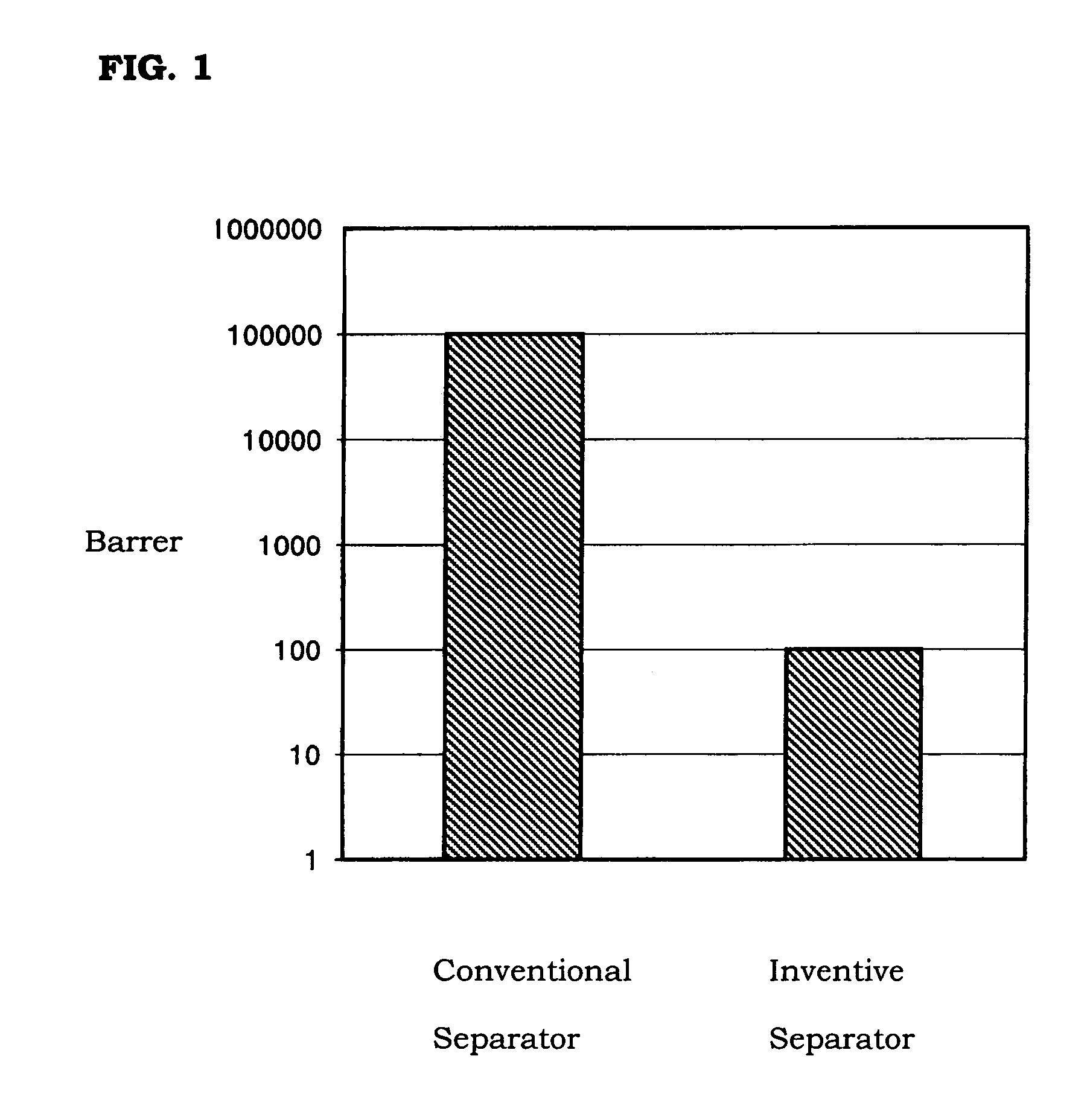
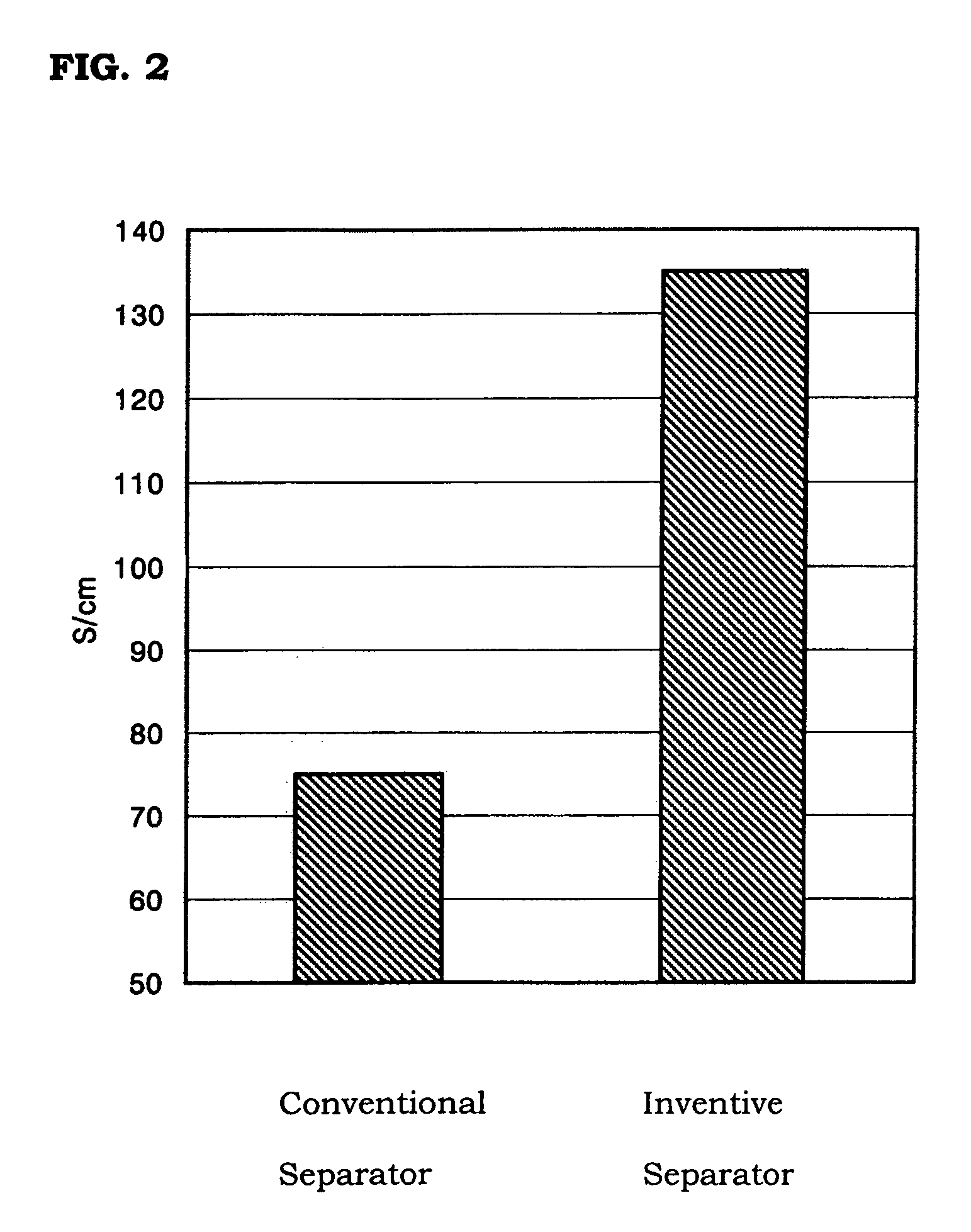
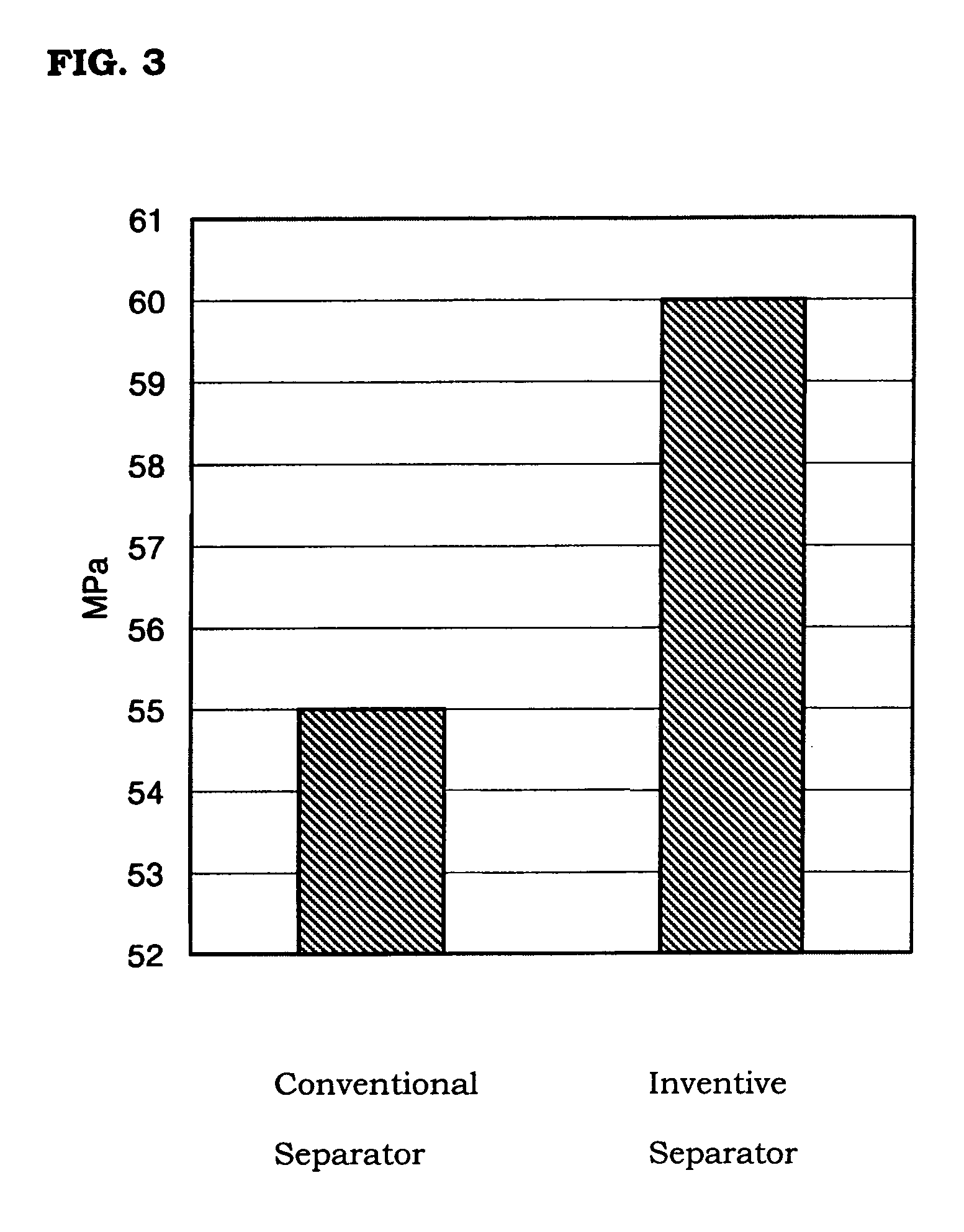
Molding material for fuel cell separator and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS7465503B2Low gas permeabilityImprove conductivityFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsEpoxyFuel cells
Disclosed herein is a method for preparing a molding material for a fuel cell separator by dissolving an epoxy resin, a hardener and other additives in acetone and mixing a planar expanded graphite powder with the solution. Further disclosed are a molding material prepared by the method and a fuel cell separator produced from the molding material. The fuel cell separator shows very low gas permeability, superior electrical conductivity, sufficient strength, and maximized uniformity throughout the overall structure of the finished product.
Owner:HANKOOK TIRE WORLDWIDE
Method and apparatus for plasma processing
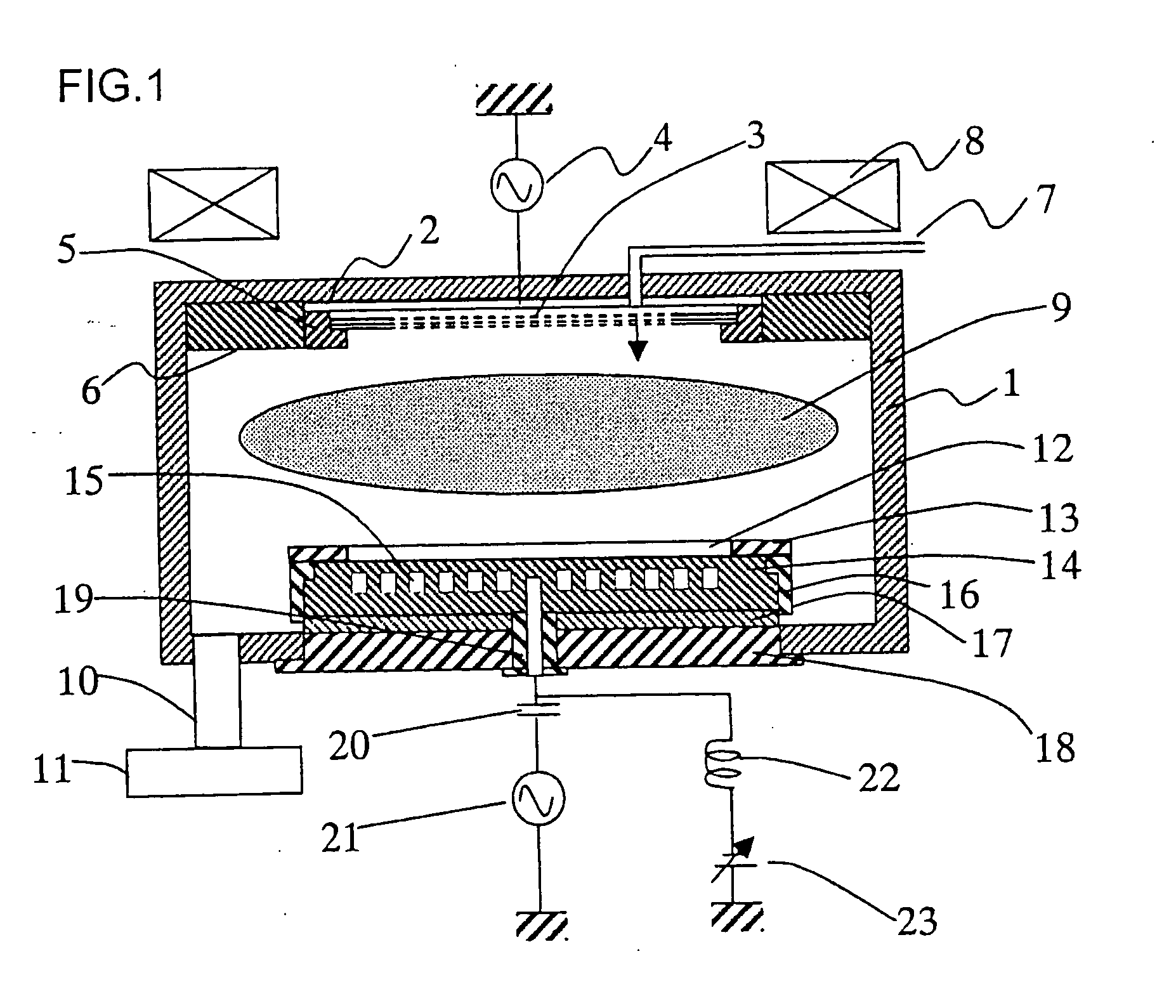
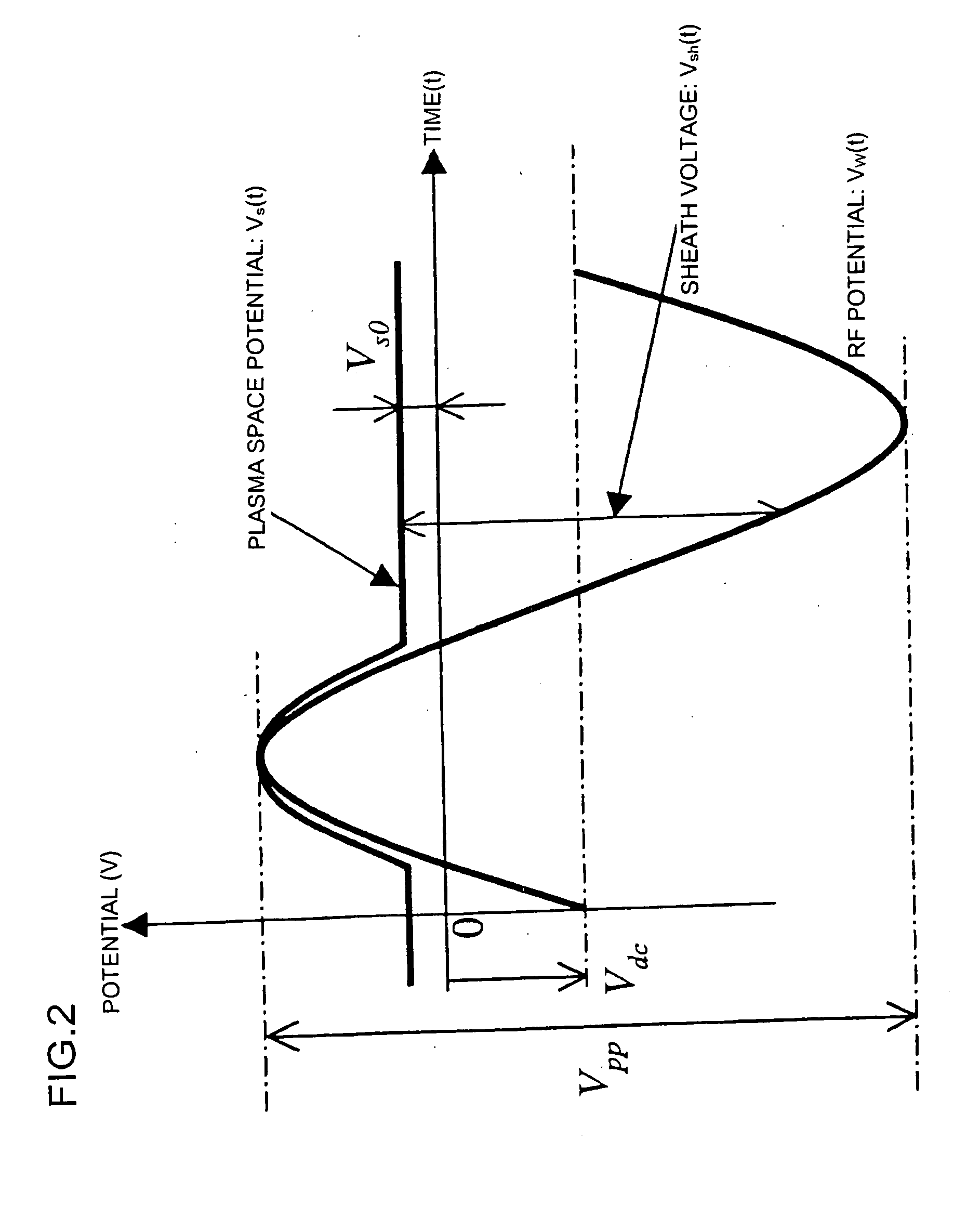
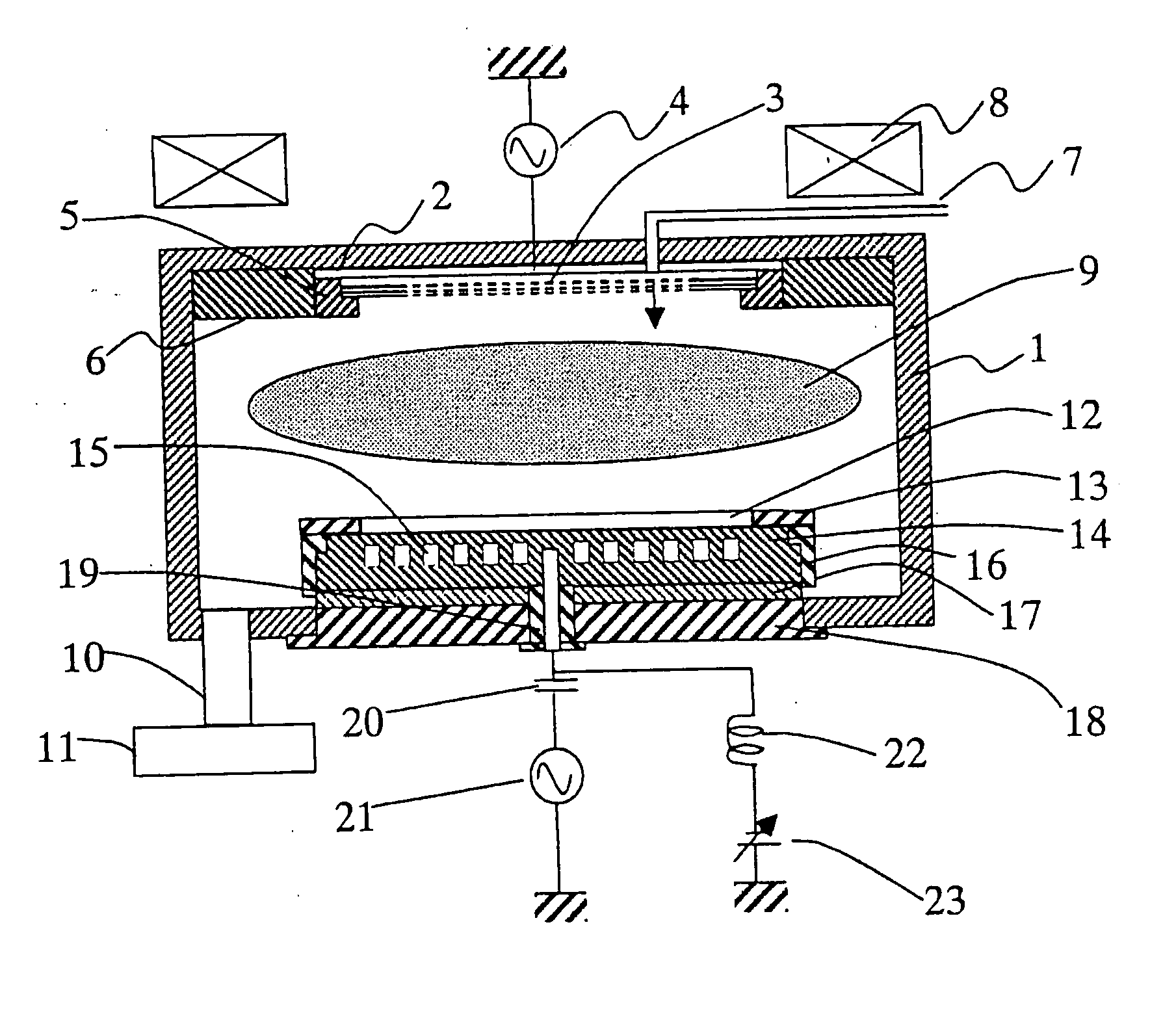
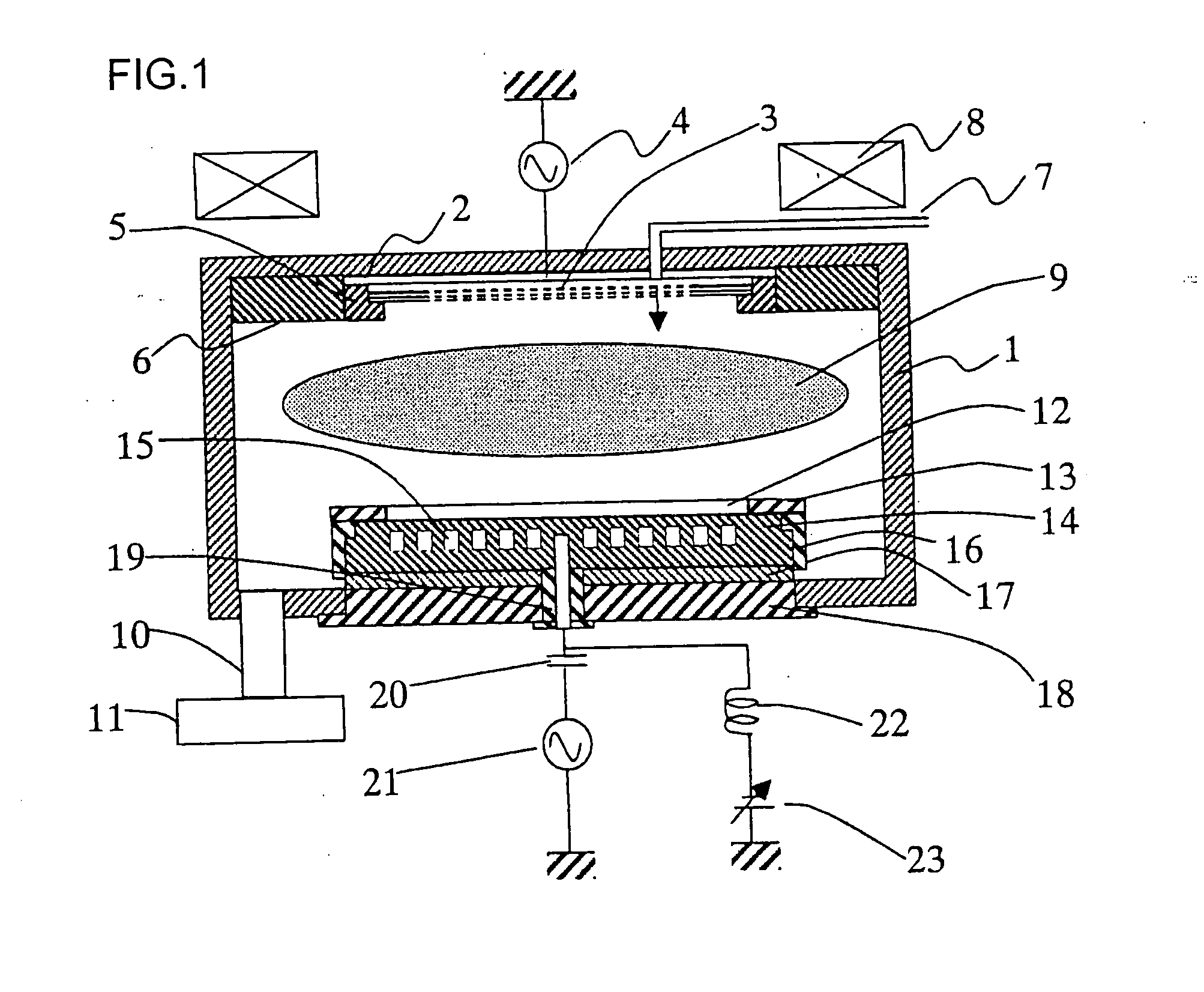
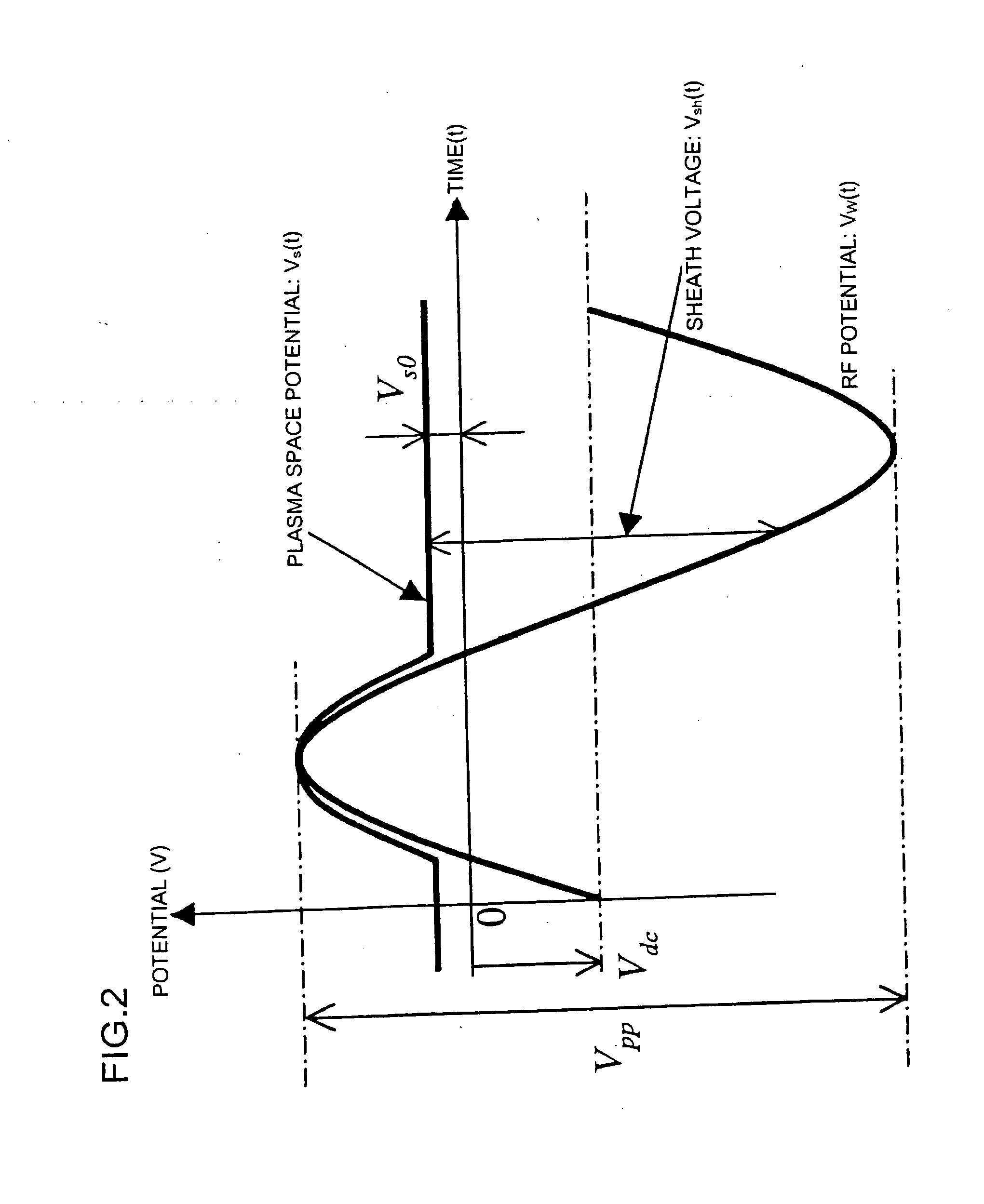
InactiveUS20070227669A1Uniformity is maximisedProlong lifeGeometric CADElectric discharge tubesDielectricElectrical conductor
Owner:NISHIO RYOJI +3
Efficient self-refocusing zero echo time mr imaging
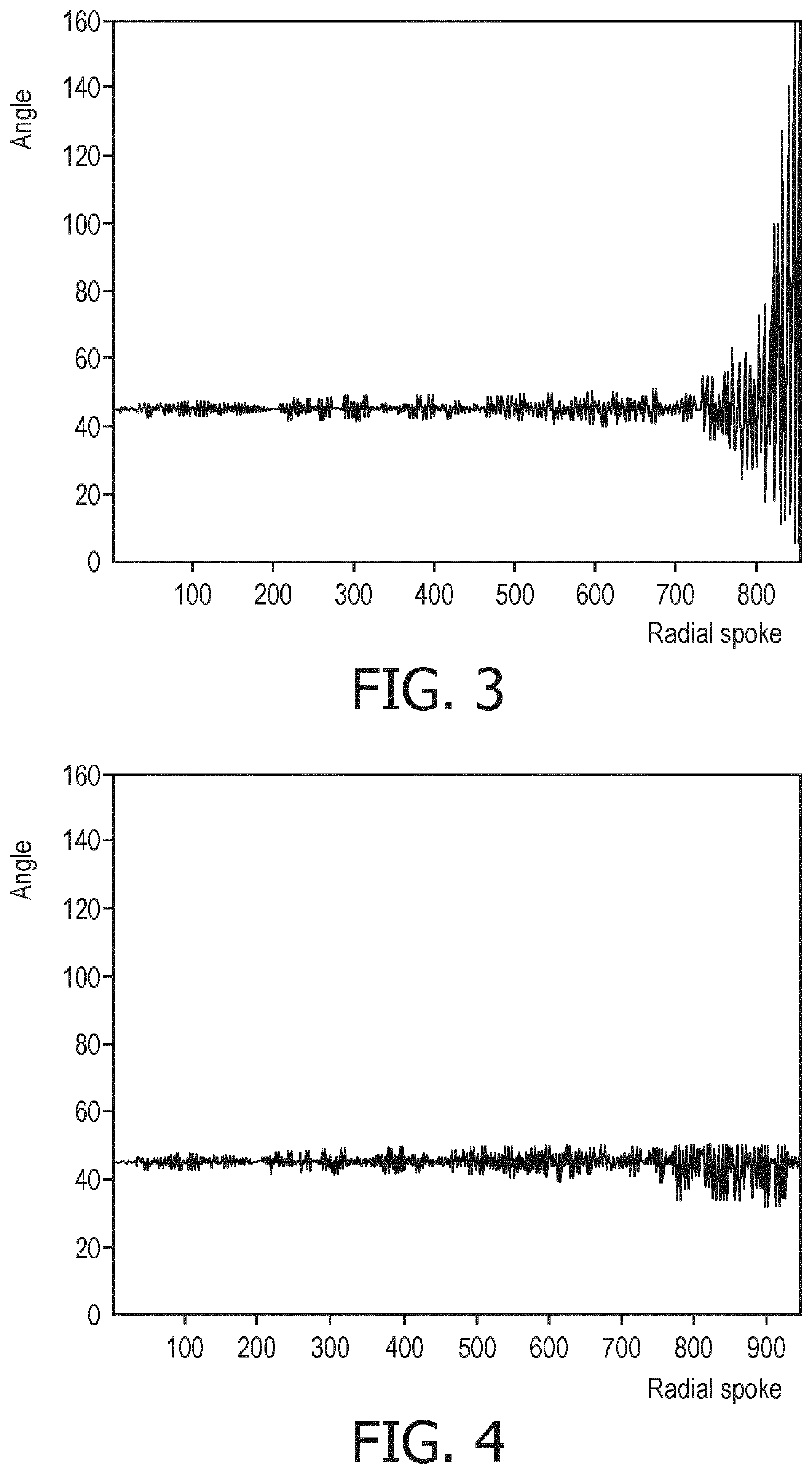
PendingUS20220308141A1Promote reconstructionReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpherical spaceGradient echo
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object positioned in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to enable efficient silent ZTE imaging with self-refocusing. The method of the invention comprises the steps of:—specification of a set of radial k-space spokes to cover a spherical k-space volume;—selection of subsets of a predetermined number of spokes from the specified set so that the concatenation of the spokes contained in each of the subsets forms a closed trajectory in k-space, wherein the selection of the subsets involves optimizing a cost function;—subjecting the object (10) to a zero echo time imaging sequence, wherein each of the subsets of spokes is acquired as a sequence of gradient echo signals; and—reconstructing an MR image from the acquired spokes. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device and to a computer program for a MR device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
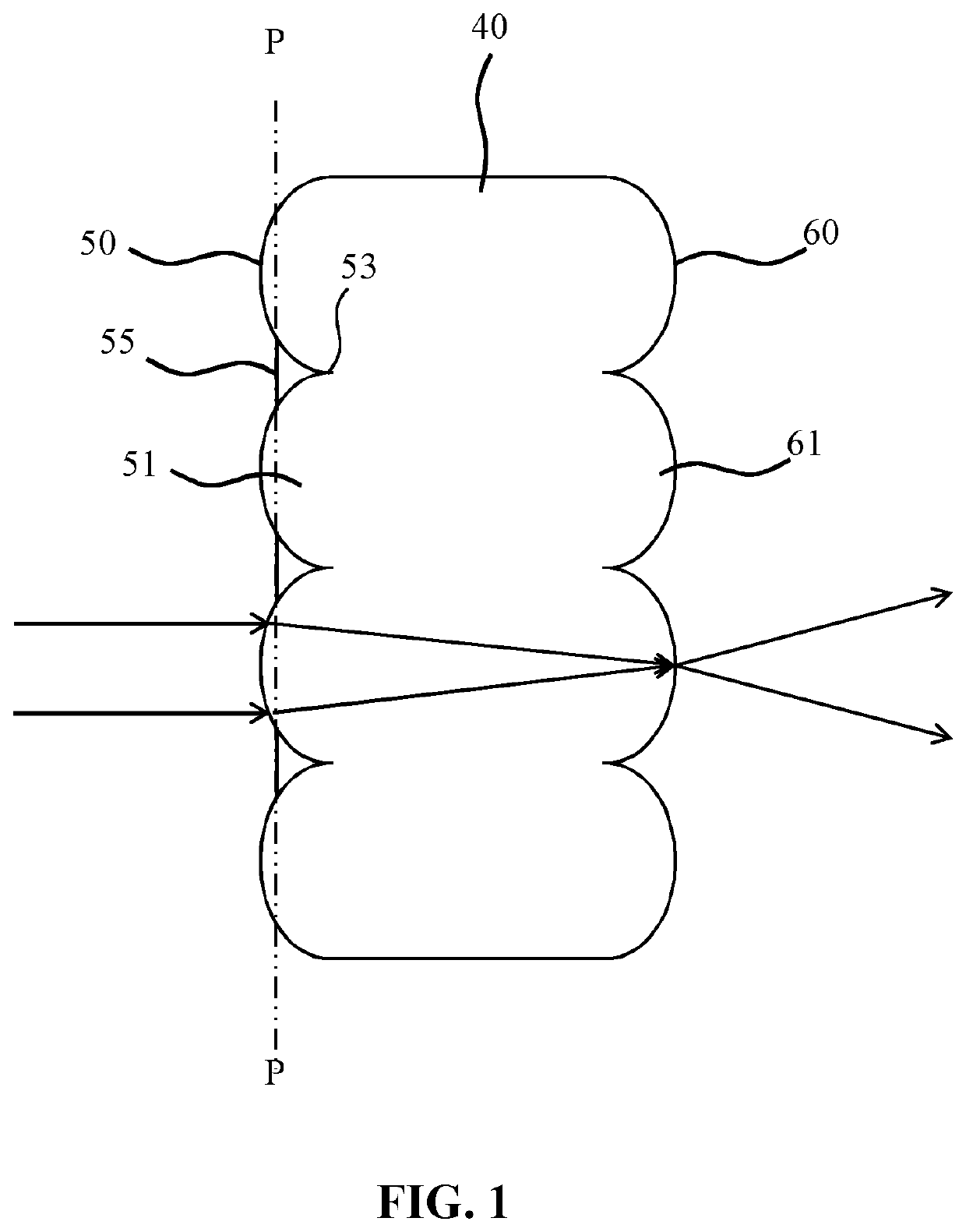
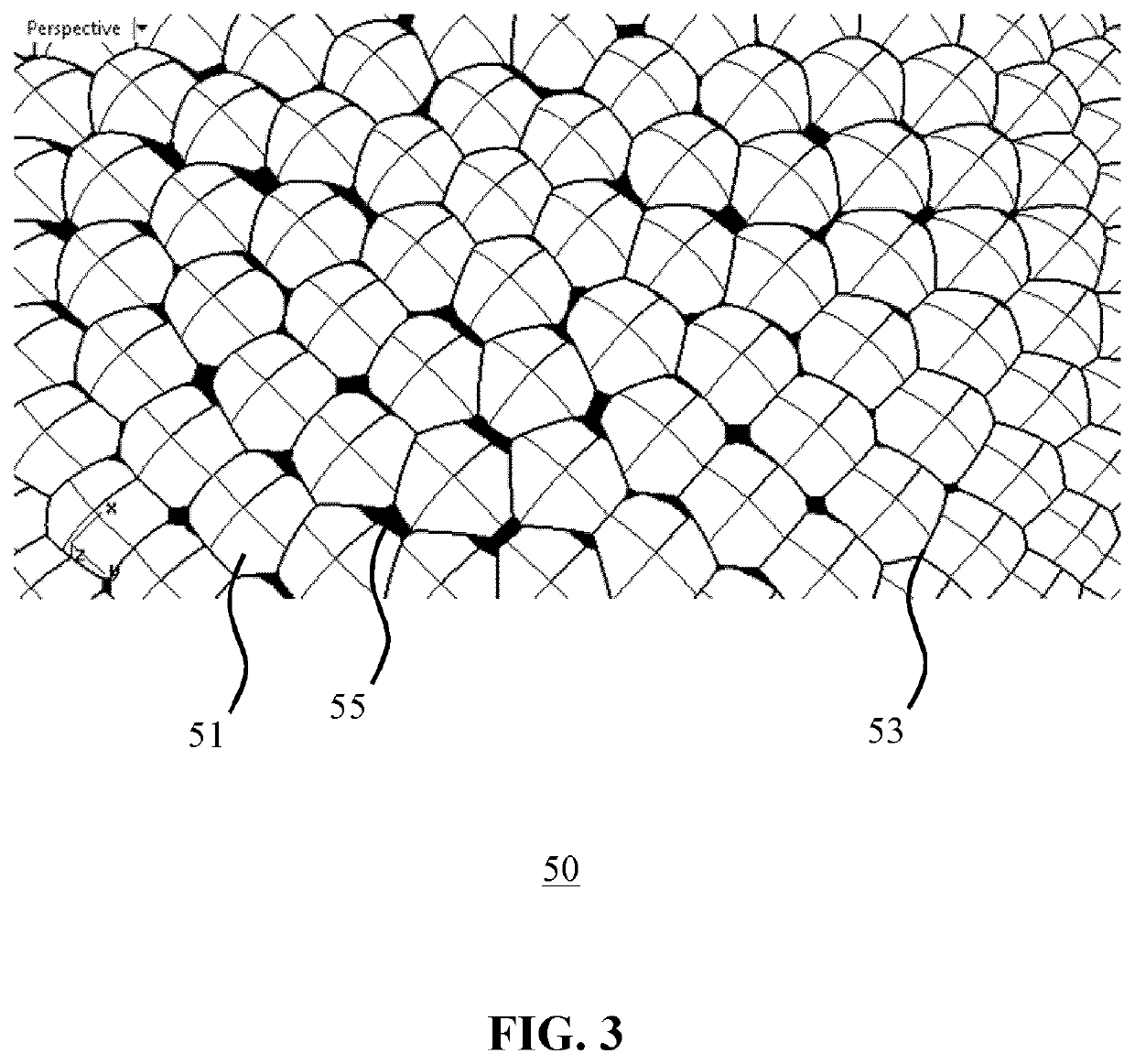
LED lighting device having opposed irregular lenslet arrays with planar facets
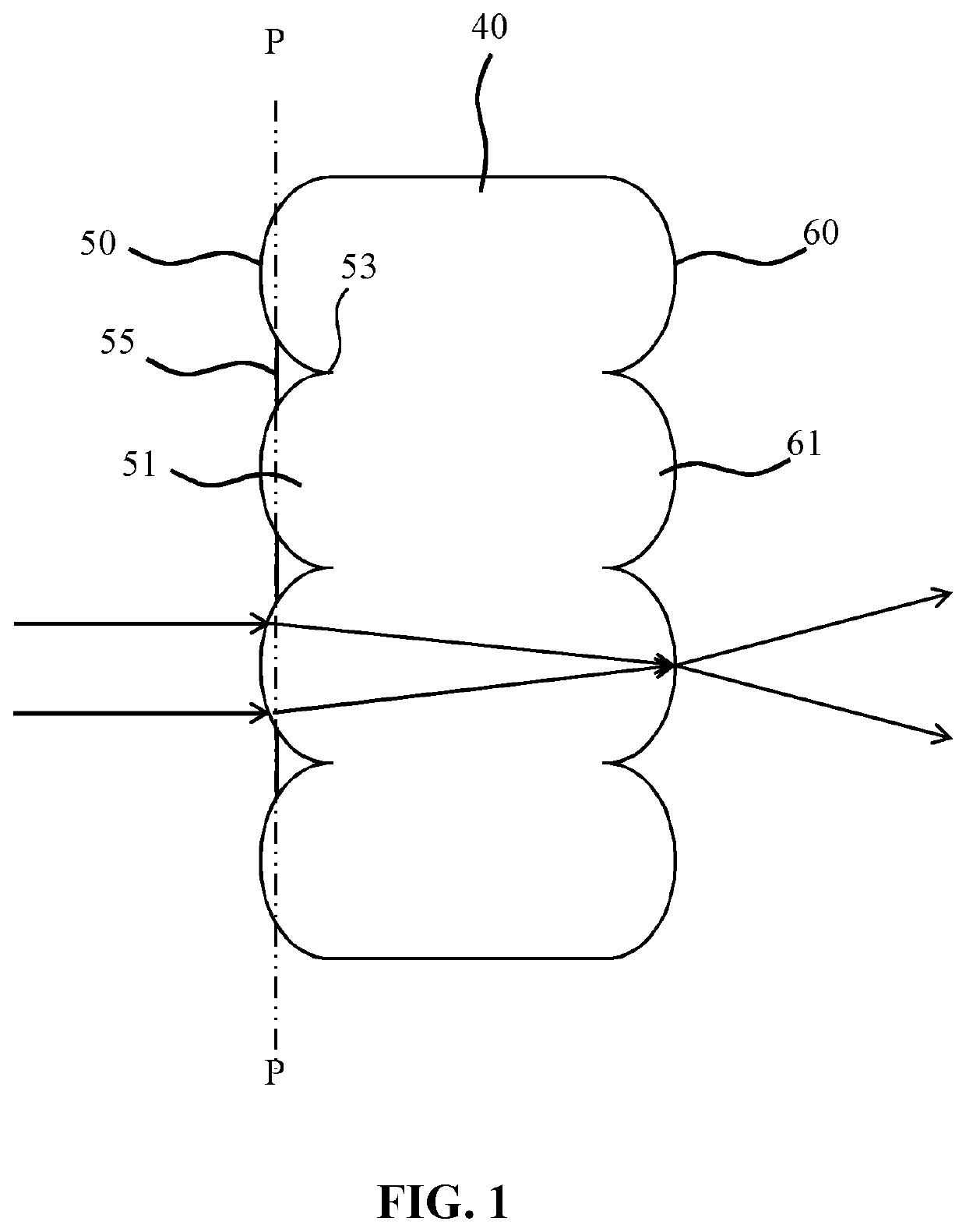
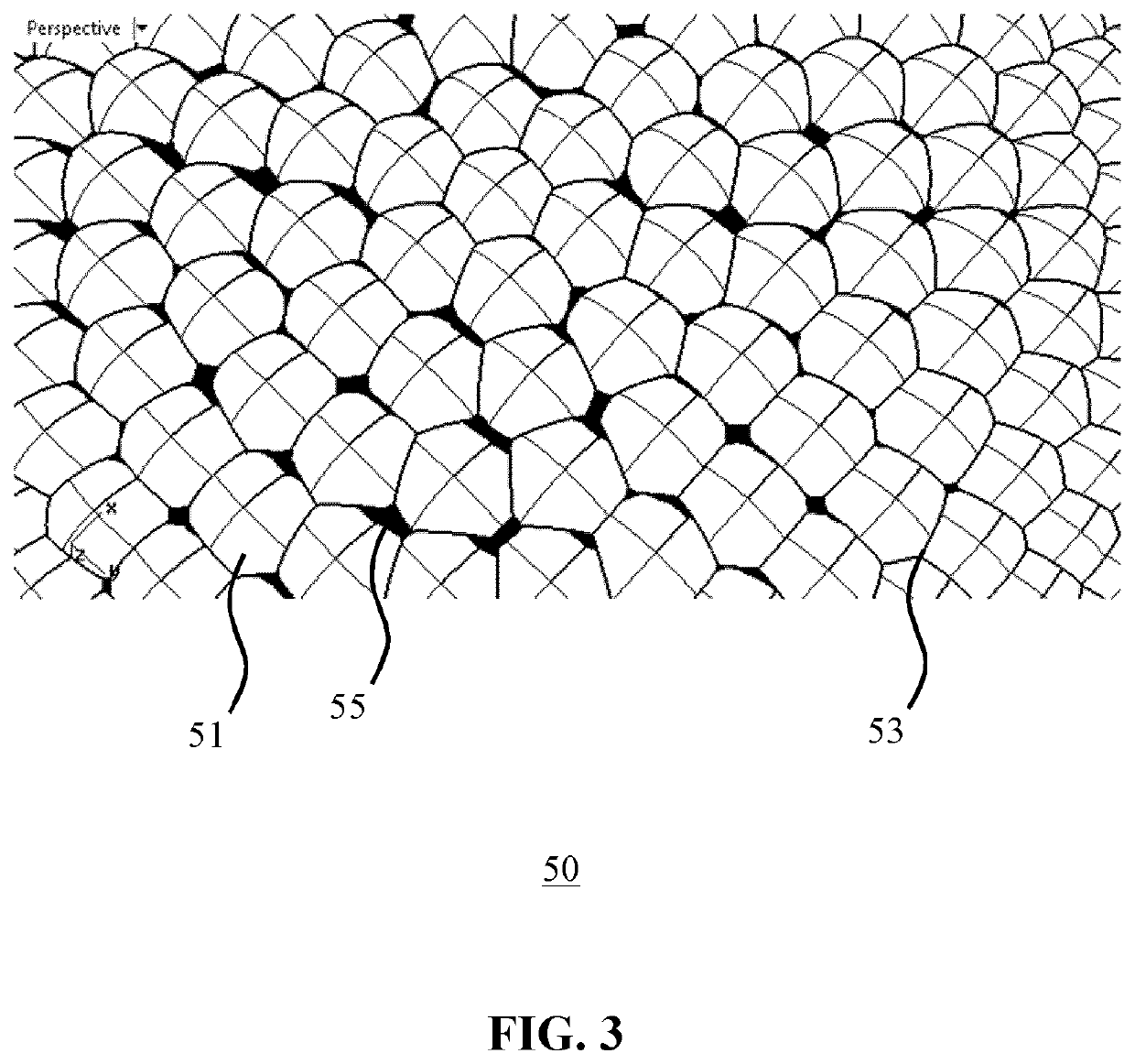
ActiveUS11333869B2Enhancement in definitionReducing the undesired artefactsCondensersSemiconductor devices for light sourcesLight equipmentLenslet array
A lighting device includes at least on LED light source, ca collimator, a first lenslet array of lenslets tessellated in an irregular pattern, and a second array of lenslets tessellated in the same irregular pattern as the first array of lenslets, such that each of the lenslets in the first array is aligned with a corresponding one of the lenslets in the second array. The first array further includes a plurality of transmissive planar facets covering an intersection between lenslet.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
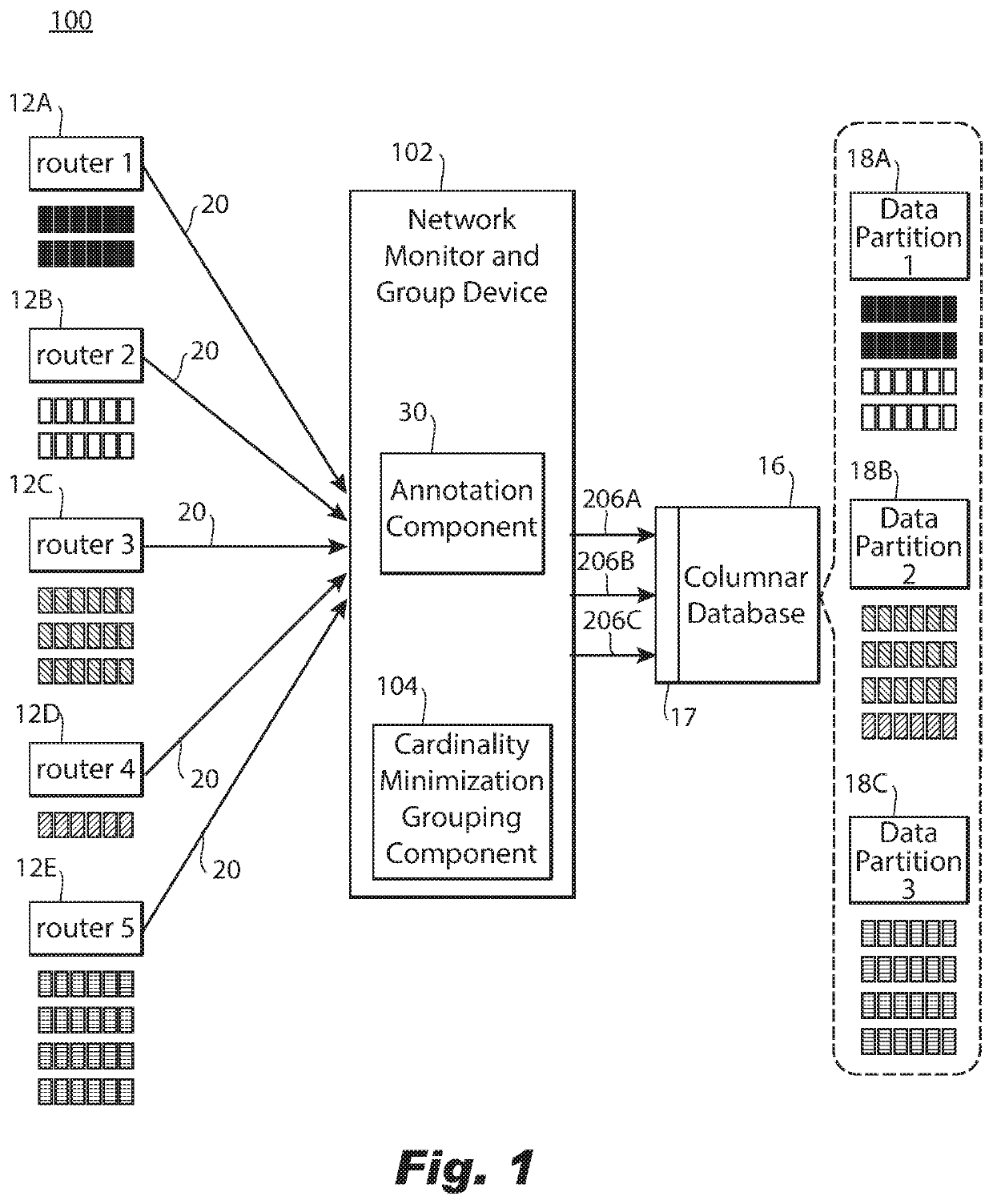
Grouping network traffic prior to storage in a columnar database
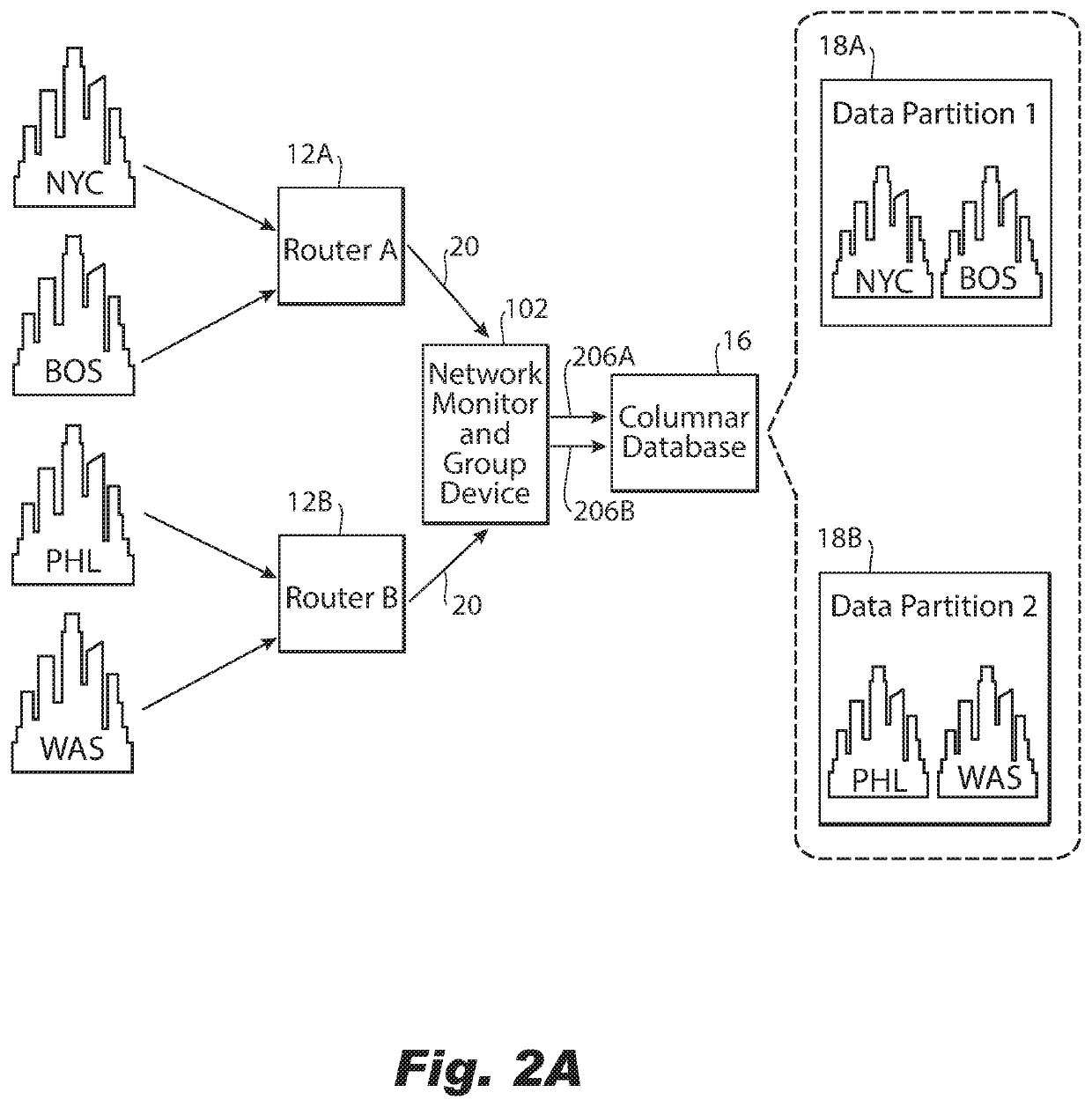
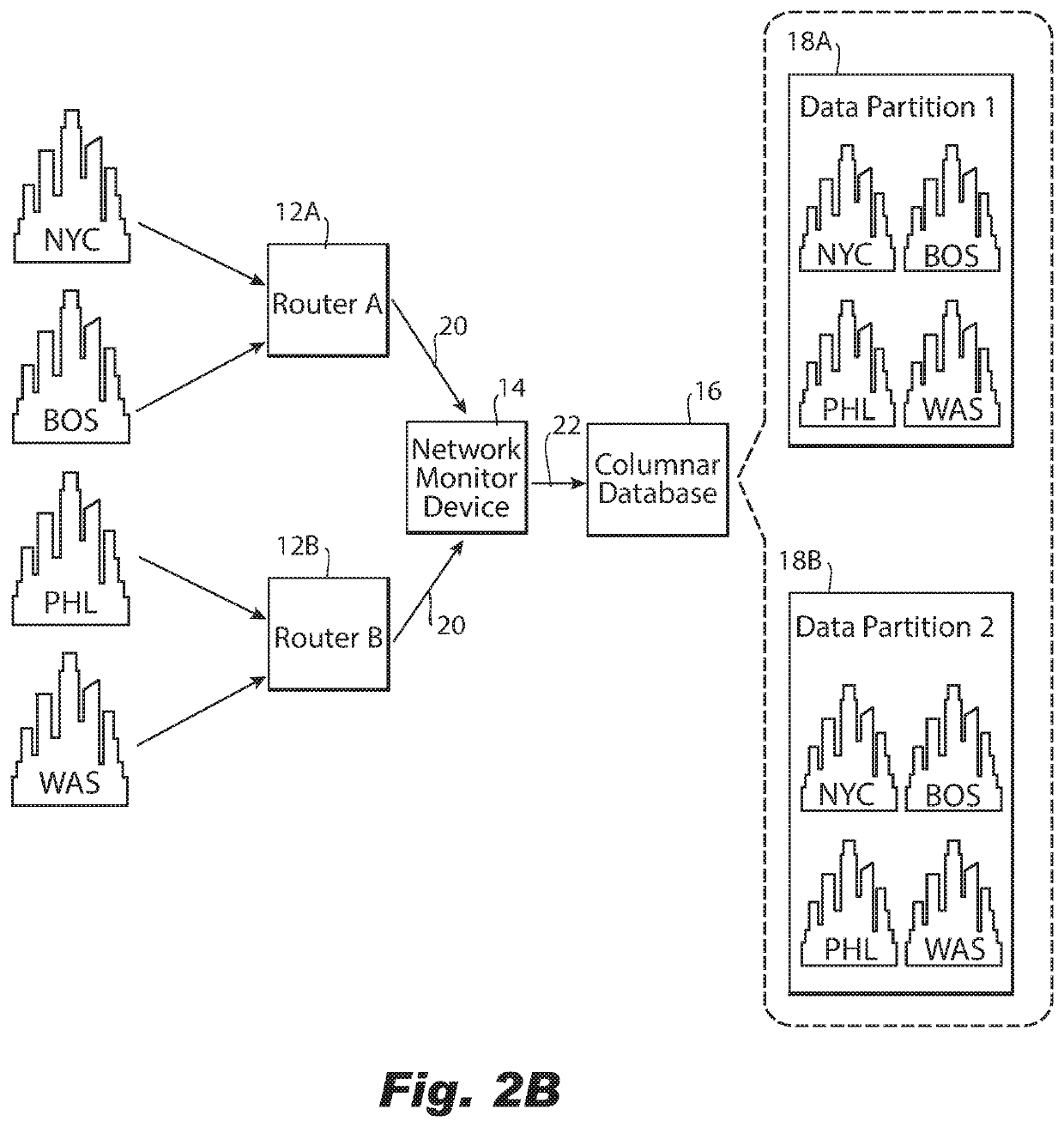
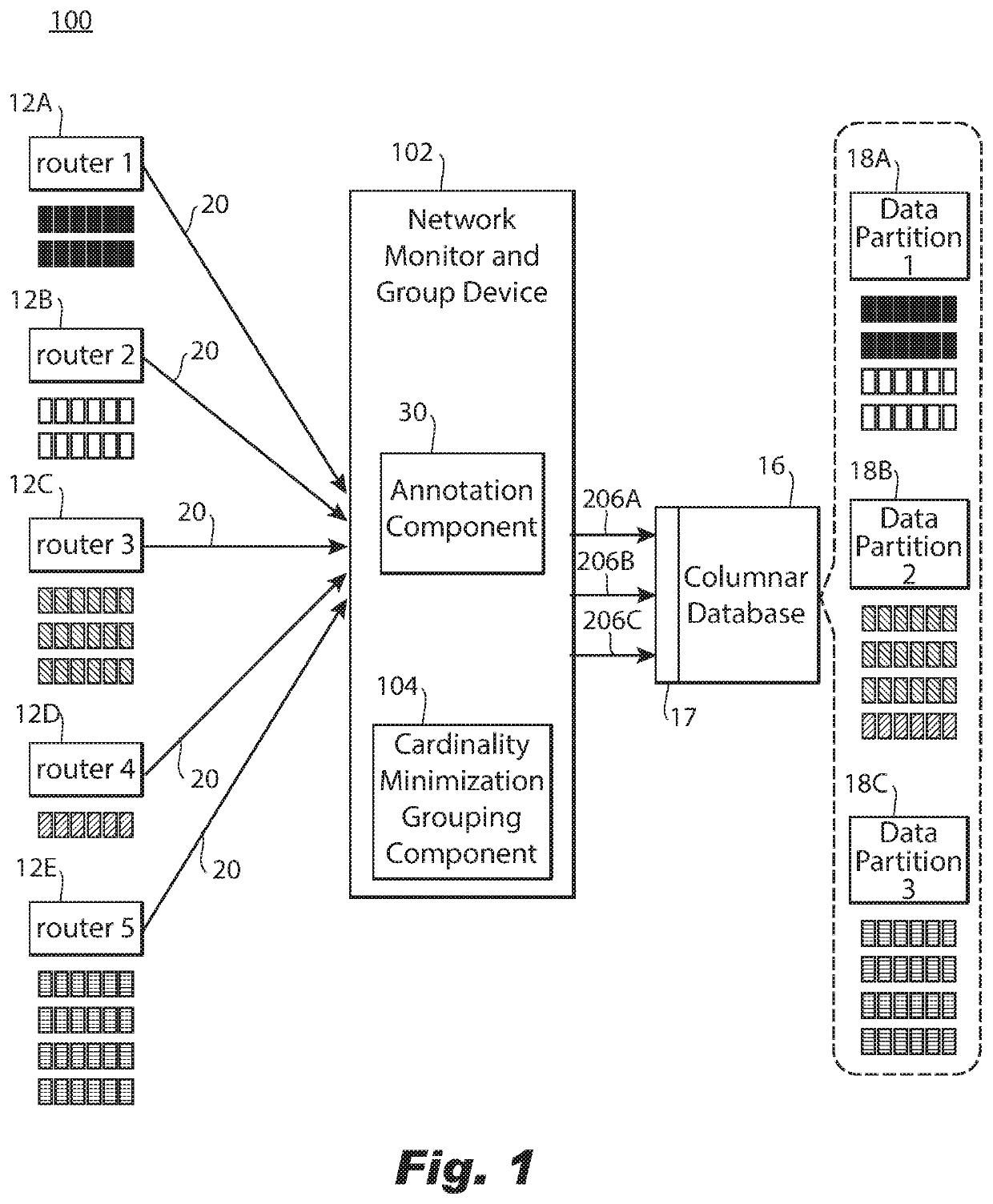
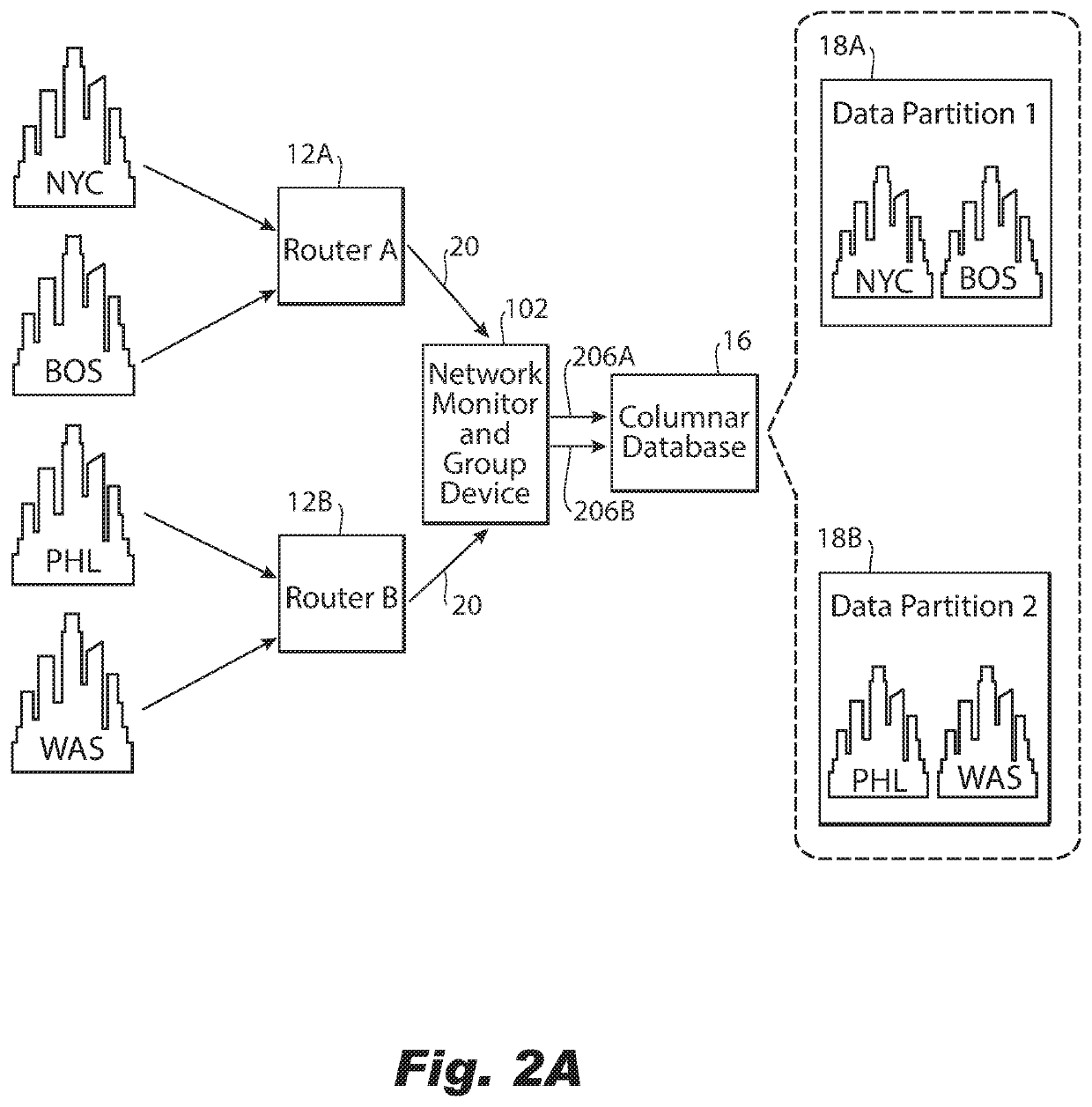
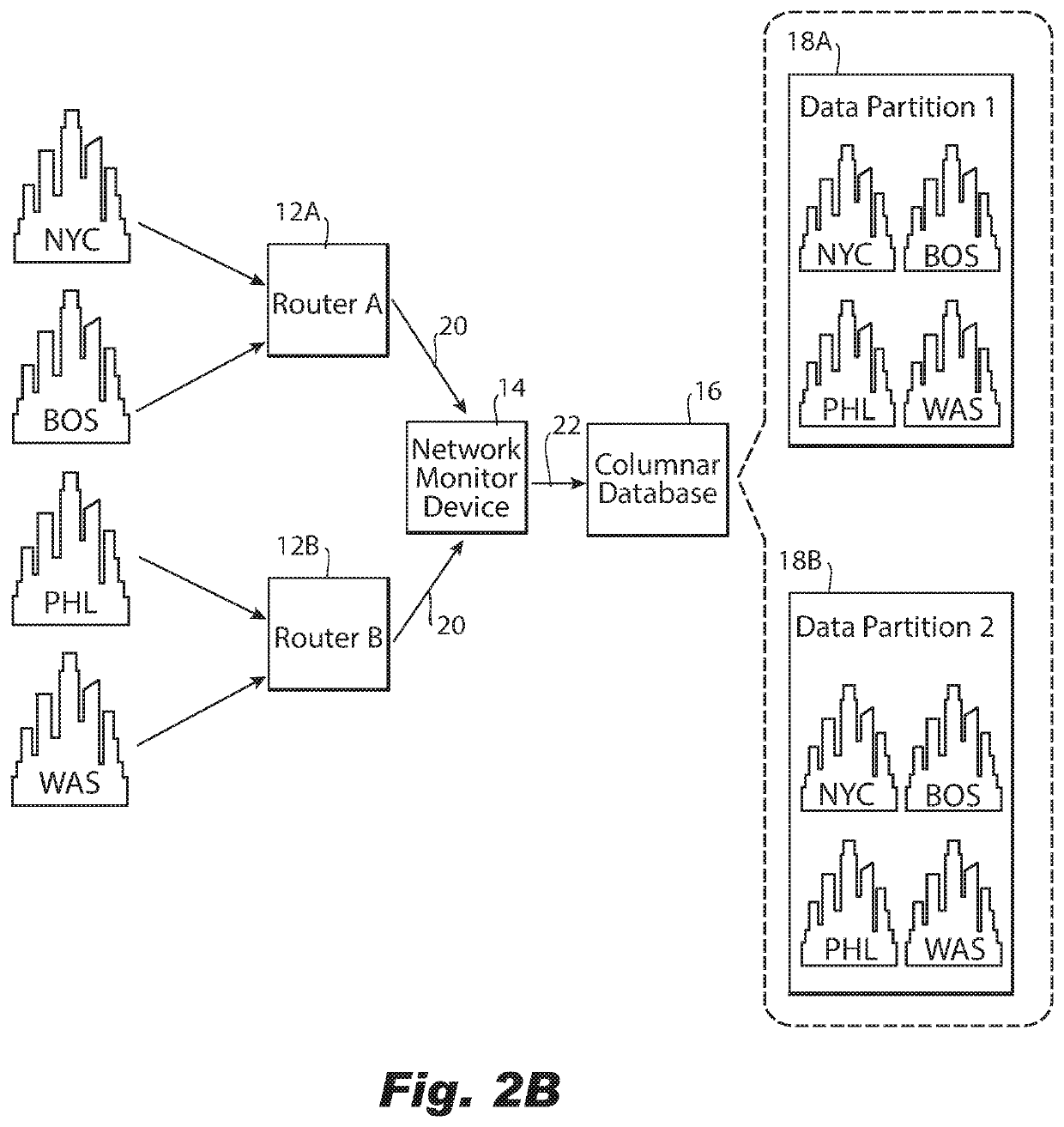
ActiveUS11153189B2Improve distributionEasy to moveDatabase distribution/replicationData switching networksData streamInternet traffic
A computer-implemented method of grouping network traffic metadata includes, based on a selected dimension of the network traffic metadata received from a network router, obtaining a statistic about a flow of network traffic metadata received over an interval for each instance of multiple instances of the dimension. The method further includes distributing the network traffic metadata into a plurality of groups for network traffic metadata from the smallest possible number of instances of the selected dimension to be distributed to each group, with the flow of network traffic metadata distributed optimally for a criteria regarding the statistic amongst the plurality of groups for minimizing cardinality of each group of the plurality of groups with respect to unselected dimensions of the network traffic metadata and providing each group to a columnar database for storage of the network traffic metadata distributed into each group in a different partition of the columnar database.
Owner:ARBOR NETWORKS
LED beam shaping
ActiveUS20210278646A1Enhancement in definitionReducing the undesired artefactsCondensersSemiconductor devices for light sourcesOphthalmologyLight beam
An integrating lenslet arrangement (40) is disclosed including a first lenslet array (50) of lenslets (51) tessellated in an irregular pattern; and a second lenslet array (60) of further lenslets (51) tessellated in said irregular pattern, each further lenslet being aligned with one of said lenslets; wherein the first lenslet array further comprises a plurality of transmissive planar facets (55), each facet covering a lenslet intersection (53). An optical arrangement, lighting device and luminaire including such an integrating lenslet arrangement are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method and apparatus for plasma processing
InactiveUS20070232085A1Uniformity is maximisedProlong lifeGeometric CADElectric discharge tubesDielectricElectrical conductor
The invention provides a plasma processing apparatus capable of minimizing the non-uniformity of potential distribution around wafer circumference, and providing a uniform process across the wafer surface. The apparatus is equipped with a focus ring formed of a dielectric, a conductor or a semiconductor and having RF applied thereto, the design of which is optimized for processing based on a design technique clarifying physical conditions for flattening a sheath-plasma interface above a wafer and the sheath-plasma interface above the focus ring. A surface voltage of the focus ring is determined to be not less than a minimum voltage for preventing reaction products caused by wafer processing from depositing thereon. The surface height, surface voltage, material and structure of the focus ring are optimized so that the height of an ion sheath formed on the focus ring surface is either equal or has a height difference within an appropriate tolerance range to the height of the ion sheath formed on the wafer surface. Optimization of the structure is realized by setting up an appropriate tolerance range taking into consideration the variation caused by consumption of the focus ring.
Owner:NISHIO RYOJI +3
Grouping network traffic prior to storage in a columnar database
ActiveUS20210135968A1Improve distributionEasy to moveDatabase distribution/replicationData switching networksData streamInternet traffic
A computer-implemented method of grouping network traffic metadata includes, based on a selected dimension of the network traffic metadata received from a network router, obtaining a statistic about a flow of network traffic metadata received over an interval for each instance of multiple instances of the dimension. The method further includes distributing the network traffic metadata into a plurality of groups for network traffic metadata from the smallest possible number of instances of the selected dimension to be distributed to each group, with the flow of network traffic metadata distributed optimally for a criteria regarding the statistic amongst the plurality of groups for minimizing cardinality of each group of the plurality of groups with respect to unselected dimensions of the network traffic metadata and providing each group to a columnar database for storage of the network traffic metadata distributed into each group in a different partition of the columnar database.
Owner:ARBOR NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com