Patents
Literature
495results about "Converting sensor output mechanically" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
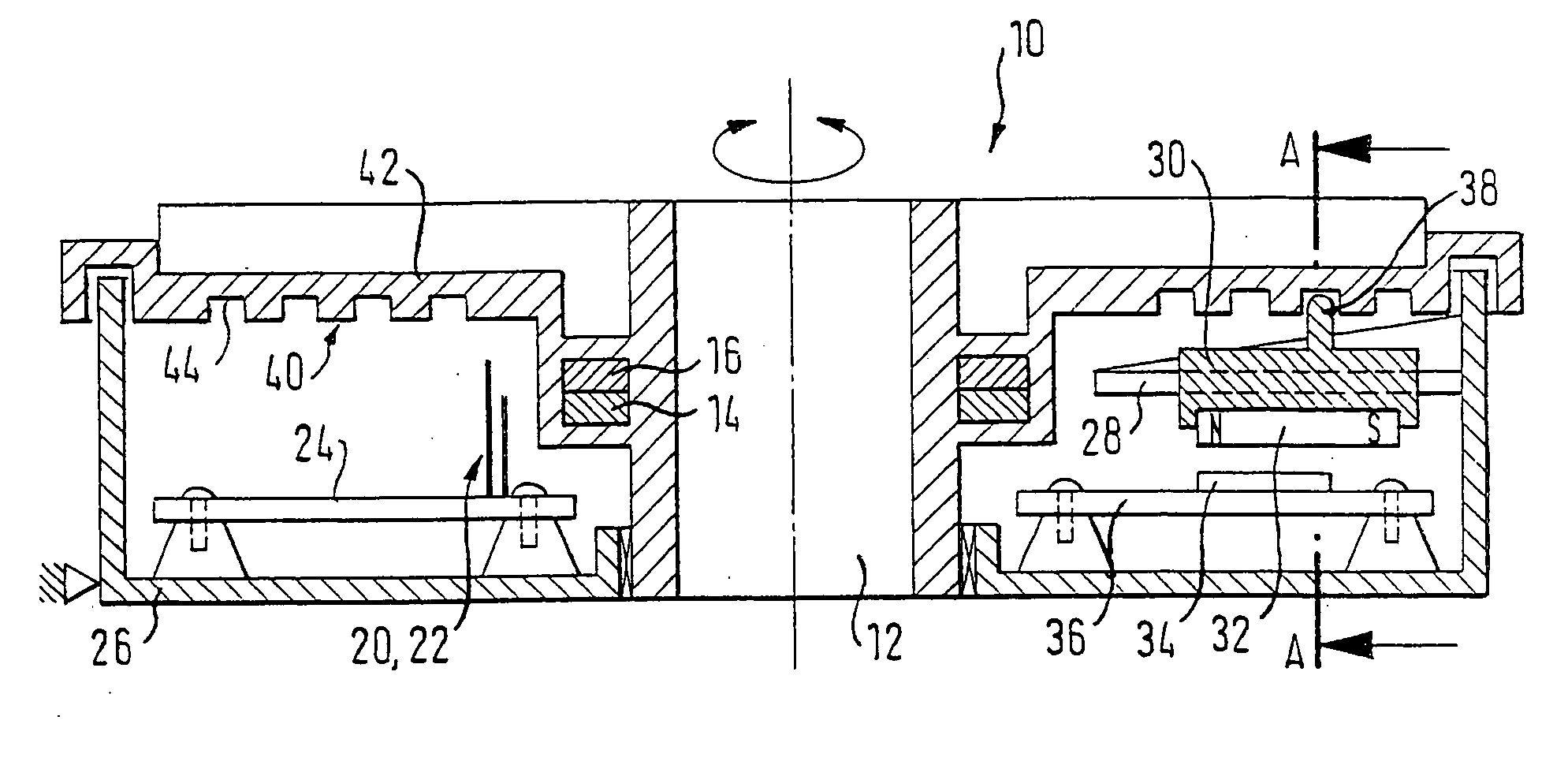
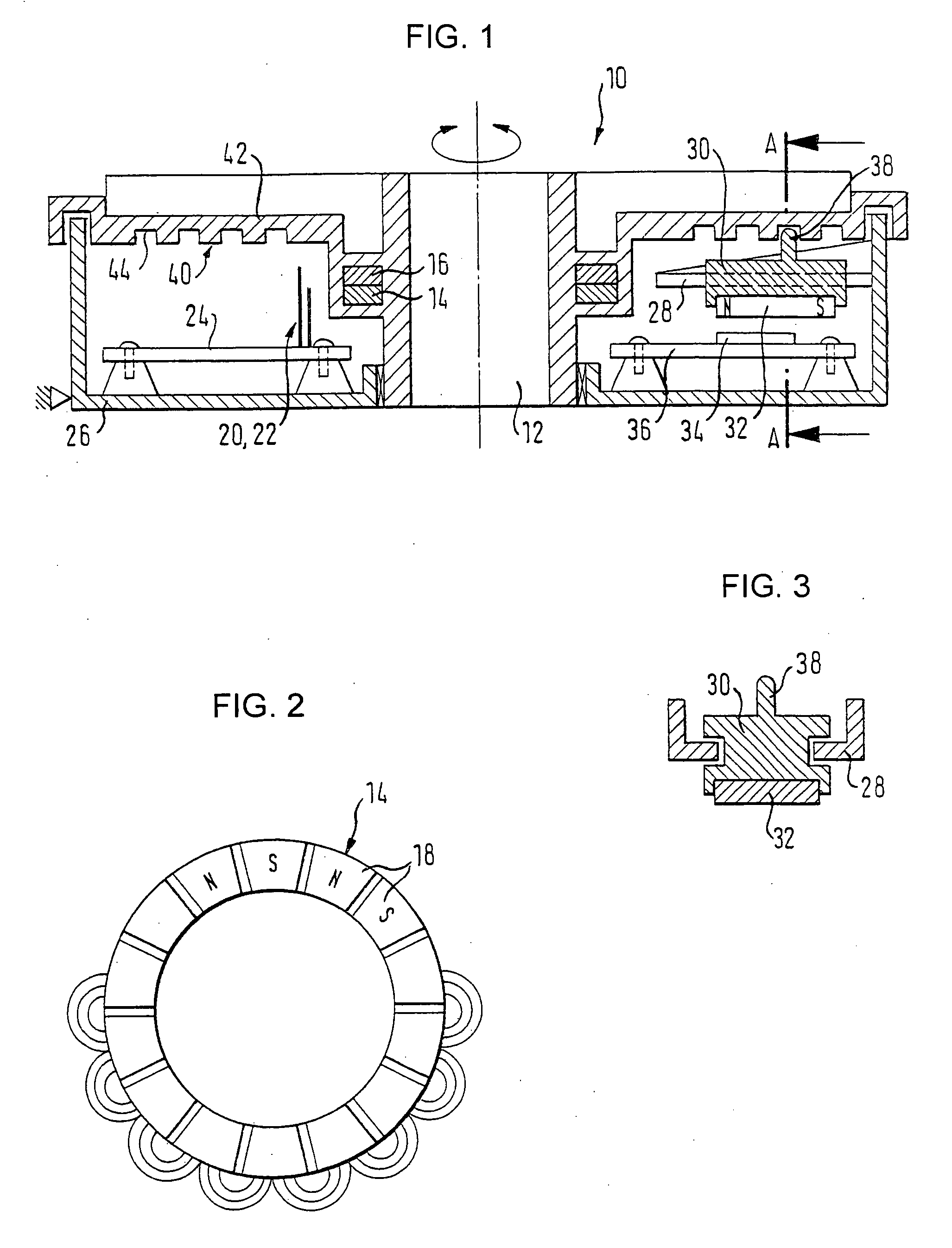
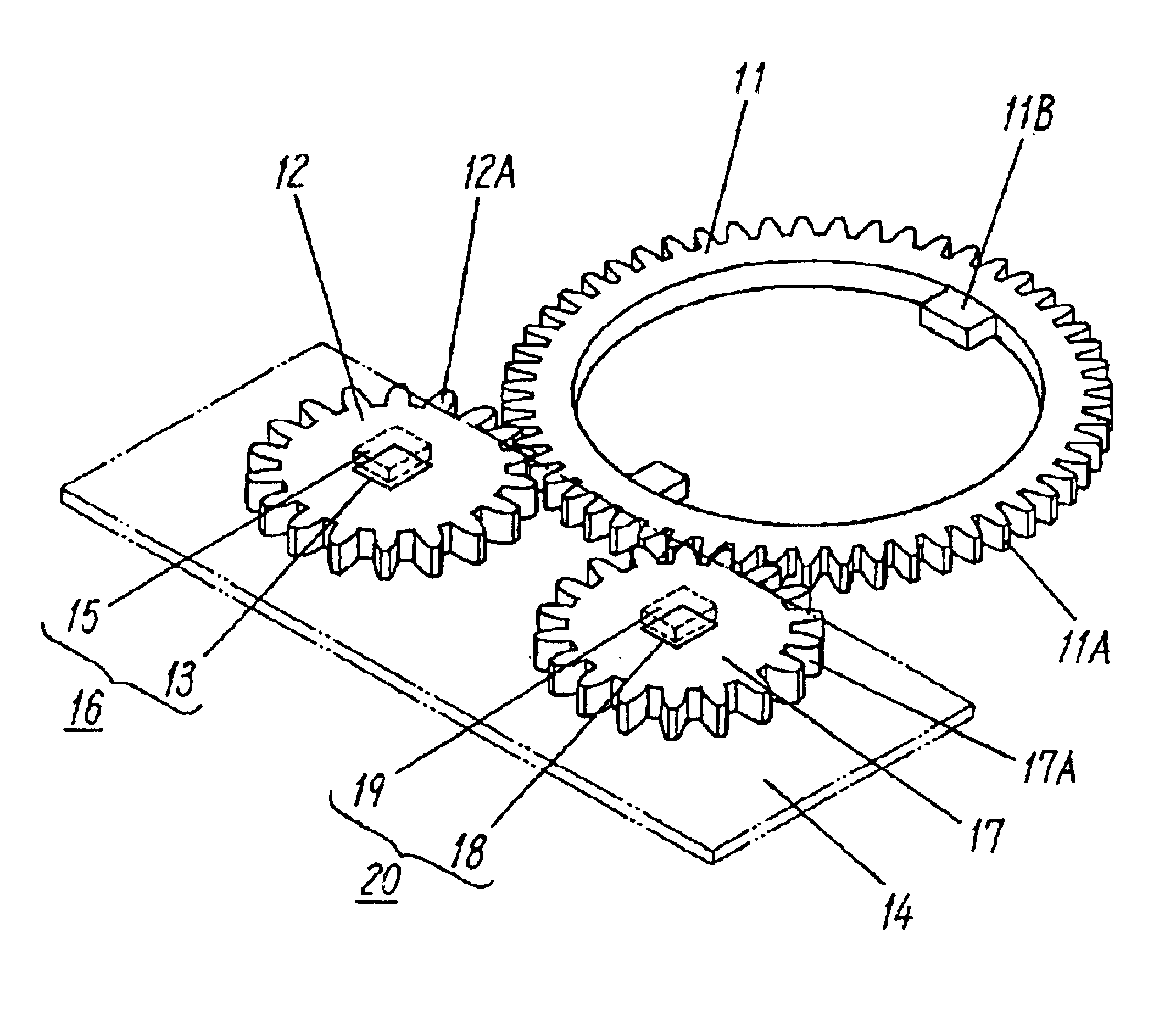
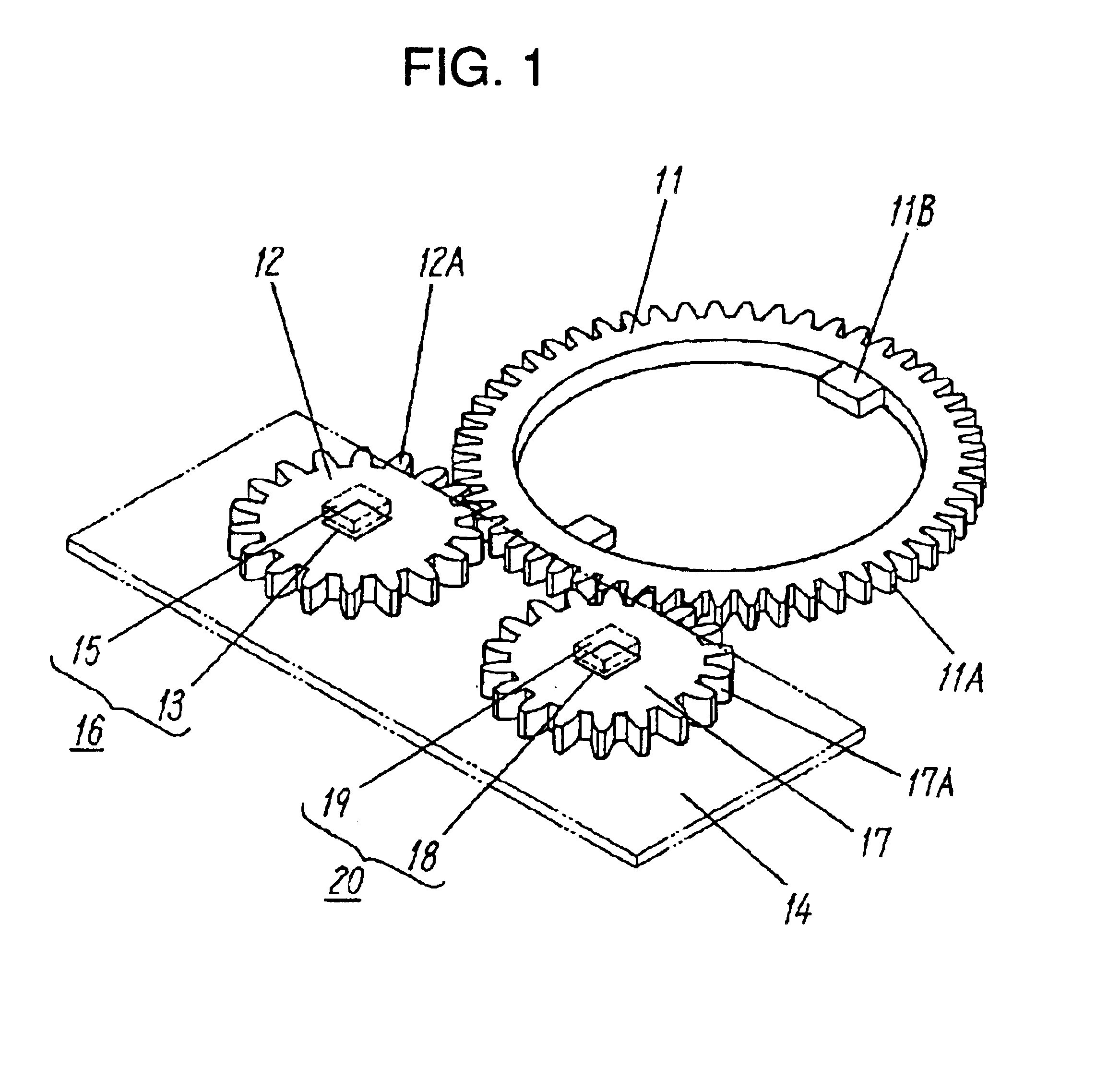
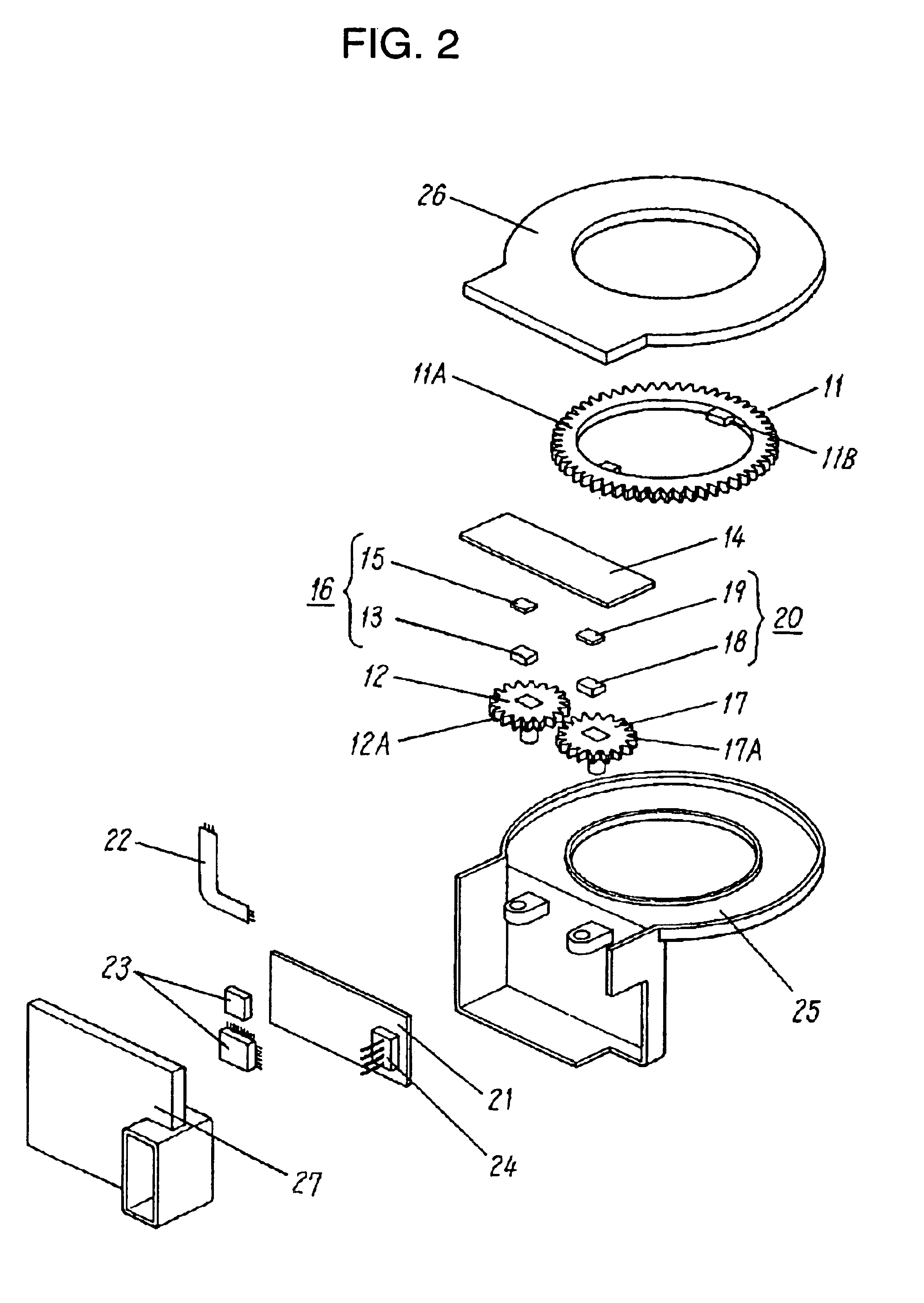
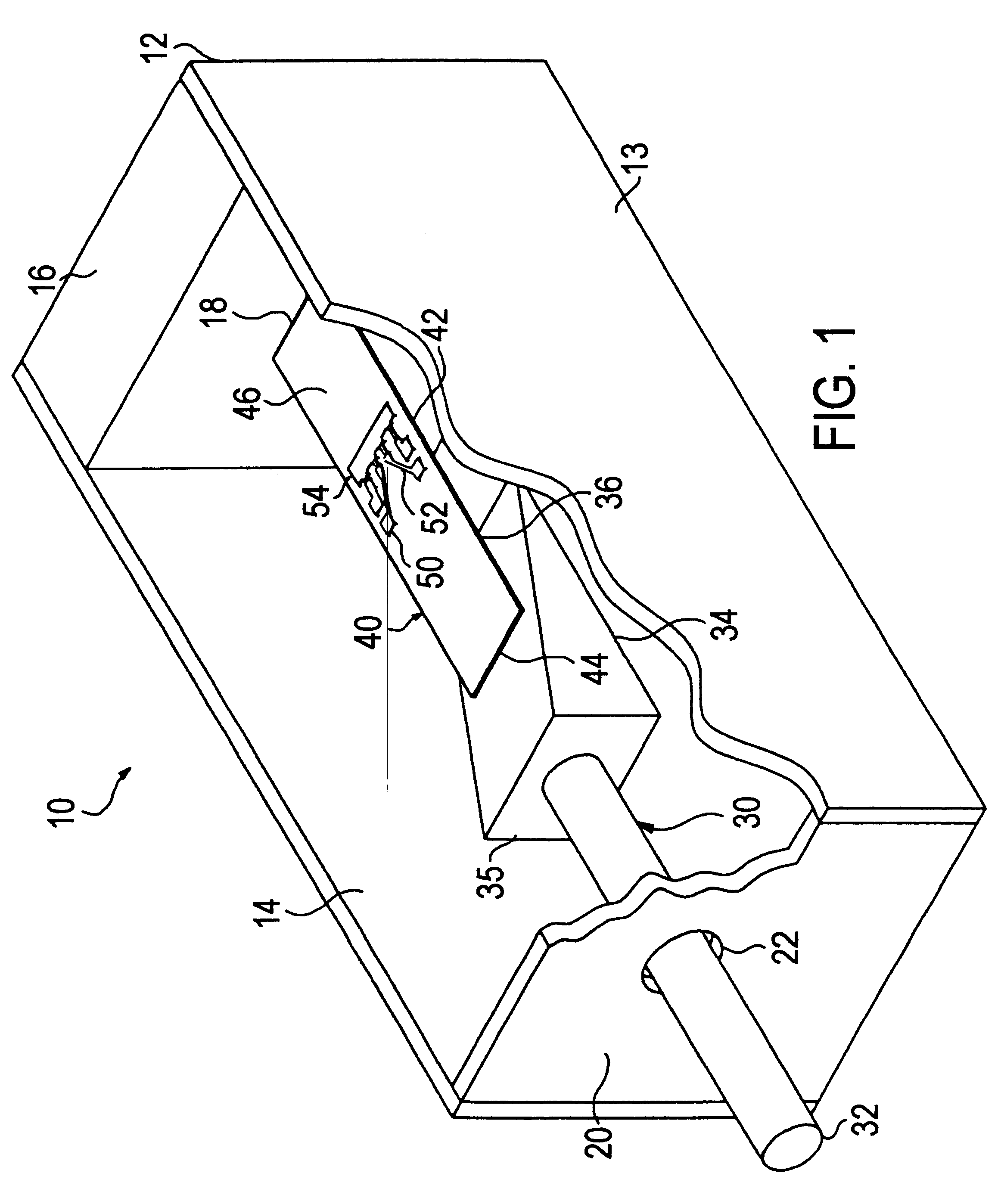
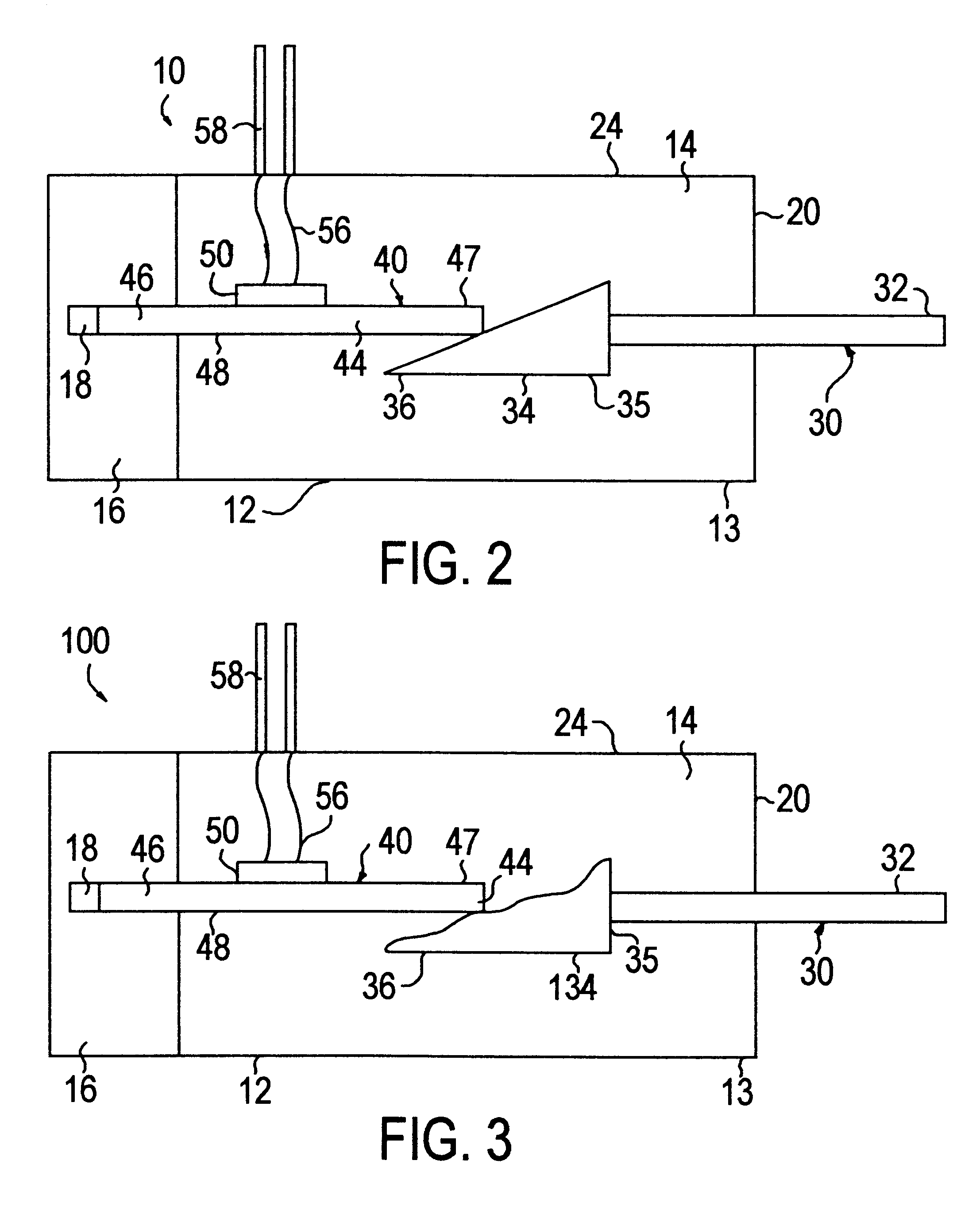
Reflective multi-turn encoder
InactiveUS20090152452A1Material analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyCatoptricsEngineering
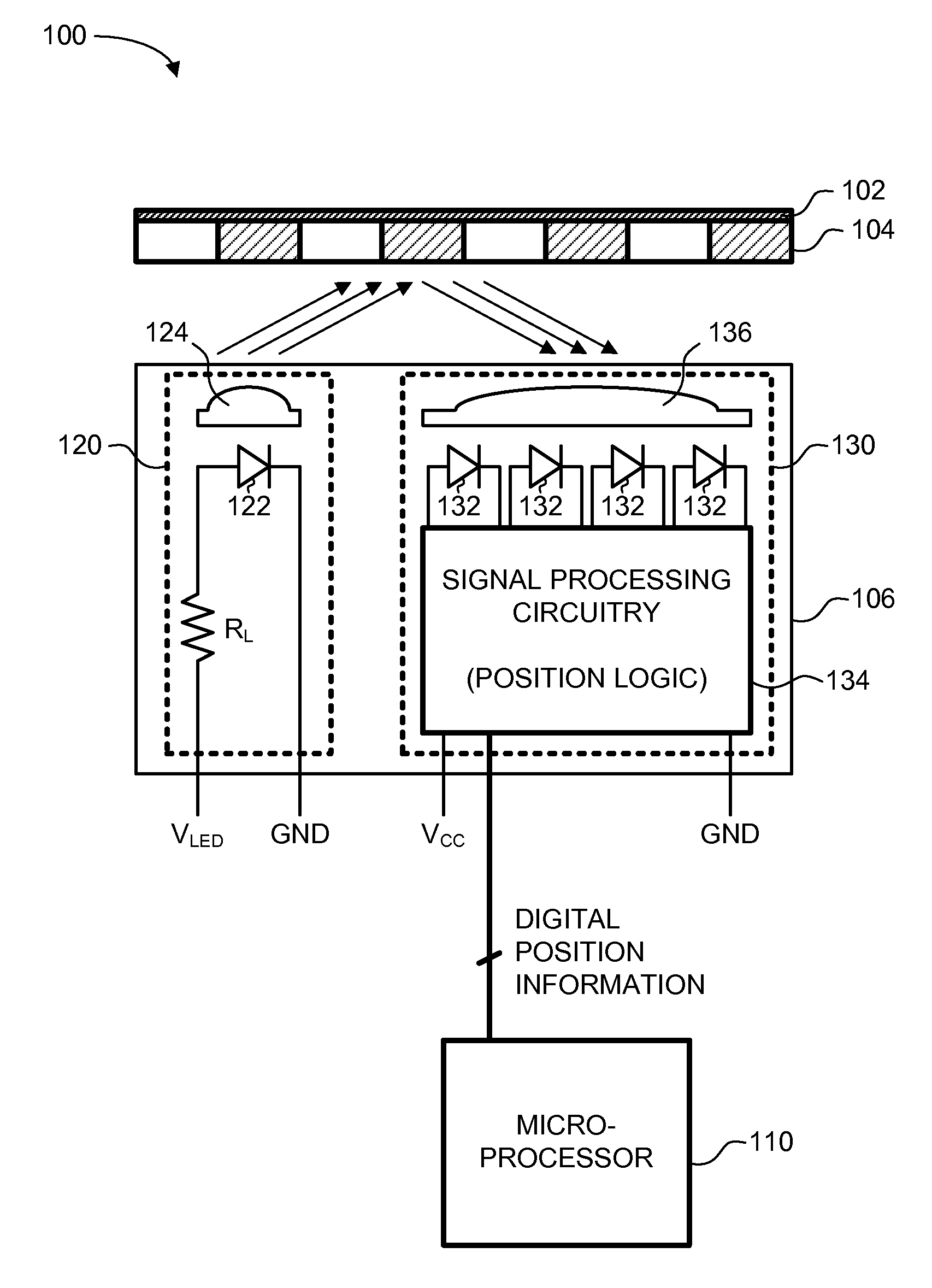
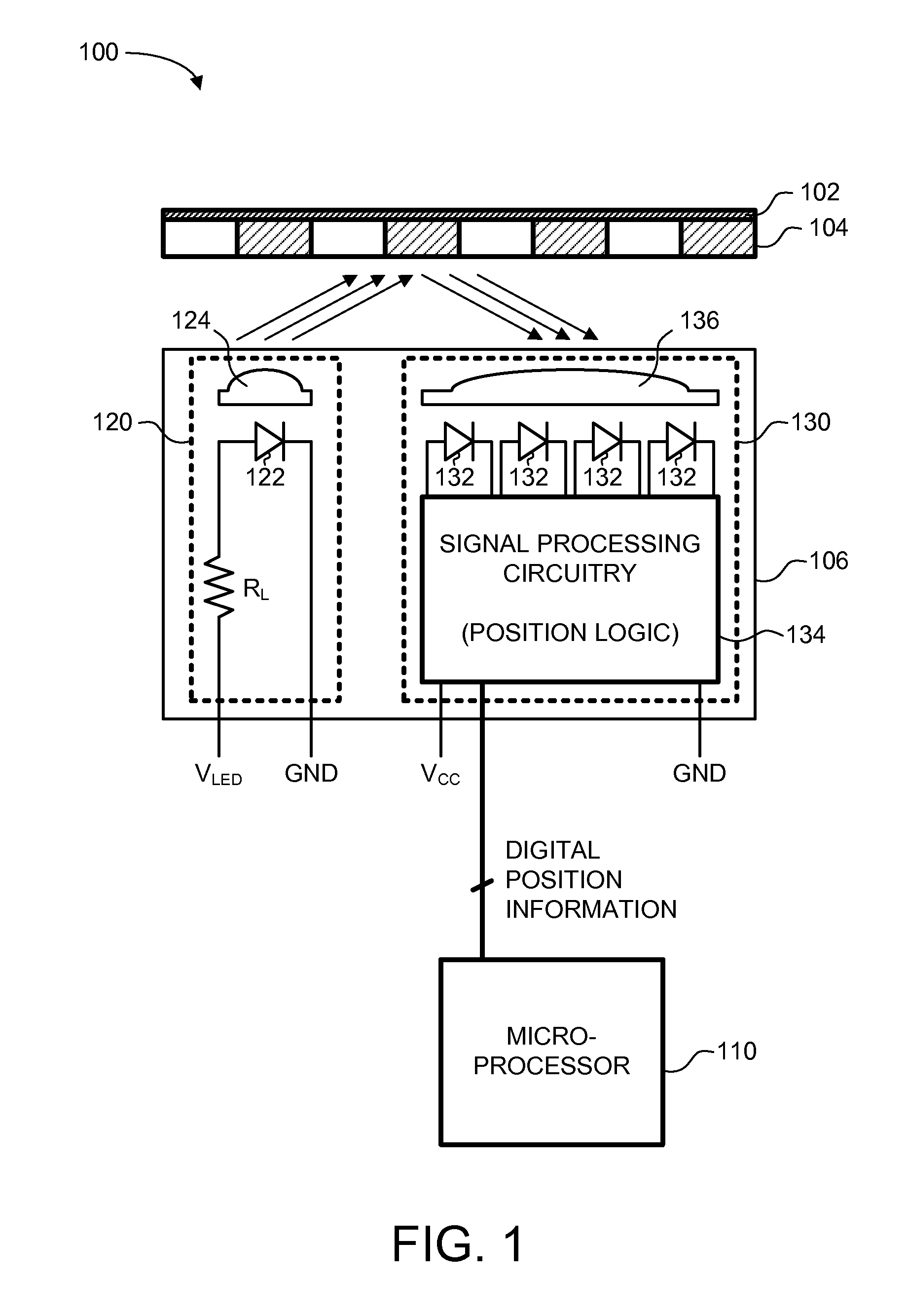
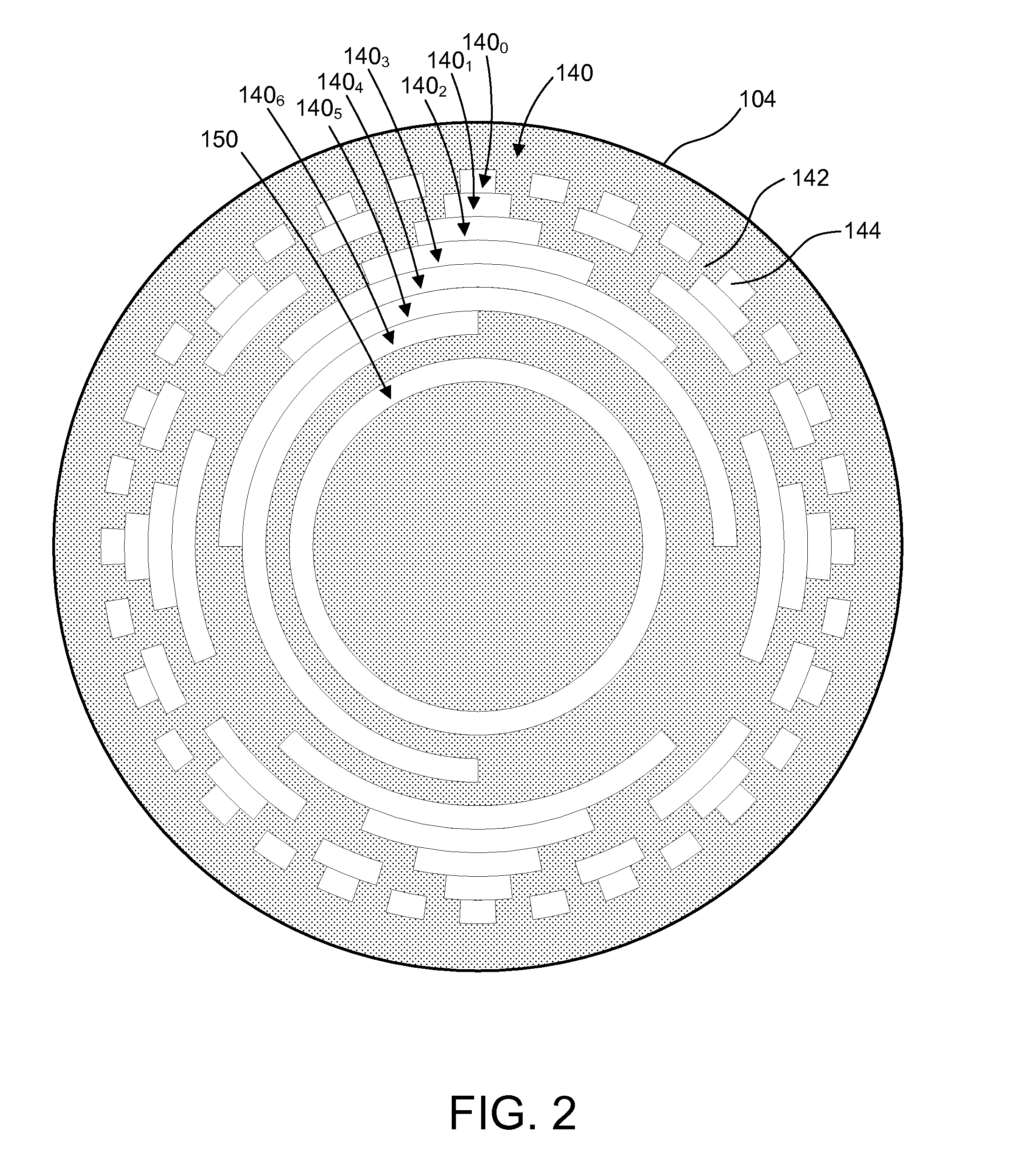
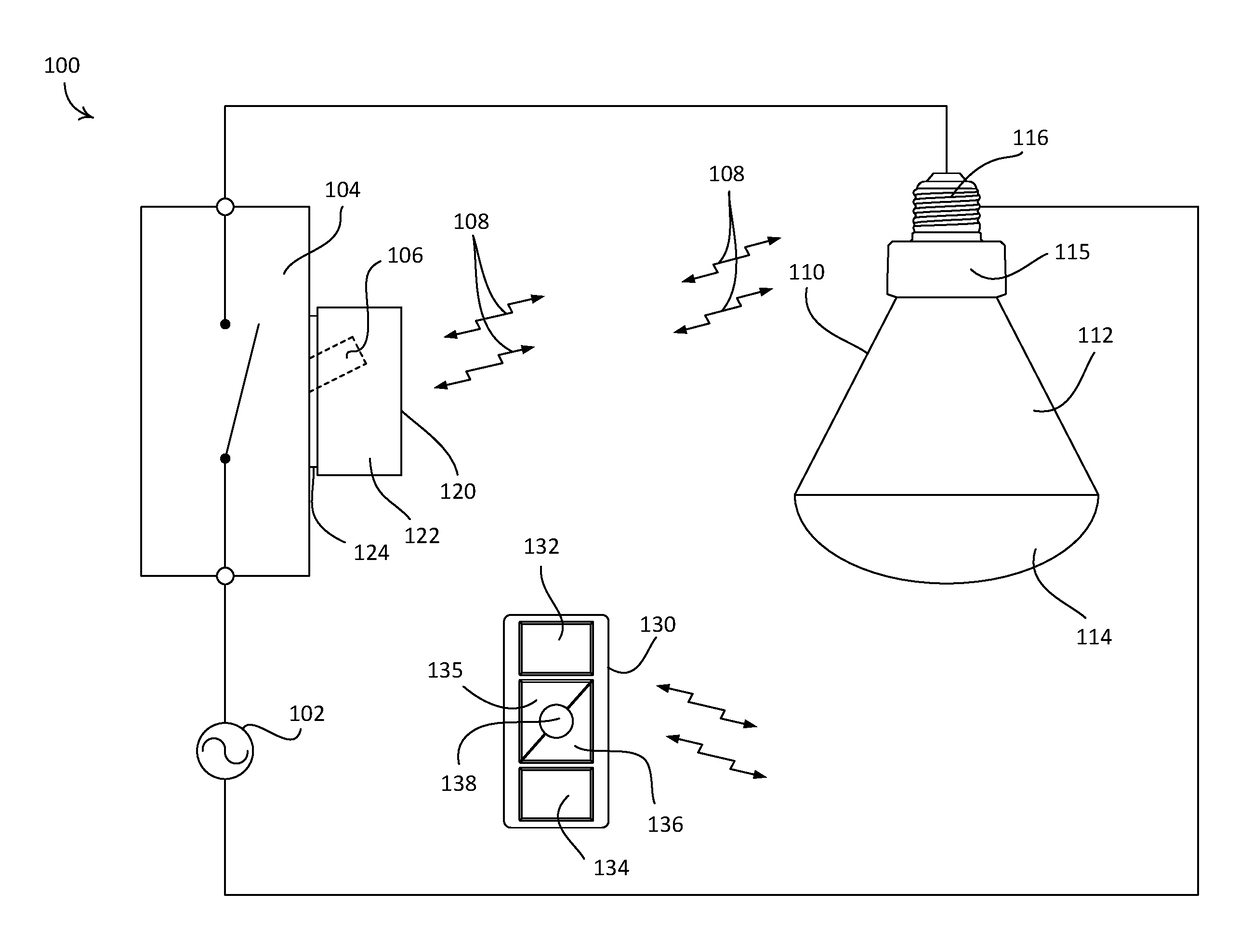
A reflective optical encoder for a gear train. The reflective optical encoder includes a gear train with a plurality of gears. Each of the gears is operably coupled to at least one other gear of the plurality of gears. A reflective code pattern is accessible on a surface of at least one of the gears. A reflective optical sensor detects light reflected by the reflective code pattern. Position logic coupled to the optical sensor determines a rotational parameter of the gear train based on the light reflected by the reflective code pattern. Additionally, the position logic may determine rotational parameter of a pinion coupled to the gear train based on the rotational parameter of the gear train.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Remote load control device capable of orientation detection
ActiveUS20170278383A1Converting sensor output electrically/magneticallyConverting sensor output opticallyElectricityUser input
A remote control device is provided that is configured for use in a load control system that includes one or more electrical loads. The remote control device includes a mounting structure and a control unit, and the control unit is configured to be attached to the mounting structure in a plurality of different orientations. The control unit includes a user interface, an orientation sensing circuit, and a communication circuit. The control unit is configured to determine an orientation of the control unit via the orientation sensing circuit. The control unit is also configured to translate a user input from the user interface into control data to control an electrical load of the load control system based on the orientation of the control unit and / or provide a visual indication of an amount of power delivered to the electrical load based on the orientation of the control unit.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Assembly for detecting more than one rotation through a position encoder magnet
ActiveUS20110080162A1Easy to implementIncrease in sizeUsing electrical meansSteering partsElectrical conductorDifferential transmission
The rotational position of an encoder magnet can be scanned over more than 360° by respective sensor elements in that magnets are disposed on different stages of a suitable transmission, in particular of a differential transmission, and the magnets are scanned by separate sensor elements, whose signals are computed with one another and yield a total number of revolutions.In particular, when an assembly of this type shall be built very small, undesirable magnetic interferences for the sensor elements have to be avoided through flux conductor elements since the interferences distort the measurement results. Thus, a differentiation is made between active and passive flux conductor elements.
Owner:ASM AUTOMATION SENSORIK MESSTECHN GMBH
Rotary position sensing apparatus
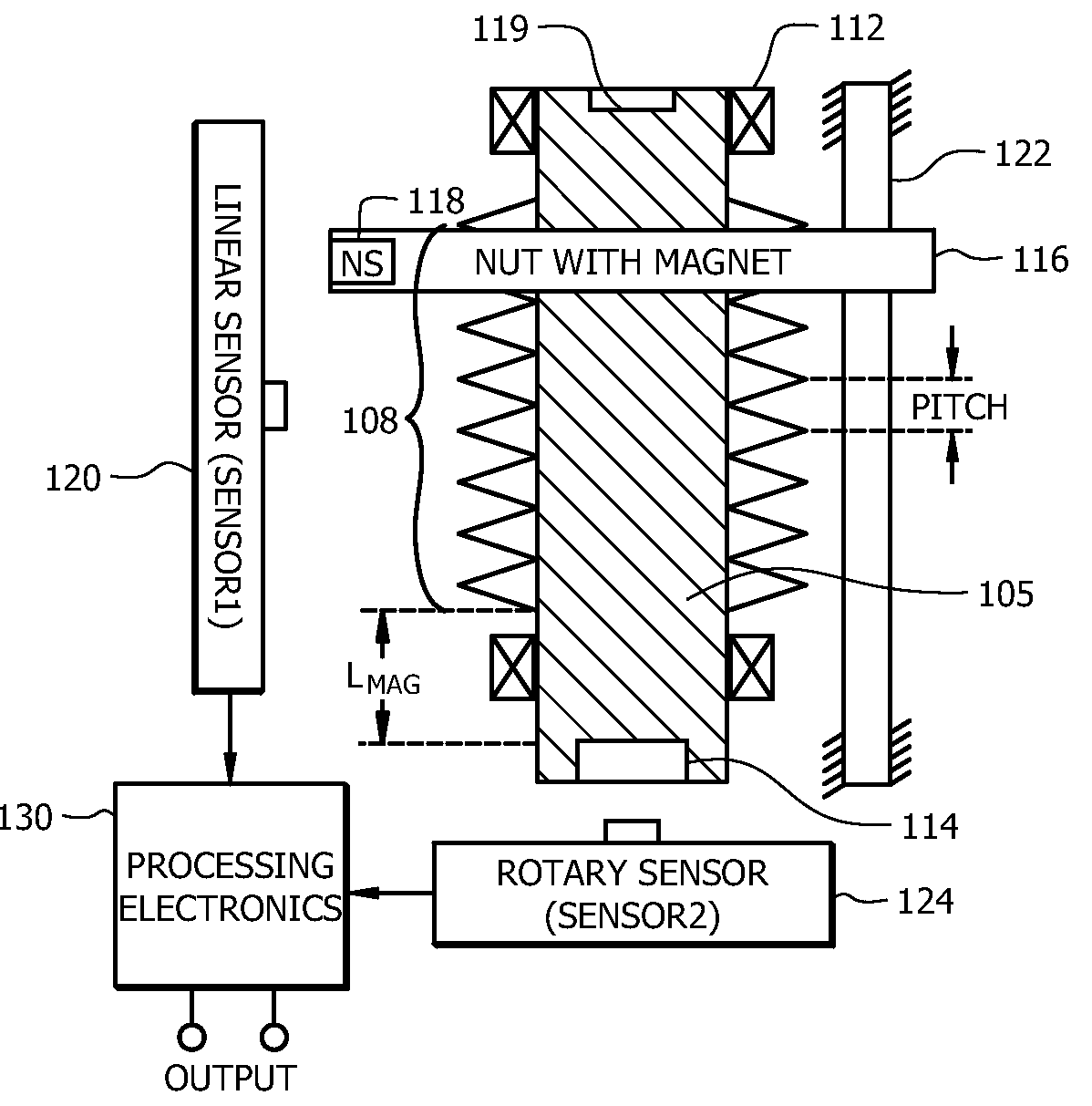
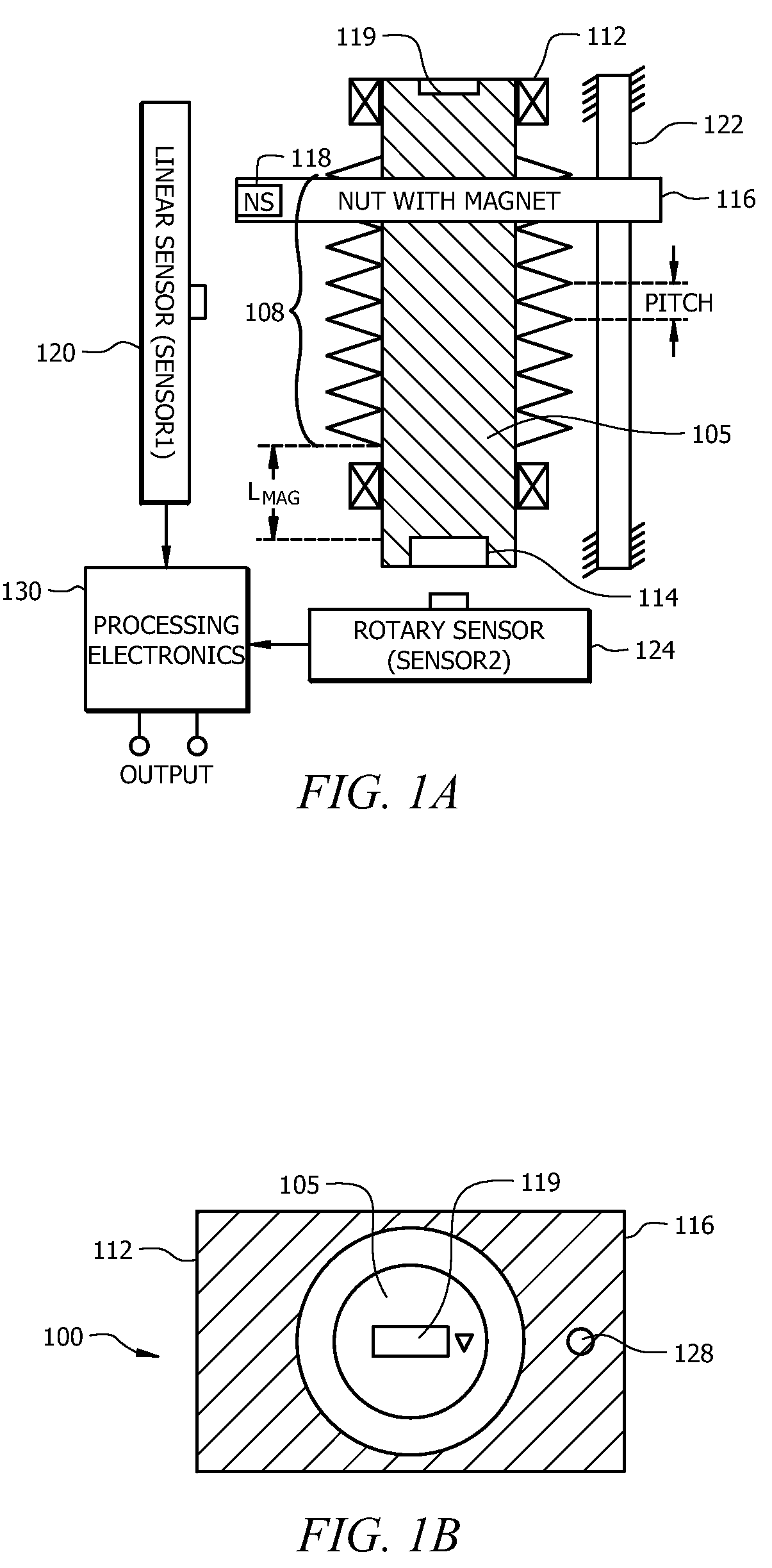
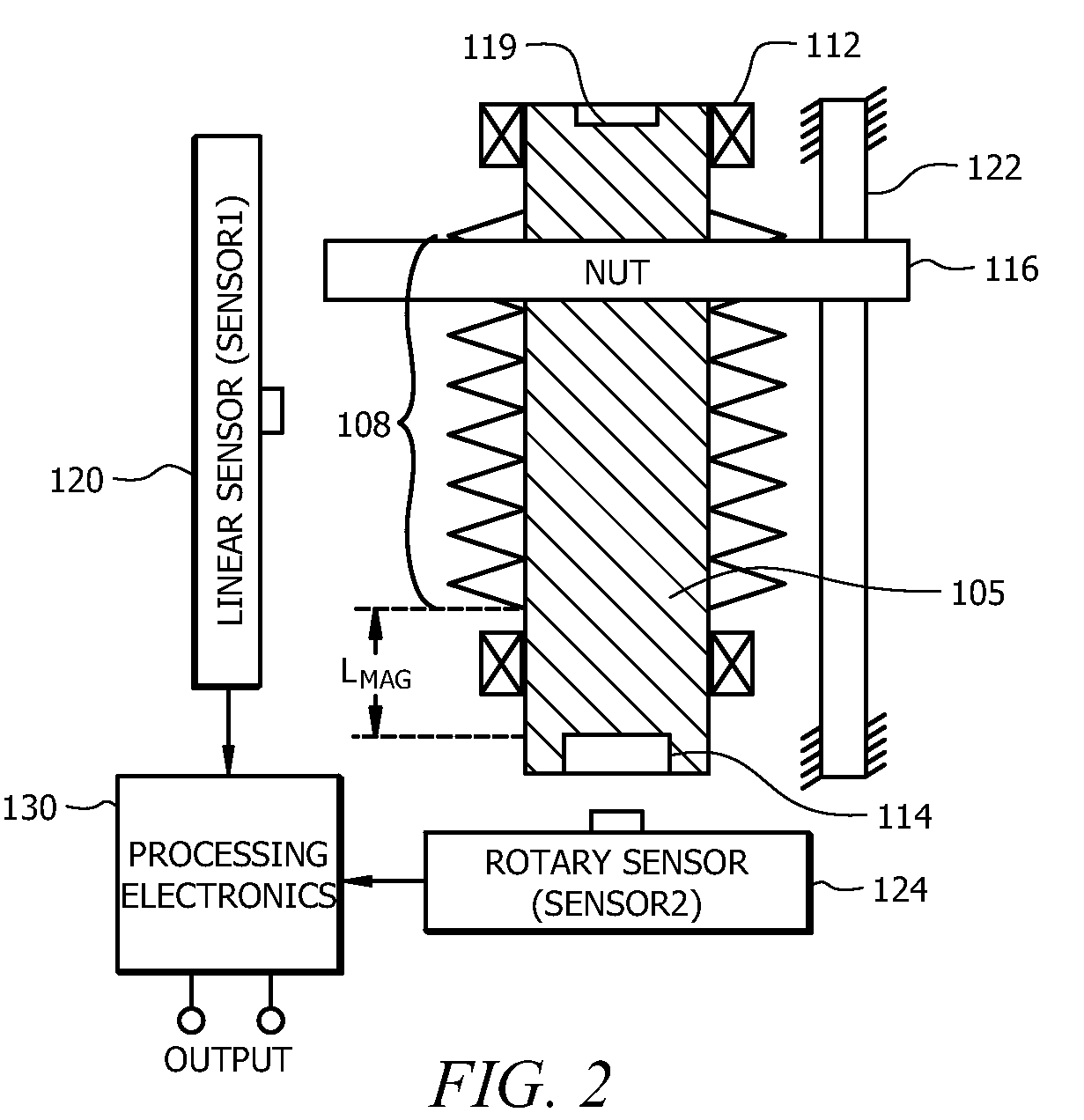
InactiveUS20100163333A1Avoid rotational movementDeflectable wheel steeringIncline measurementLinear motionSignal processing circuits
An angular position sensor (100) for determining angular position includes a shaft (105) having a threaded portion (108), and a structure for engaging an external application (119). The shaft (105) includes a first permanent magnet (114). A nut (116) is threaded on the threaded portion (108). The nut (116) is formed from a first magnetic permeable material or includes a second permanent magnet (118). At least one constraint (122) is coupled to the nut (116) for preventing rotational movement of the nut (116) while allowing linear motion of the nut (116). A first magnetic sensor (120) is positioned along a length of the threaded portion (108) of the nut (116) for measuring a linear position of the nut (116). A second magnetic sensor (124) is provided for measuring an angular position of the shaft (105). Signal processing circuitry (130) is coupled to receive outputs from both the first magnetic sensor (120) and second magnetic sensor (124) for calculating a parameter relating to an angular position of the rotatable member.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Rotation detecting device using magnetic sensor
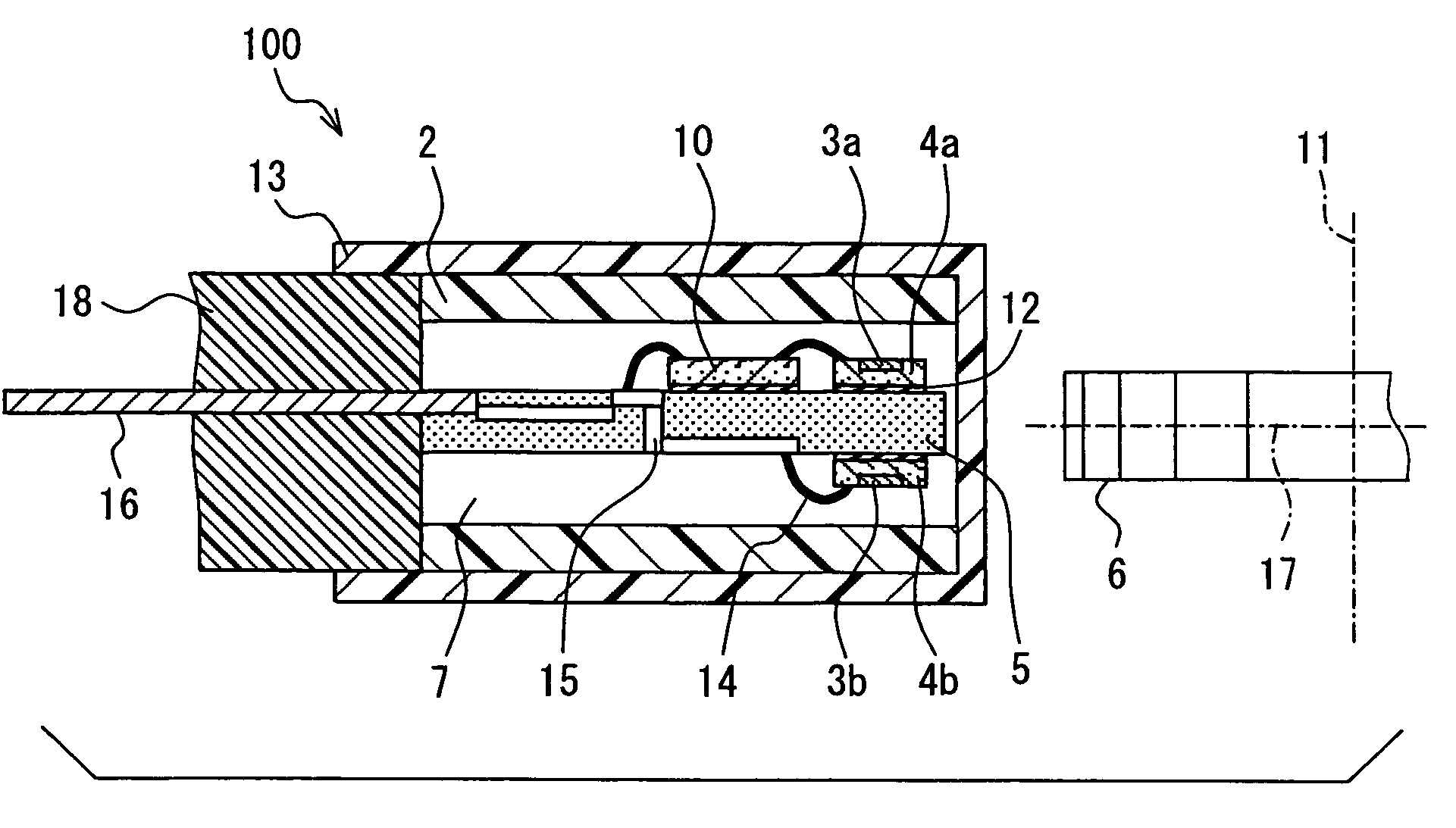
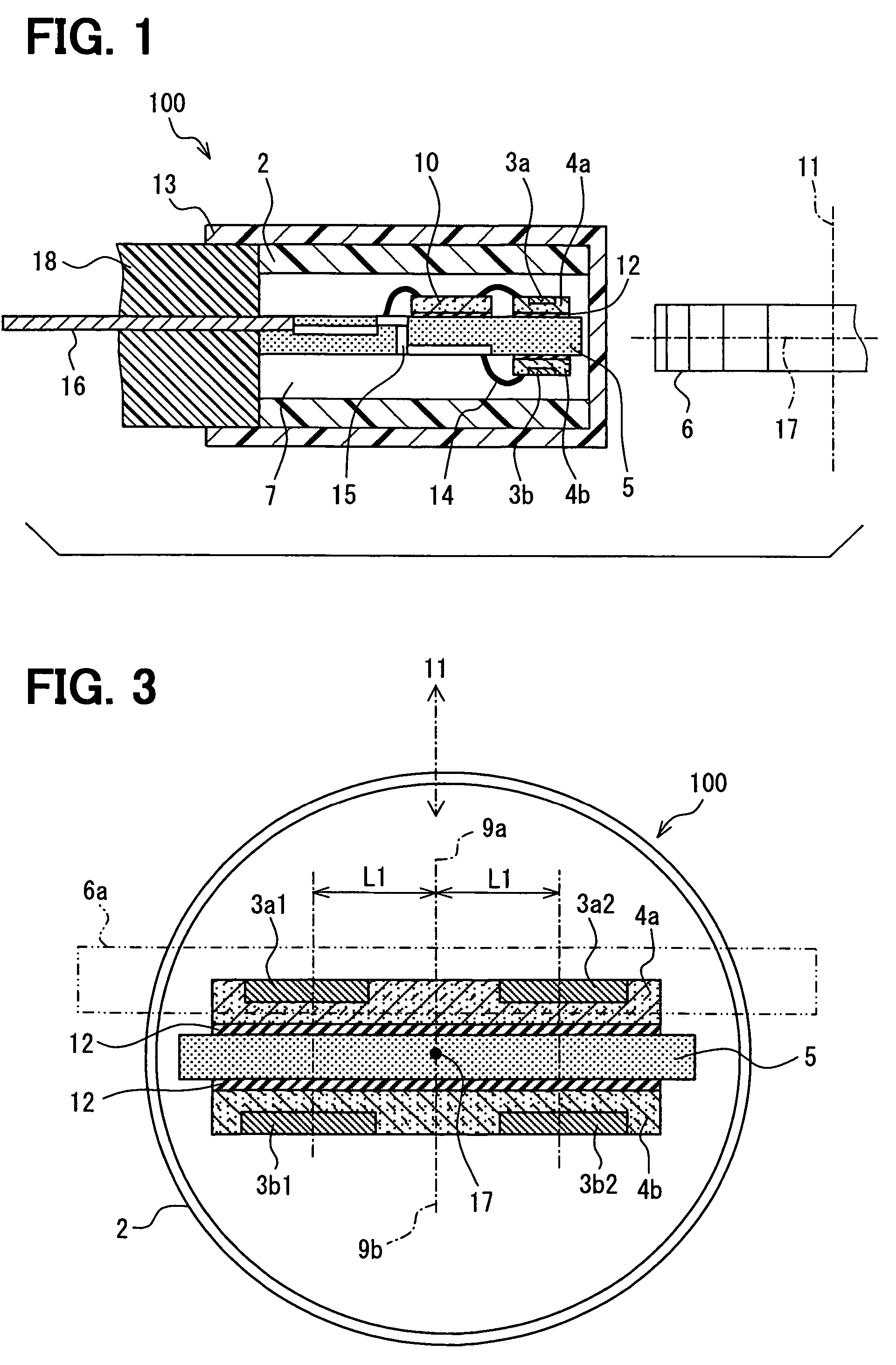
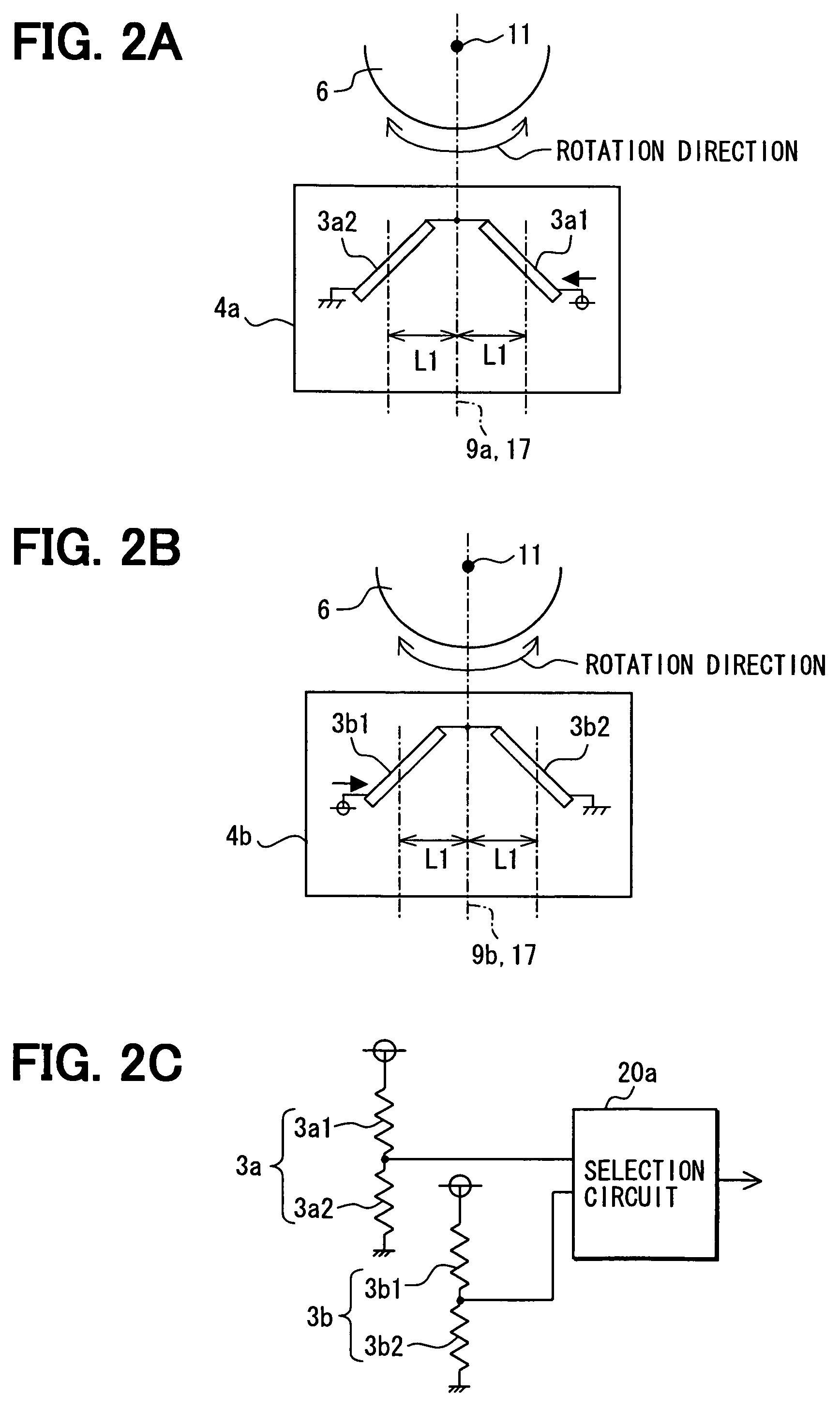
InactiveUS7355388B2Sufficient magnitudeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMultiple sensorMagnet
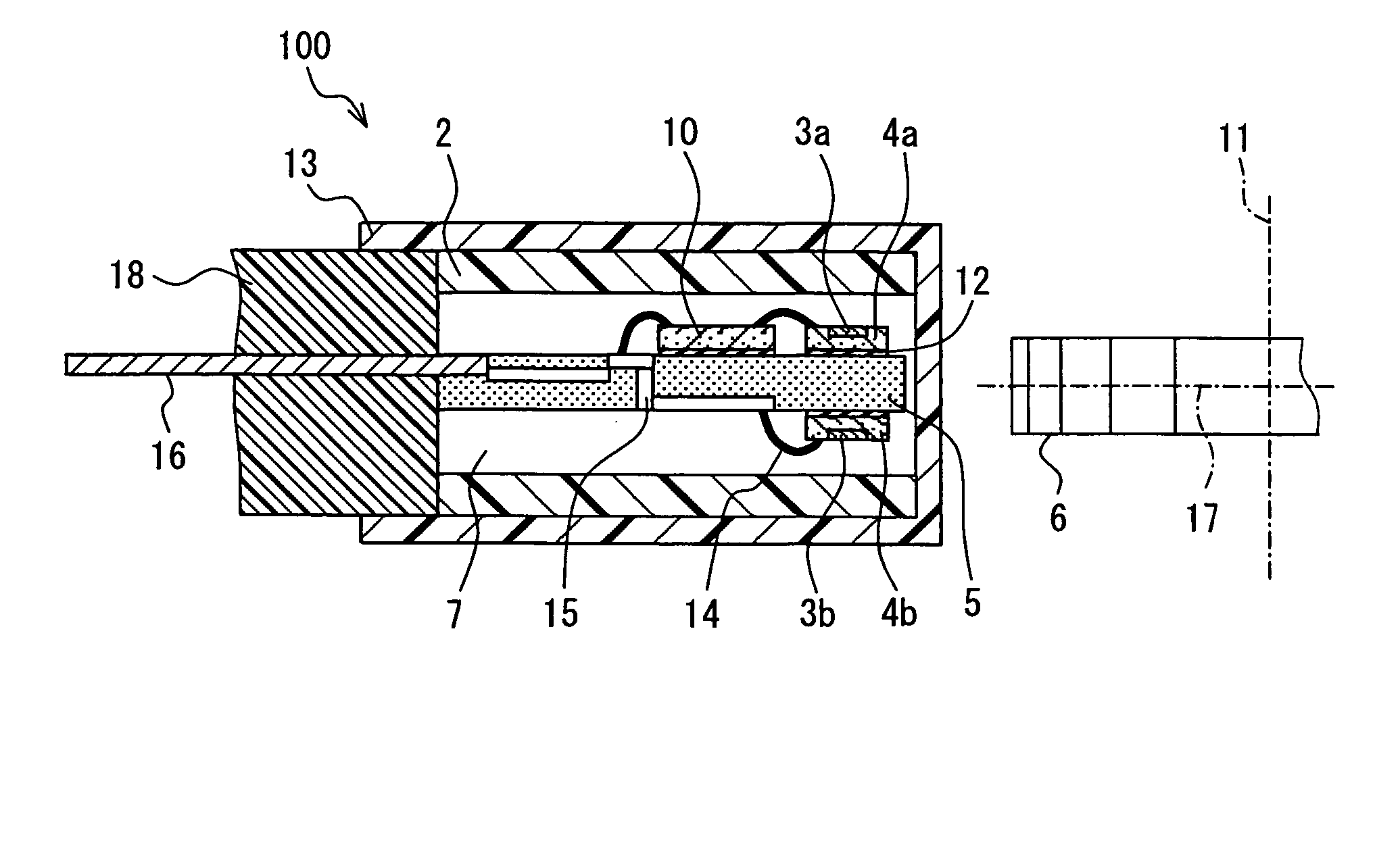
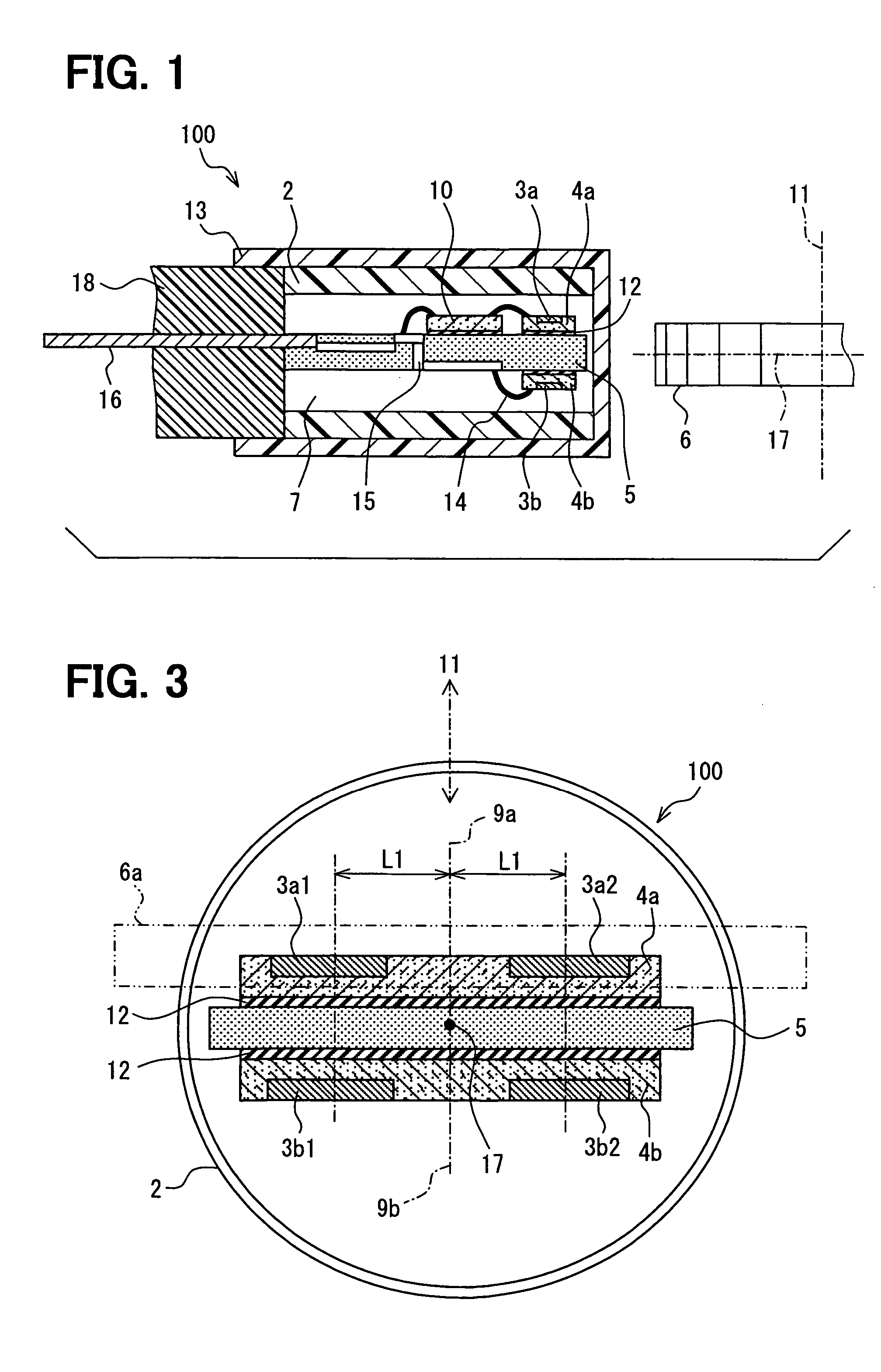
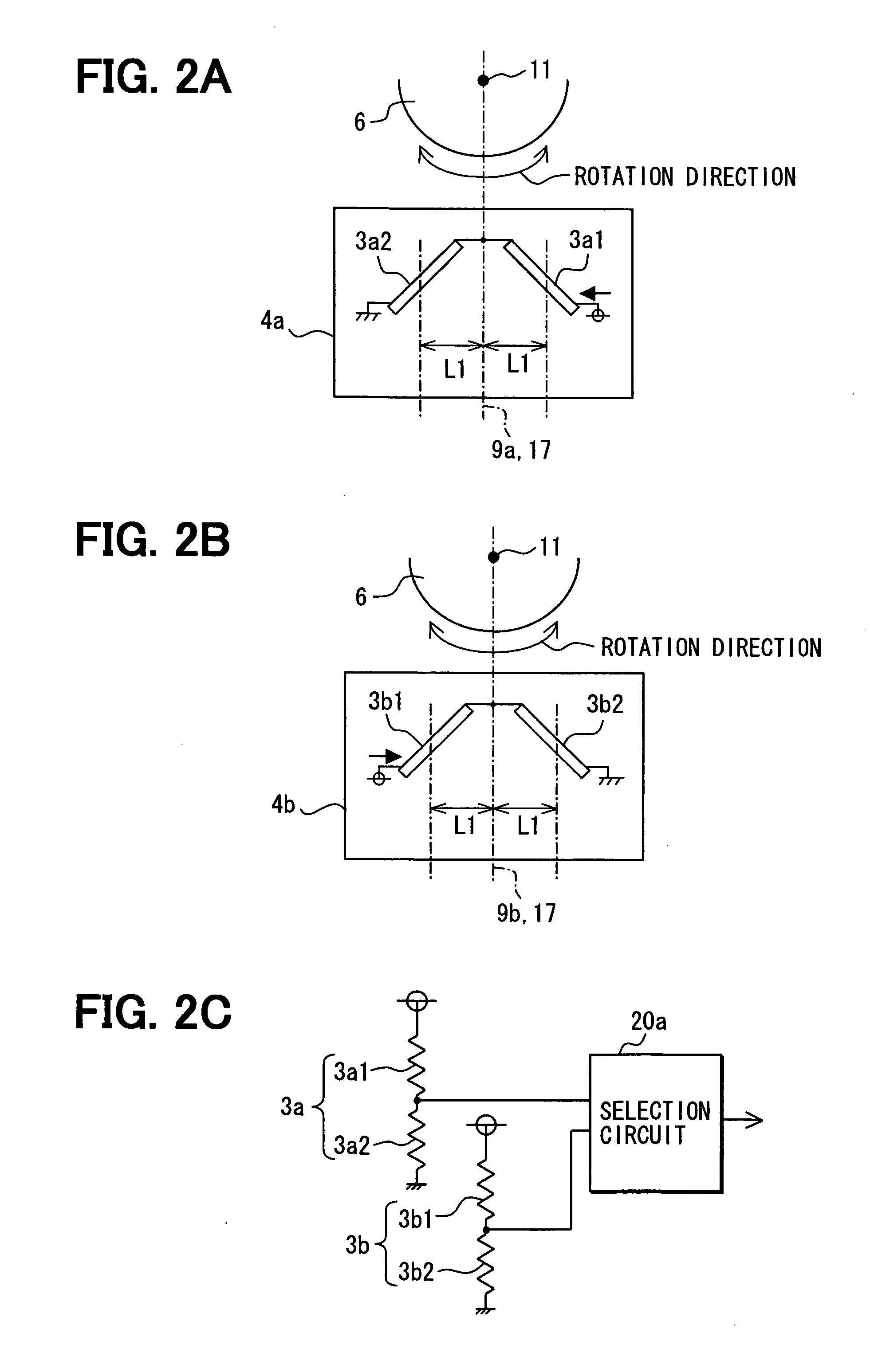
A rotation detecting device is provided that detects the rotation of a rotating object by means of a biasing permanent magnet and multiple sensor chips. The sensor chips are disposed on front and back sides of a mounting chip along the rotation direction of the rotating object, aligned with a line perpendicular to the direction or rotation of the rotating object, so as to convert magnetic vectors of a magnetic field to a plurality of sensor signals. A selection circuit is connected to the magnetoresistance sensors and selects the one of the sensor signals whose magnitude is the largest.
Owner:DENSO CORP
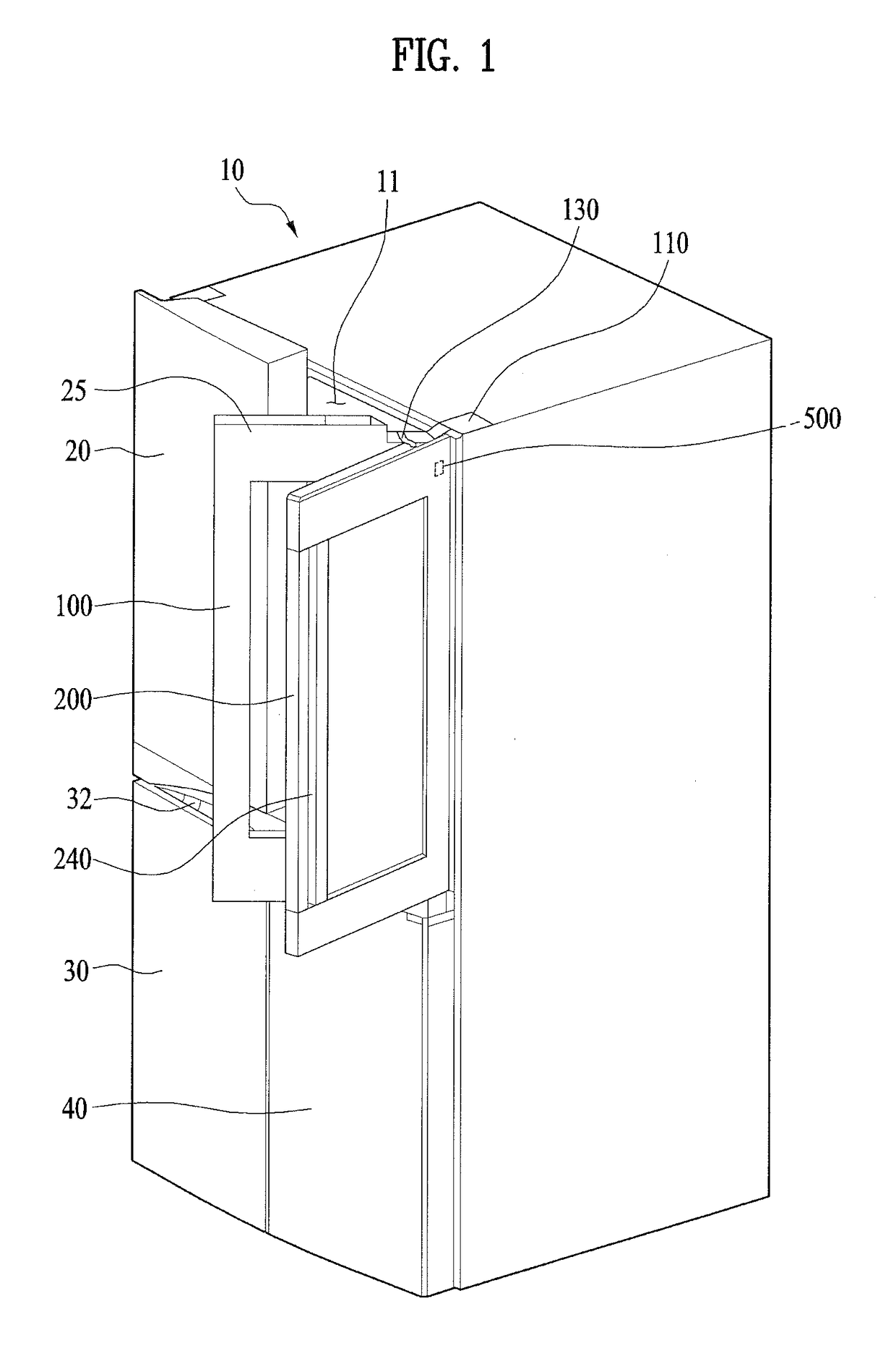
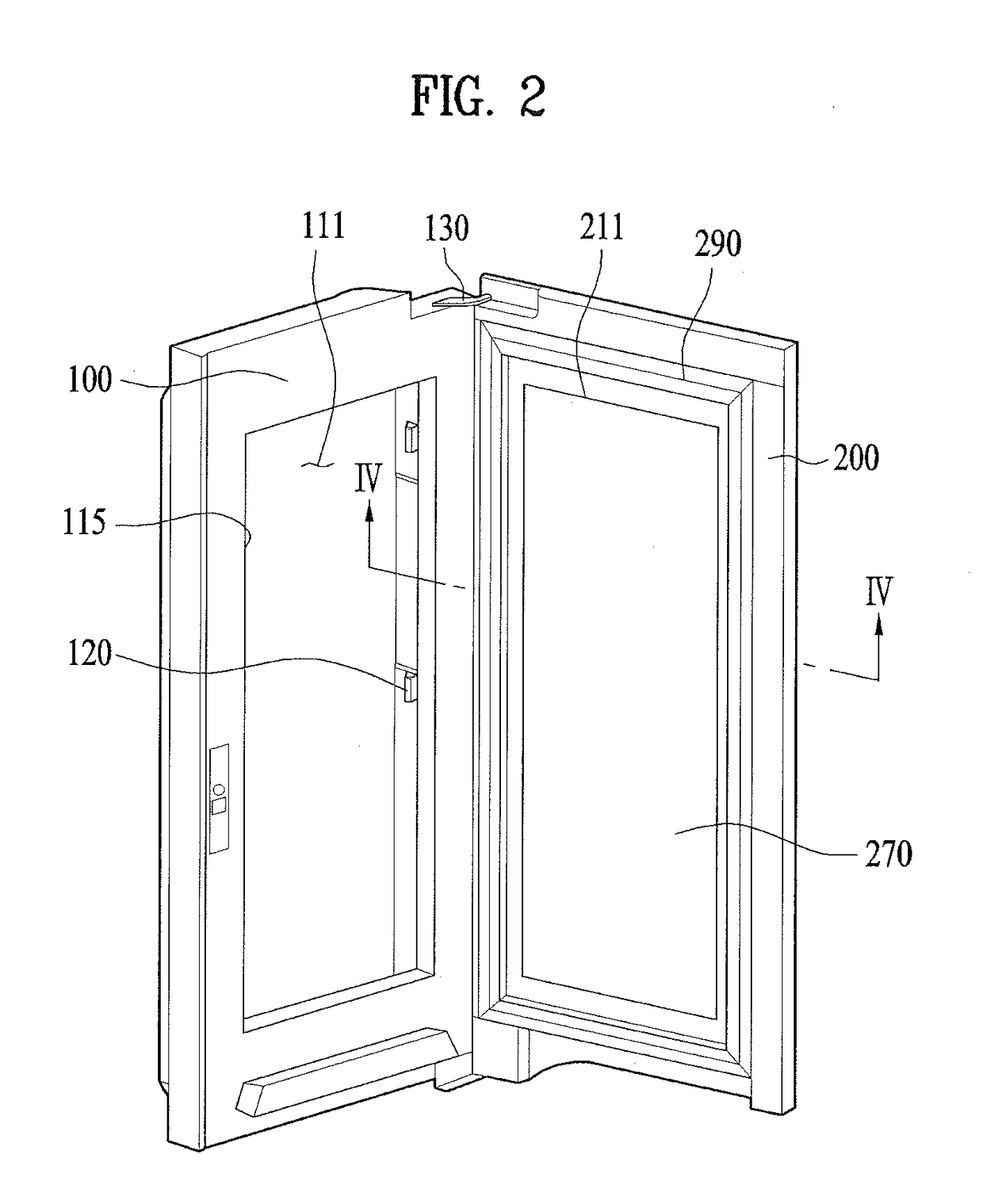
Refrigerator
ActiveUS20170211874A1Efficient use ofReduce input errorVibration measurement in solidsVibration measurement in fluidEngineeringAcoustic wave
A refrigerator equipped with a door that becomes transparent as necessary to make the interior thereof visible is disclosed. The refrigerator includes a cabinet having a storage compartment defined therein, a lighting device for illuminating the interior of the storage compartment, a door, which is hingedly coupled to the cabinet to open and close the storage compartment, and has an opening and a panel assembly including a front panel disposed on the front surface thereof, a sensor for detecting sound waves, which are generated by a knock input applied to the door and are transmitted through the front panel, and a controller for controlling the lighting device to allow light to be transmitted through the panel assembly, thus making the storage compartment visible from outside the door through the opening when a predetermined knock input is detected.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
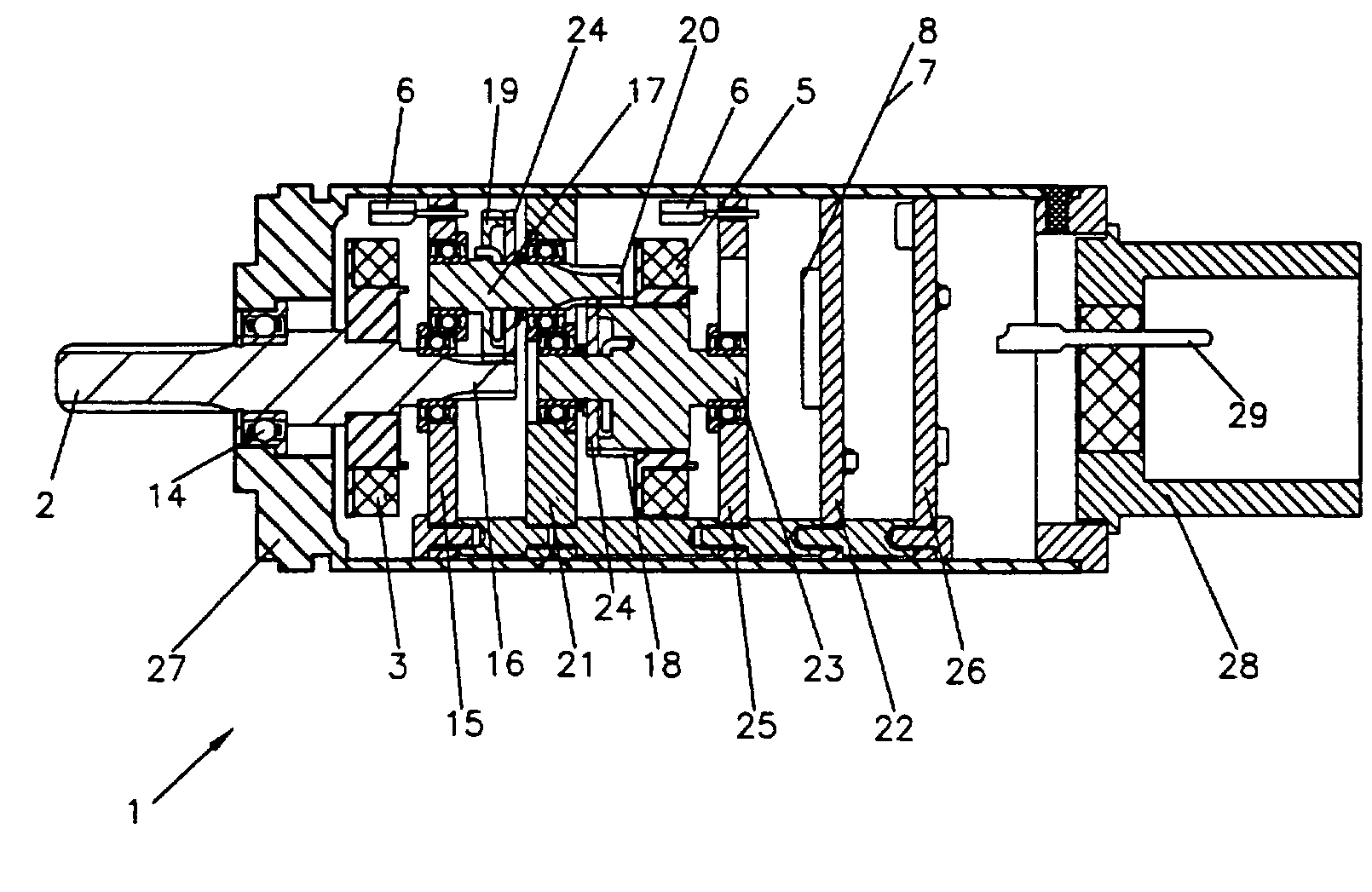
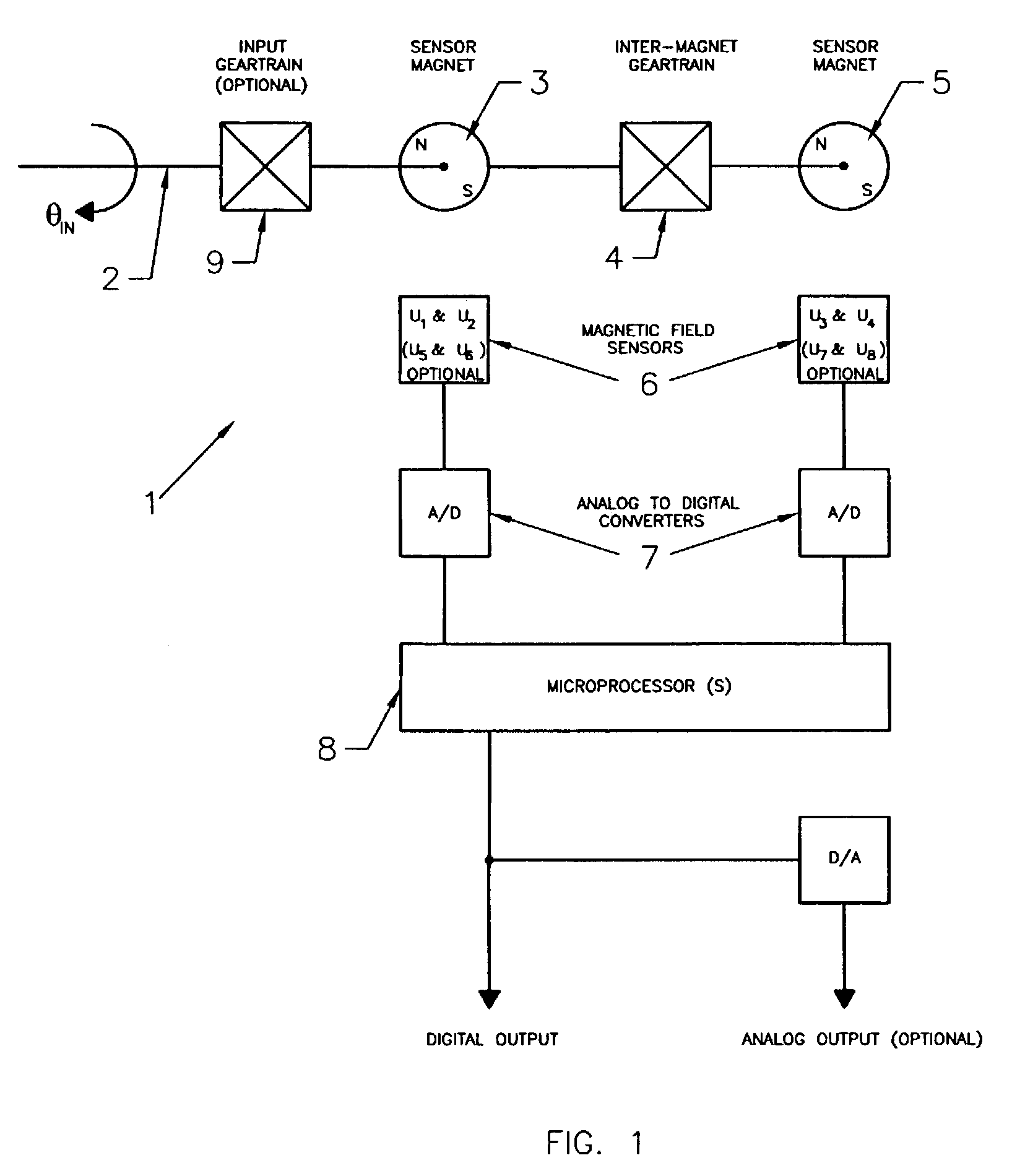
Contactless angular position sensor and method for sensing angular position of a rotatable shaft
InactiveUS7307415B2Improve accuracyRobust constructionSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSignal conditioning circuitsAngular rotation
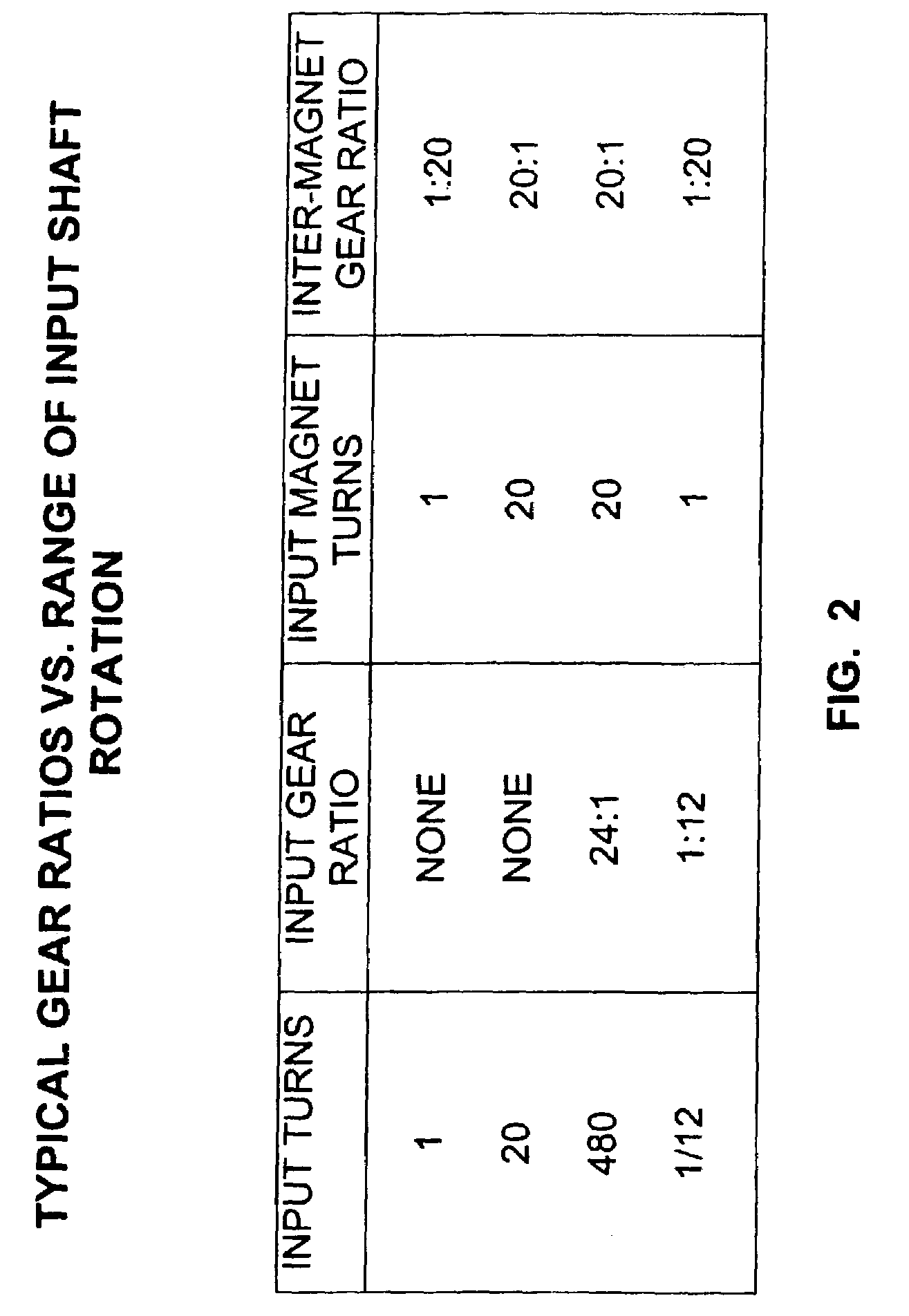
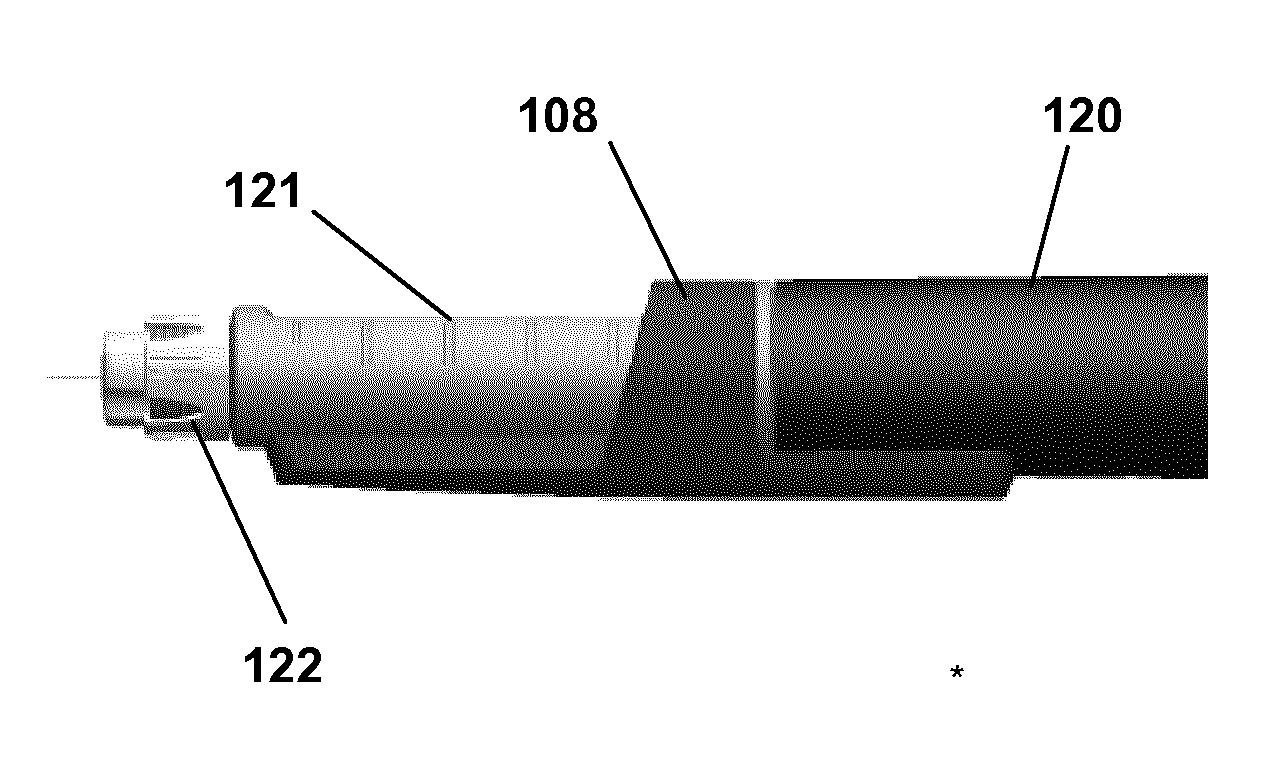
A contactless rotary shaft position sensor provides for precision computation of shaft angle for a wide range of input shaft rotational angles. The sensor includes two annular two-pole magnets which are connected by a precision, motion-transmitting gear train. An optional second gear train between one of the magnets and the input shaft can provide additional angular rotation scaling to accurately measure either fractional or a large number of multiple turns of the input shaft. The gear ratios are selected such that one of the magnets does not rotate more than one revolution. Pairs of ratiometric Hall-effect or magnetoresistive sensors provide differential voltage signals which are used for sensing angular position of each magnet over a full 360 degrees of rotation. The single-turn magnet provides an absolute, coarse indication of input shaft rotation with a typical accuracy of 2%. The gear ratio between the magnets produces several turns of the second magnet for each turn of the single-turn magnet. Since the gear ratio between the magnets is fixed, the angle sensed for the multi-turn magnet can be predicted from the position of the single-turn magnet. This is compared to the multi-turn magnet's actual sensed rotation. The result is an improvement in accuracy directly proportional to the gear ratio between the magnets. Computation of the individual magnet rotation angles and the input shaft angle is performed using a microprocessor and appropriate signal conditioning circuits. Utilizing two magnets, input shaft rotation can be accurately measured to within 0.1% of maximum range.
Owner:BVR TECH
System for Determining Position of Element
ActiveUS20140243750A1Simpler and more cost efficient productionImprove securityAmpoule syringesMedical devicesEngineeringMagnet
System comprising a sensor assembly (3, 4, 5, 6) adapted to measure a magnetic field, and a moveable element (1) adapted to be moved relative to the sensor assembly between two positions by a combined axial and rotational movement, the rotational movement having a pre-determined relationship to the axial movement. A magnet (3) is mounted to the moveable element and configured to generate a spatial magnetic field which relative to the sensor assembly varies corresponding to both the axial and rotational movement of the magnet and thus the moveable element. A processor is configured to determine on the basis of measured values for the magnetic field an axial position of the moveable element.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
System for determining position of element
ActiveCN103957961AImprove securityLow costAmpoule syringesDiagnosticsMoving between two positionsMagnet
System comprising a sensor assembly adapted to measure a magnetic field, and a moveable element adapted to be moved relative to the sensor assembly between two positions by a combined axial and rotational movement, the rotational movement having a pre-determined relationship to the axial movement. A magnet is mounted to the moveable element and configured to generate a spatial magnetic field which relative to the sensor assembly varies corresponding to both the axial and rotational movement of the magnet and thus the moveable element. A processor is configured to determine on the basis of measured values for the magnetic field an axial position of the moveable element.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Angle of rotation sensor
InactiveUS6894487B2High resolutionImprove accuracyUsing electrical meansSteering partsControl theoryAngle of rotation
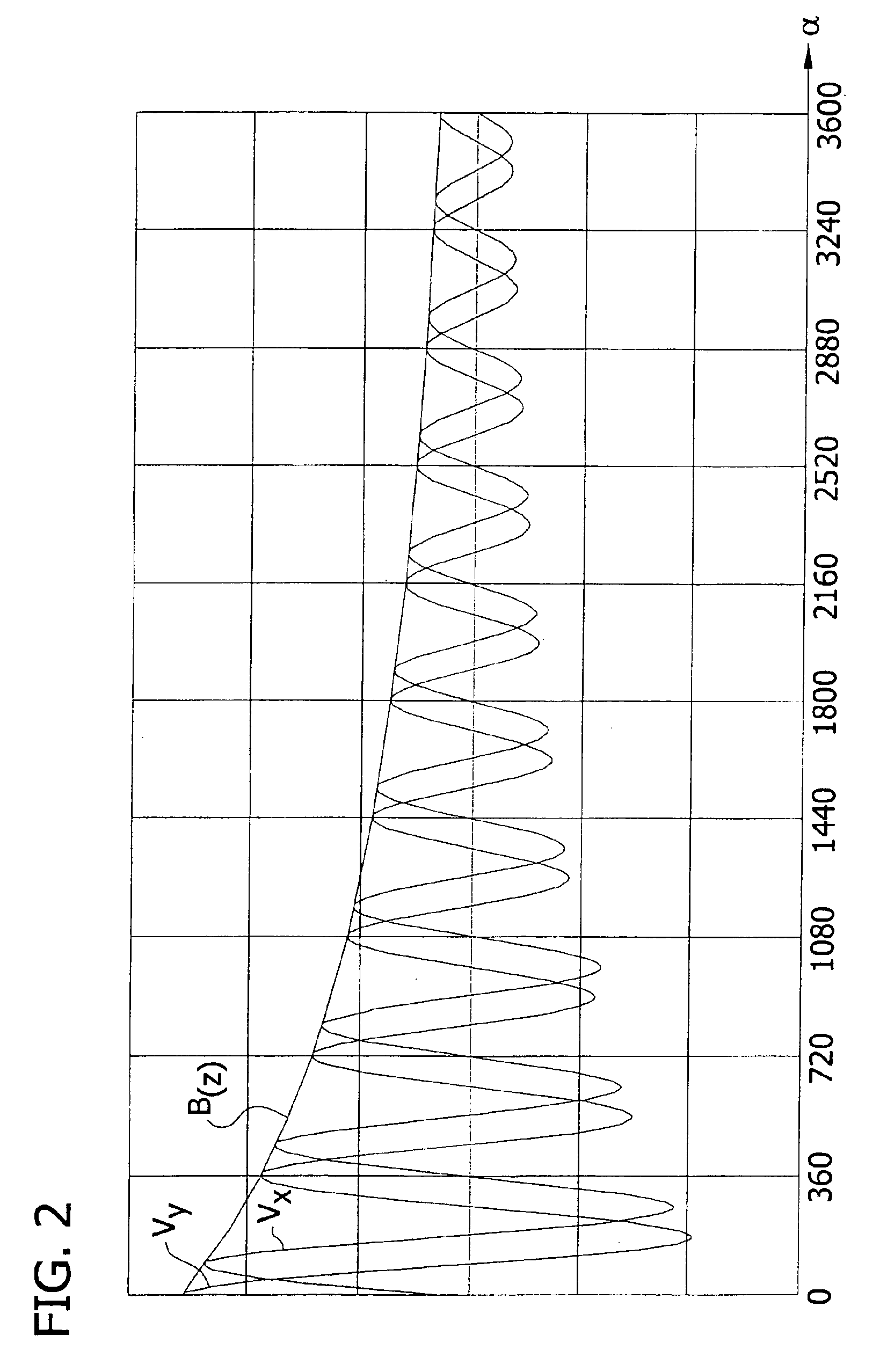
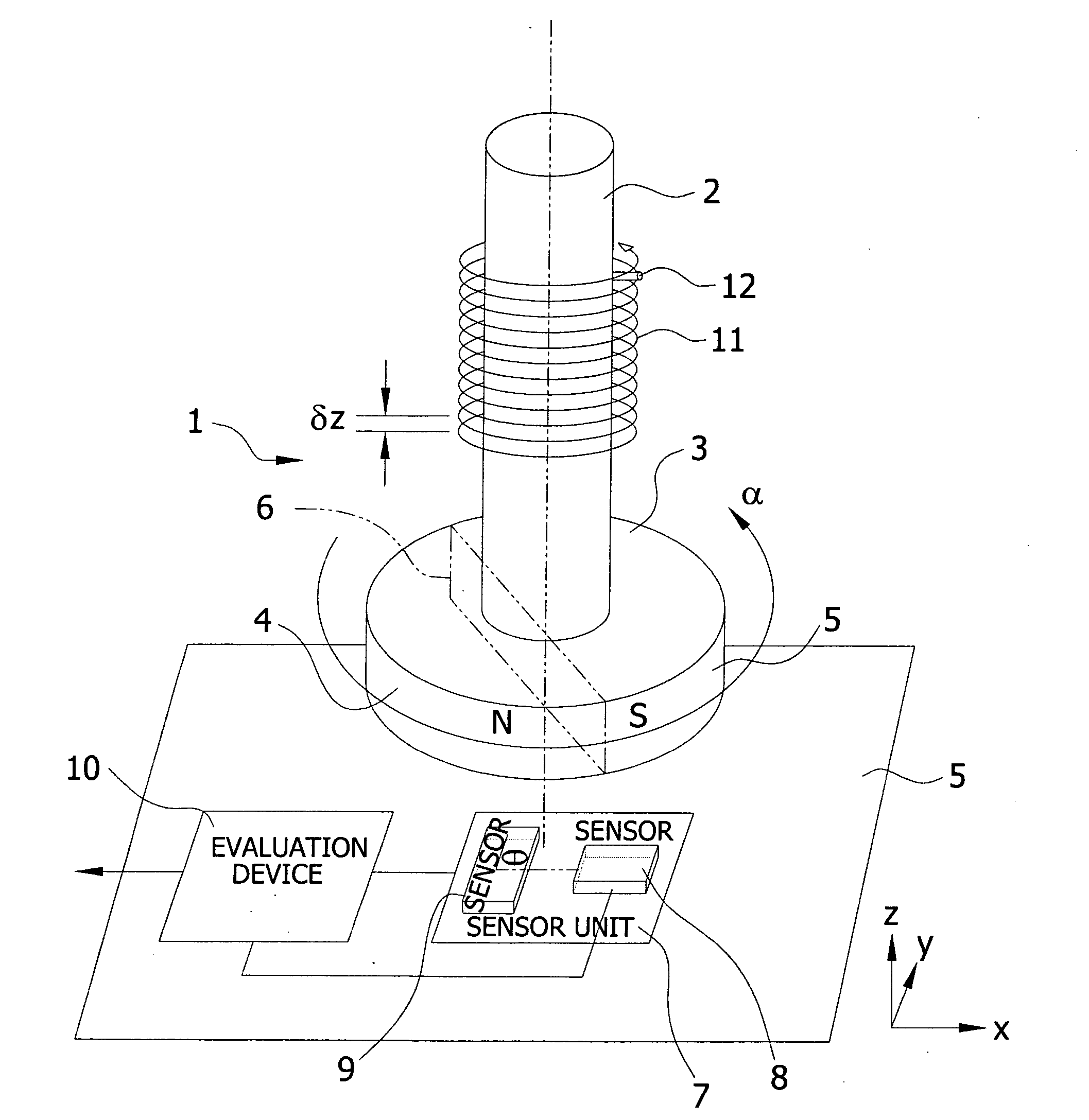
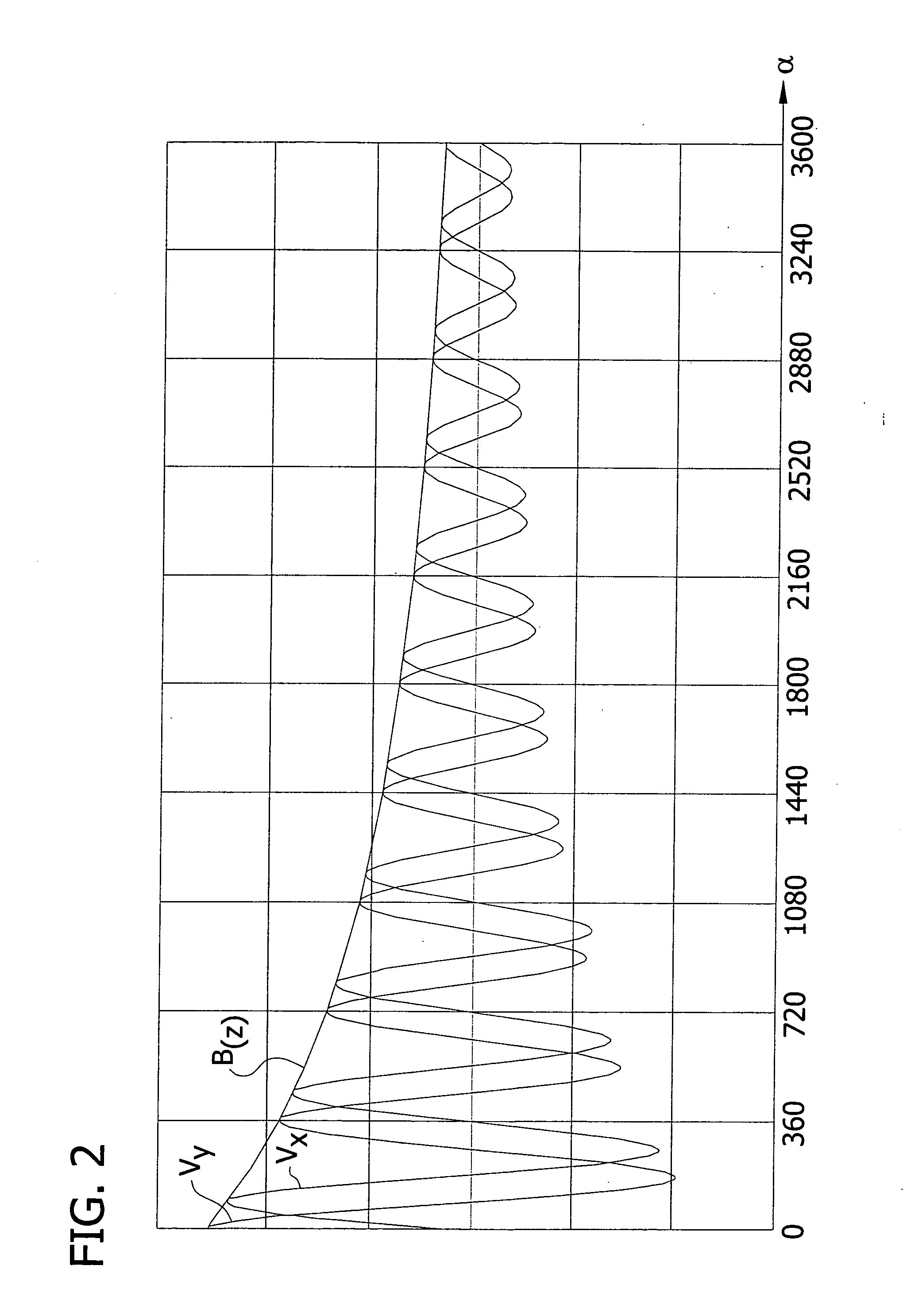
An angle of rotation sensor includes a rotary shaft coupled to a permanent magnet. A magnet-sensitive sensor element generates a sinusoidal output signal and a cosinusoidal output signal (Vx, Vy) as a function of the relative angle of rotation (a) between magnet and sensor element. Evaluation electronics generate from the output signals a signal corresponding to the angle of rotation. When the shaft rotates about its axis it moves linearly parallel to its axis along a guide track, and changes the distance between the magnet and sensor. From the sensor signals, a signal (B(z)) is determined, which corresponds to the magnitude of the field strength dependent on the distance. From this signal, a gross signal is determined, from which the number (n) of rotations can be determined. From the sinusoidal and cosinusoidal sensor signals, a fine signal is determined, which is added to the number of rotations multiplied by 360°.
Owner:TECH3 E K
Rotation detecting device
InactiveUS20060238190A1Sufficient magnitudeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesRotation sensorMagnet
A rotation detecting device detects rotation of a rotating object by means of a biasing permanent magnet and plural magnetoresistance sensors. The sensors are disposed along the rotation direction of the rotating object to convert magnetic vectors of a magnetic field to a plurality of sensor signals. A selection circuit is connected to the magnetoresistance sensors and selects one of the sensor signals whose magnitude is the largest.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Angle of rotation sensor
InactiveUS20050030012A1High resolutionImprove accuracyUsing electrical meansSteering partsEngineeringControl theory
An angle of rotation sensor includes a rotary shaft coupled to a permanent magnet. A magnet-sensitive sensor element generates a sinusoidal output signal and a cosinusoidal output signal (Vx, Vy) as a function of the relative angle of rotation (α) between magnet and sensor element. Evaluation electronics generate from the output signals a signal corresponding to the angle of rotation. When the shaft rotates about its axis it moves linearly parallel to its axis along a guide track, and changes the distance between the magnet and sensor. From the sensor signals, a signal (B(z)) is determined, which corresponds to the magnitude of the field strength dependent on the distance. From this signal, a gross signal is determined, from which the number (n) of rotations can be determined. From the sinusoidal and cosinusoidal sensor signals, a fine signal is determined, which is added to the number of rotations multiplied by 360°.
Owner:TECH3 E K
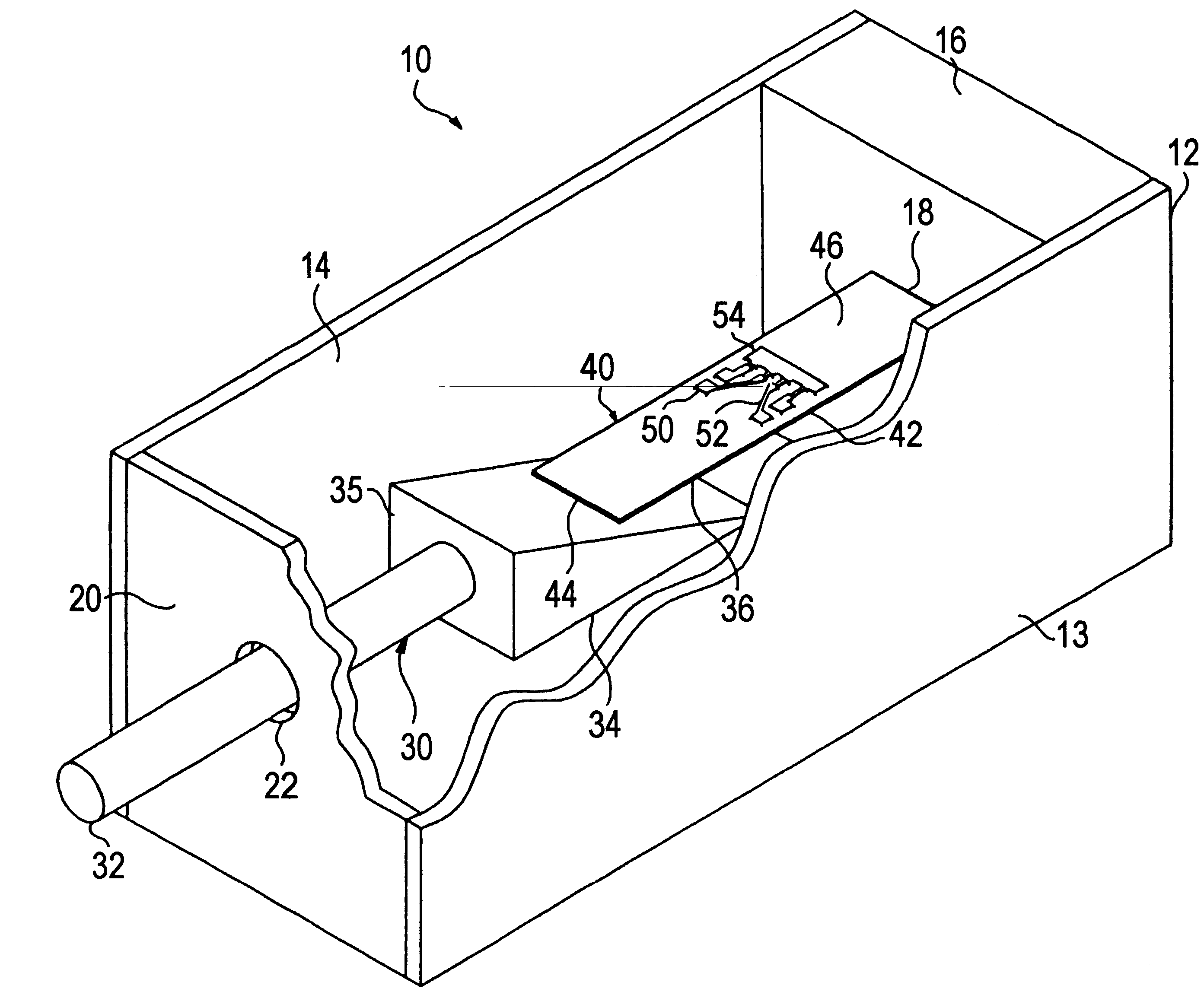
Method and apparatus for countering mold deflection and misalignment using active material elements
InactiveUS20050236725A1Effectively and efficiently detectingAuxillary shaping apparatusConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringStructural coupling
Method and apparatus for controlling an injection mold having a first surface and a second surface includes an active material element configured to be disposed between the first surface and a second surface. The active material element may be configured to sense a force between the first surface and the second surface, and to generate corresponding sense signals. Transmission structure is coupled to the active material element and is configured to carry the sense signals. Preferably, an active material element actuator is also disposed between the first surface and a second surface, and is configured to provide an expansive force between the first surface and a second surface in accordance with the sense signals. The method and apparatus may be used to counter undesired deflection and / or misalignment in an injection mold.
Owner:HUSKY INJECTION MOLDING SYST LTD
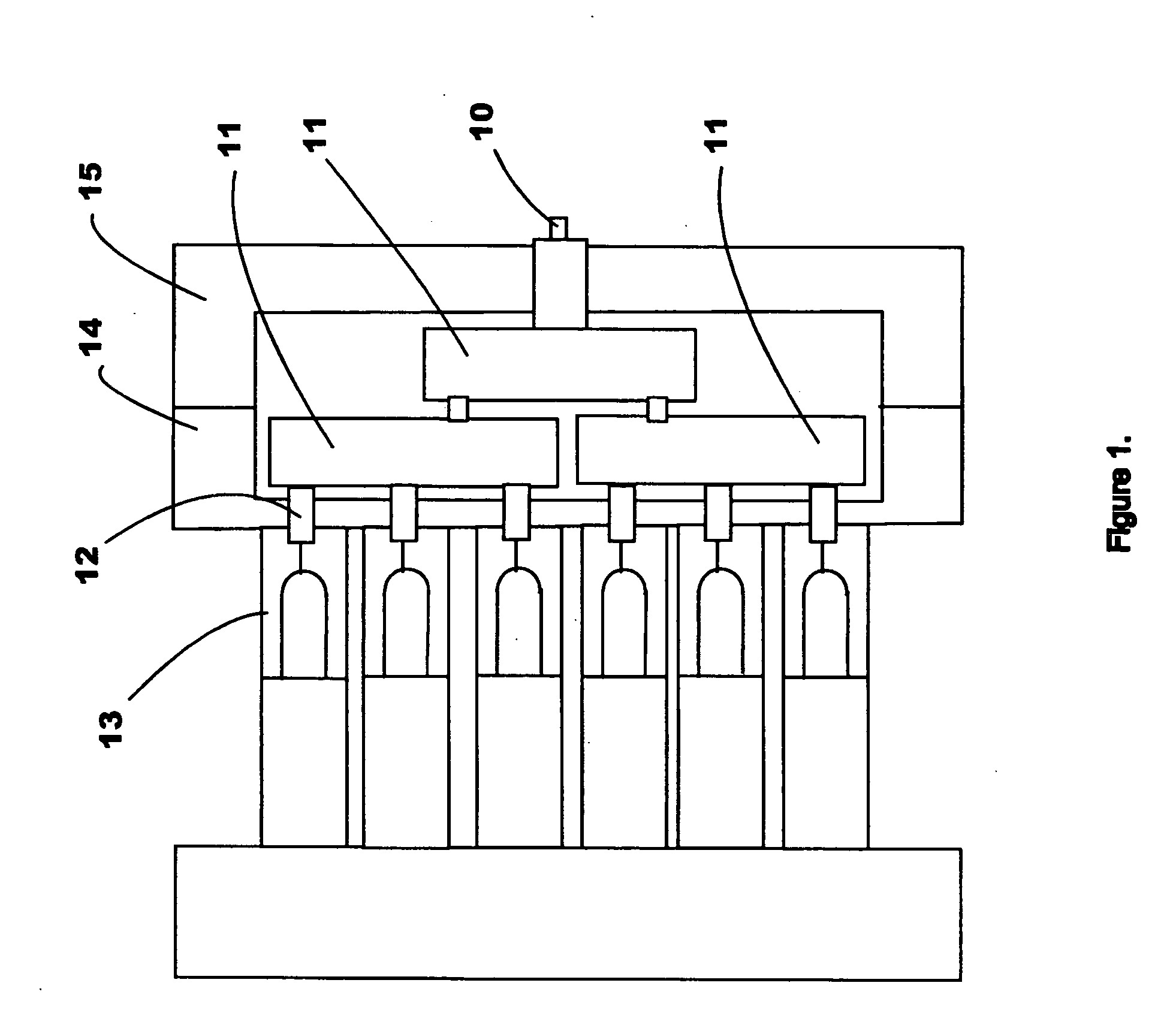
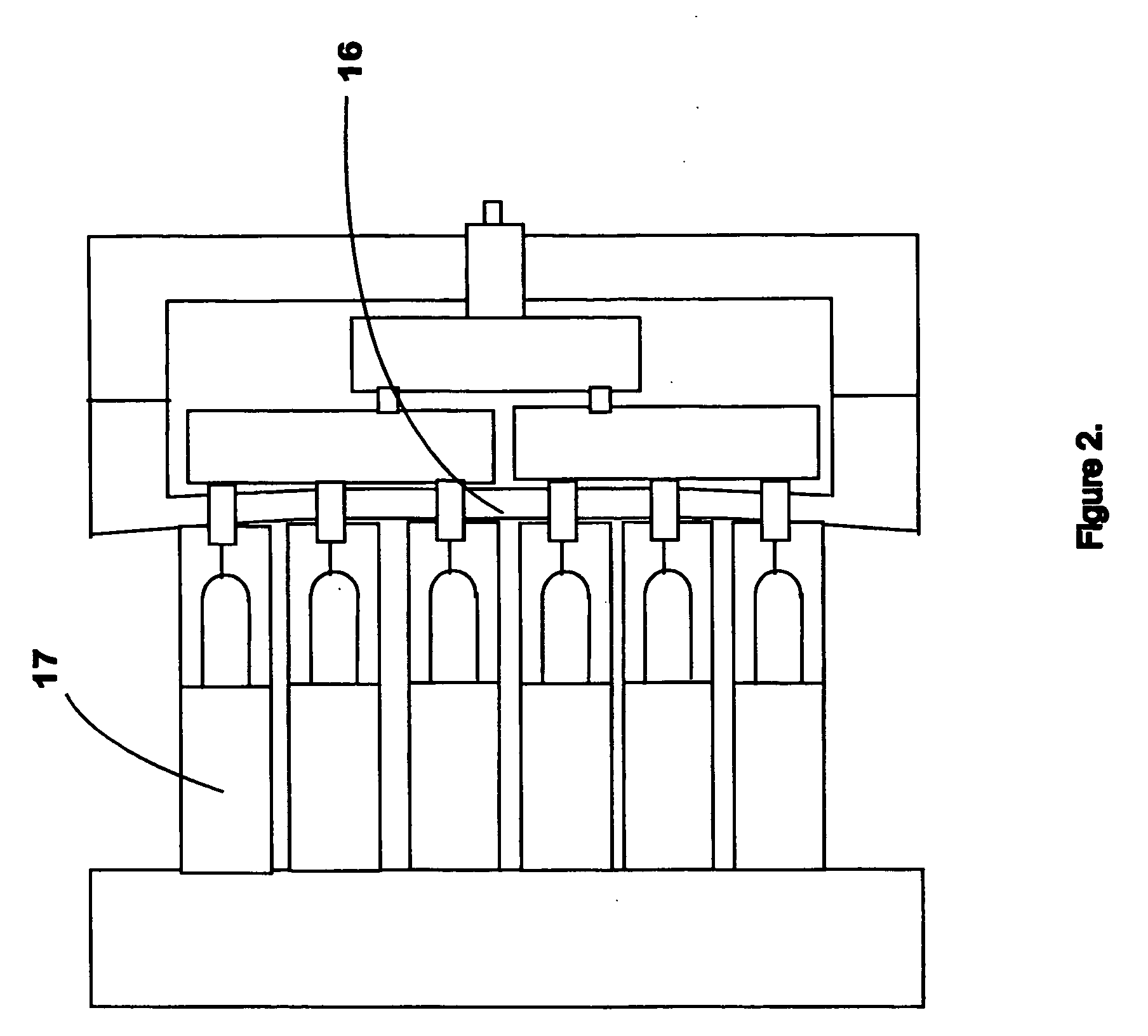
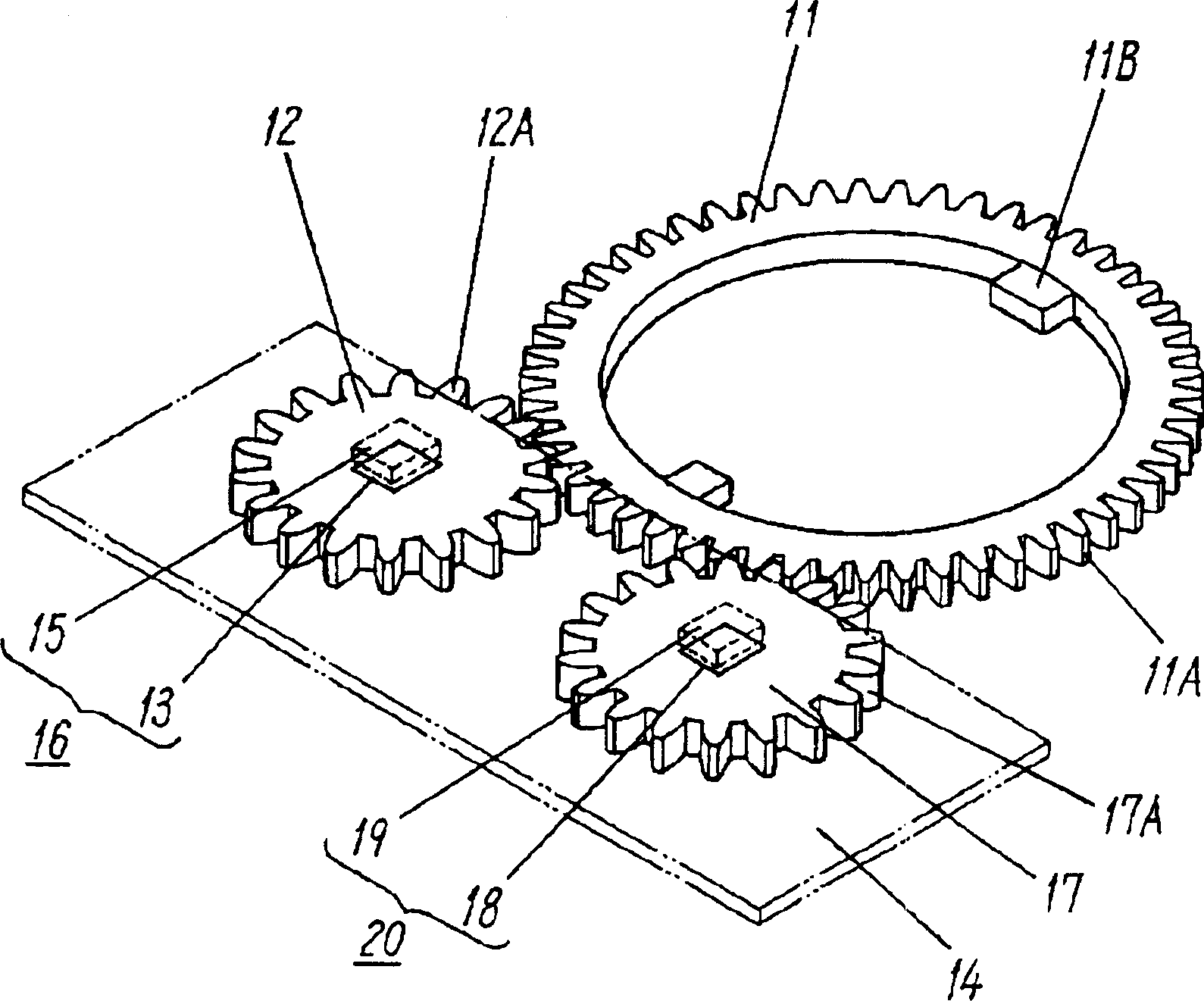
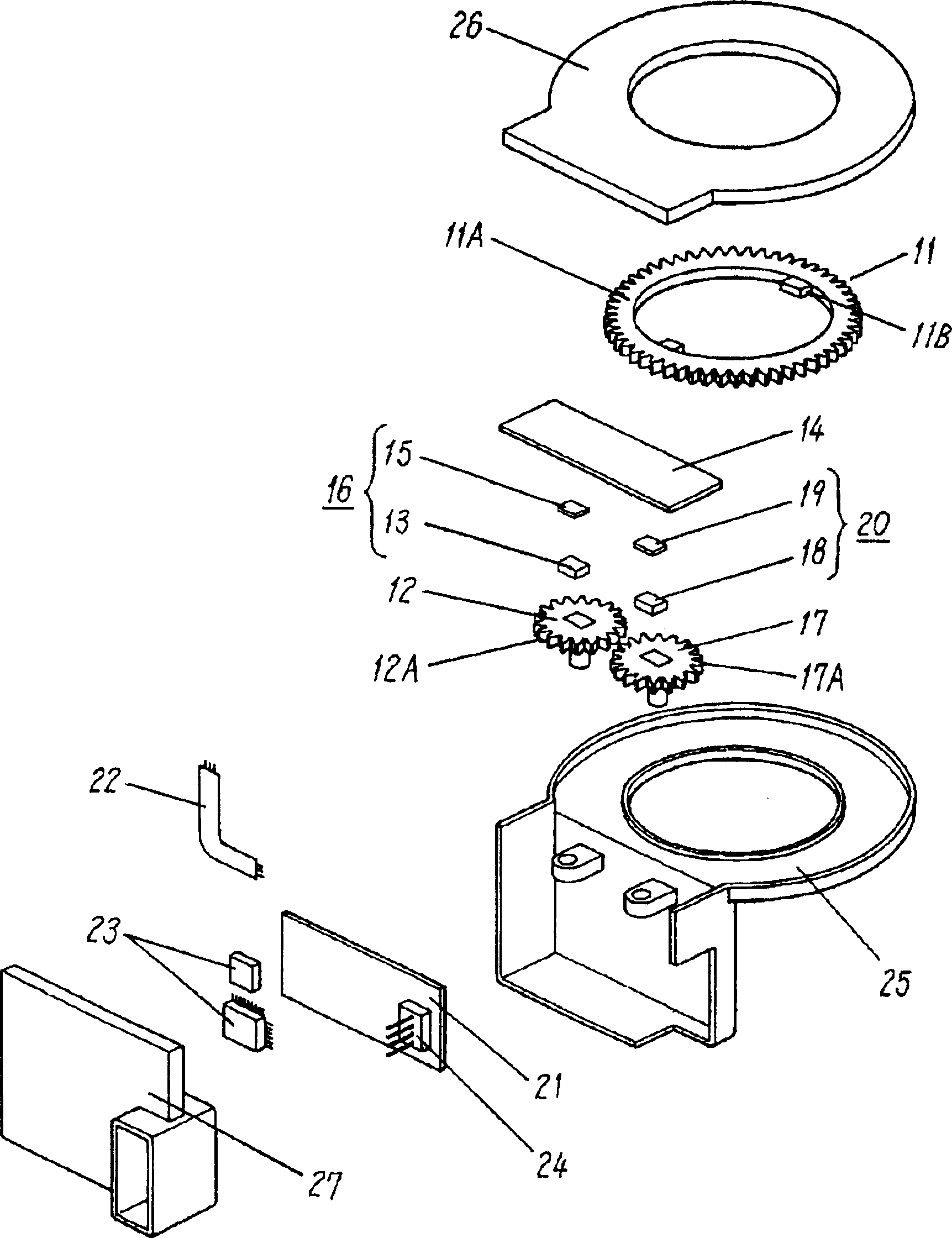
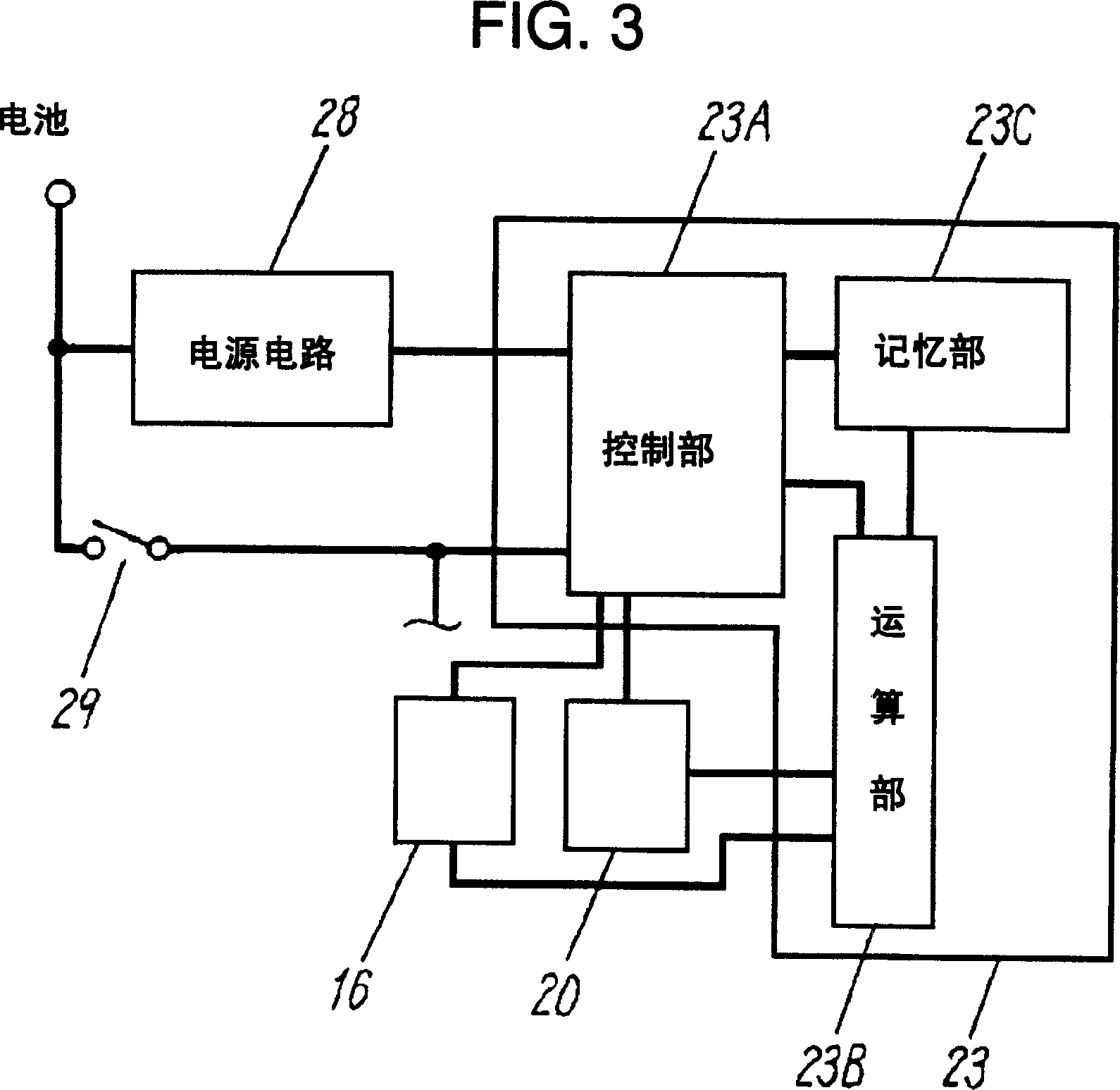
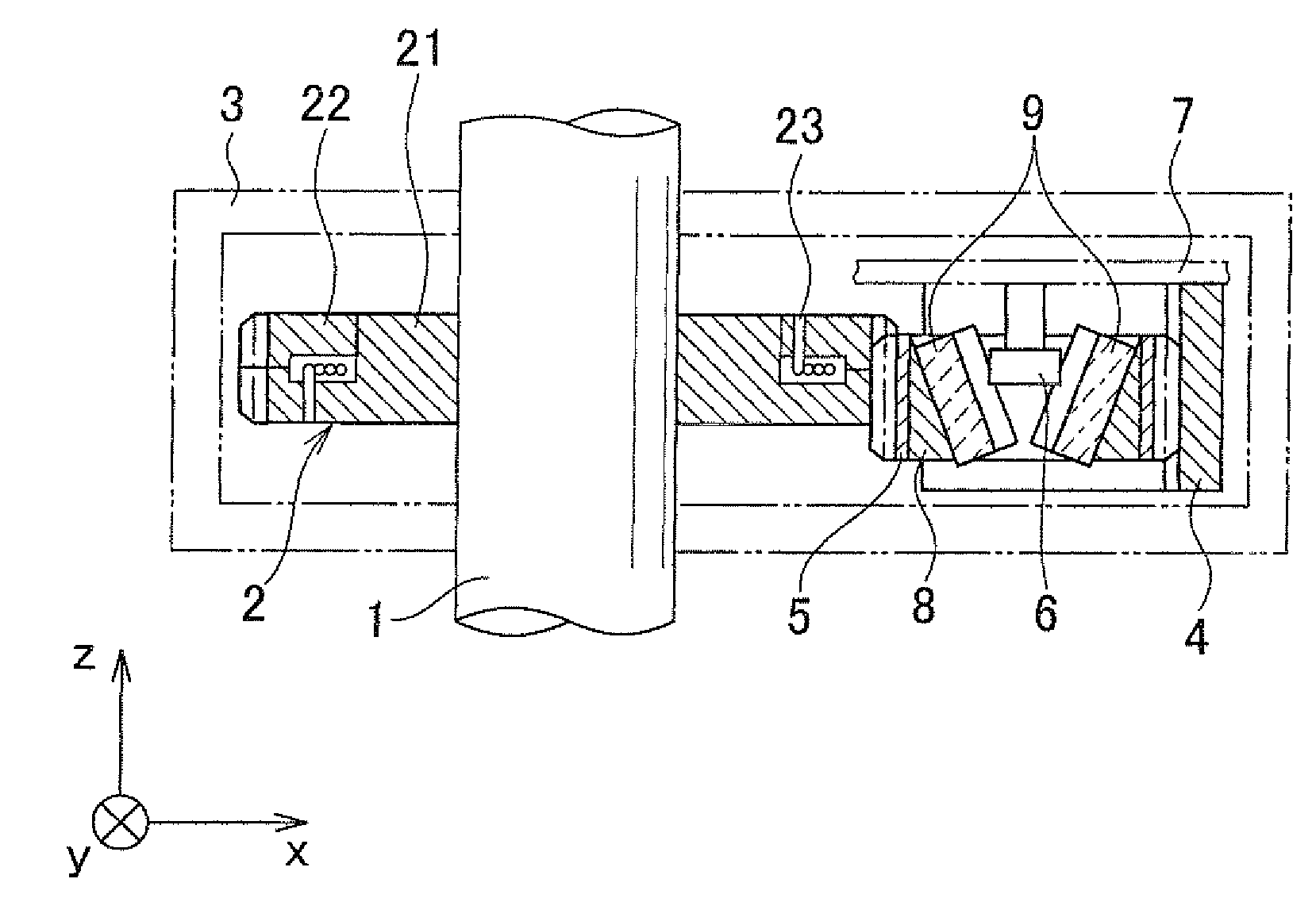
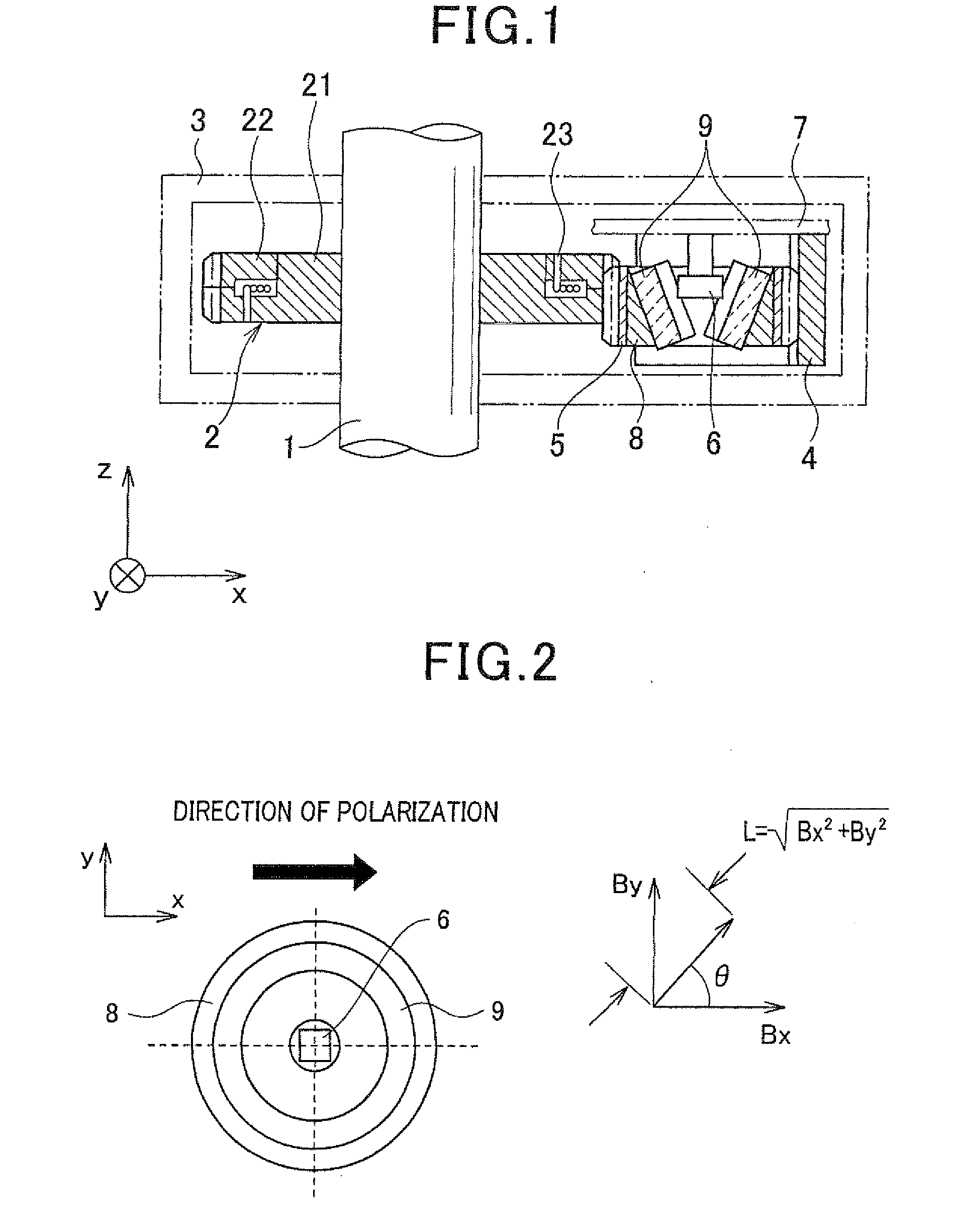
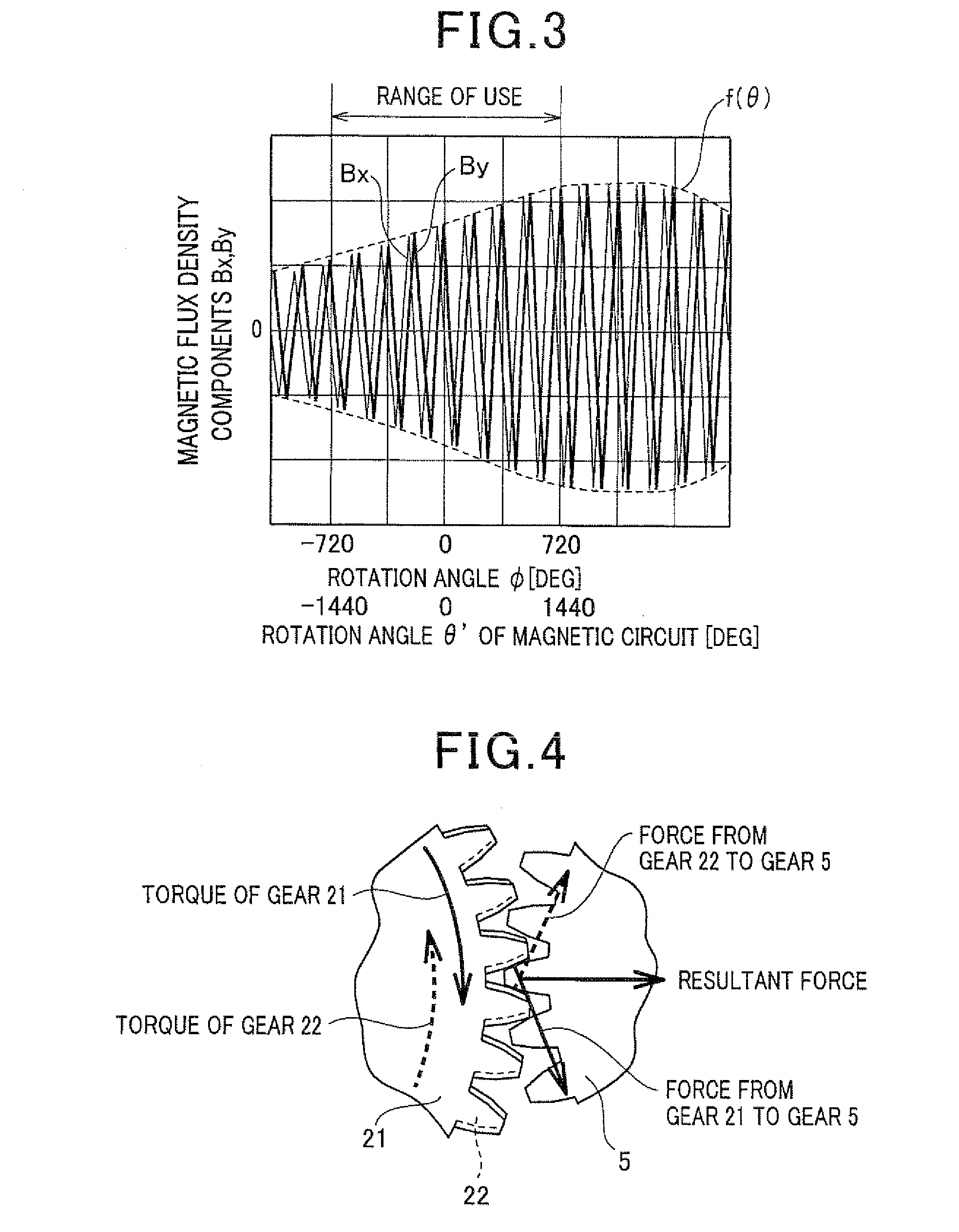
Multi-turn angle transducer
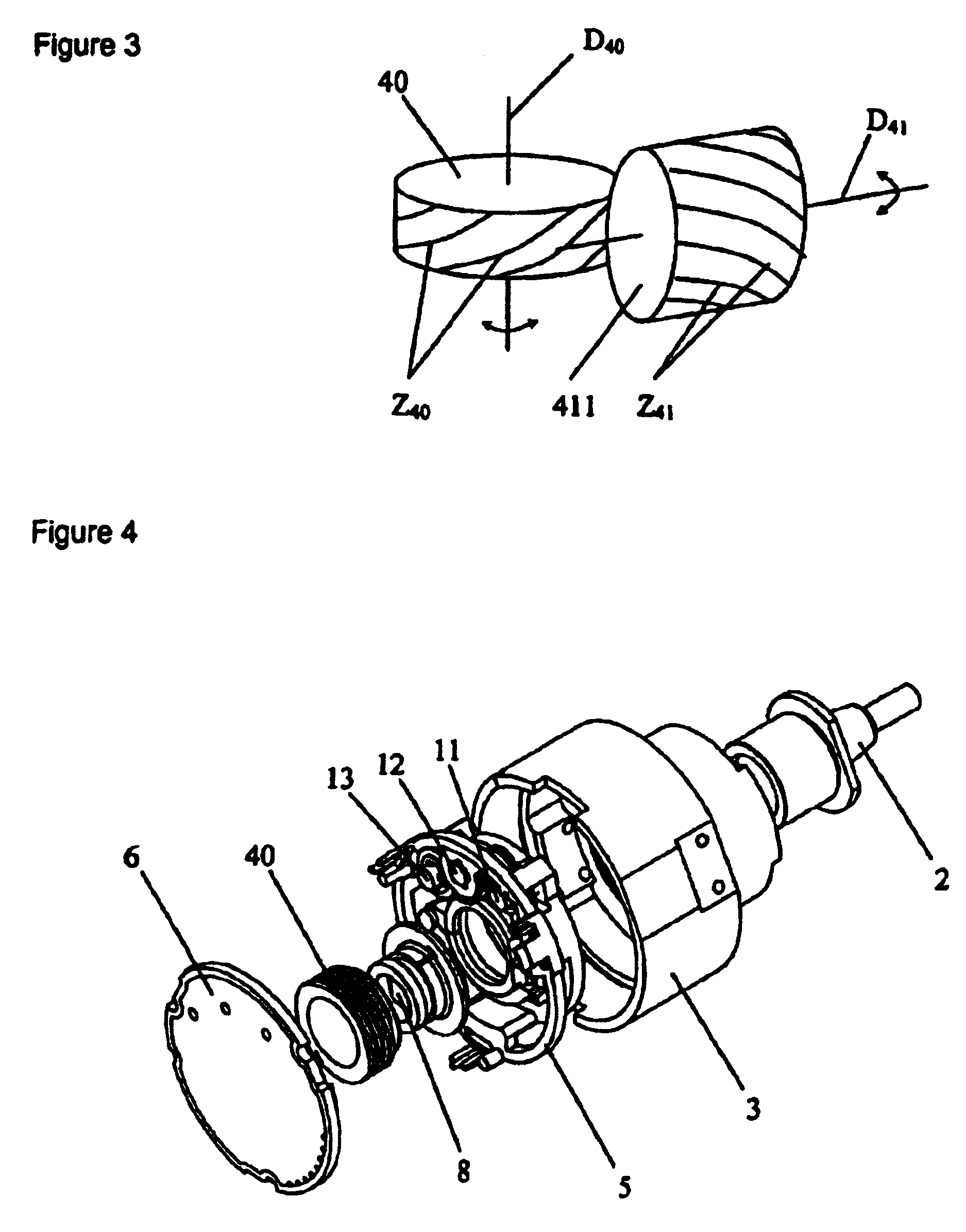
ActiveUS7017274B2Increase the number of revolutionsLarge caliberElectric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansTurn angleDrive wheel
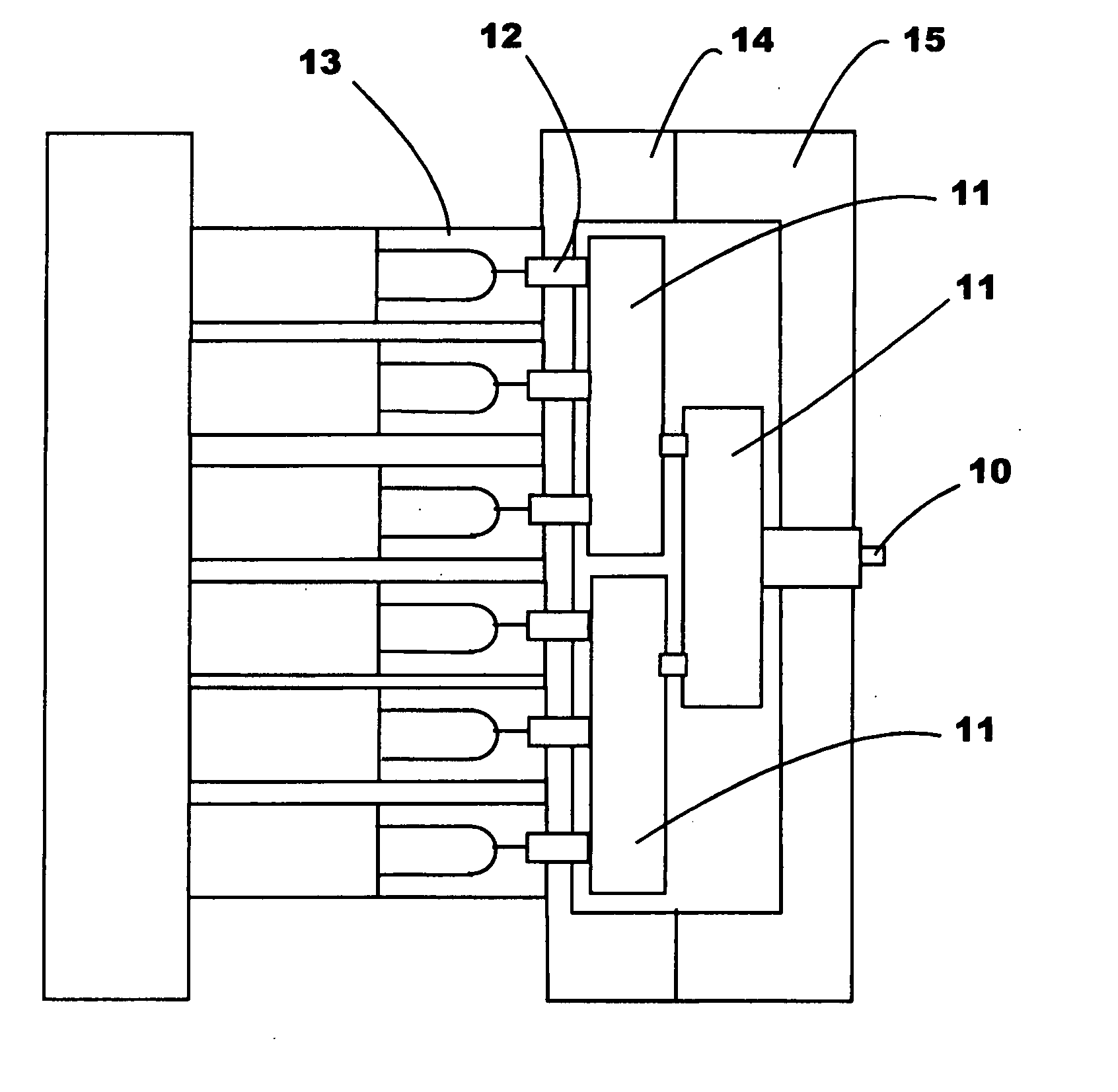
A multiturn angle measuring device (1) with a first dimensional standard (9) that is non-rotatably connected to an input shaft (2) and which is sampled by a first scanning unit (10) to determine the angular position of the input shaft. Additional dimensional standards (11, 12, 13) measure the number of turns of the input shaft (2) and are arranged in parallel to each other. The rotational speed of each additional dimensional standard (11, 12, 13) is reduced by means of a reduction gearing from the preceding dimensional standard (9, 11, 12). A scanning device (21, 22, 23) for the sampling of each dimensional standard (11, 12, 13) is arranged on a circuit board (6). To provide a multiturn shaft encoder able to measure a high number of turns, even at high rotational speeds and / or large diameter input shafts, with compact construction and comparatively few multiturn stages, the input drive gear (40) fixed to the input shaft (2) and the first driven transmission gear (41) have axes of rotation (D40, D41) that are not parallel to each other. The flanks of the teeth (Z40, Z41) of the input drive gear (40) and of the wheel (411) of the first driven transmission gear (41) are not parallel to the axes of rotation (D40, D41) of the respective gears (40, 41), and the number of teeth (Z40) of the input gear (40) is smaller than the number of teeth (Z41) of the wheel (411) of the first transmission gear (41). The following transmission gears are again arranged parallel to the input shaft, and the drive pinion (412) of the first transmission gear (41) and the driven wheel of the second transmission gear (31) have helical gears.
Owner:SICK STEGMANN
Angle sensor
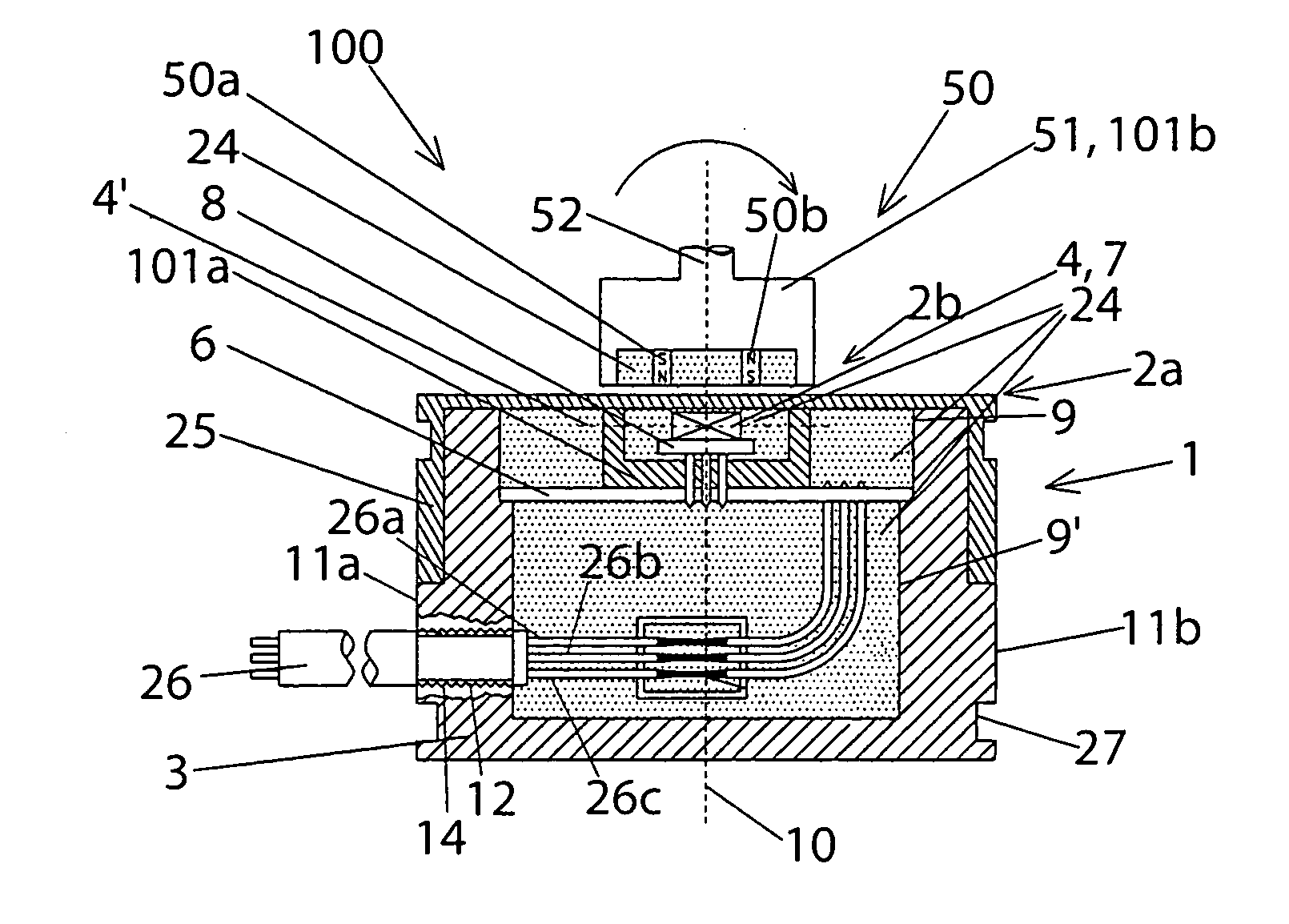
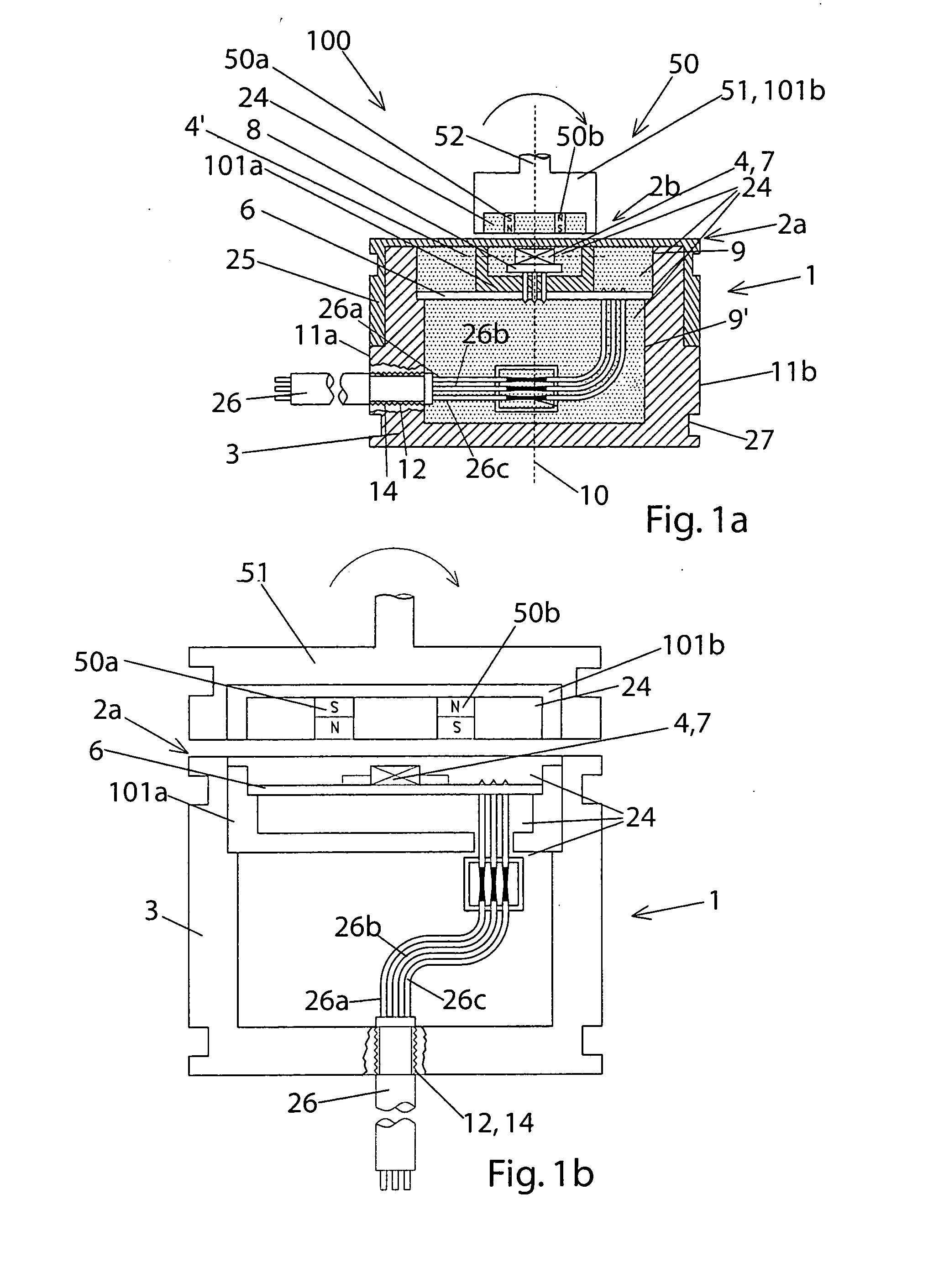
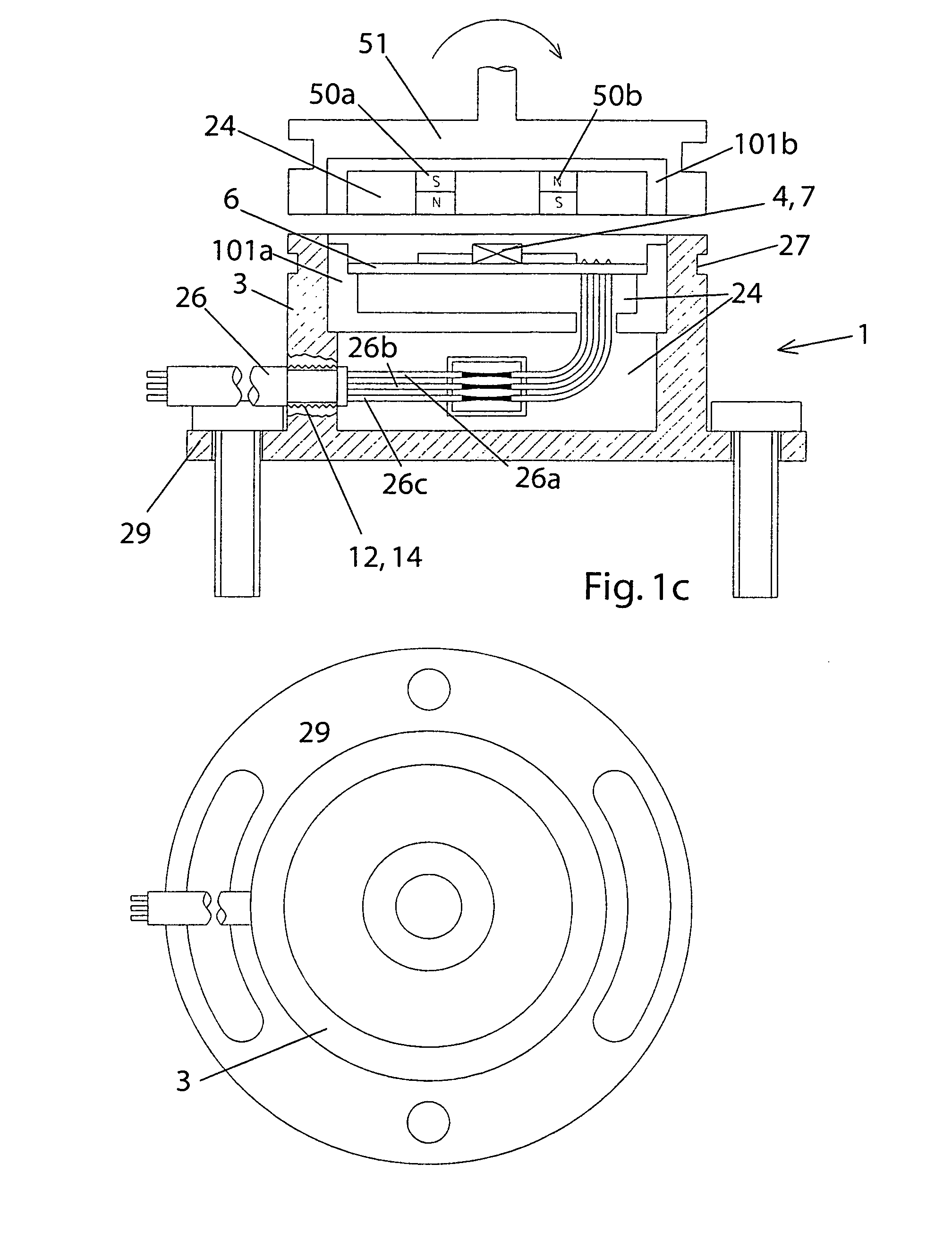
ActiveUS20080164866A1Easy to shapeSmall sizeMeasurement apparatus componentsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGeometric designEngineering
In order to provide an angle sensor in an embodiment, which is axially short in particular and on the other hand radially wider, with a functionality that is as good as possible, on the one hand certain shielding measures against interfering magnetic fields are proposed, and on the other hand a certain geometric design is proposed, in particular comprising an intermediary magnet.
Owner:ASM AUTOMATION SENSORIK MESSTECHN GMBH
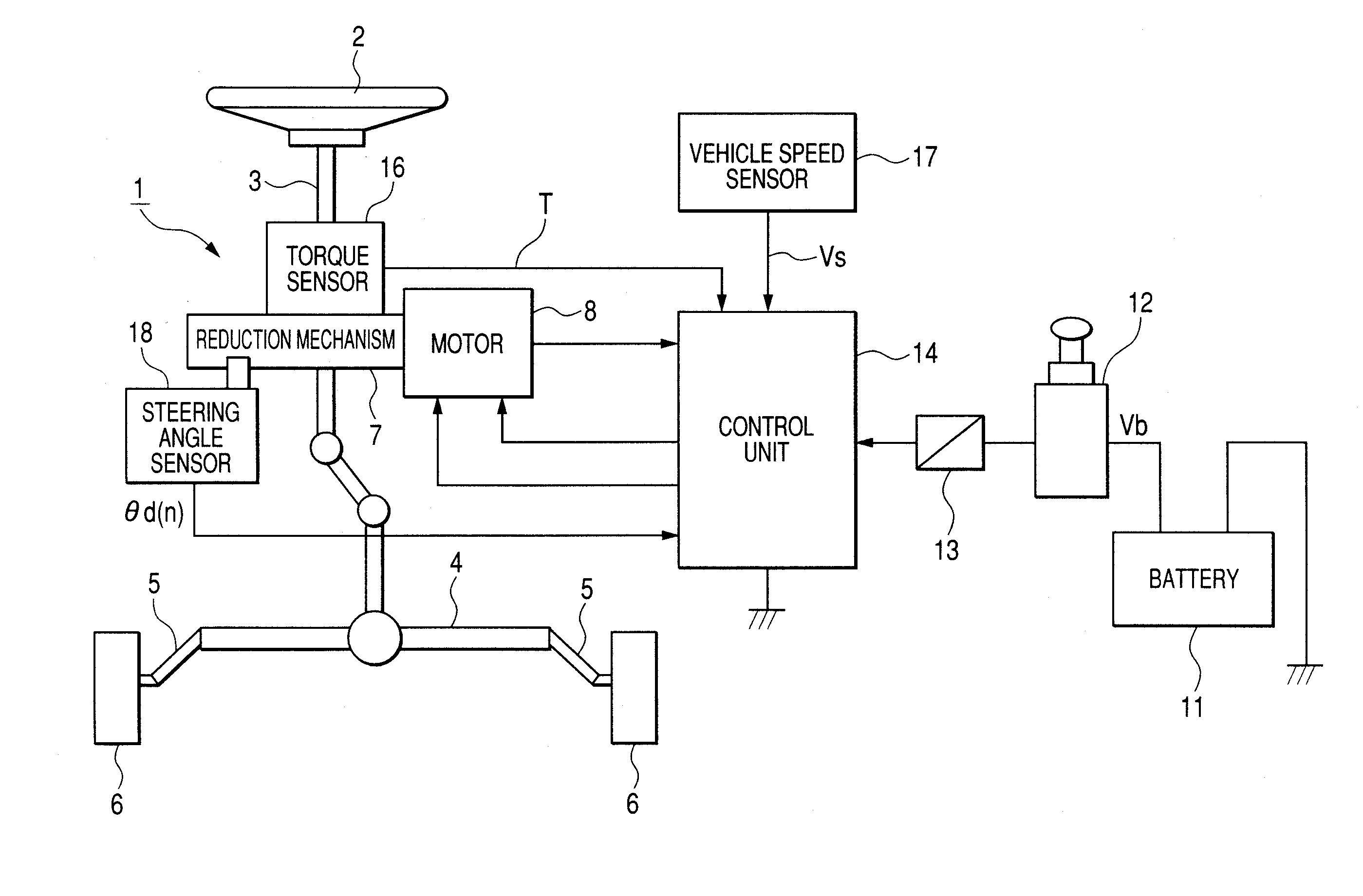
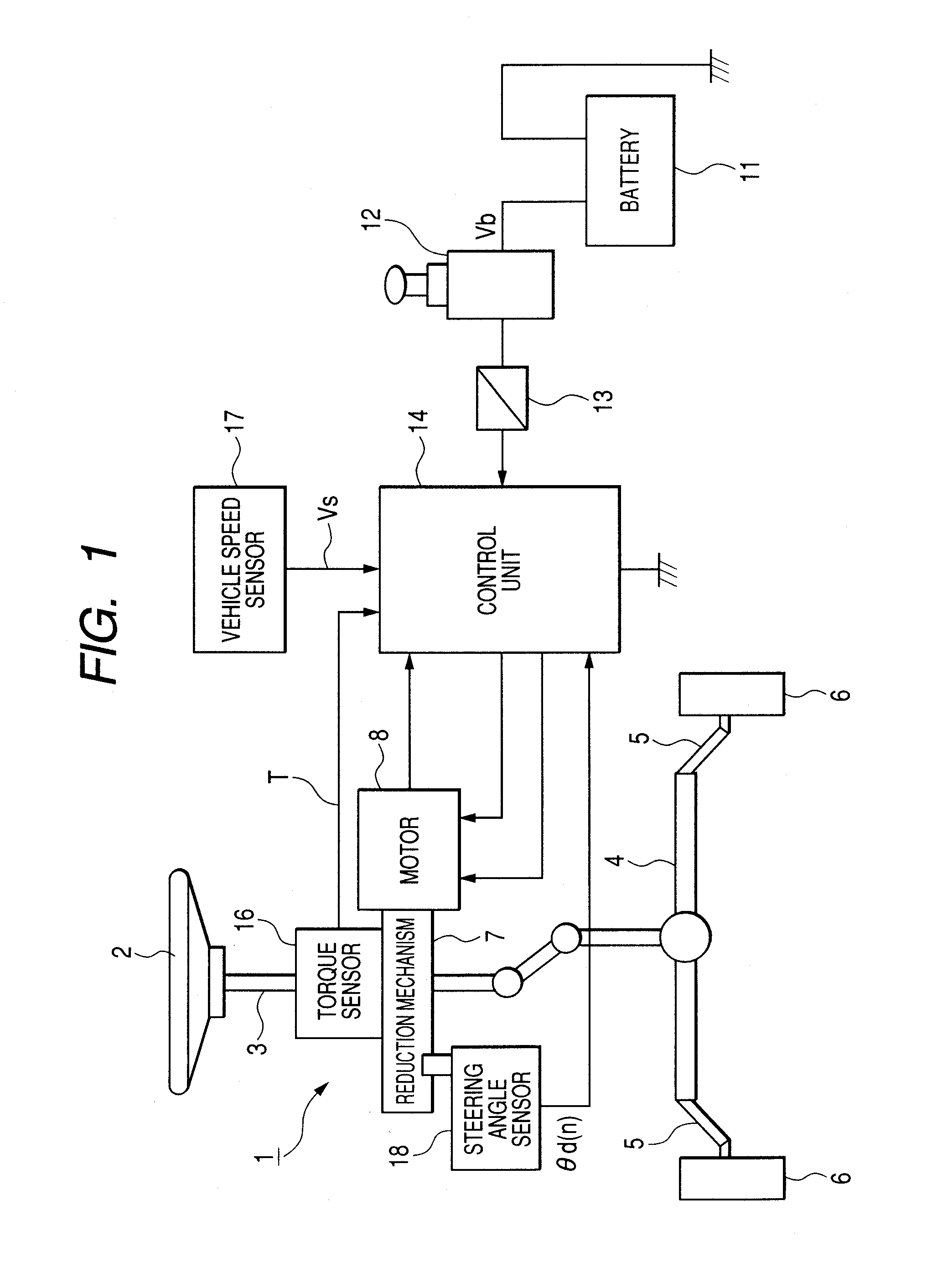
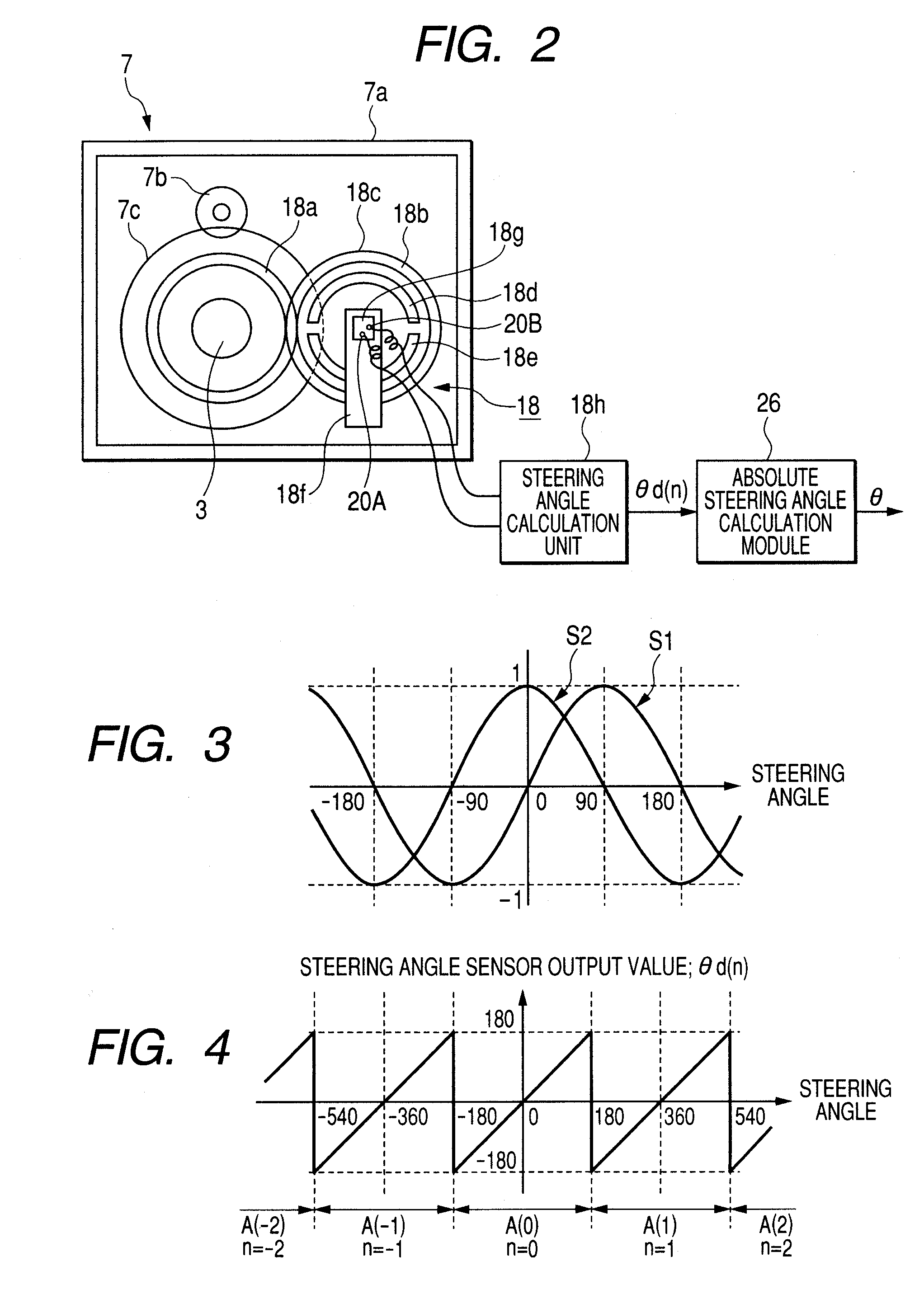
Absolute steering angle detecting device
InactiveUS20080119986A1Quick checkMaintaining resolutionSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleEngineering
There is provided an absolute steering angle detecting device for detecting an absolute steering angle of a steering control device of a vehicle, including a sensor wheel 18c adapted to rotate by linking with rotation of the steering control device, a magnetism detector 18g having a bridge circuit made up of a GMR element, magnetized portions 18d, 18e provided to surround the magnetism detector 18g, and a steering angle operation module 26 which calculates an absolute steering angle based a detection signal outputted from the magnetism detector 18g, wherein either the magnetism detector 18g or the magnetized portions 18d, 18e is mounted on the sensor wheel 18c, while the other is mounted on a fixed portion, and the magnetism detector 18g outputs a detection signal which completes a single period when the steering control device completes a single rotation.
Owner:NSK LTD
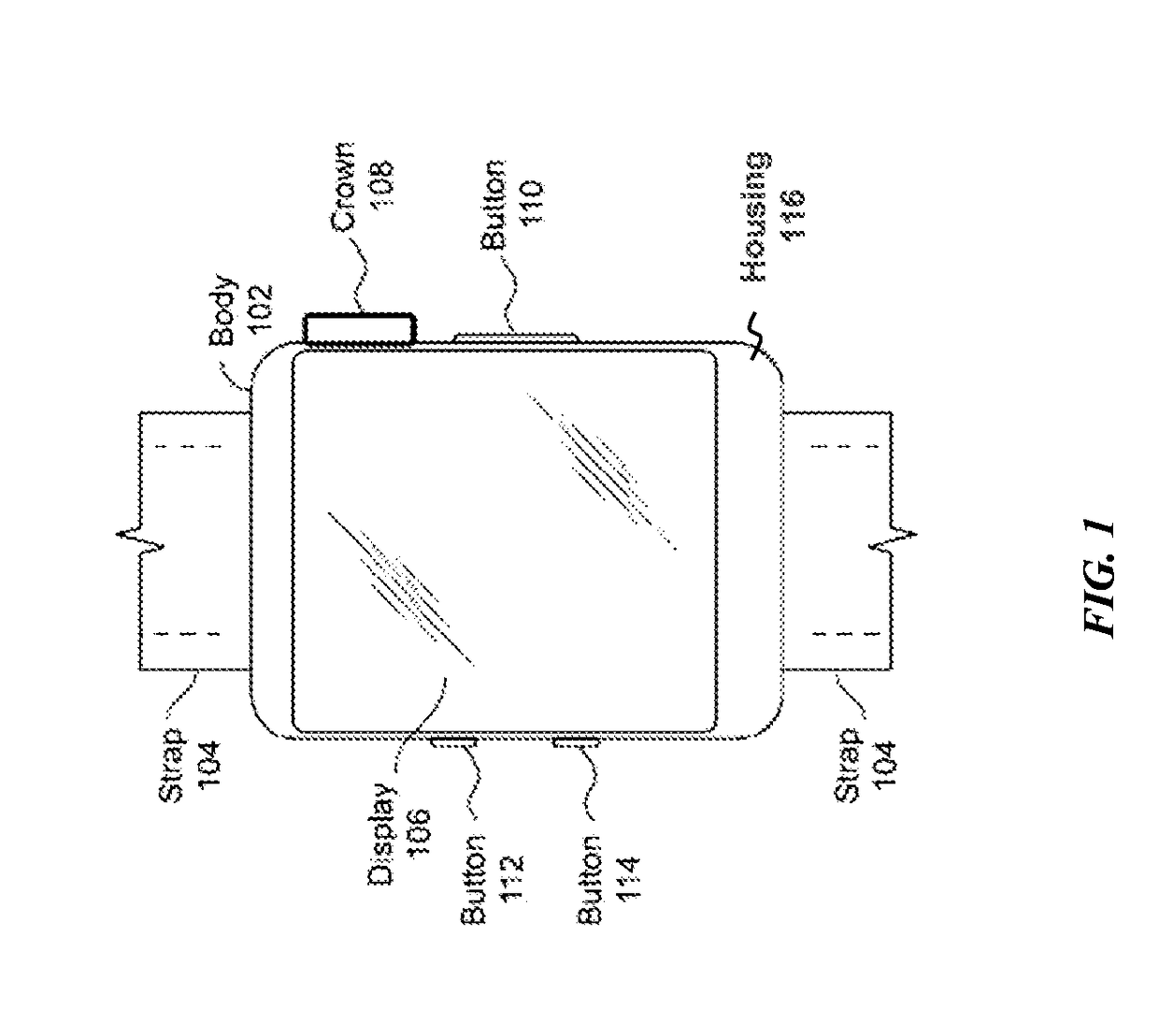
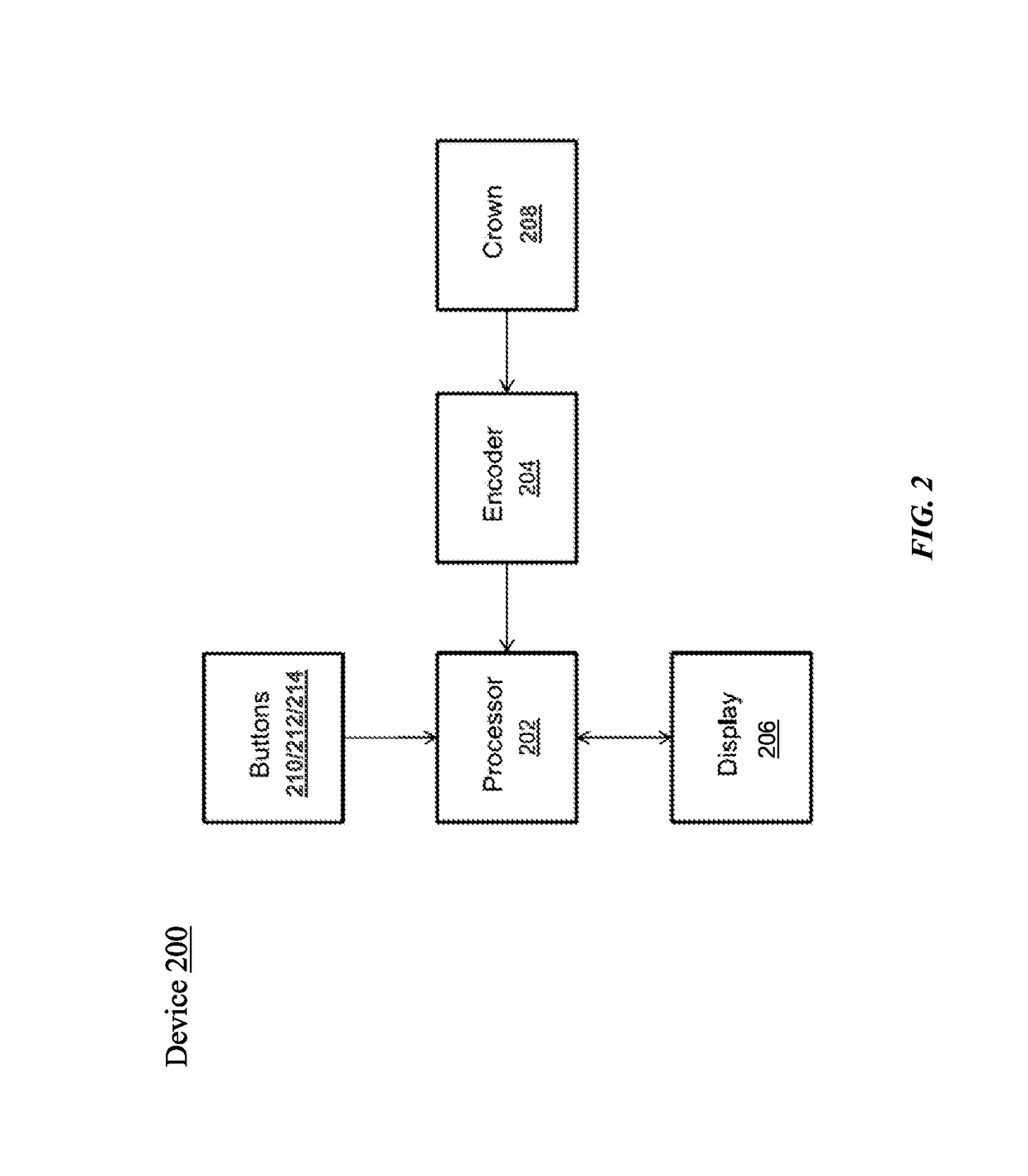
Crown with three-dimensional input
ActiveUS20170089735A1High speedElectric windingConverting sensor output opticallyUser inputForce sensor
An apparatus is disclosed. In some examples, the apparatus comprises a mechanical input mechanism comprising a rotatable shaft. In some examples, the apparatus comprises an optical sensor configured to detect a rotation of the shaft and detect a movement of the shaft toward or away from the optical sensor. In some examples, the apparatus comprises an optical sensor configured to detect light incident on the optical sensor, the light having a position and an orientation, the orientation of the light based on at least a position of the rotatable shaft, detect a rotation of the shaft, and detect a movement of the shaft based on at least a change in the orientation of the light. In some examples, the apparatus comprises a housing. In some examples, a mechanical input mechanism comprising a rotatable shaft is coupled to the housing and configured to contact a force sensor coupled to the housing in response to a user input. In some examples, the force sensor is configured to detect a position of the shaft and detect an amount of force between the shaft and the force sensor that is based on the user input.
Owner:APPLE INC
Device for determining an absolute angle of rotation
ActiveUS20060059698A1Easy to measureCost-effectiveAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansRotational axisMeasurement device
A device for determining an absolute angle of rotation of a rotational axis has a first measuring device for measuring an angle of rotation in a limited first measuring range and a second measuring device for determining an absolute angle range. The second measuring device transforms a rotation of the rotational axis into a linear shift.
Owner:TRW AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY SYST
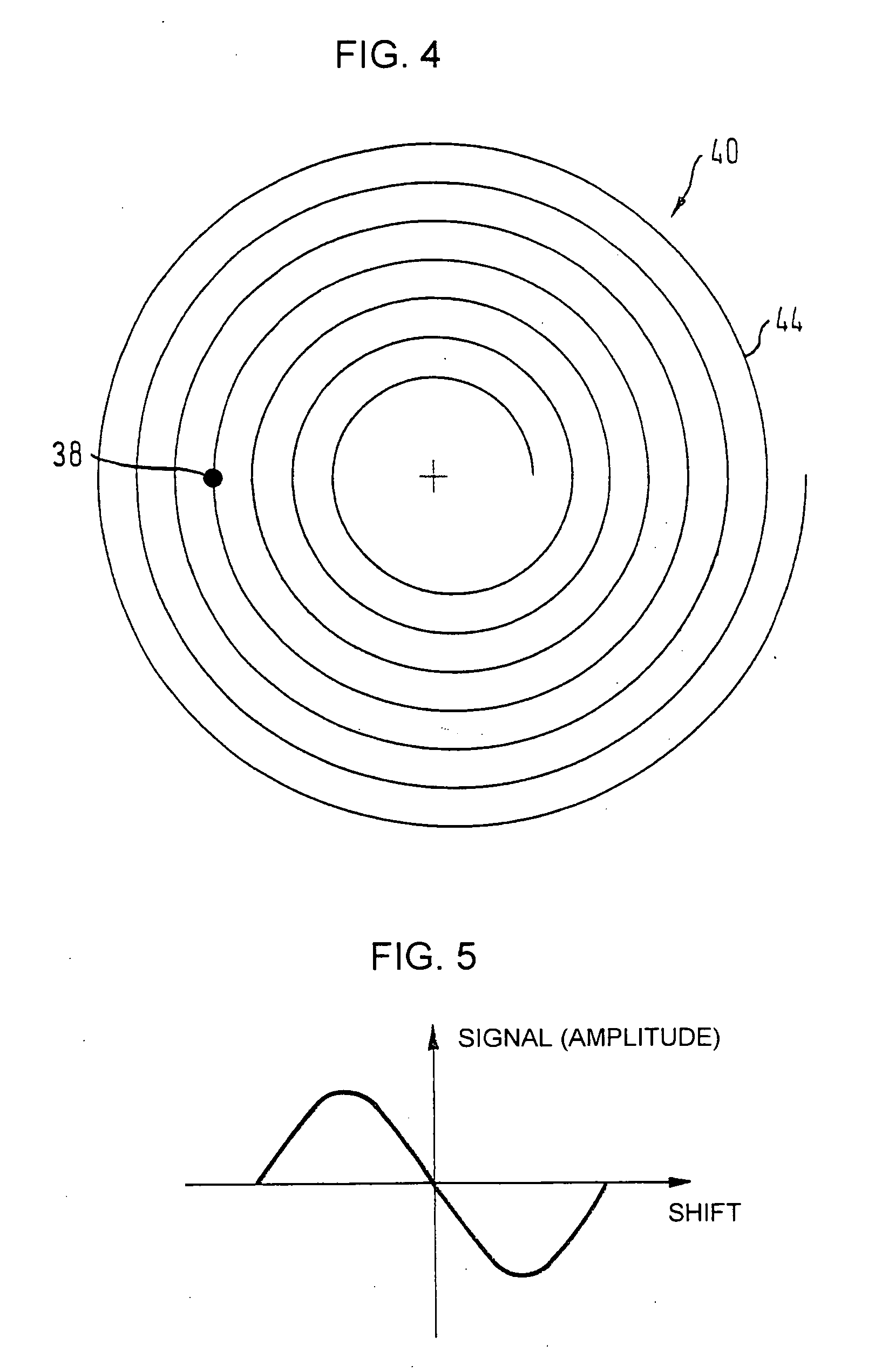
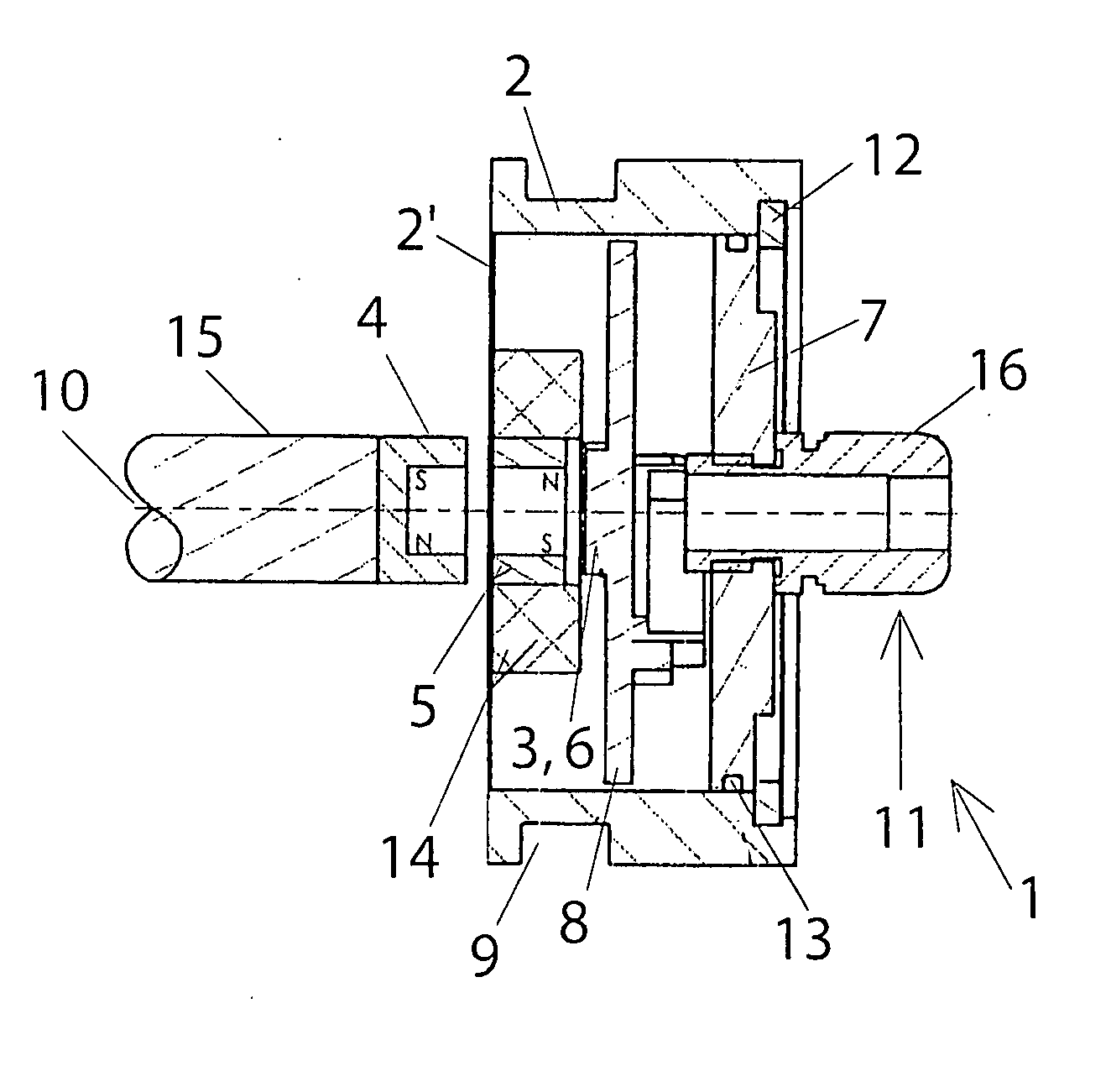
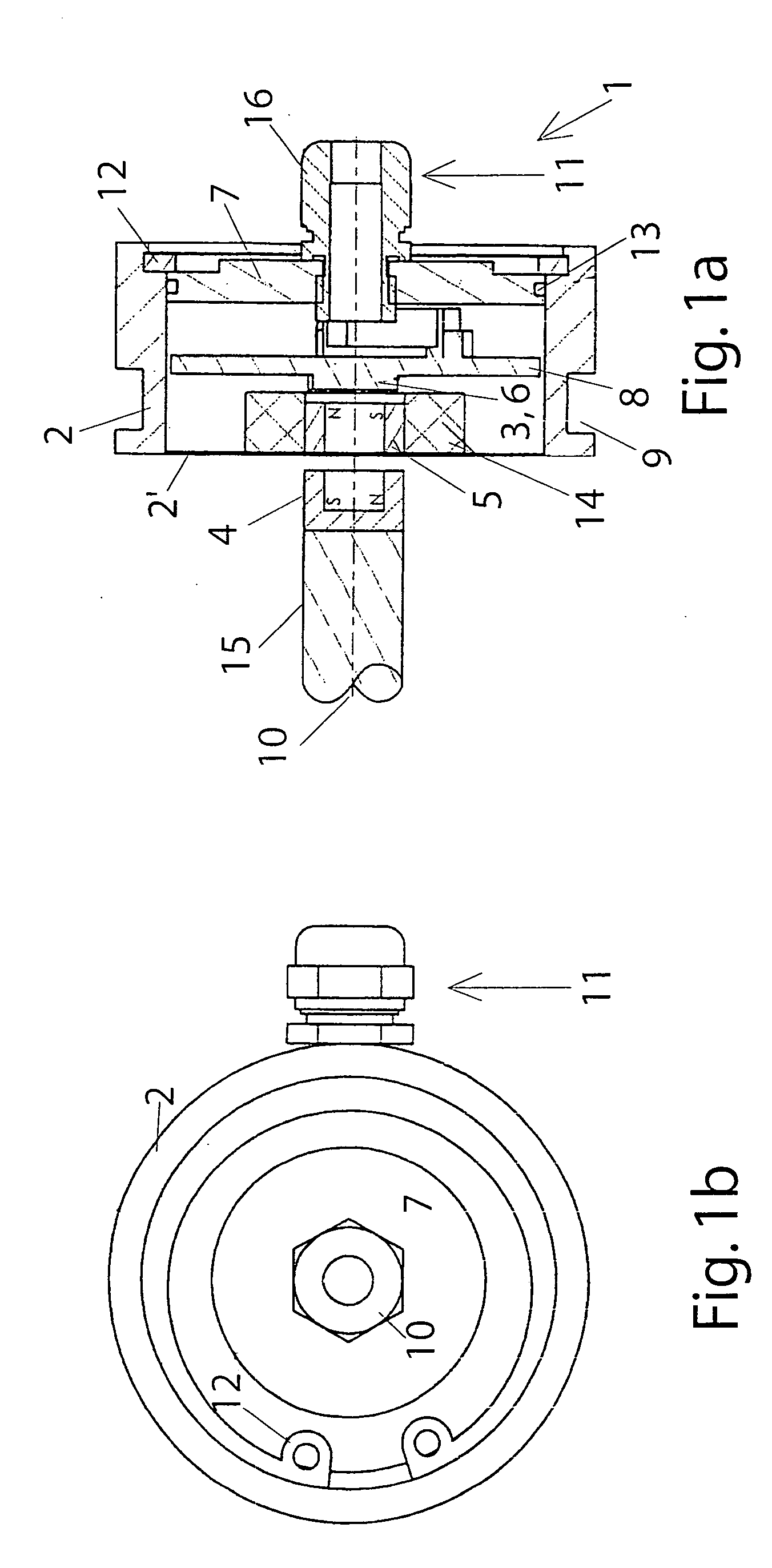
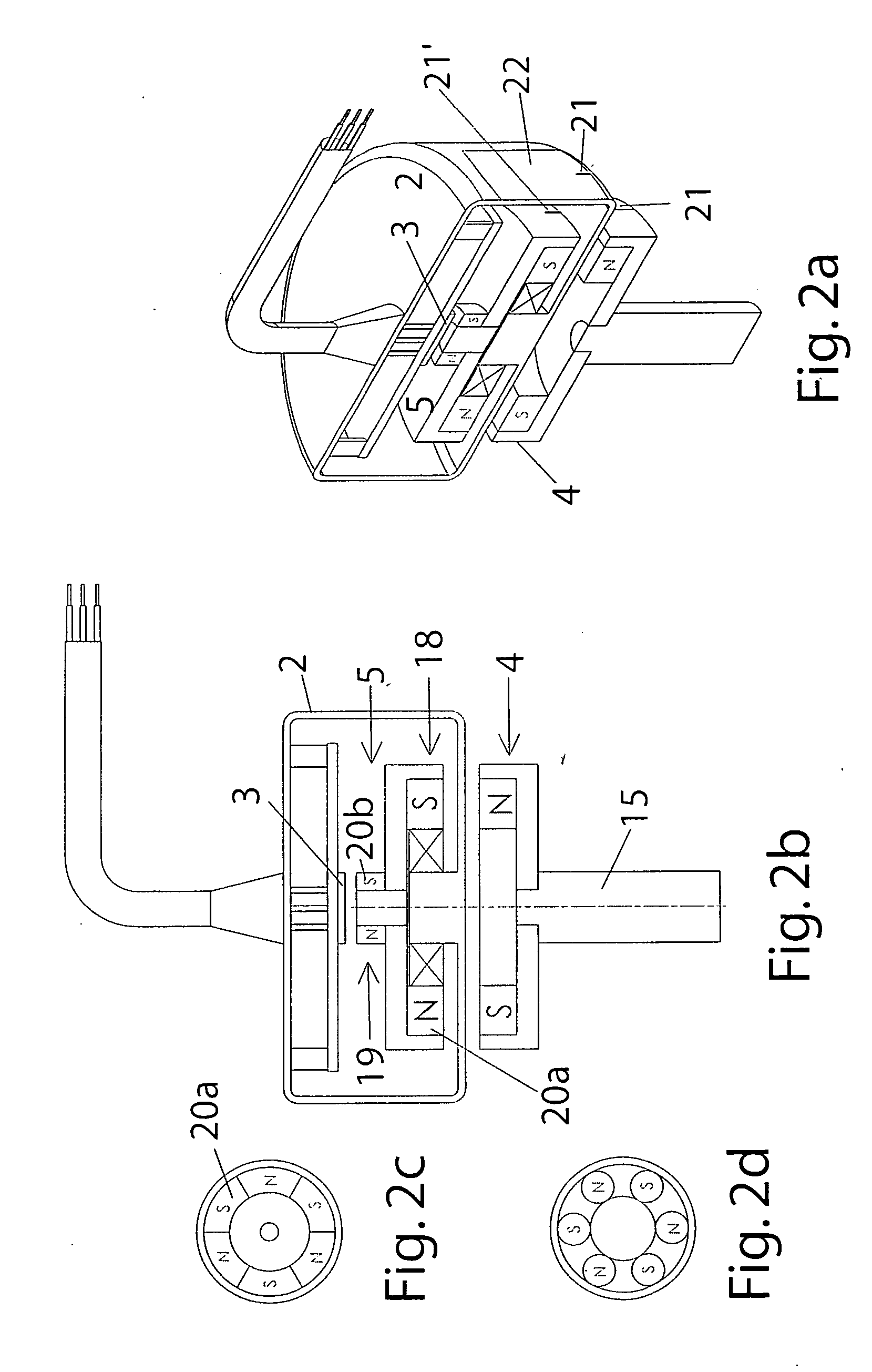
Rotation angle sensor
InactiveUS20070151322A1High-quality signalEnhanced signalWave based measurement systemsDigital computer detailsElectricityEngineering
A rotation angle sensor is provided for determining mechanical angular positions and transposing them into signals transferable through electricity. The sensor includes a housing (2), a rotation indicator (4) located outside of the sensor housing (2a) so that it can rotate and coupled with the sensor element (3) so it operates in a non-contracting manner through the wall of the housing (2). A sensor element (3) is located in the interior of the housing (2). An intermediary element (5) is rotationally supported in the interior of the housing (2) between the sensor element (3) and the rotation indicator (4) and coupled to the rotation indicator (4) in a rotationally fixed, but non-contacting manner.
Owner:ASM AUTOMATION SENSORIK MESSTECHN GMBH
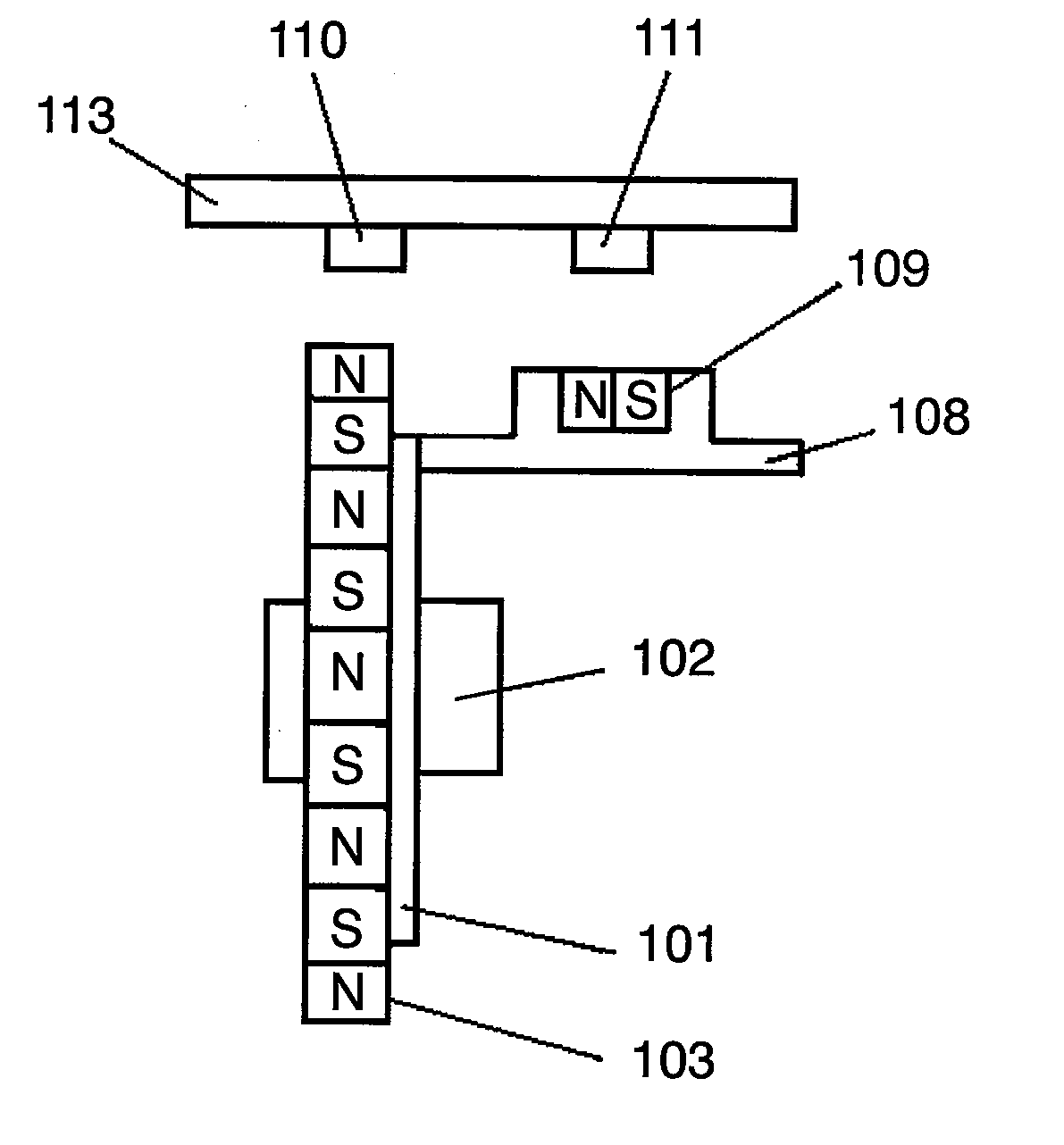
Stroke sensor and rotation angle sensor
ActiveUS20100188074A1Accurate output valueHigh magnetic flux densityElectrical controlSolid-state devicesClassical mechanicsMagnetic flux
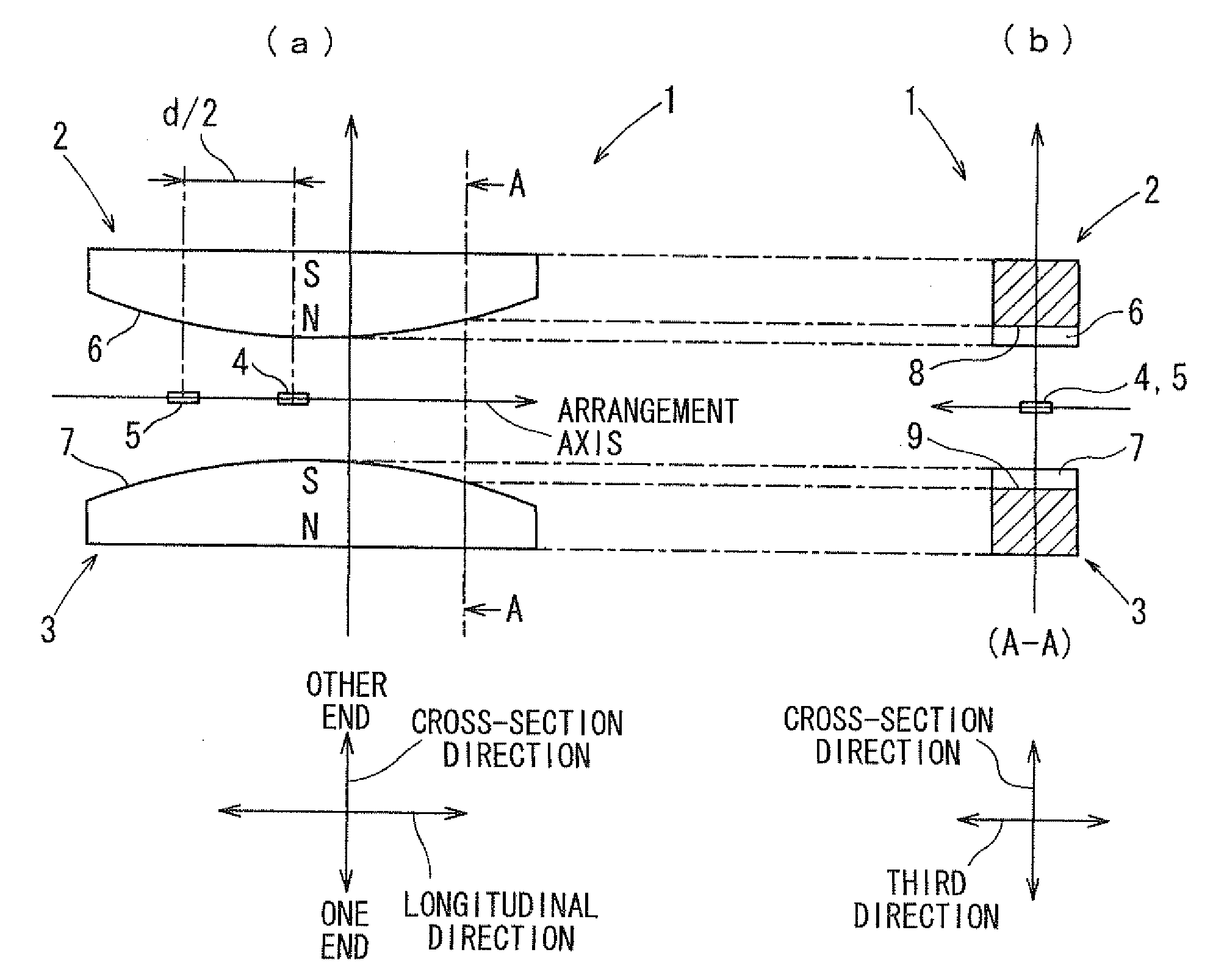
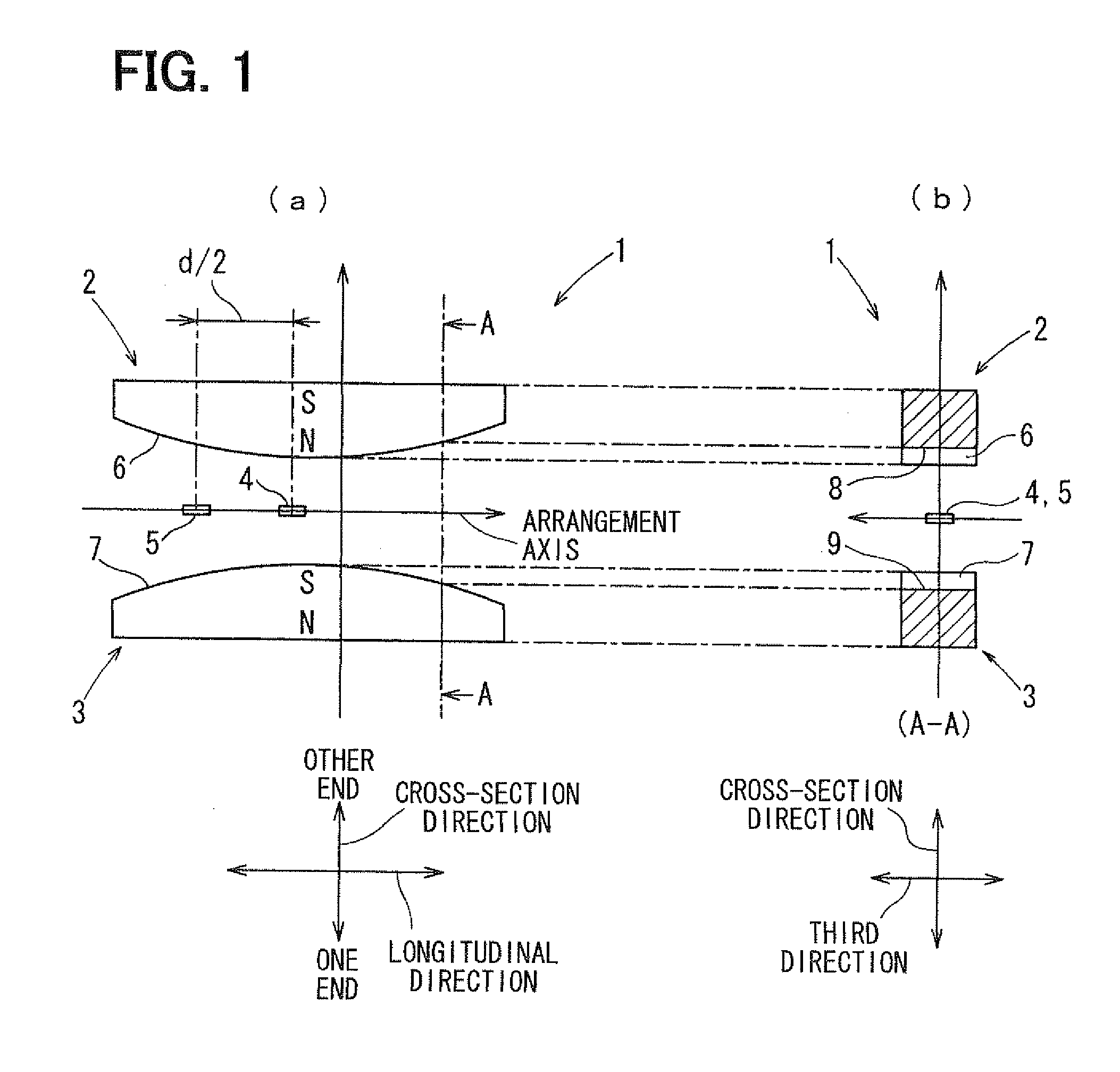
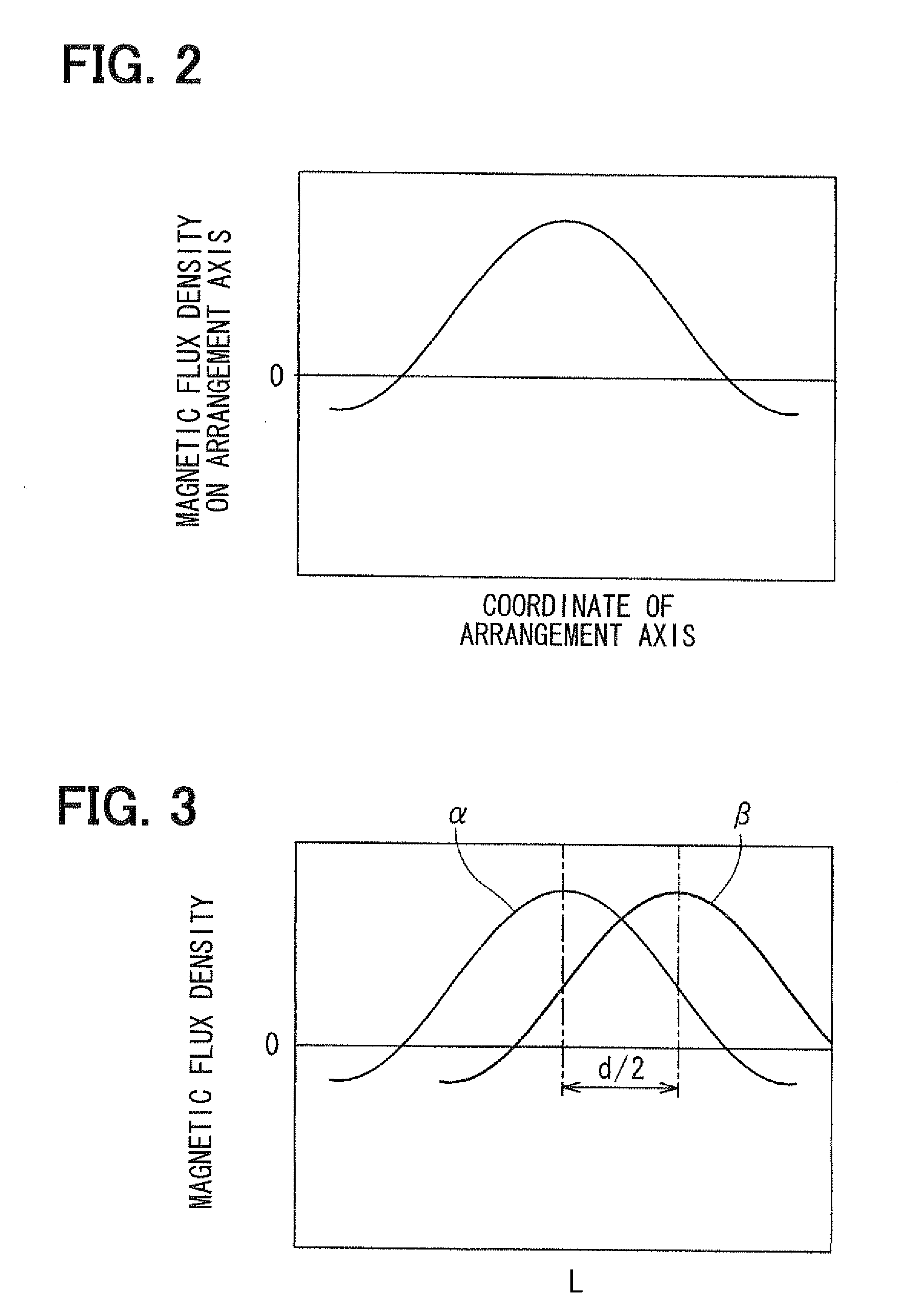
A stroke sensor has two magnets, which are magnetized in a cross-section direction and are displaced in a longitudinal direction, and two magnetism sensitive sections arranged parallel to the longitudinal direction. The magnets have circular-arc-shaped swelling end edges respectively and are magnetized such that the swelling end edges have opposite polarities. Thus, a distribution of a magnetic flux density on an arrangement axis substantially coincides with a sine curve. The magnetic flux having such the distribution is displaced in the longitudinal direction together with the magnets. The magnetism sensitive sections are arranged on the arrangement axis to be distant from each other by a distance of one fourth of a cycle of the sine curve. Thus, the stroke sensor that is not affected by temperature and that has high sensing accuracy can be provided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Encoder assembly for an appliance knob
A knob assembly is provided that includes a knob having a rotatable shaft, a rotatable first circuit board rigidly attached to the rotatable shaft, and a fixed second circuit board positioned near the first circuit board. The first circuit board includes an encoding portion configured to provide positioning data of the knob, and an eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motor mounted to the rotatable, first circuit board with a shaft of the ERM motor perpendicular to the rotatable shaft of the knob. The ERM motor is configured to produce and transfer vibration to the rotatable shaft of the knob. The second circuit board includes a sensor configured to determine a position of the first circuit board and thereby the knob at least in part from the positioning data provided by the encoding portion.
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
Rotation detecting device and automobile with the same
ActiveUS20050022617A1Large gear reduction ratioReduce the number of partsMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing electrical meansControl theory
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Detecting apparatus for angle of rotation
InactiveCN1504720ADetect rotation angleAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansAngle of rotationControl unit
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rotation angle sensor and scissors gear suitable therefor
A driving gear, which is a scissors gear, fixed to a rotating body, engages with a driven gear, and the driven gear engages with a fixed screw receiver. A first gear and a second gear of the driving gear elastically bias the tooth of the driven gear by a coil spring in the direction of an inner side of a diameter; consequently the driven gear 5 is forced on the screw receiver. Gears formed in the tooth tips of the driven gear engage with a partial spiral screw of the screw receiver.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
Rotation angle detection device and rotation angle correction method
InactiveUS20090021246A1Improve detection accuracyLess capacityMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesAbsolute rotationLow speed
A device for detecting an absolute rotation angle of multiple rotation with a high accuracy and high resolution by using a target connected to the rotation axis and having an outer circumferential surface to which magnetic poles of alternate polarities are magnetized. The device includes: a first rotor holding a target connected to an input axis and having an outer circumferential surface to which magnetic poles of alternate polarities are magnetized at an identical interval and having a multi-rotatable gear; a second rotor connected to the gear of the first rotor, rotated at a low speed by the first rotor, and having a magnet at the center portion; a first detection unit and a second detection unit for detecting the rotation angles of them. With a simple configuration, it is possible to detect an absolution rotation angle with a high accuracy and a high resolution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rotating angle sensor
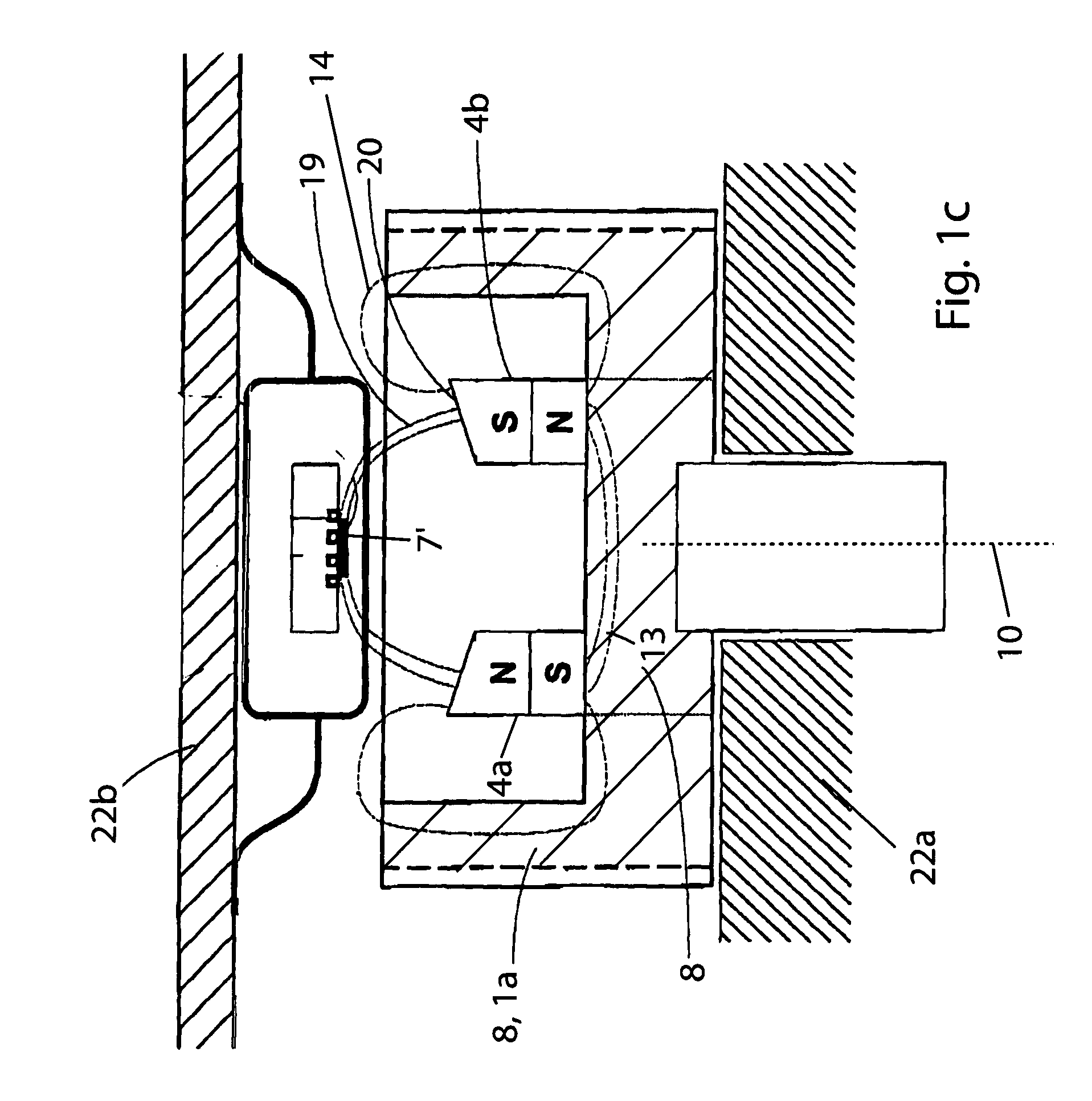
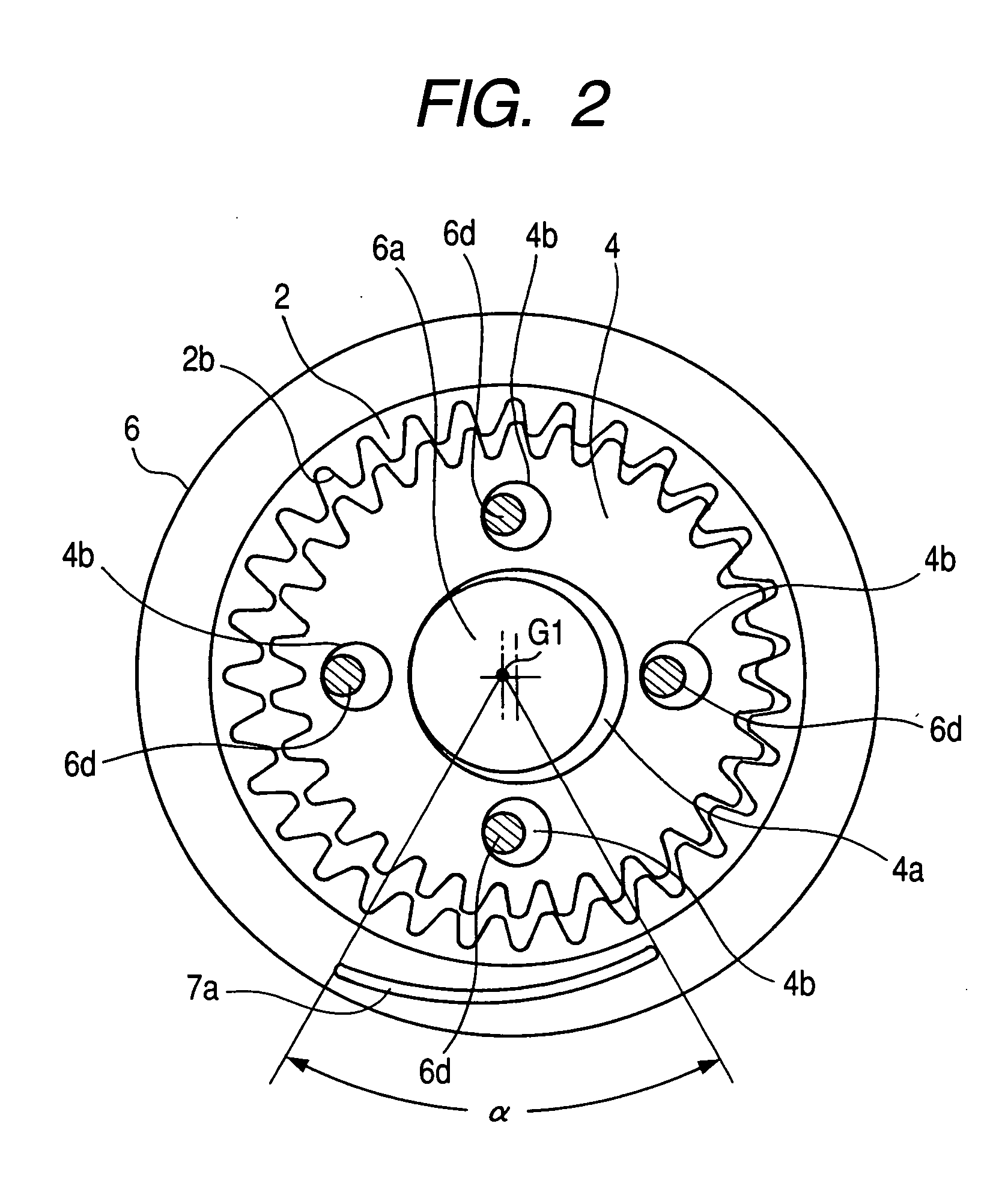
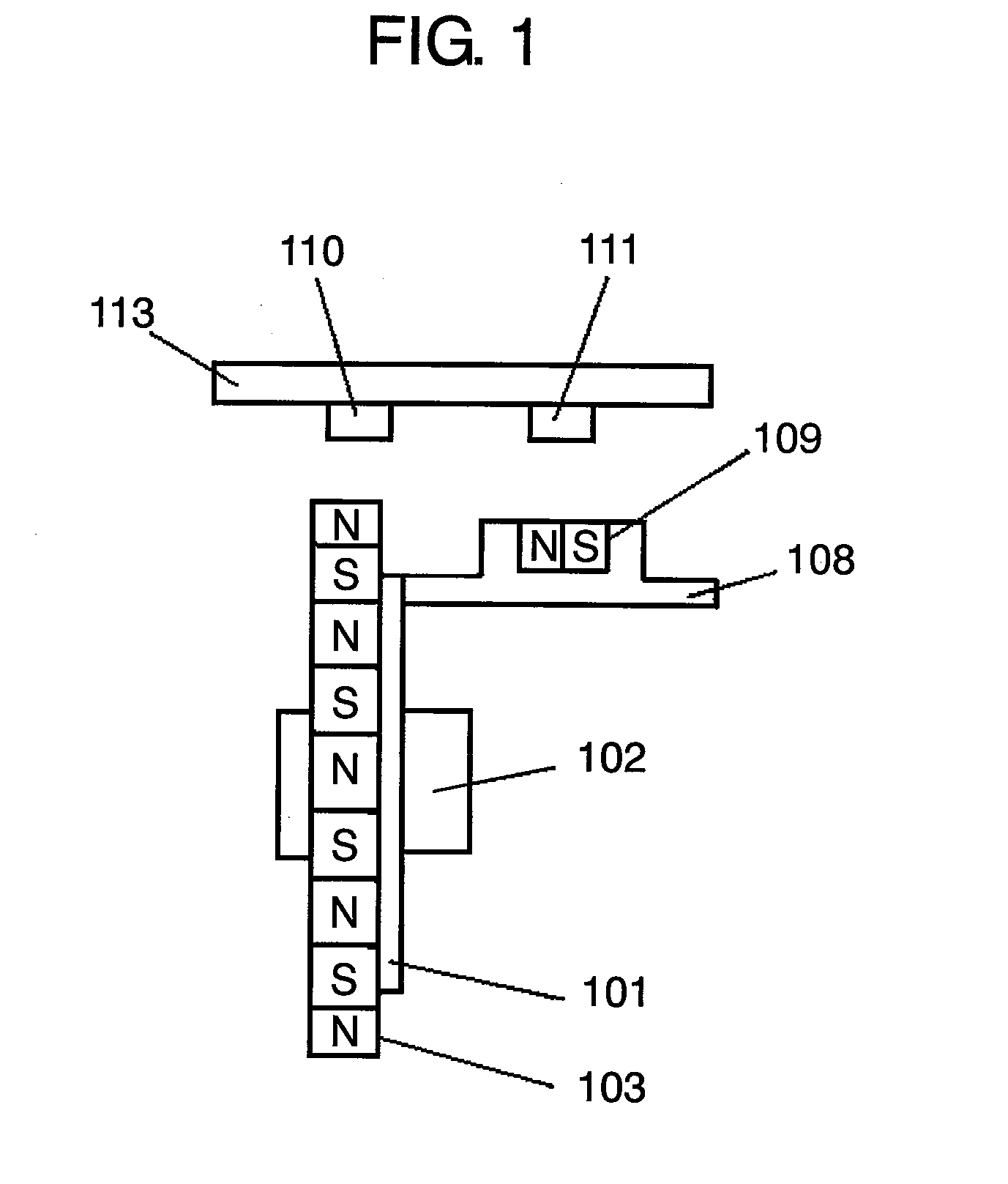
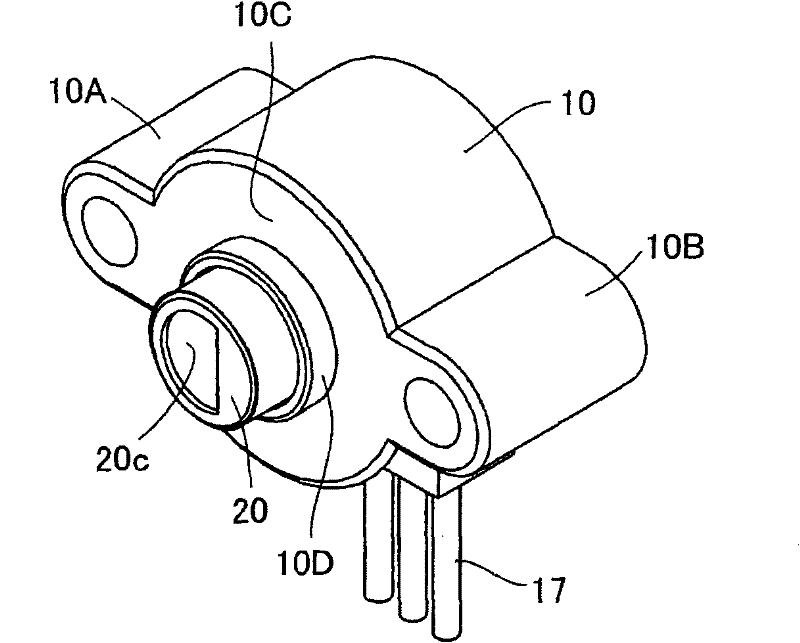
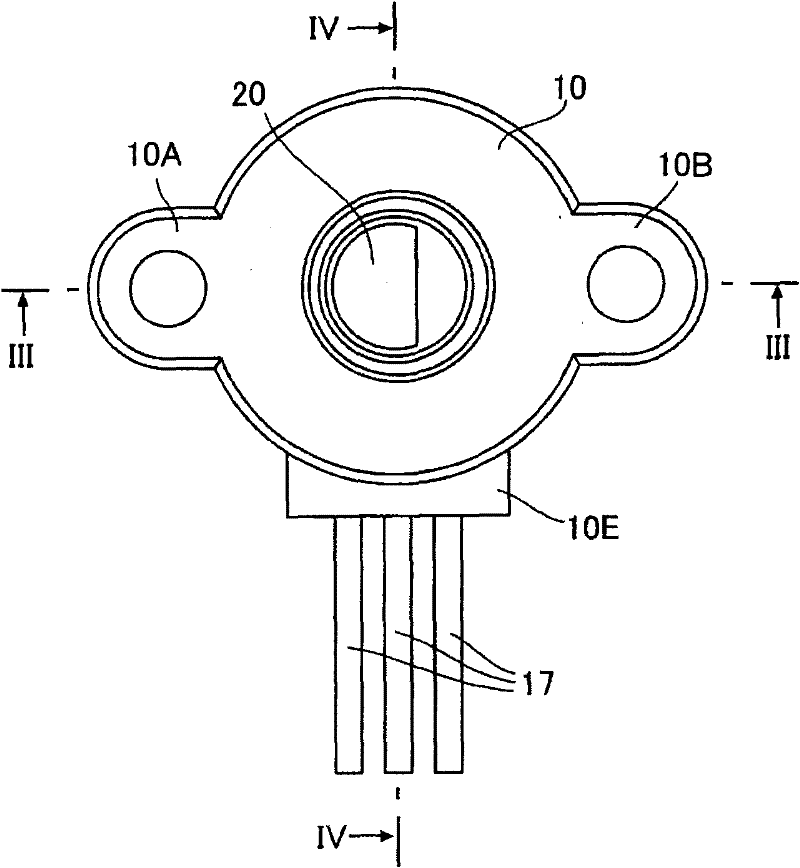
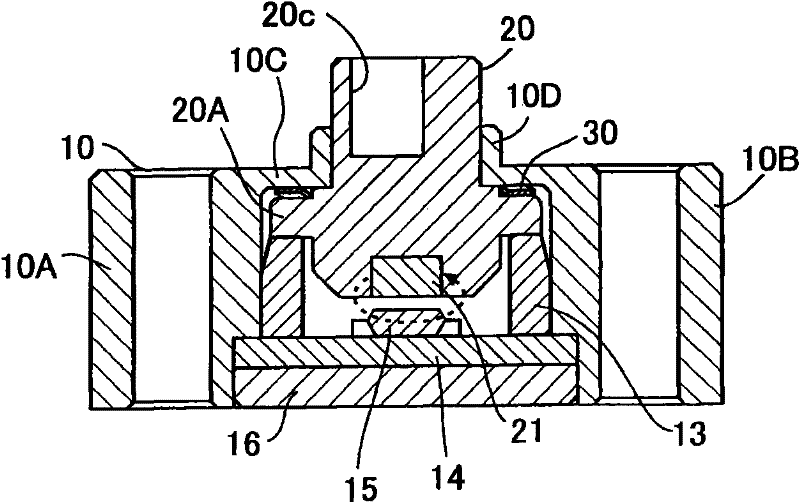
ActiveCN101750100AHigh measurement accuracyThe measurement deviation is smallUsing electrical meansConverting sensor output mechanicallyEngineeringFlange
The invention relates to a rotating angle sensor. A rotor (20) with a flange (20A) can be rotatably configured in a housing (10), the front end of the rotor is projected from an opening formed on the front wall (10C) of the housing. In the housing (10), the front of an annular bearing (13) supports the rear end of the flange (20A) by a resilient waveform washer (30), and the rear end of the annular bearing is fixed on a distribution substrate (14). A magnet (21) is fixed at the rear end of the rotor, and a magnetic sensor IC (15) is mounted on the distribution substrate (14) at an interval from the magnet and opposite to the magnet.
Owner:TOKYO COSMOS ELECTRIC CO LTD
Rotation angle detecting device
ActiveUS20060000969A1Smooth rotationEasy to assembleOptical measurementsMeasurement apparatus componentsEngineeringSpeed reduction
A rotation angle detecting device includes a housing which is constituted by a combination of a case and a cover; a resistance board; a code wheel; a slider rotating plate; a slider; a circuit board; signal detecting elements; and a gear which transmits the rotation of the code wheel at a predetermined speed reduction ratio to the slider rotating plate, which are enclosed in the housing. Circular pin insertion holes are formed in positions where the code wheel, the case, and the cover face each other, respectively. A pin insertion hole having a circular-arc shape is formed in the slider rotating plate.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Rotation angle detector
InactiveUS6909282B2Simple structurePrecise angle of rotationSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesControl unitPhysics
A rotation angle detector includes a rotor, first and second detecting elements which rotate according to a rotation of the rotor, first and second detecting units for detecting rotations of the first and second detecting elements, respectively, and a control unit for detecting a rotation angle of the rotor based on a first signal when a difference between the first and second signals output from the first and second detecting units ranges within a predetermined range. The rotation angle detector has a simple structure and detects the rotation angle of the rotor accurately
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Linear position sensor using a strain gage
A linear position sensor for sensing the position of an attached object. The linear position sensor uses a strain gage to detect the position of the object. The sensor includes a housing and a ramp shaped actuator located in the housing. The actuator is attachable to the object. A strain gage is positioned in contact with the actuator. The actuator applies a strain to the strain gage as the actuator is moved. The strain gage generates an electrical signal that is proportional to the position of the object.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Method for mfg. microstructure resonance beam pressure sensor using SiNx as beam
InactiveCN1401980ARealize integrationAchieve integrationFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsConverting sensor output mechanicallyResonanceNitrogen
A process for preparing the pressure sensor using SiNx as micro resonant beam includes depositing SiN film on polished silicon substrate, depositing sacrificial layer, etching, depositing SiNx film, preparing vibration exciting and picking up resistors, preparing metal leading wires, etching beam slot, preparing resonant beam, etching low-stress nitrogen silicide film on the back of Si substrate to form corrosion windows, corrosion, preparing pressure-sensitive film, corrosiding out sacrificial layer, releasing SiNx beam, welding leading wire and vacuum packaging.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com