Methods for assessing risk for cardiac dysrythmia in a human subject
a human subject and risk assessment technology, applied in the field of detecting the risk of cardiac disease, can solve the problem that patients may have a heightened risk of cardiac dysrhythmia
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
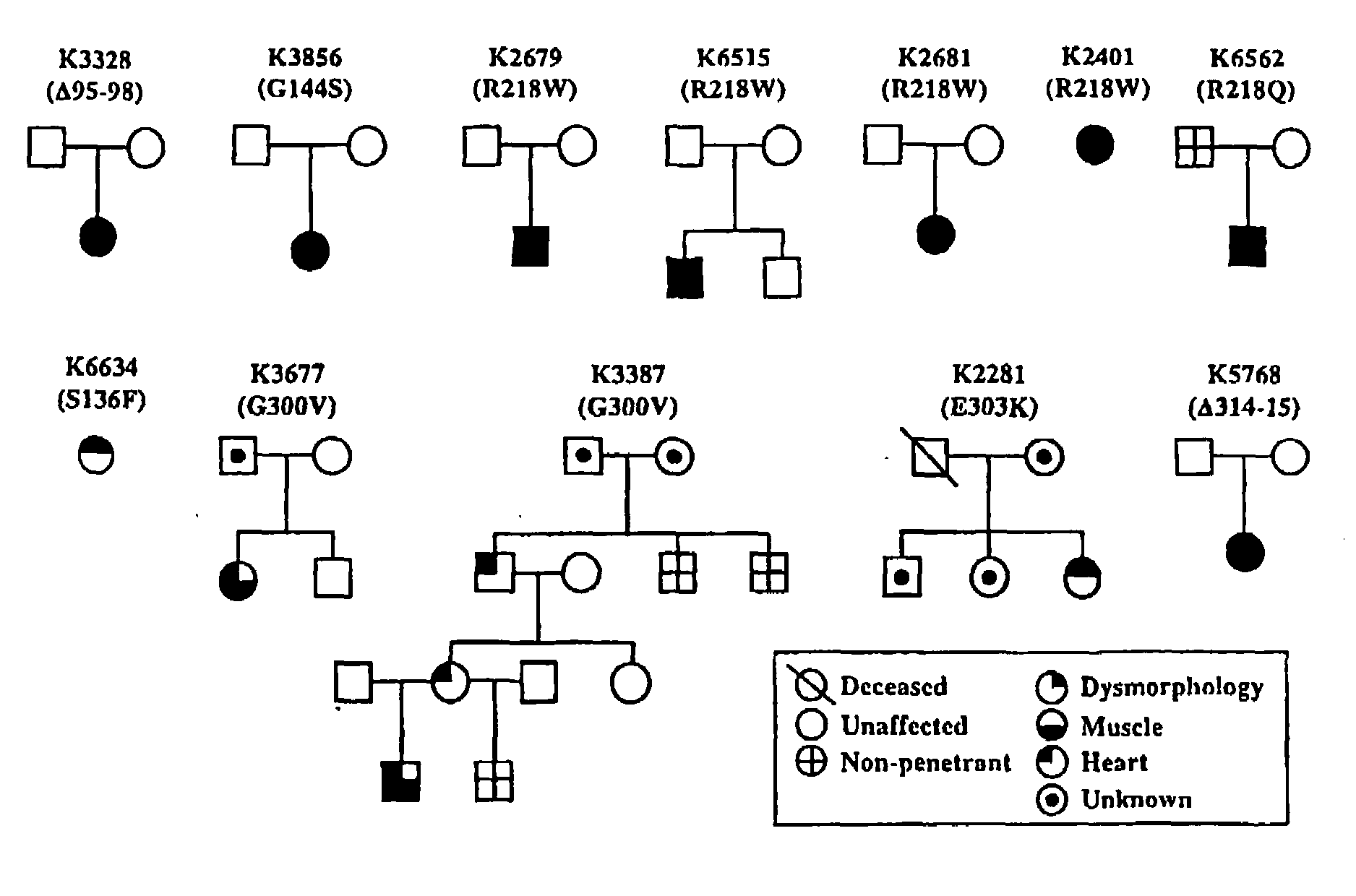
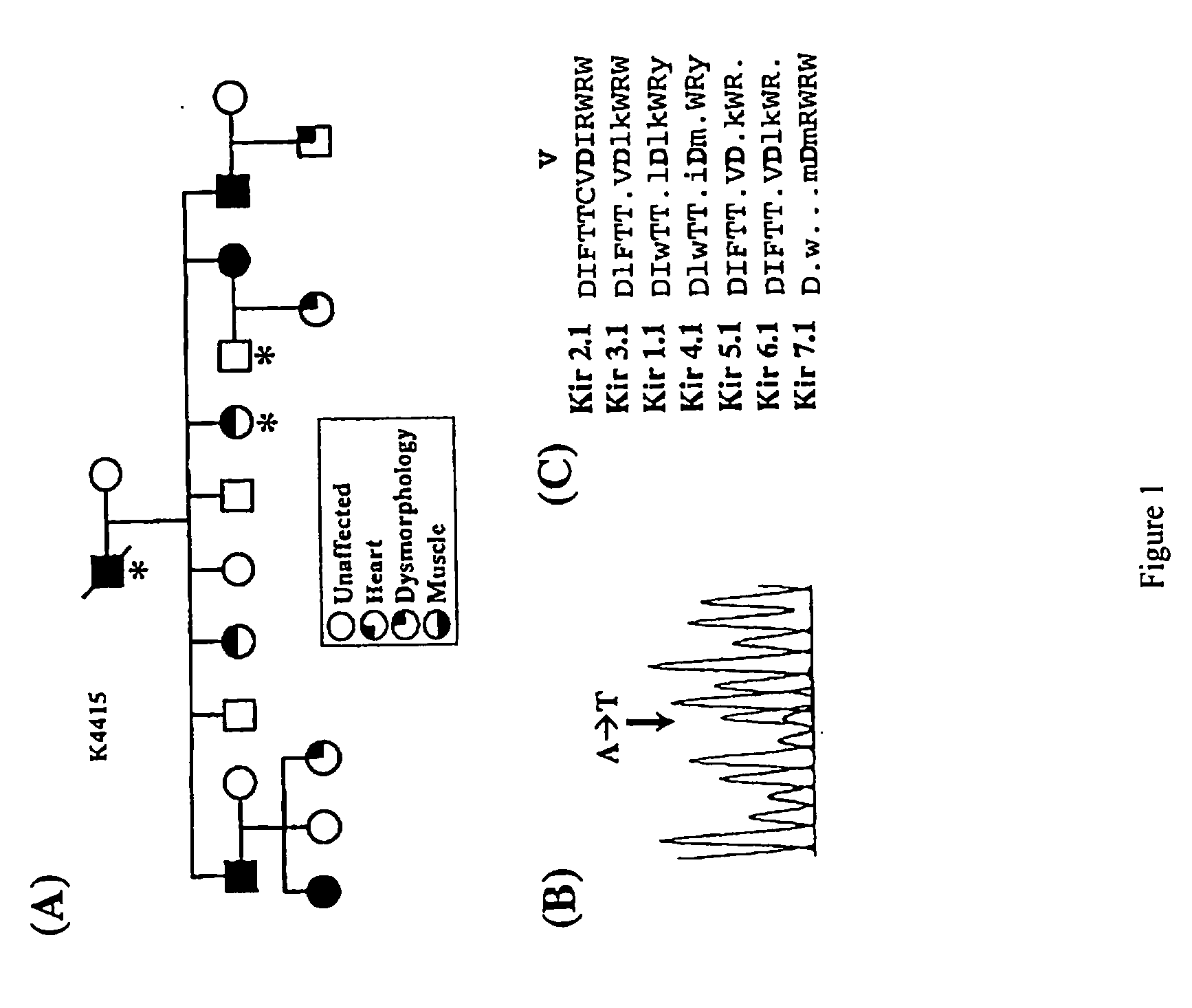
[0035]As discussed previously, Andersen's Syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by periodic paralysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and dysmorphic features. In the past Andersen's Syndrome has been diagnosed based on the phenotypic expression of the dysmorphic features, paralysis, and cardiac arrhythmias. AS occurs either sporadically or as an autosomal dominant trait. In AS families, expression of the characteristic traits is highly variable. Thus, AS may seemingly skip a generation because of the low level of phenotypic expression or non-penetrance in a person within the AS kindred. It is likely that the AS protein plays a complex role in development and cell excitability with some redundancy with other proteins.
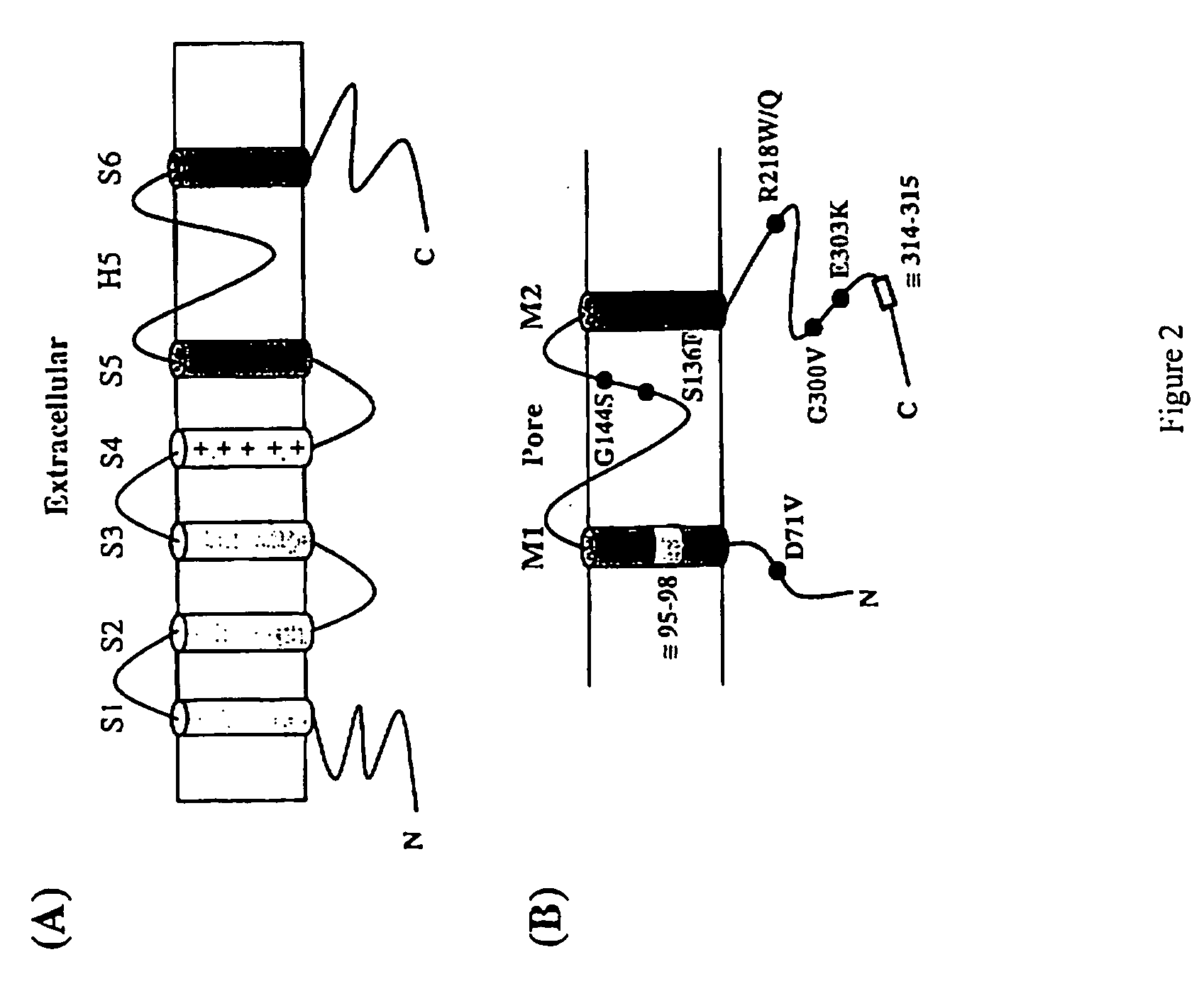
[0036]The invention is based on the discovery that mutations in the Kir2.1 gene, KCNJ2, cause the triad of phenotypes in Andersen's Syndrome, including periodic paralysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and dysmorphic features. Andersen's Syndrome mutations involve residues in important...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com