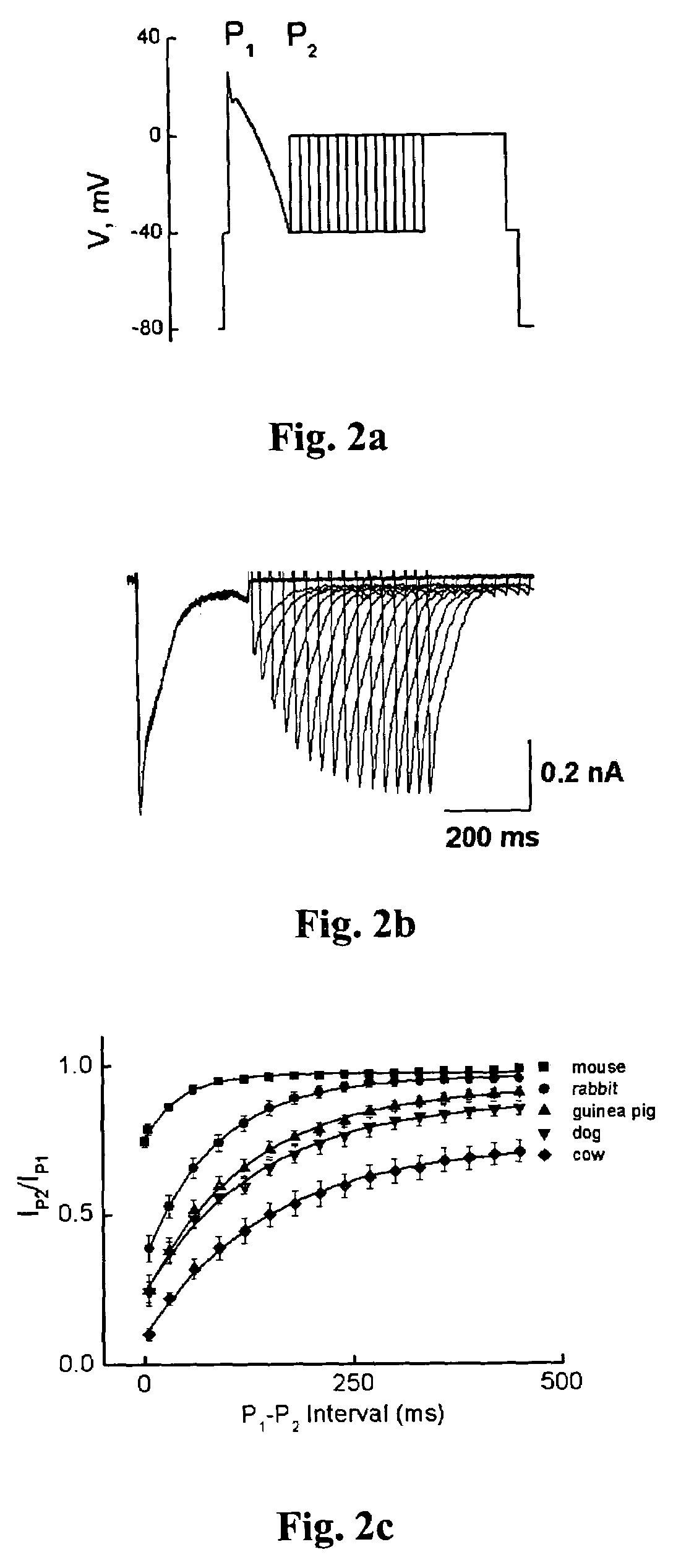
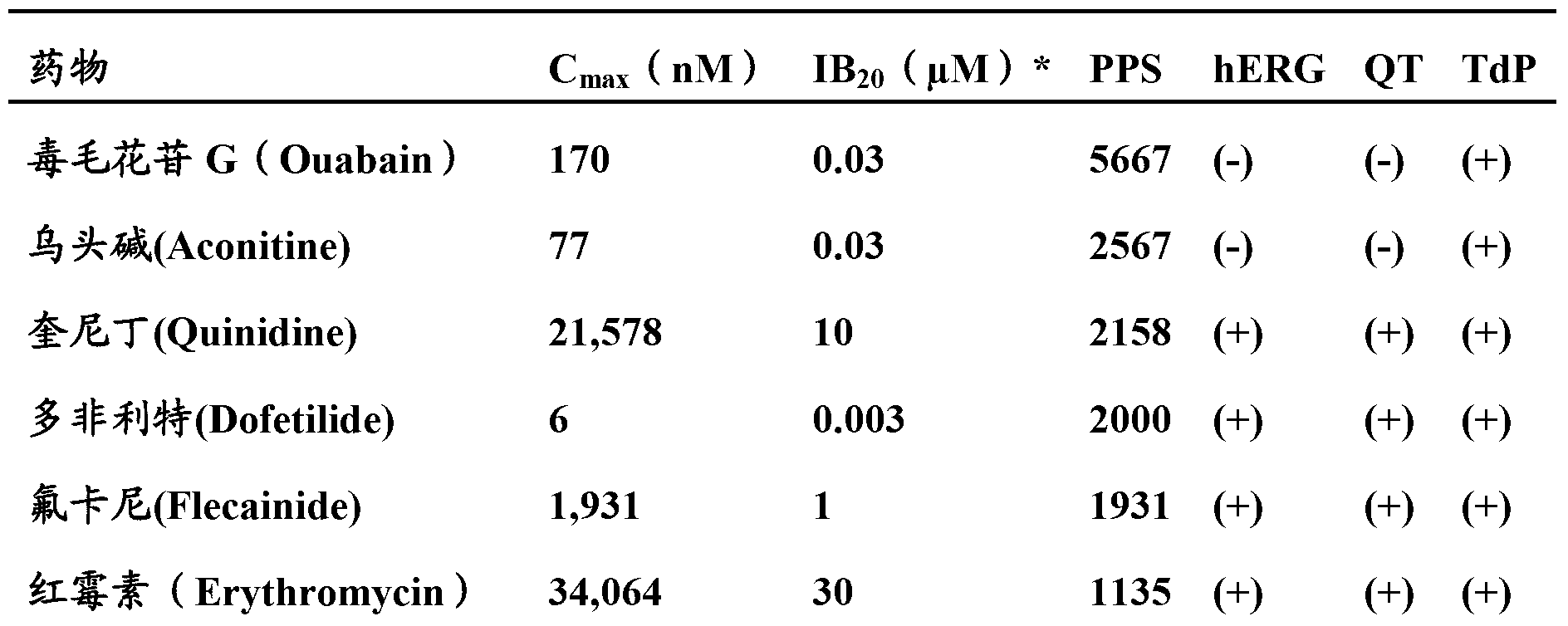
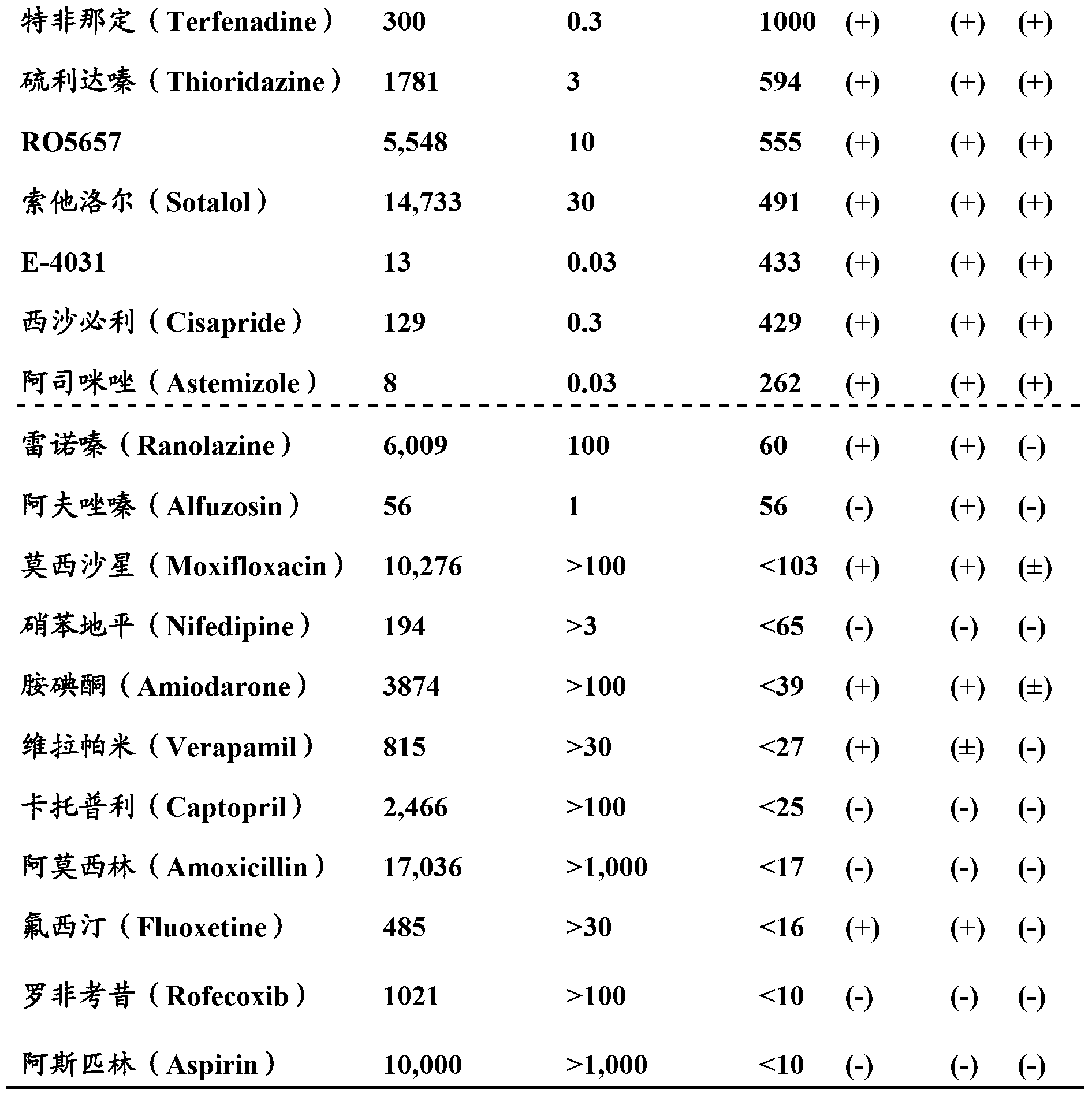
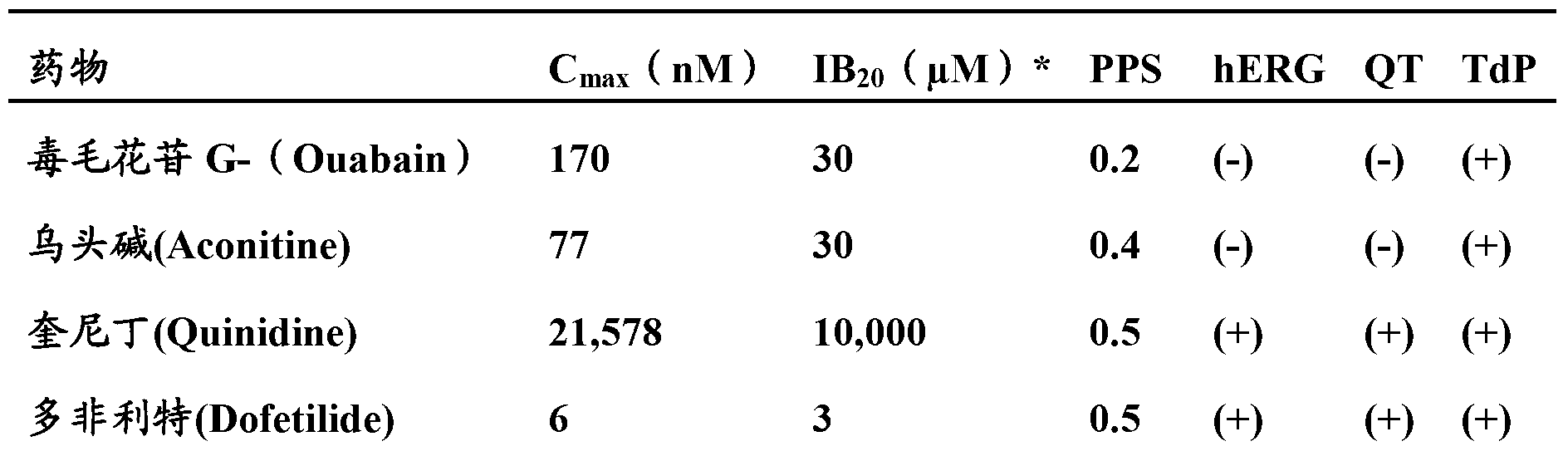
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Arrhythmic risk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Risk factors for arrhythmia include: Heart disease: Some types of heart disease, such as high blood pressure, are risk factors for AFib, which is a type of arrhythmia.
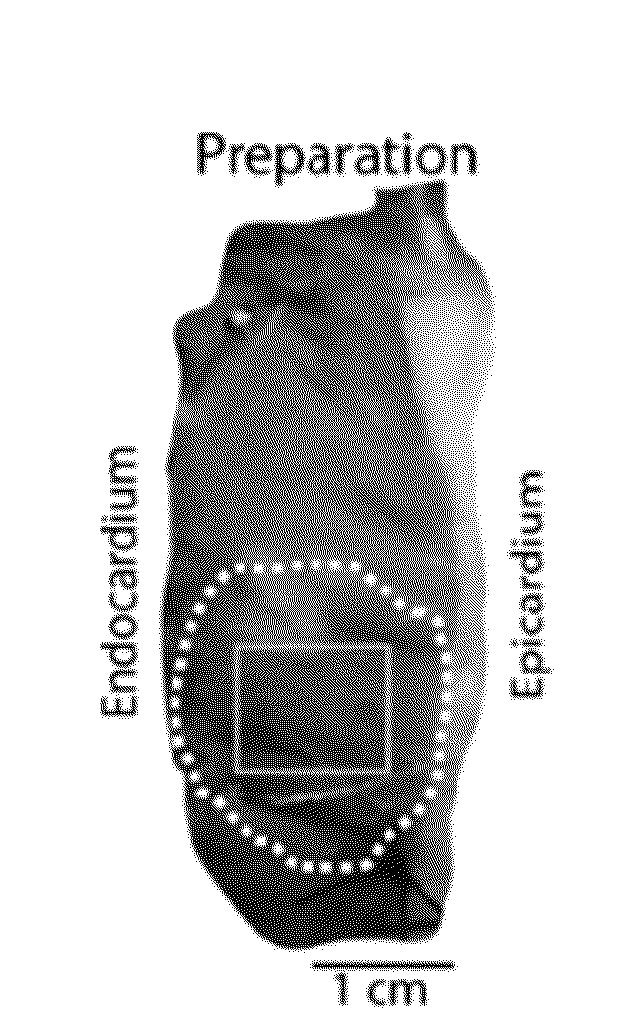
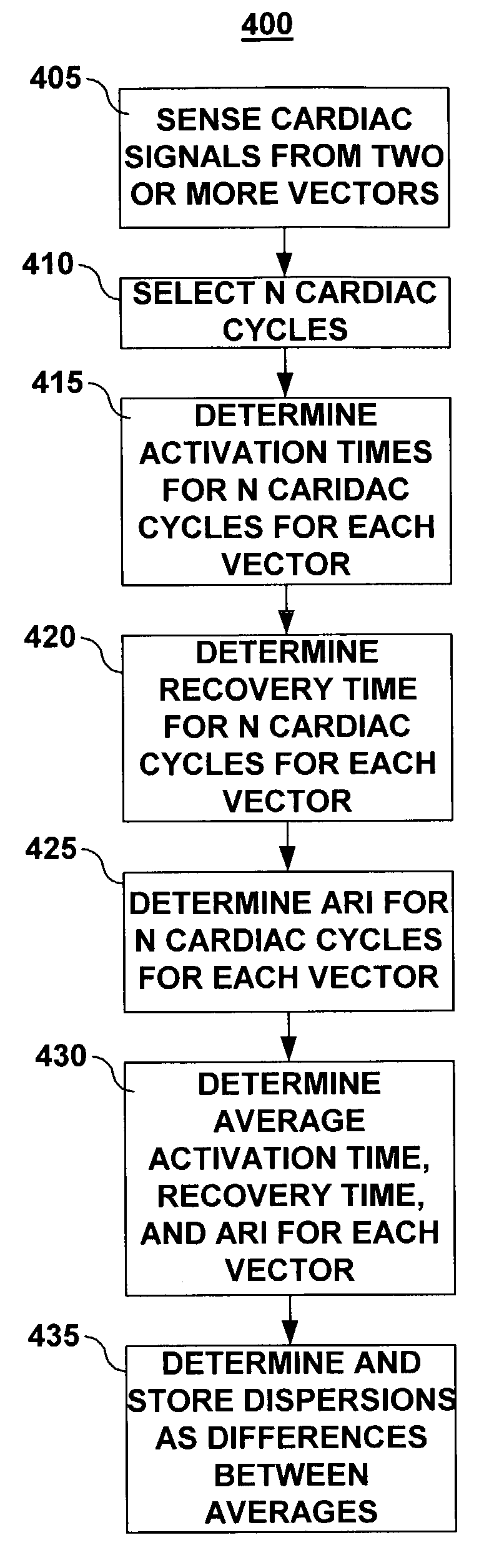
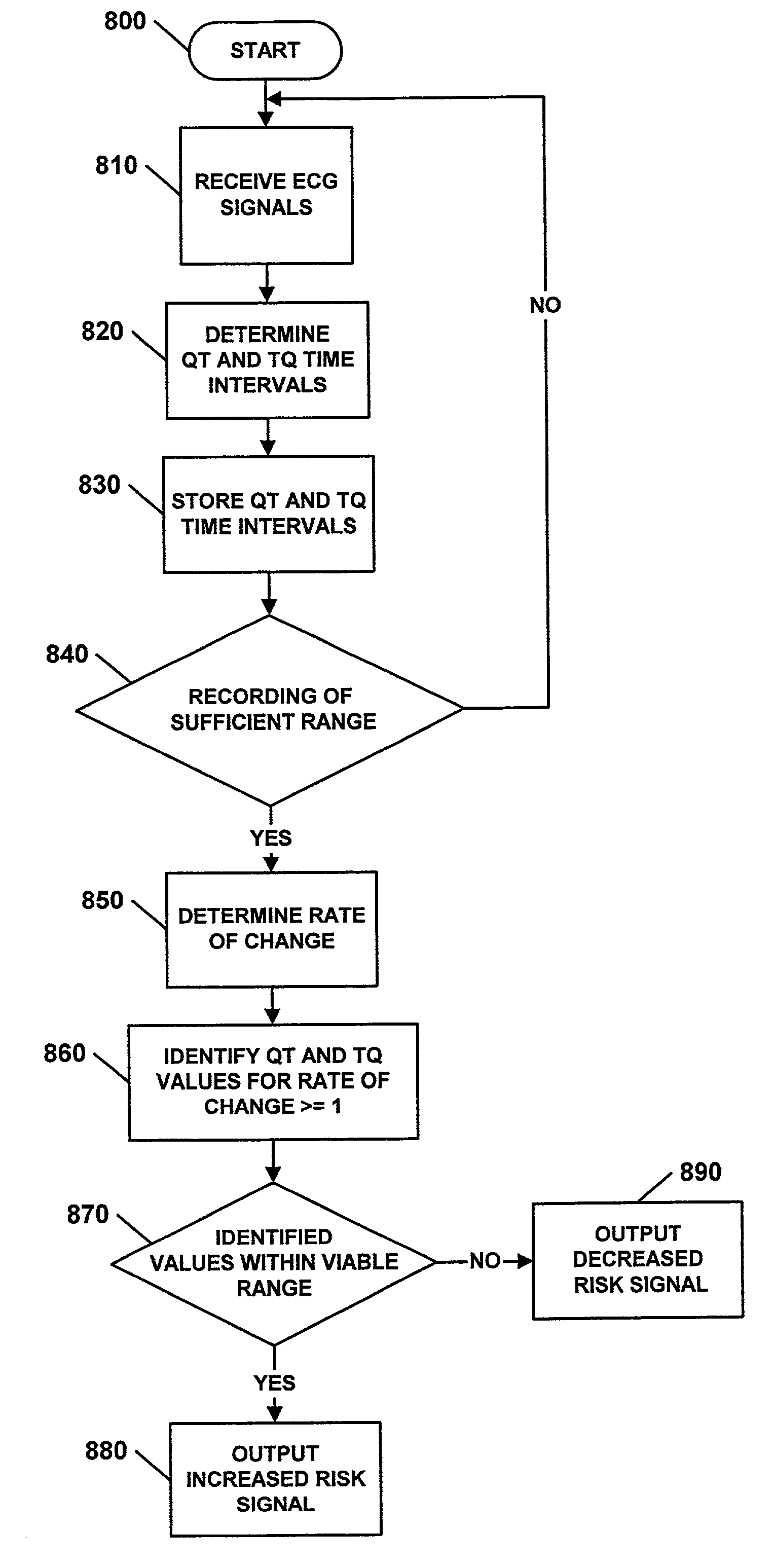
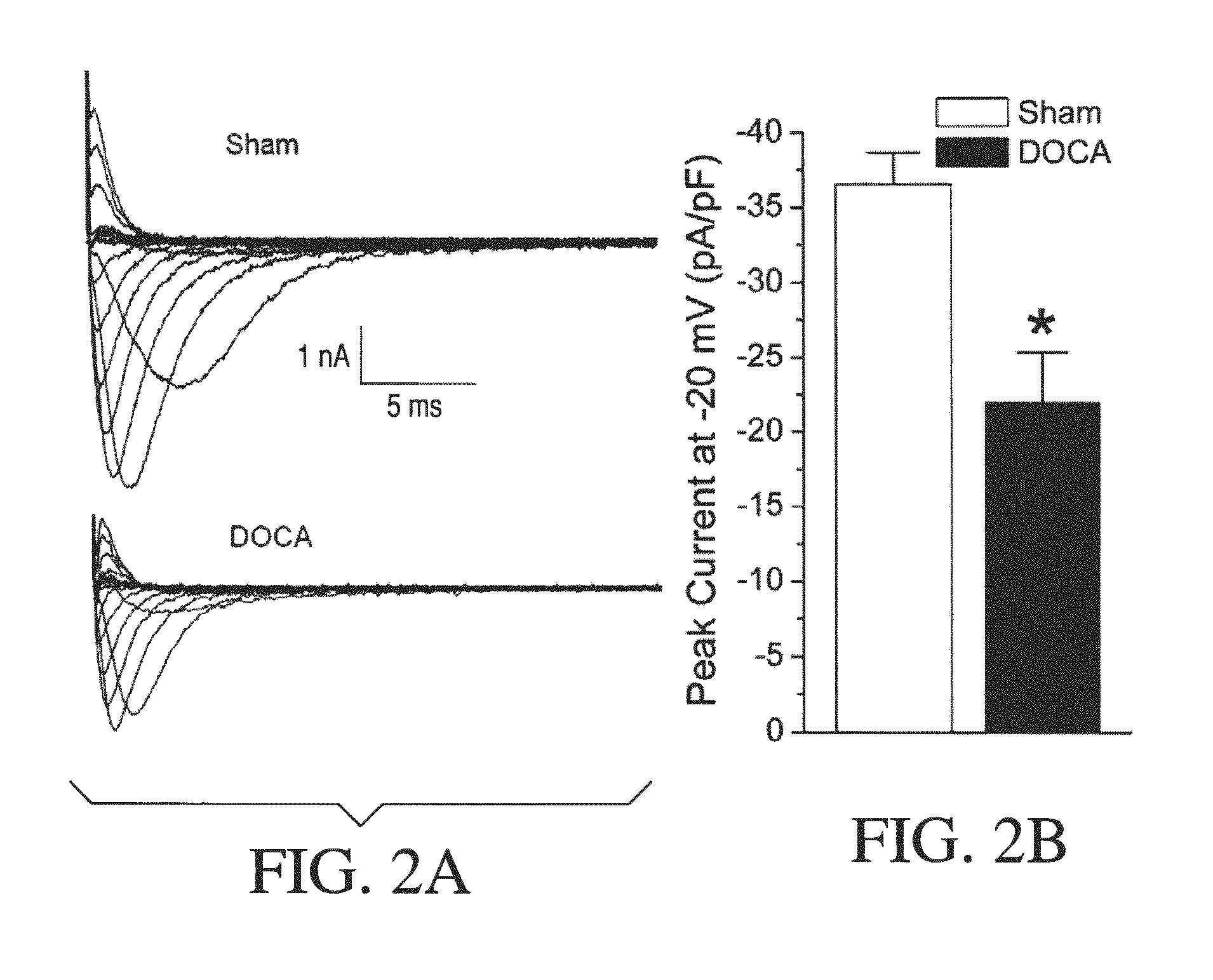
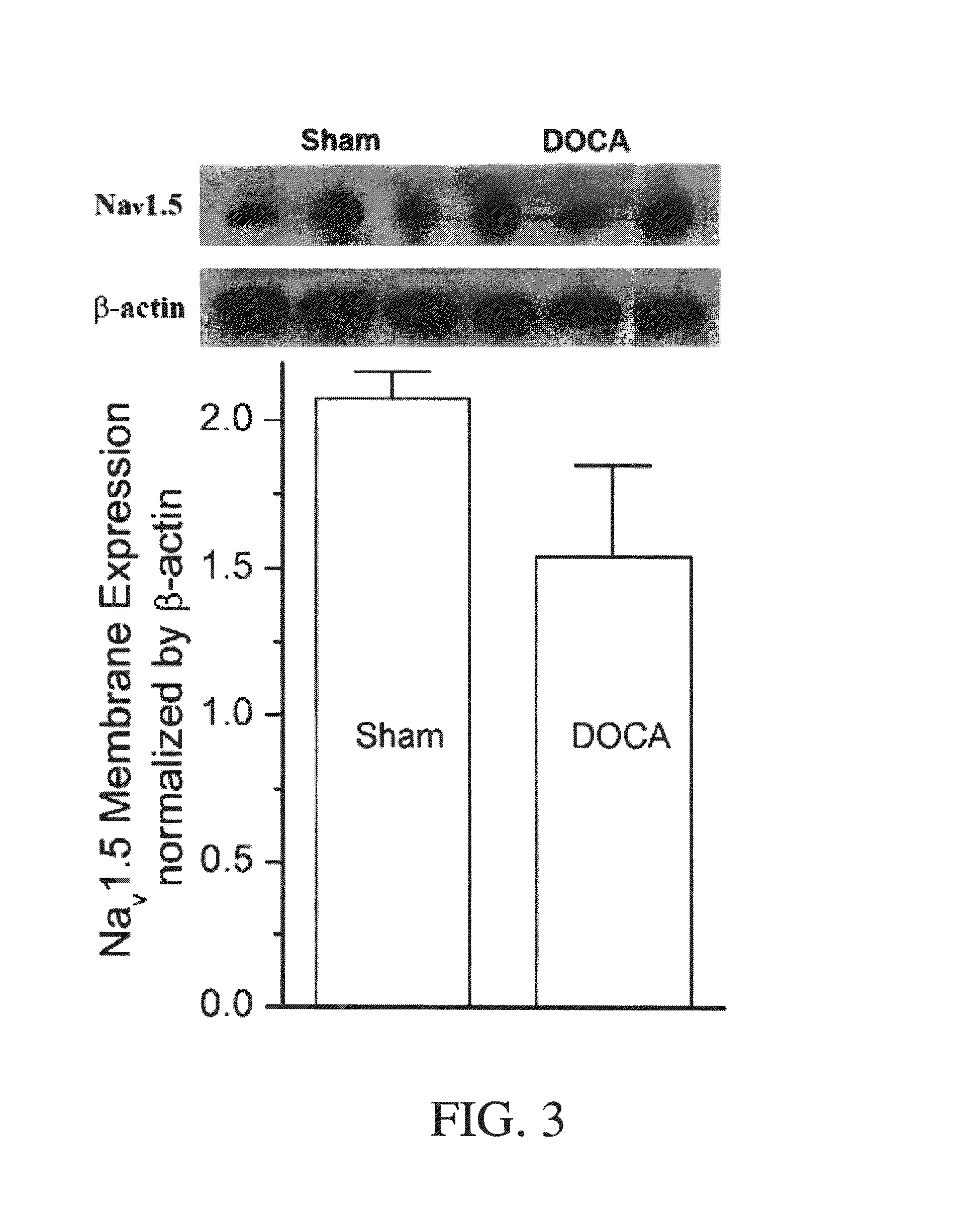
Use of activation and recovery times and dispersions to monitor heart failure status and arrhythmia risk
InactiveUS7107093B2Reduce dispersionOptimize delivery of therapyHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac cycleIncreased risk
A system and method for monitoring electrical dispersion of the heart is provided including an implantable medical device and associated electrode system for sensing cardiac signals from a combination of two or more local and / or global EGM sensing vectors and / or subcutaneous ECG sensing vectors. Activation and recovery times and the activation-recovery intervals are measured from a selected cardiac cycle for each sensing vector. Dispersion is determined as the differences between activation times, recovery times and / or ARIs measured from each of the sensing vectors. An increase in dispersion indicates a worsening of heart failure and / or an increased risk of arrhythmias. Accordingly, a cardiac therapy may be delivered or adjusted in response to a detected increase in dispersion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
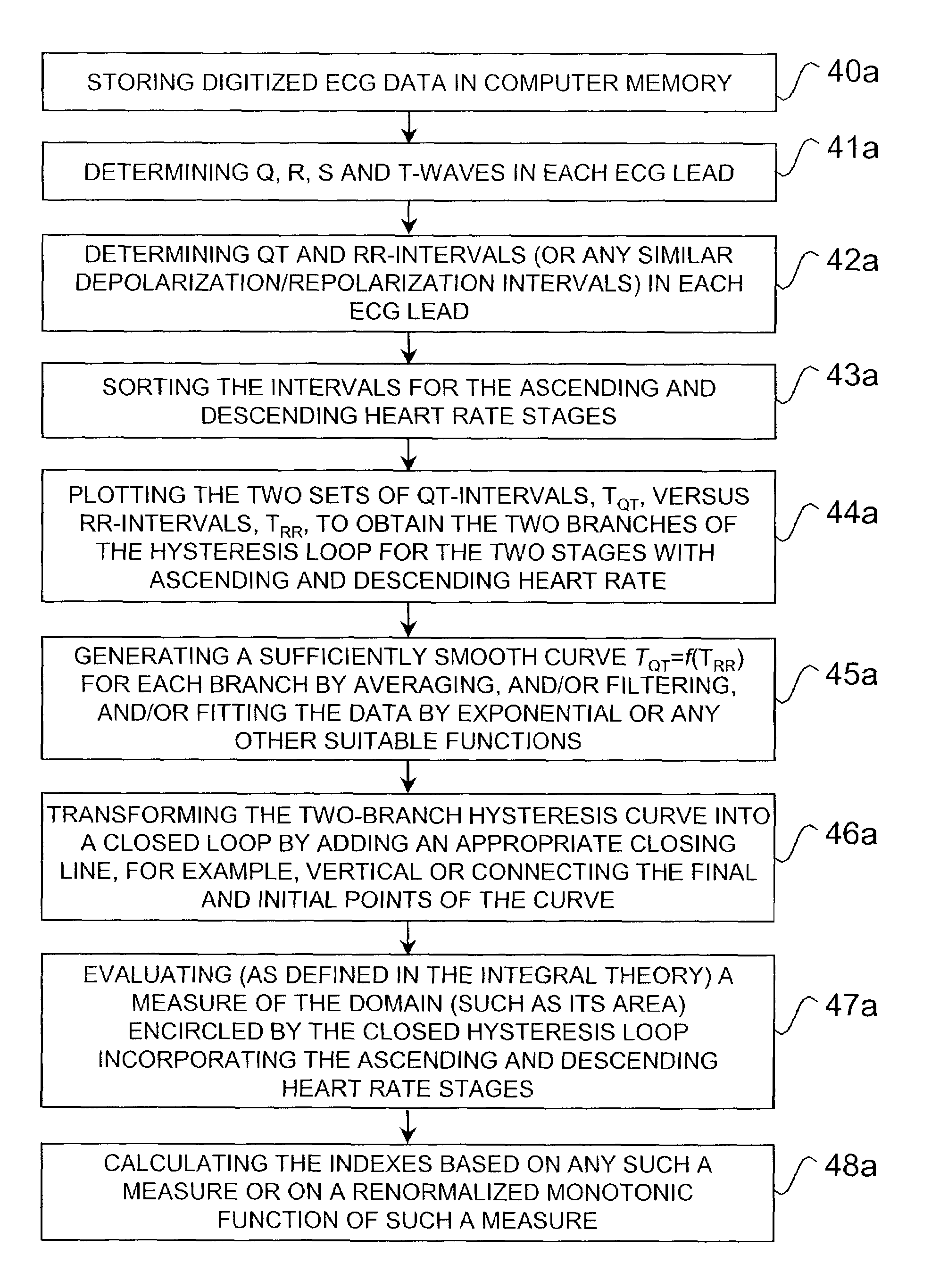
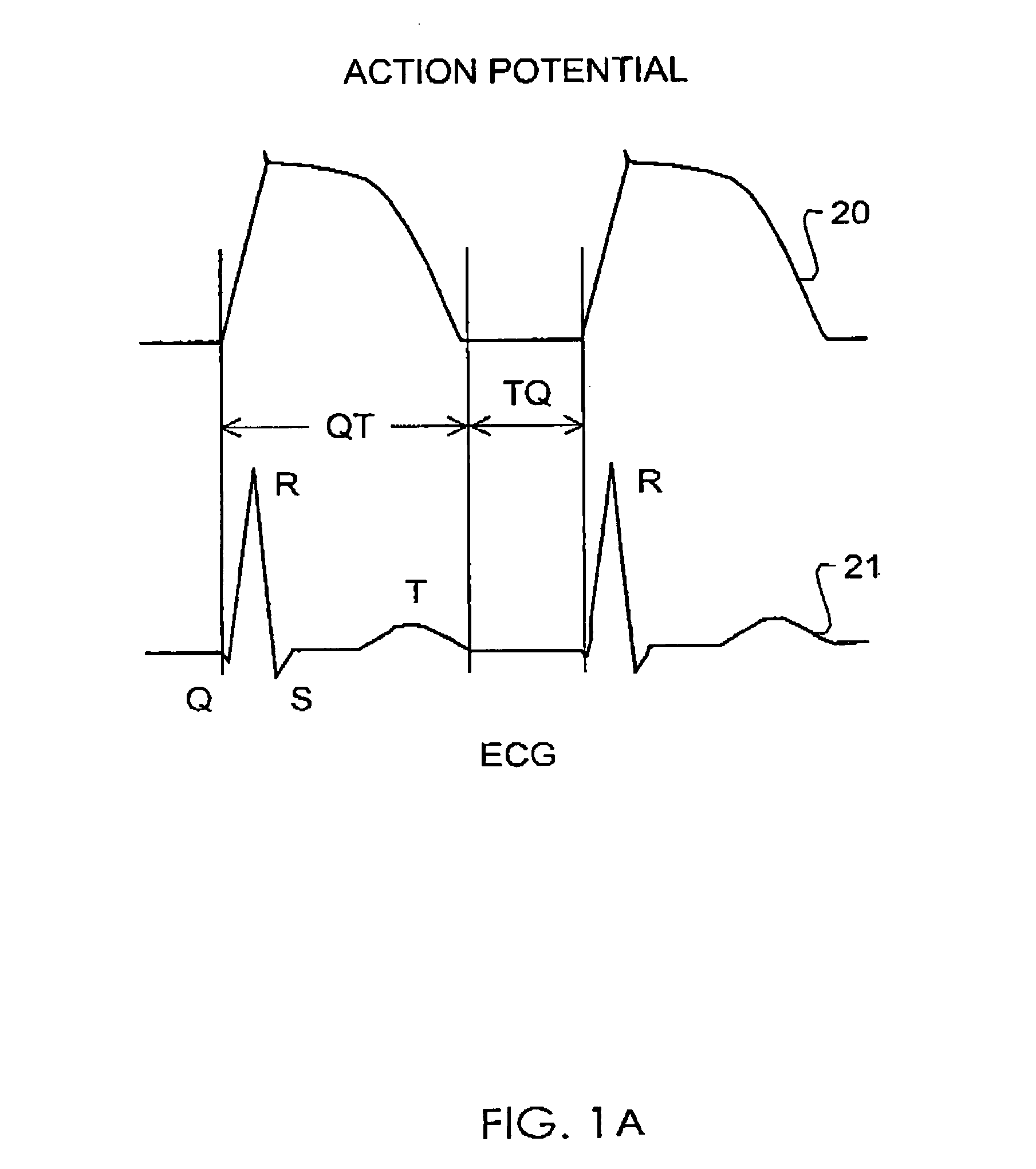
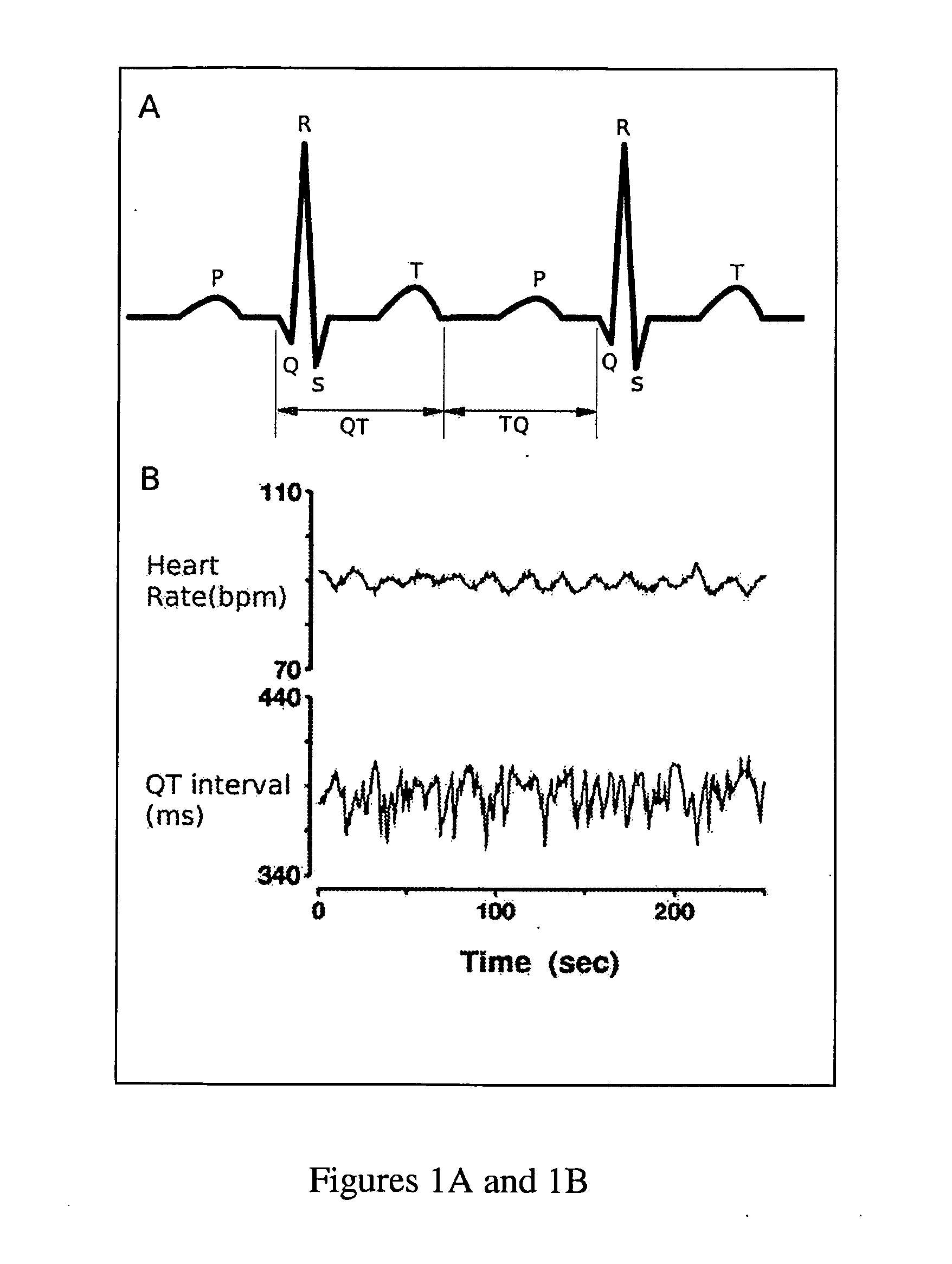
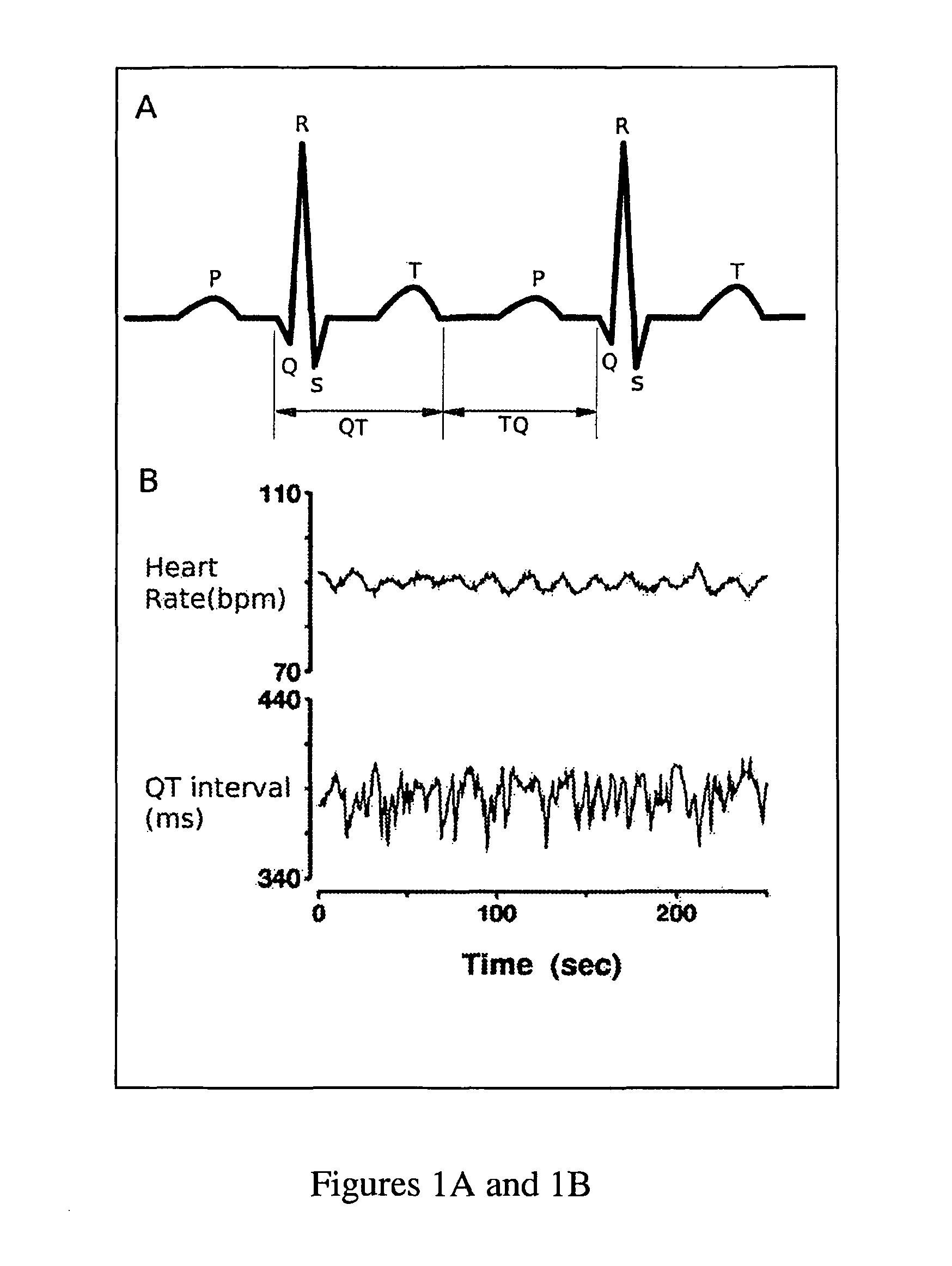
Method and system for evaluating arrhythmia risk with QT-RR interval data sets
A method of assessing the cardiac arrhythmia risk in a subject to provide a measure of cardiac or cardiovascular health in that subject is described herein. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: (a) collecting at least one QT and RR interval data set from the subject; (b) separating fluctuations from slow trends in said at least one QT and RR interval data set; (c) comparing said QT and RR fluctuations to one another and (d) generating from the comparison of step (c) partial measures of risk of cardiac arrhythmia in said subject. A greater difference between QT and RR fluctuations indicates greater risk of cardiac arrhythmia in said subject. The data sets are collected in such a manner that they reflect almost exclusively the conduction in the heart muscle and minimize the effect on the data sets of rapid transients due to autonomic nervous system and hormonal control.
Owner:MEDIWAVE STAR TECH
Identifying patients at risk for life threatening arrhythmias
The invention is a method for identifying proteins associated with sudden cardiac death (SCD) and for assessing a patient's risk of SCD by determining the amount of one or more SCD-associated proteins in the patient. Typically, the patient submits a sample, such as a blood sample, which is tested for one or more SCD-associated proteins. Based upon the results of the tests, the patient's risk of SCD may be assessed.
Owner:YOUGENE
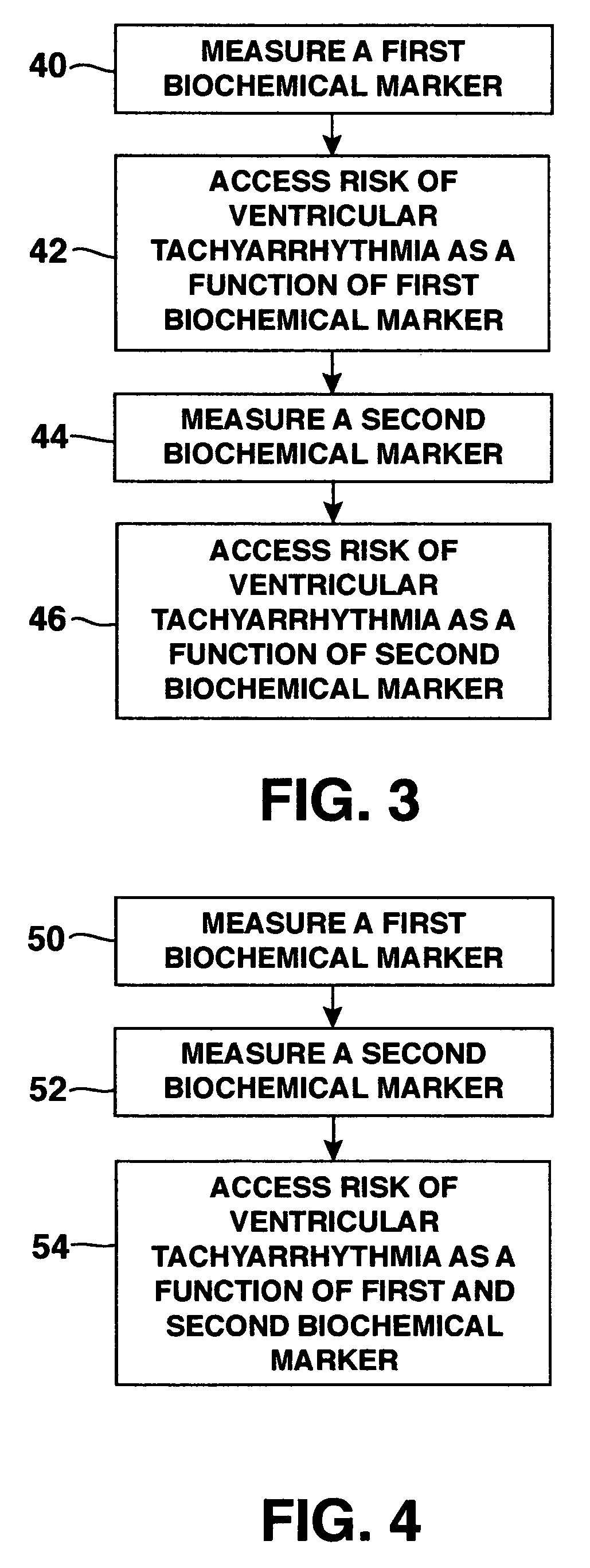
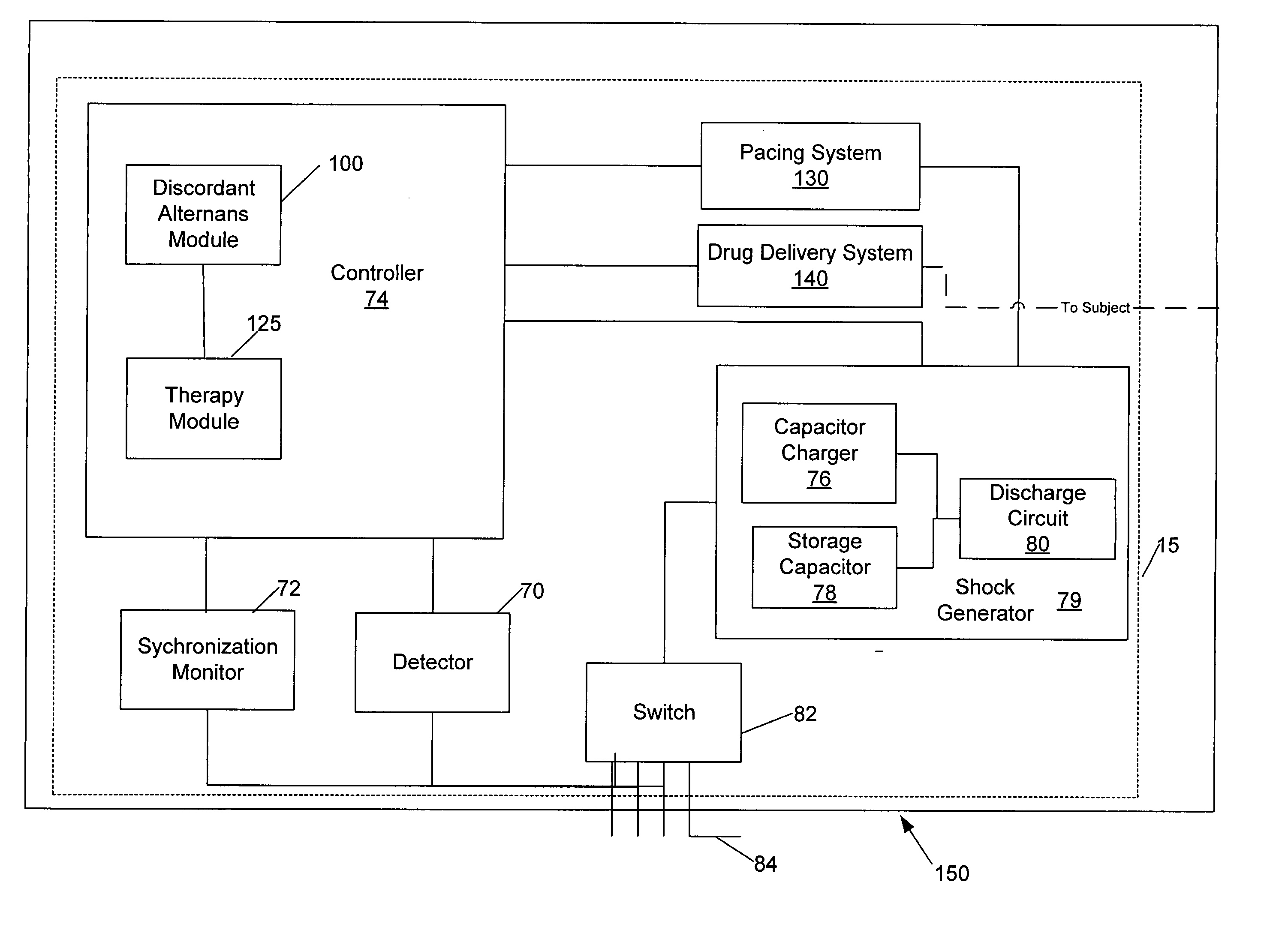
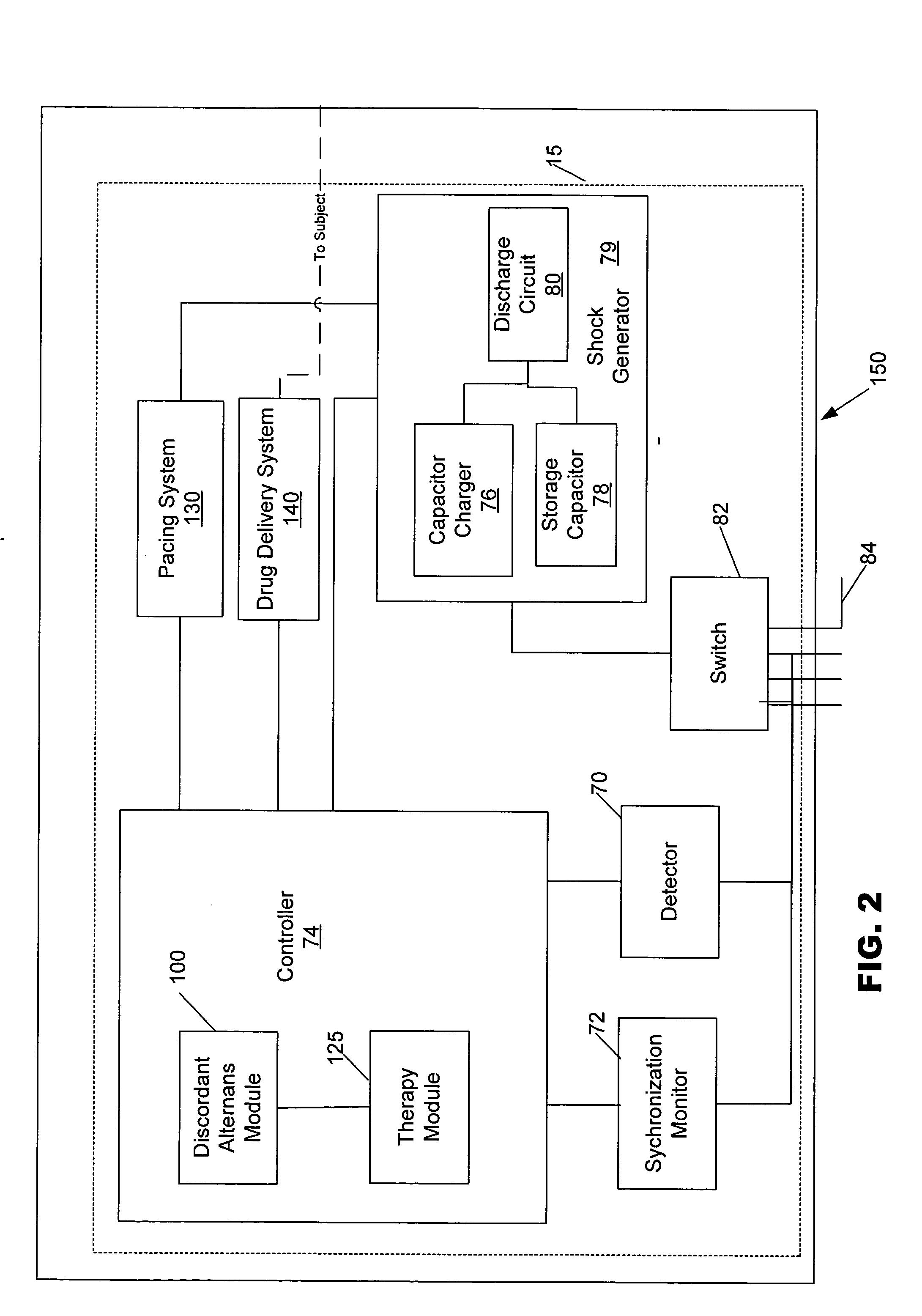
Methods, systems and computer program products for selectively initiating interventional therapy to reduce the risk of arrhythmia
InactiveUS20050049516A1Reduce riskHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringInterventional therapyArrhythmic risk
Electrical activity can be chronically detected in first and second cardiac regions in the subject. Discordant alternans in at least one component of the detected electrical activity can by identified. Interventional therapy can be initiated in the subject responsive to the identification of discordant alternans.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Apparatus, methods, and computer program products for evaluating a risk of cardiac arrhythmias from restitution properties
Methods, systems, and computer program products can be provided for evaluating a risk of the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias in a heart. The system can include at least one sensing electrode and a controller. The sensing electrode can be configured to sense electrical signals from a heart over a range of heart rates. The controller can be configured to determine values of a at least one restitution property of the heart from the sensed electrical signals and to evaluate the risk of the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias from the determine values of the at least one restitution property.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
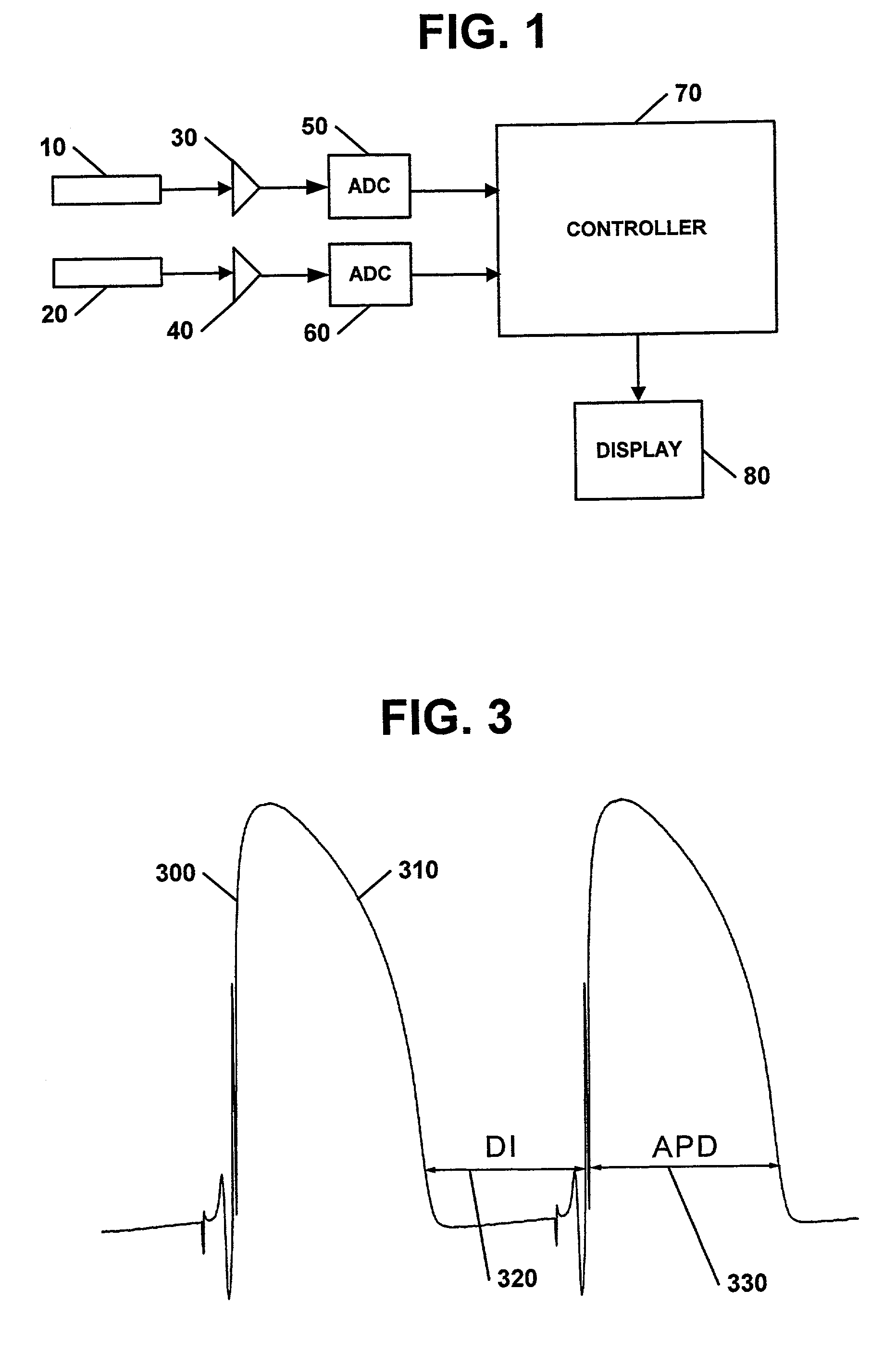
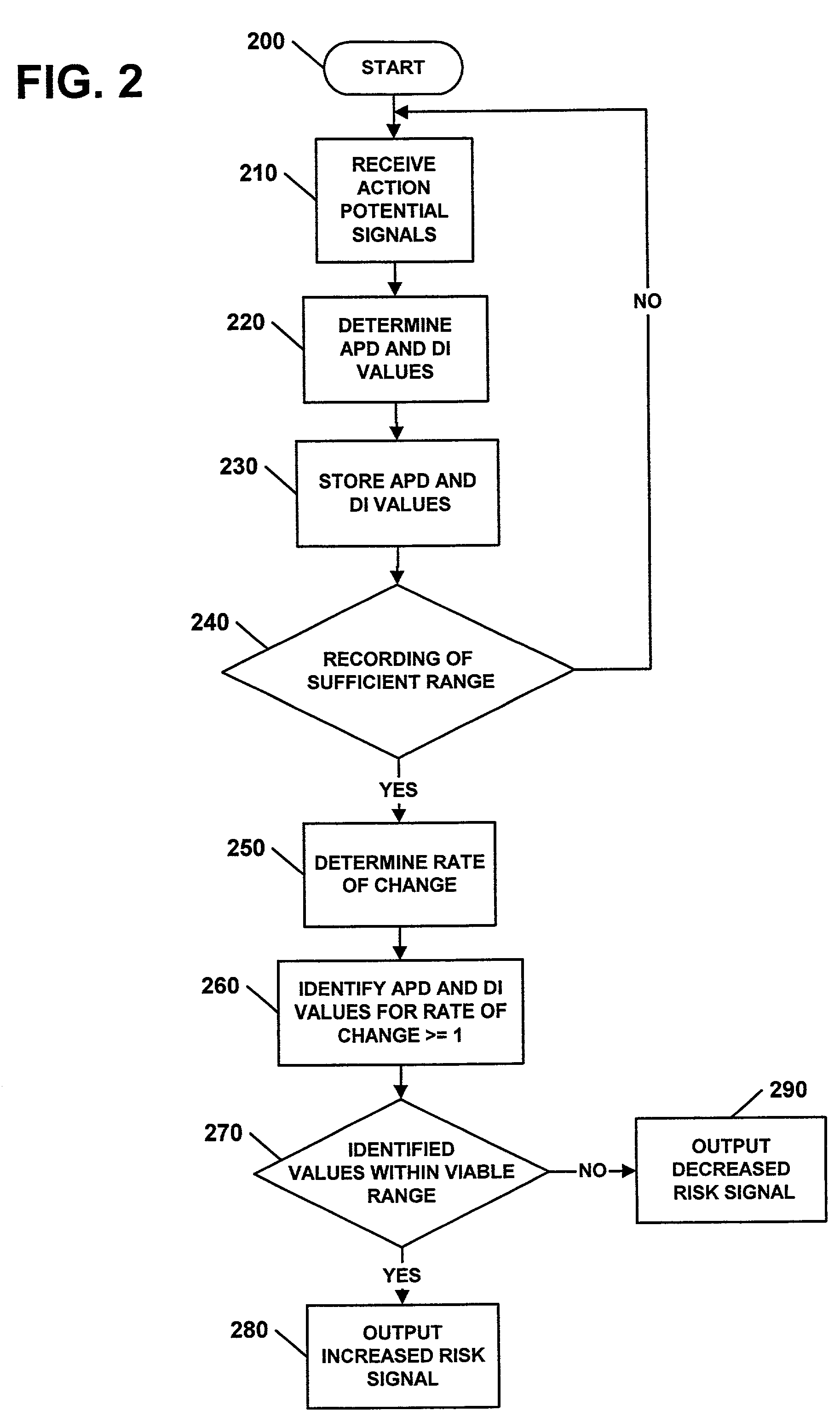
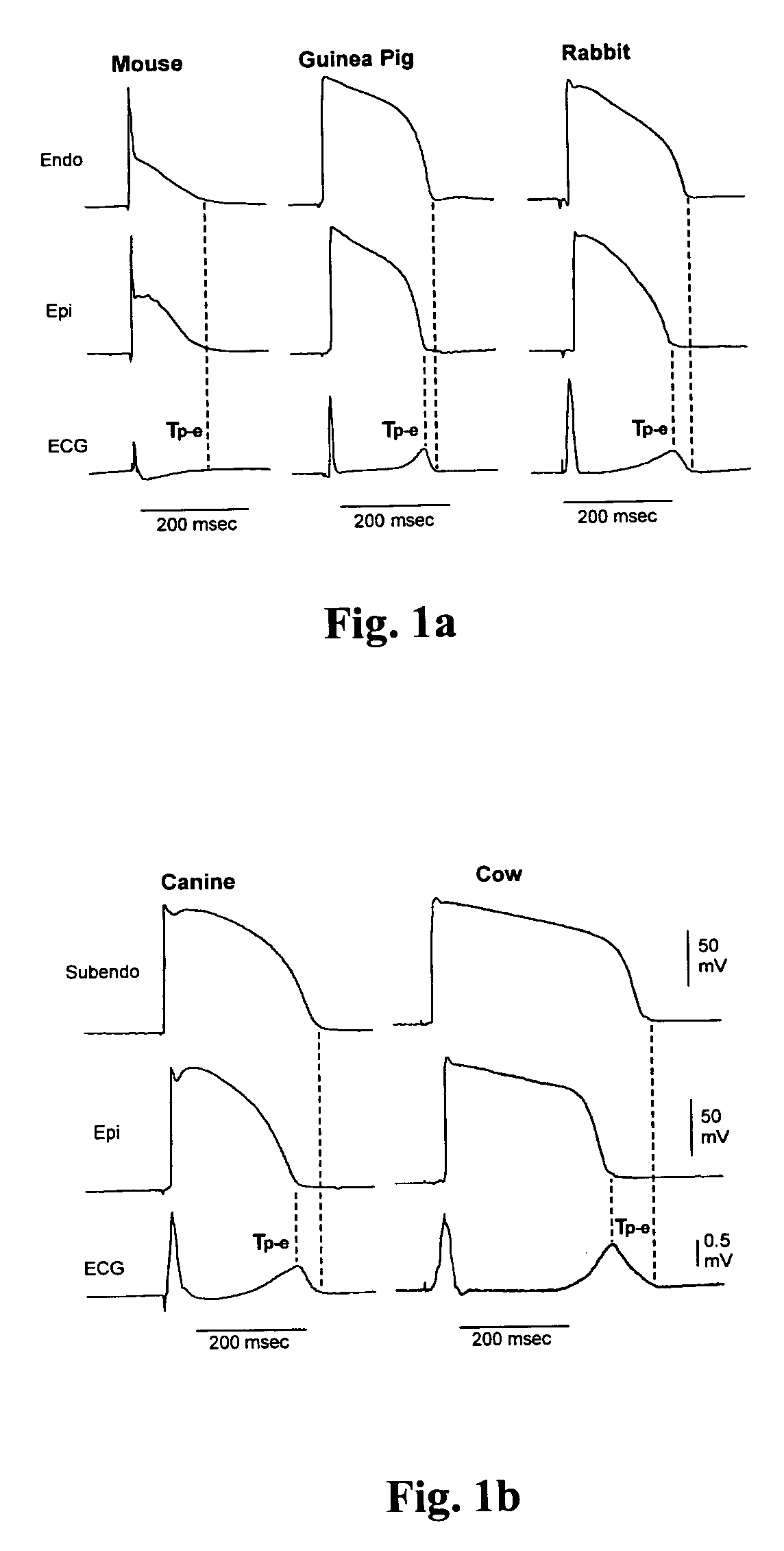
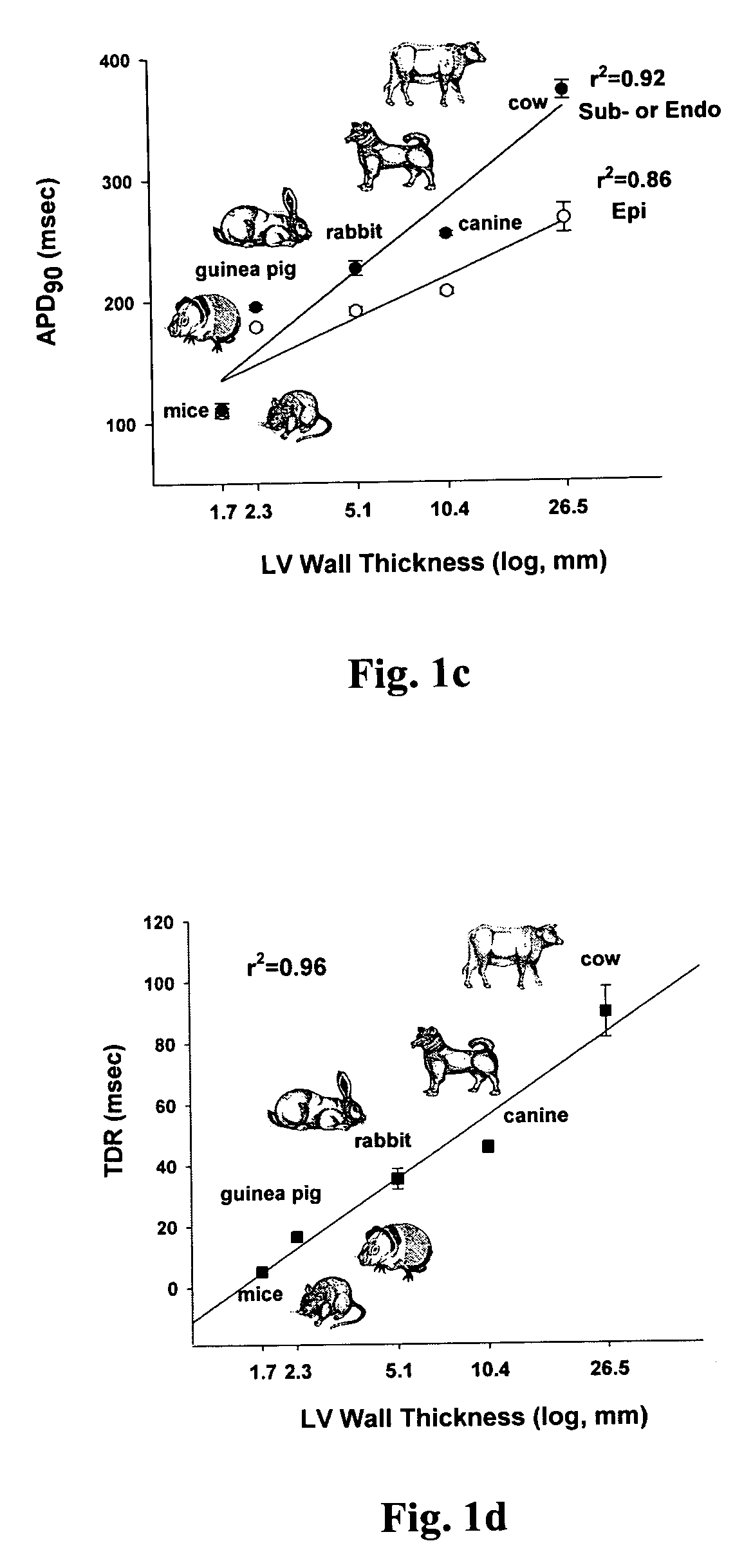
Method and apparatus for monitoring arrythmogenic effects of medications using an implantable device
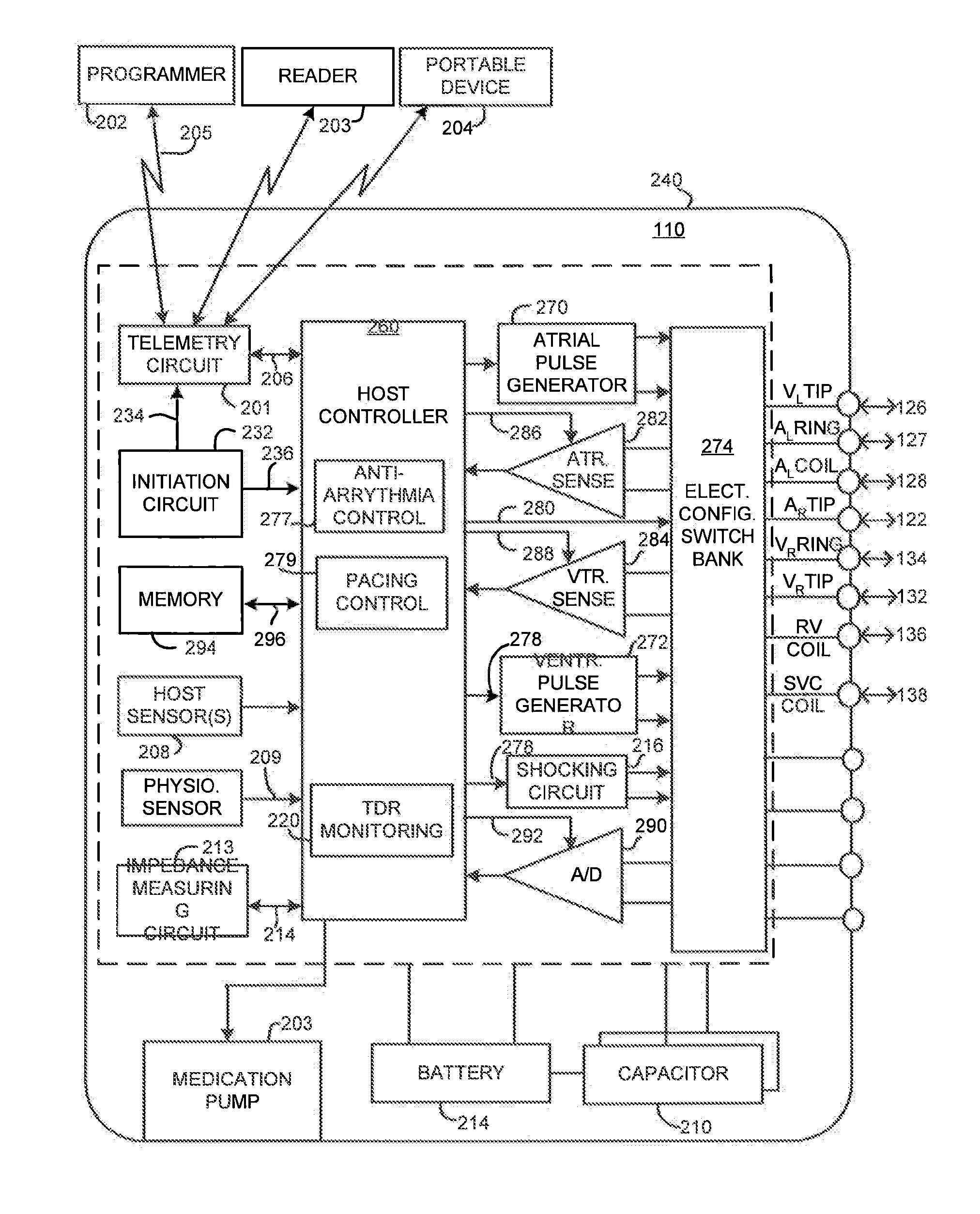
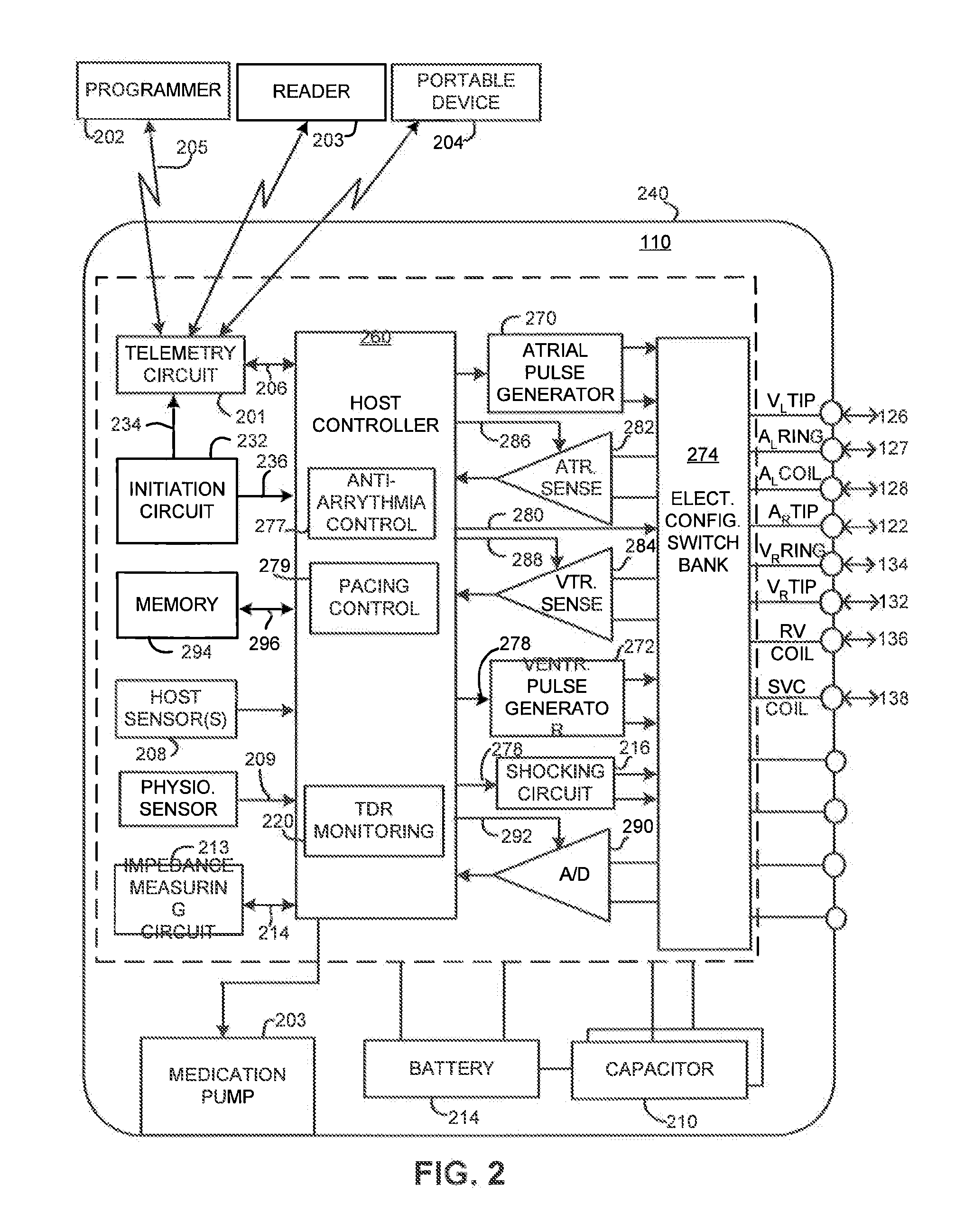
ActiveUS8934963B1Reduce riskContinuous monitoringElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyT waveErythropoiesis
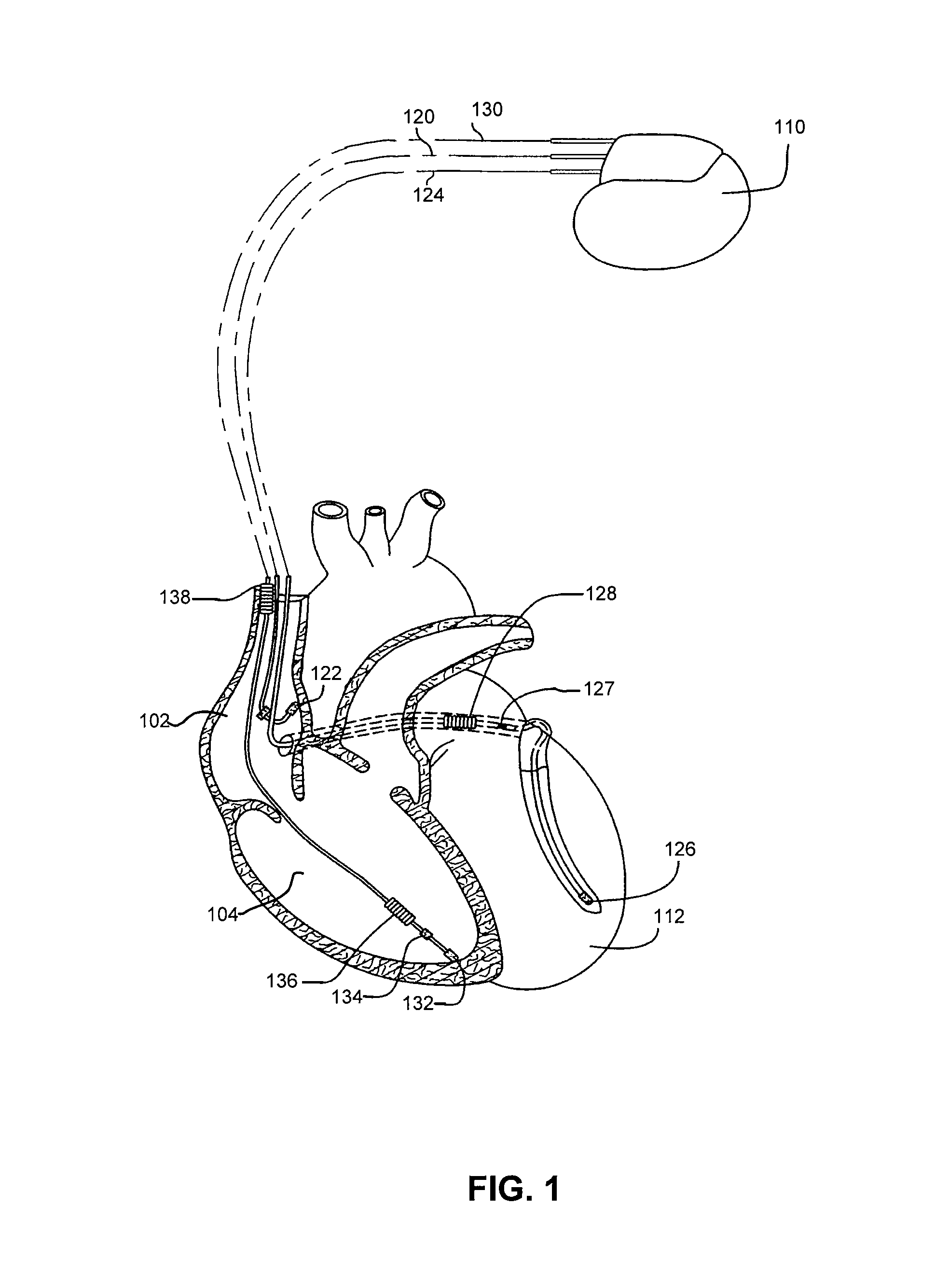
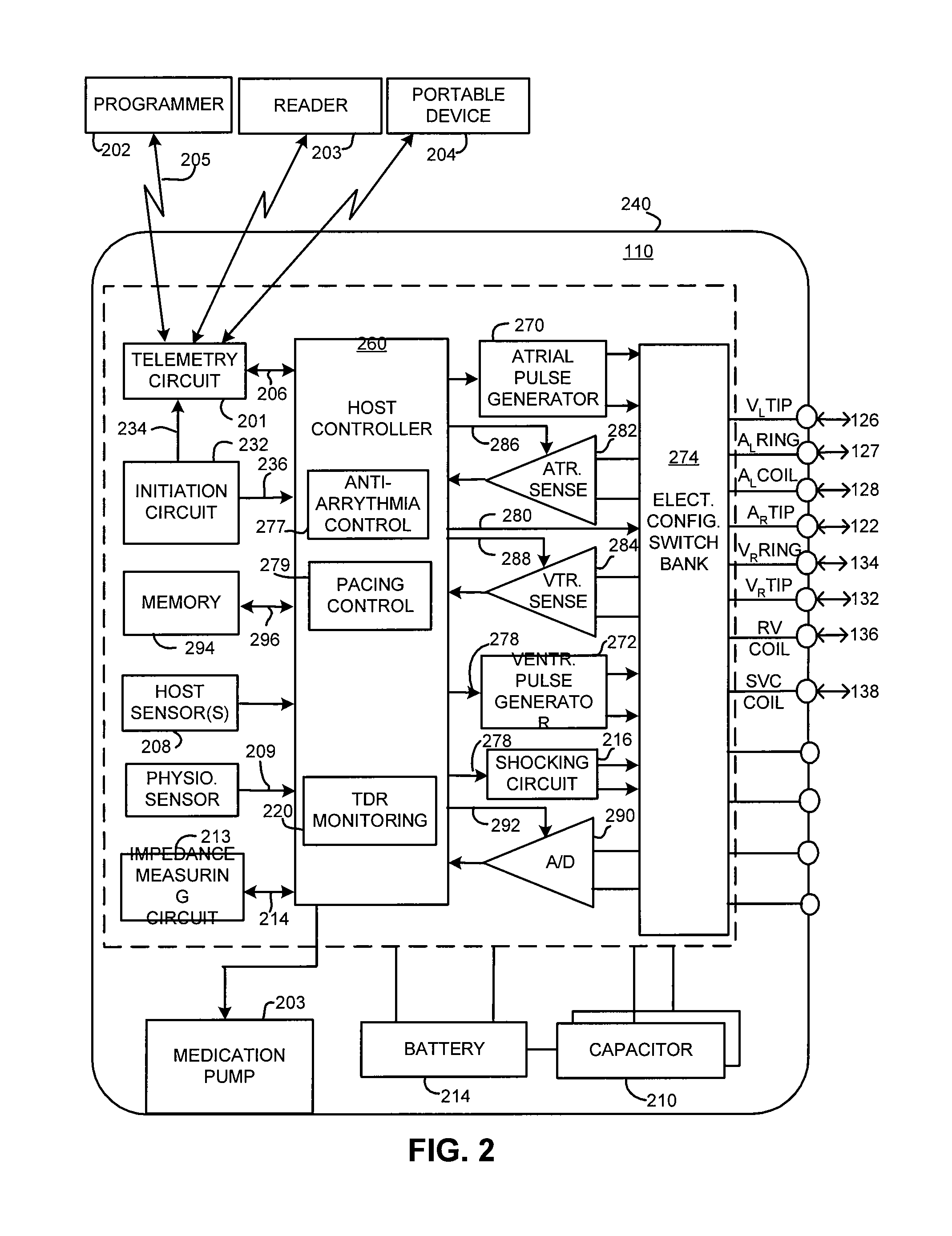
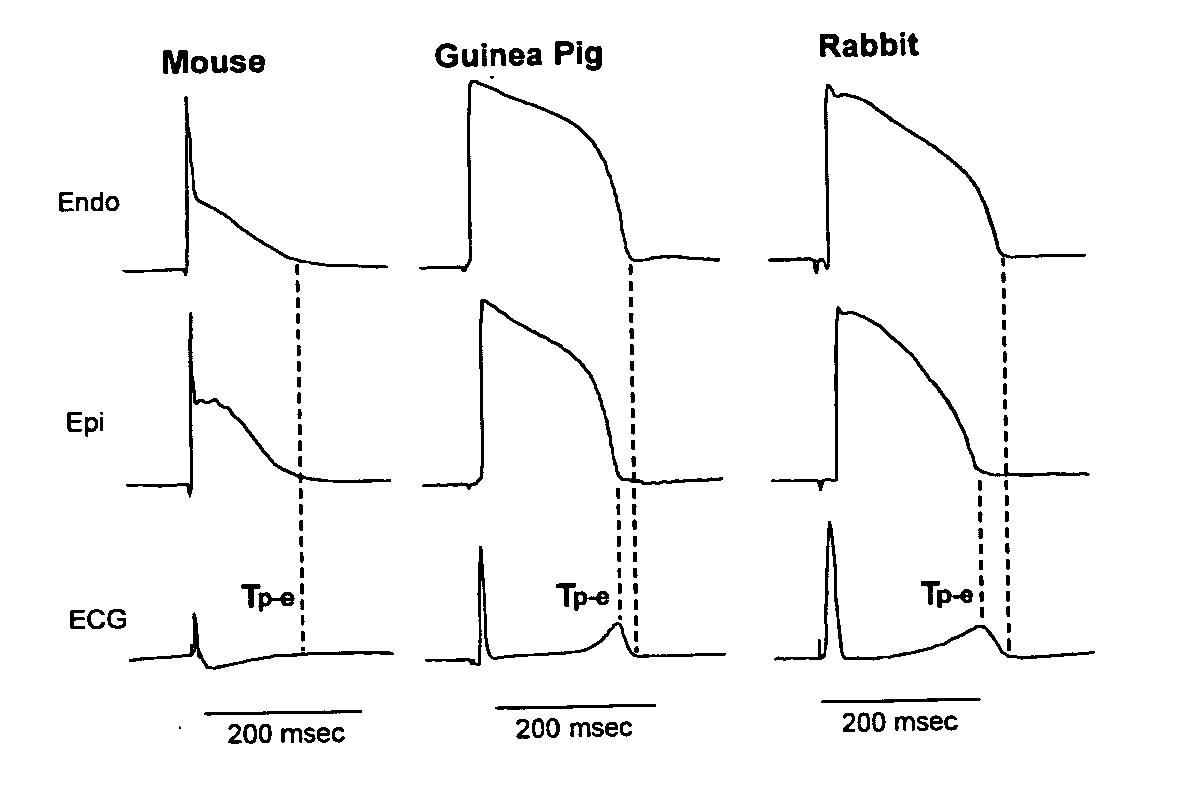
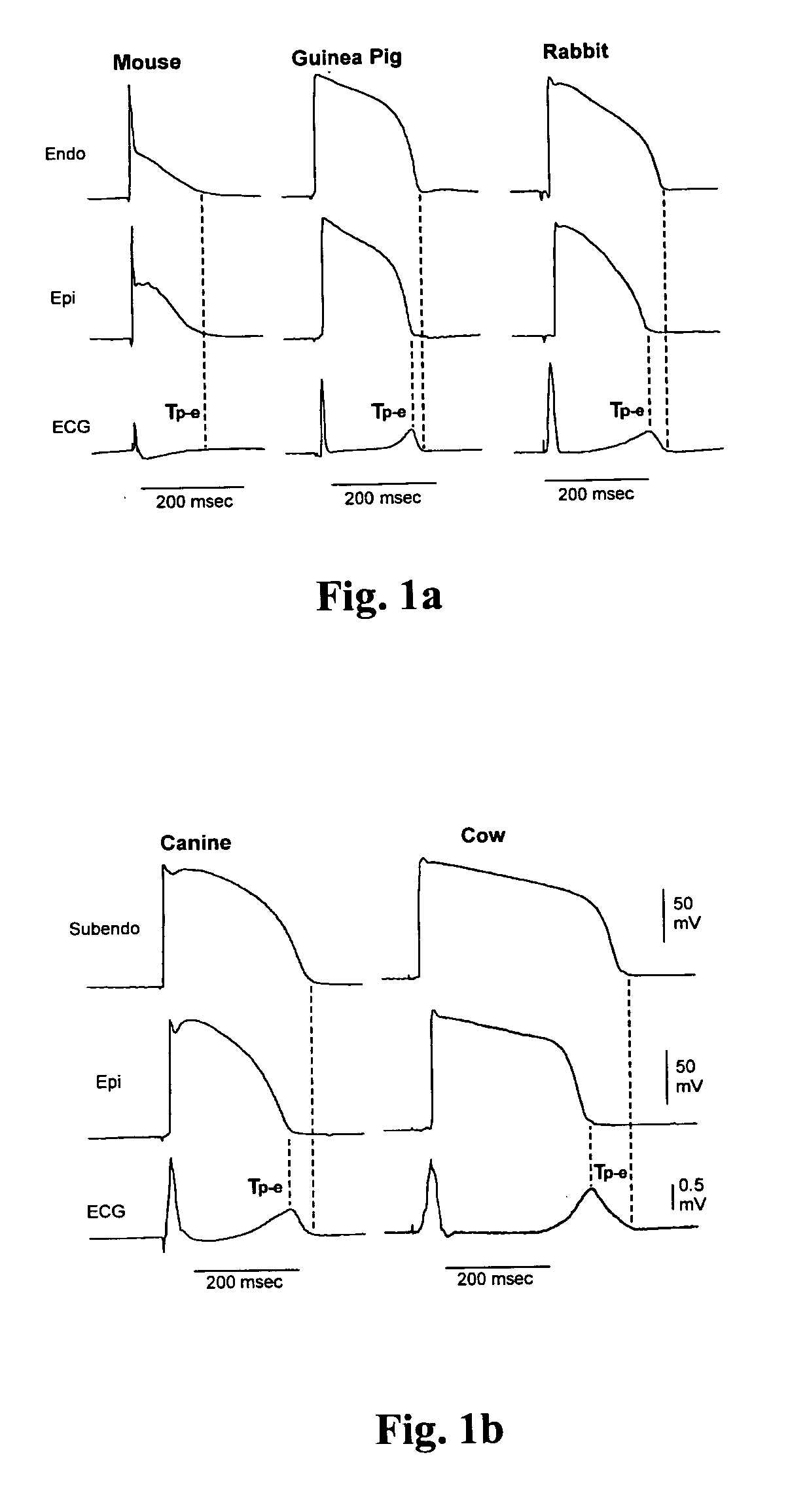
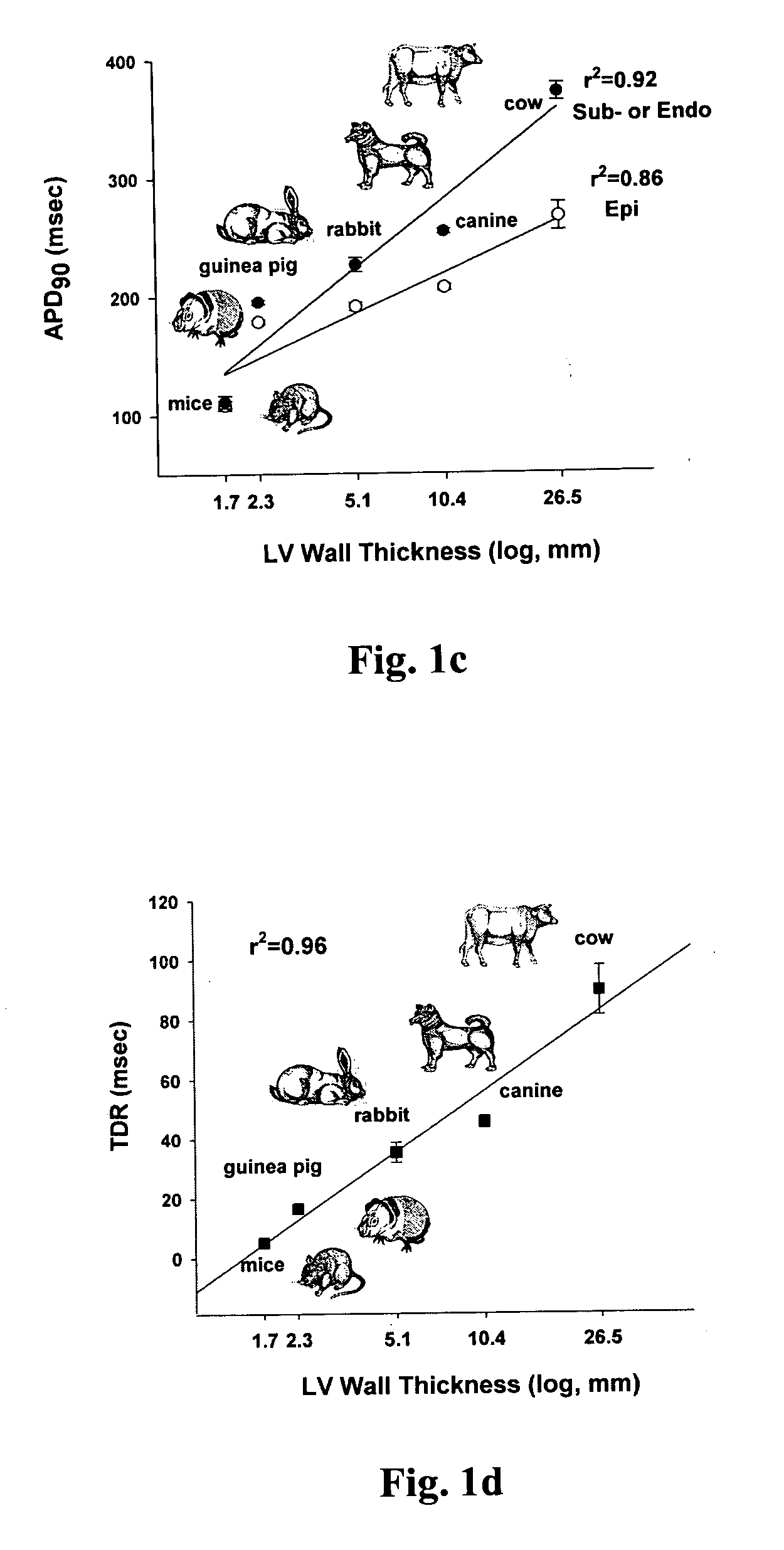
An implantable device and method for monitoring changes in the risk of arrhythmia induced by medications. The implantable device monitors risk of arrhythmia by analyzing an aspect of T-wave morphology to generate a metric of transmural dispersion of repolarization (“TDR”) as a proxy for the risk of arrhythmia. The implantable device generates an index of change in the risk of arrhythmia by comparing values of the metric of TDR obtained for different time periods. The implantable device generates a warning if the change in risk of arrhythmia is outside acceptable limits. The implantable device can also communicate with other devices to correlate changes in risk of arrhythmia with medications taken by the patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Identifying patients at risk for life threatening arrhythmias
The invention is a method for identifying proteins associated with sudden cardiac death (SCD) and for assessing a patient's risk of SCD by determining the amount of one or more SCD-associated proteins in the patient. Typically, the patient submits a sample, such as a blood sample, which is tested for one or more SCD-associated proteins. Based upon the results of the tests, the patient's risk of SCD may be assessed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
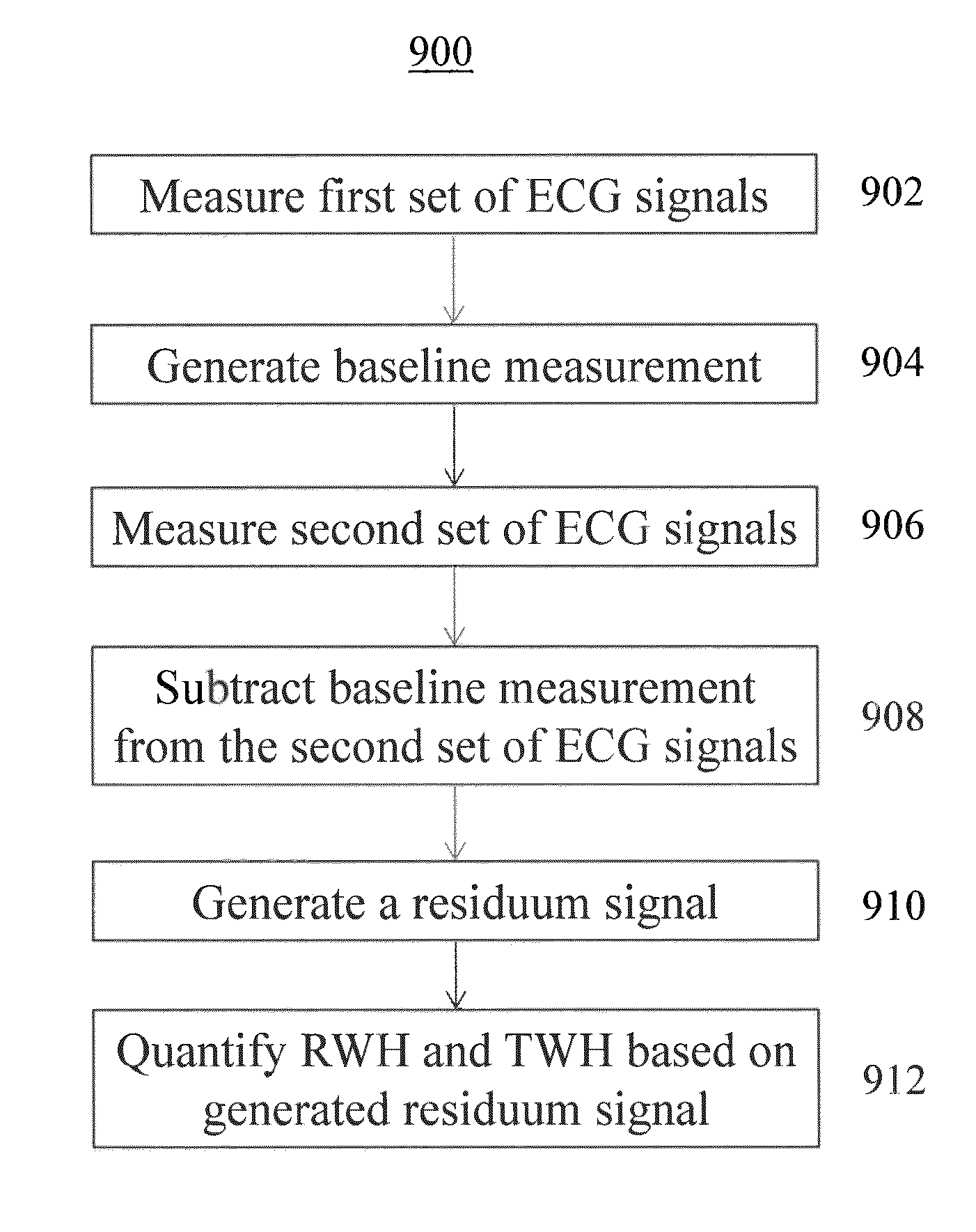
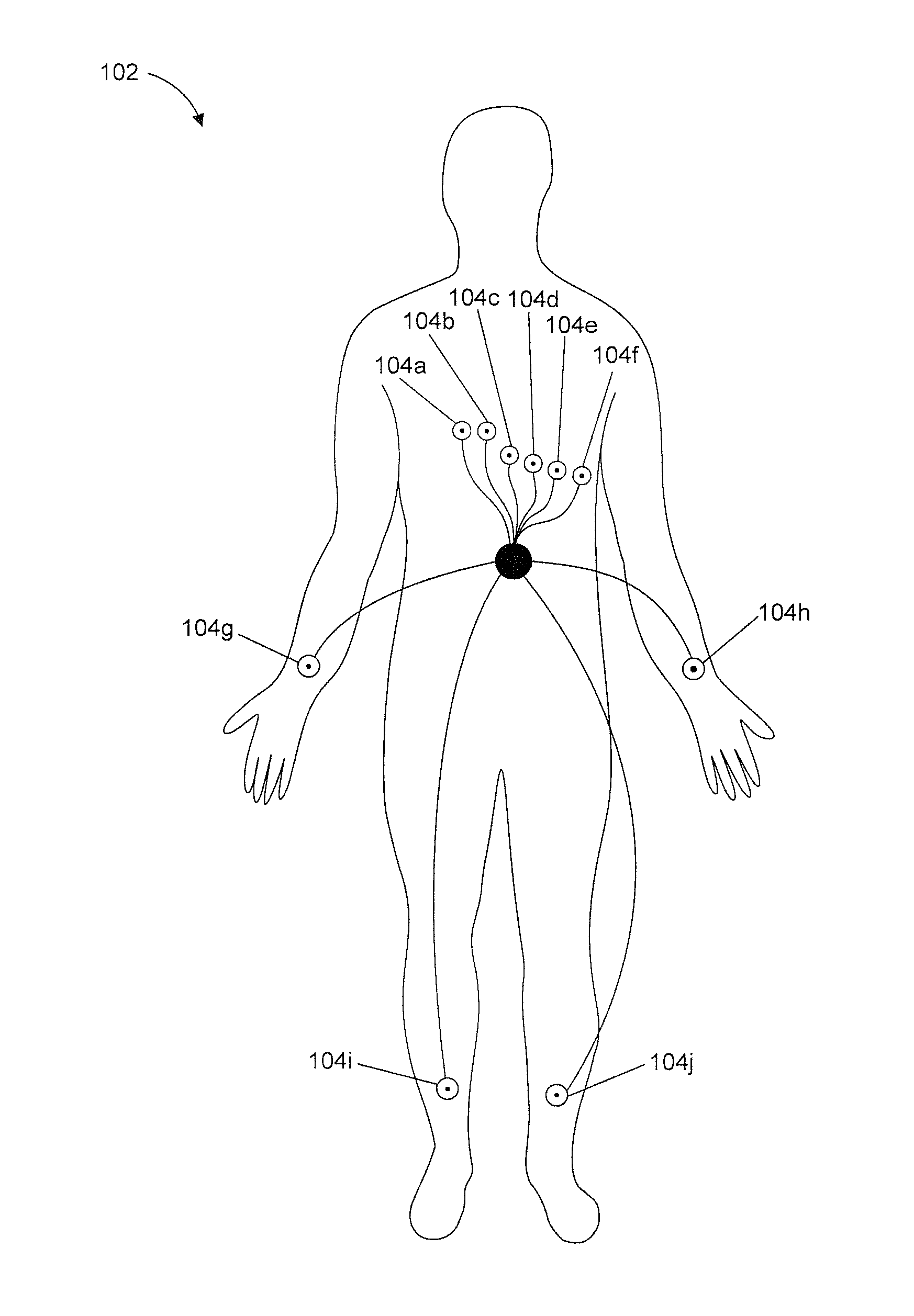
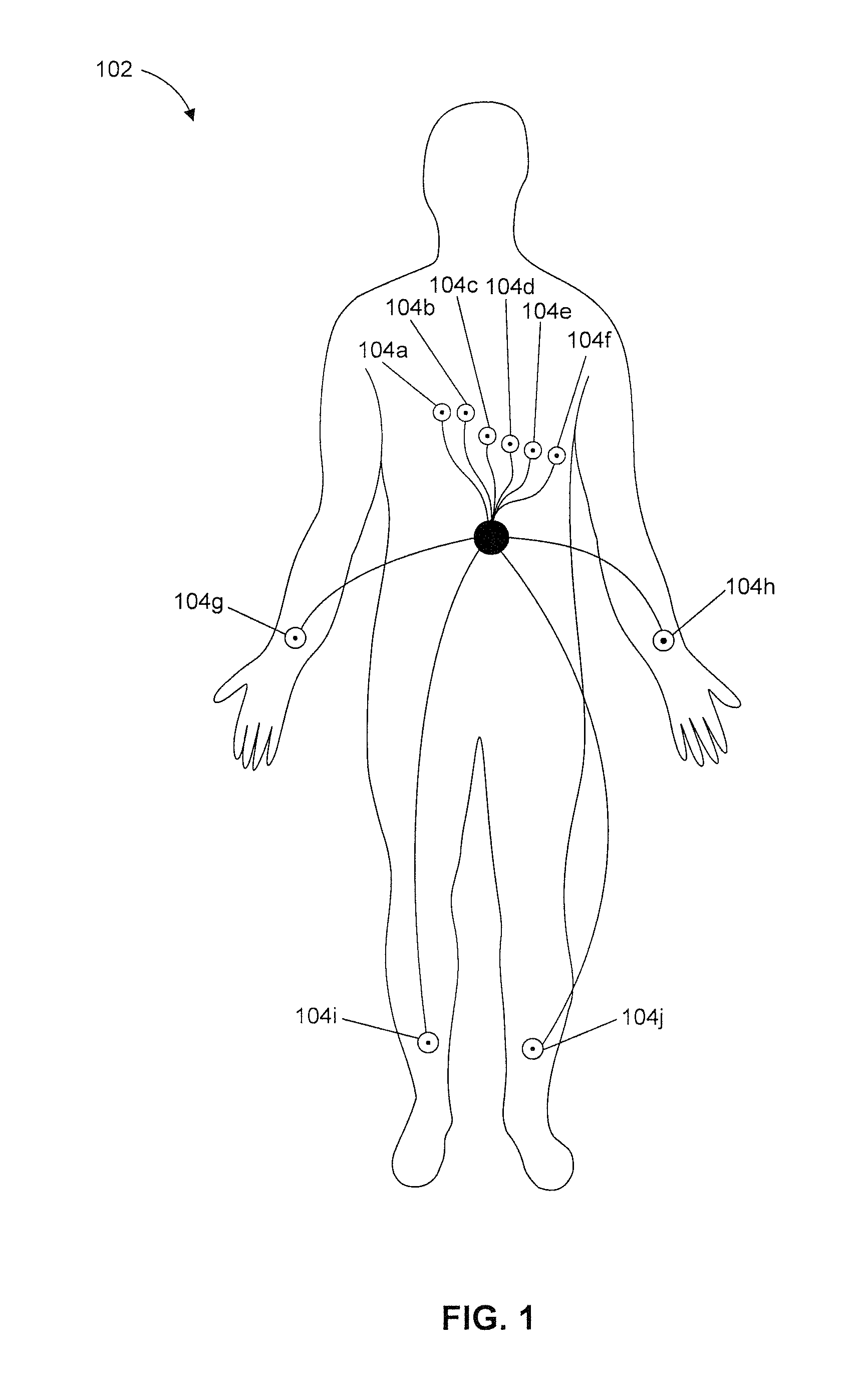
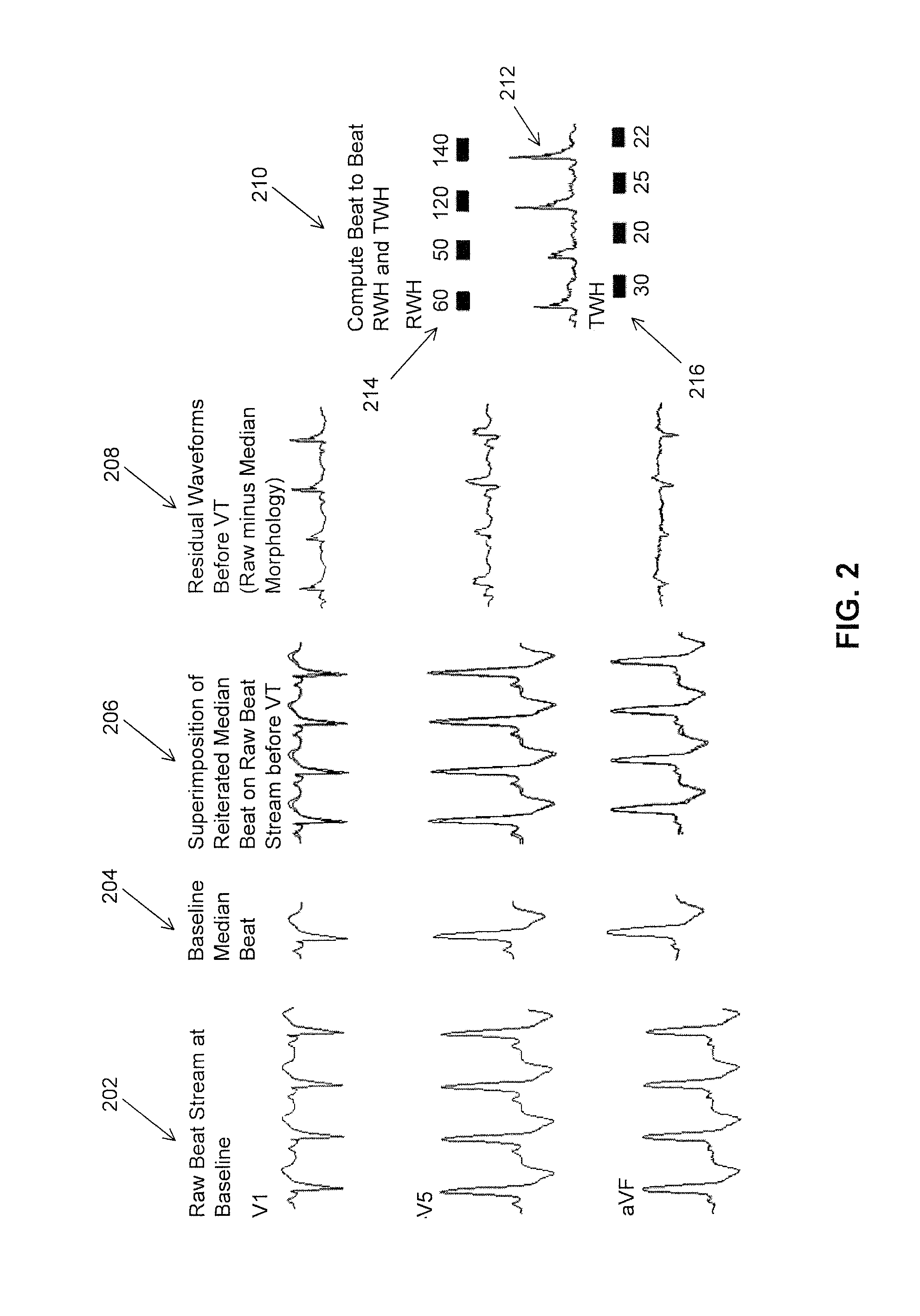
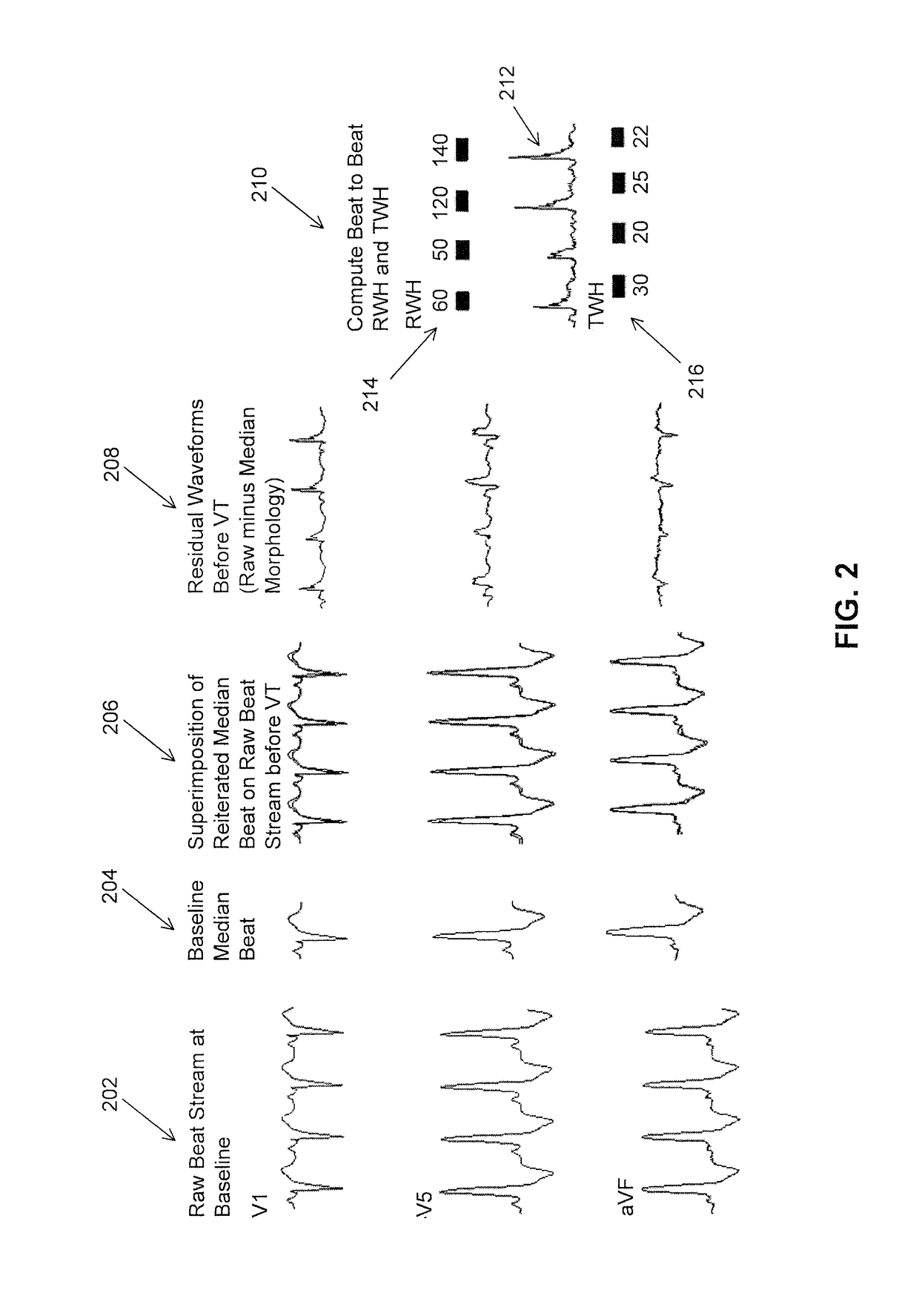
Multilead ECG template-derived residua for arrhythmia risk assessment
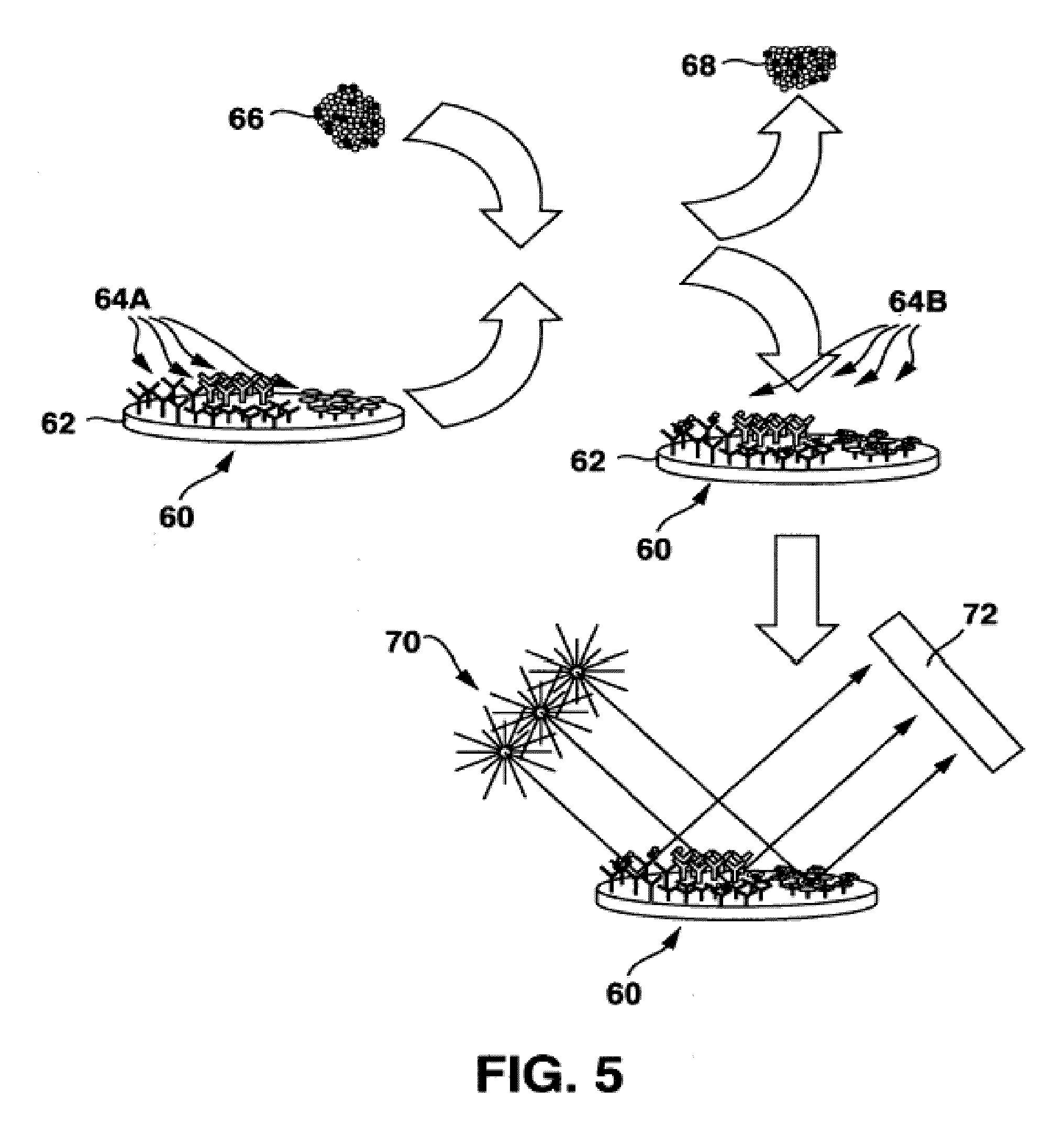
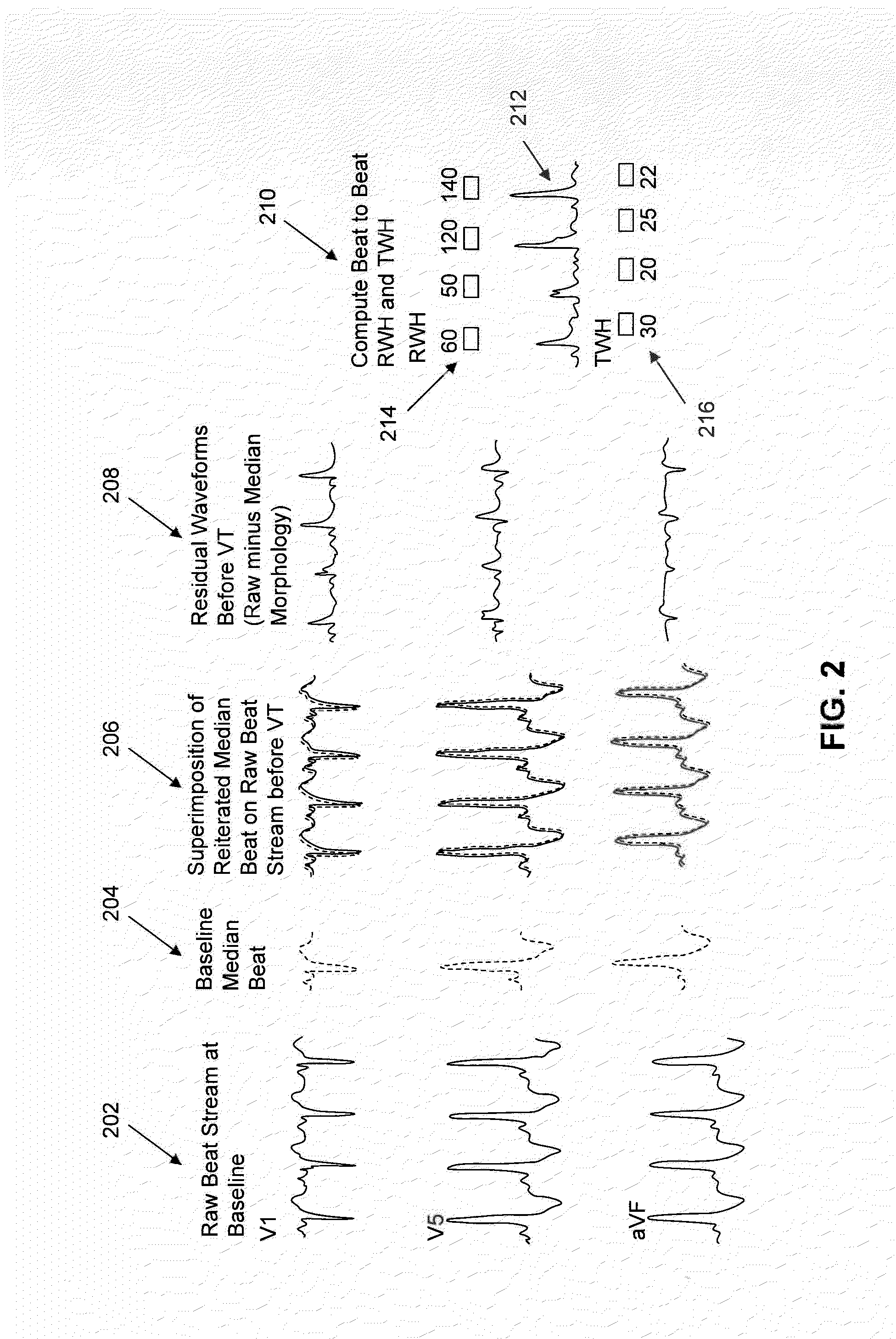
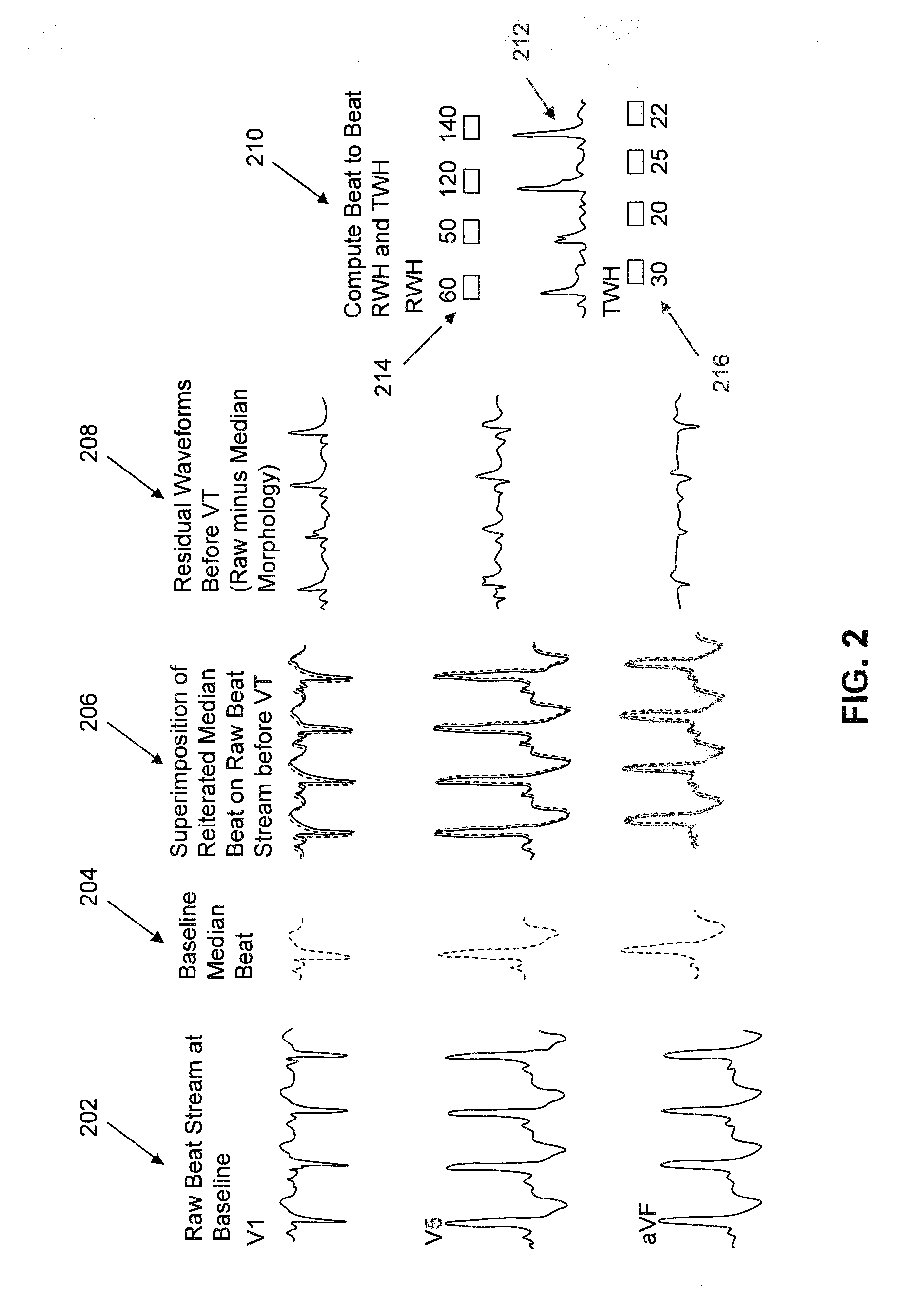
A method and system for predicting the onset of heart arrhythmias more accurately observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and the baseline measurement is subtracted from the second set of ECG signals on a beat-to-beat basis. Afterwards, a residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the subtraction. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Methods and systems for inhibiting arrhythmia
InactiveUS20050182071A1Reduce in quantityWidely distributedOrganic active ingredientsArrhythmic riskIntravascular catheter
Methods and systems for treating patients suffering from or at risk of cardiac arrhythmias rely on the injection of amiodarone and other class III anti-arrhythmic drugs into the perivascular space surrounding a cardiac blood vessel. Injection may be achieved using intravascular catheters which advance needles radially outward from a blood vessel lumen or by transmyocardial injection from an epicardial surface of the heart.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
Identifying patients at risk for life threatening arrhythmias
InactiveUS20050266576A1Increased and decreased concentrationDisease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringIntensive care medicineArrhythmic risk
The invention is a method for identifying proteins associated with sudden cardiac death (SCD) and for assessing a patient's risk of SCD by determining the amount of one or more SCD-associated proteins in the patient. Typically, the patient submits a sample, such as a blood sample, which is tested for one or more SCD-associated proteins. Based upon the results of the tests, the patient's risk of SCD may be assessed.
Owner:YOUGENE
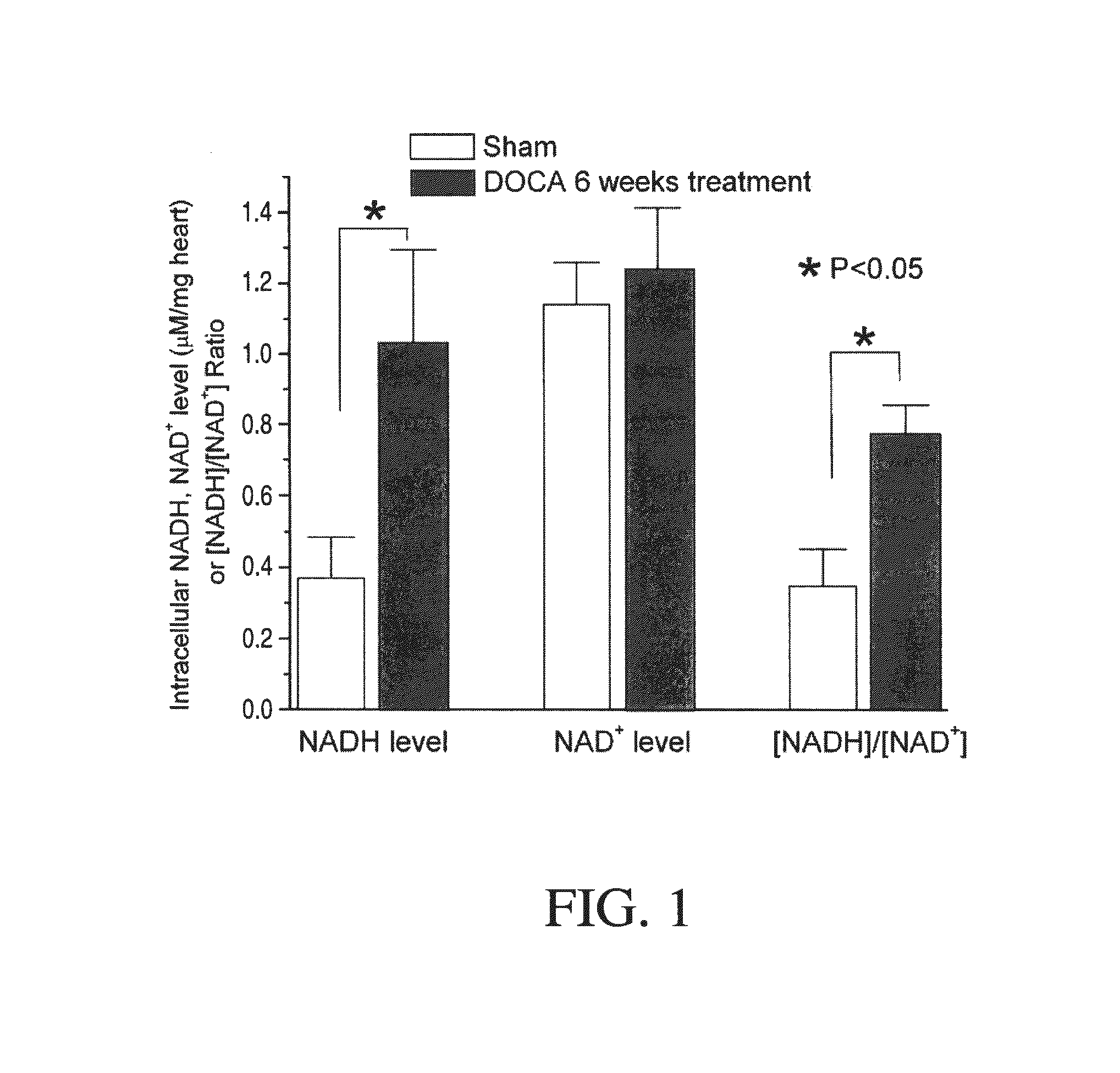
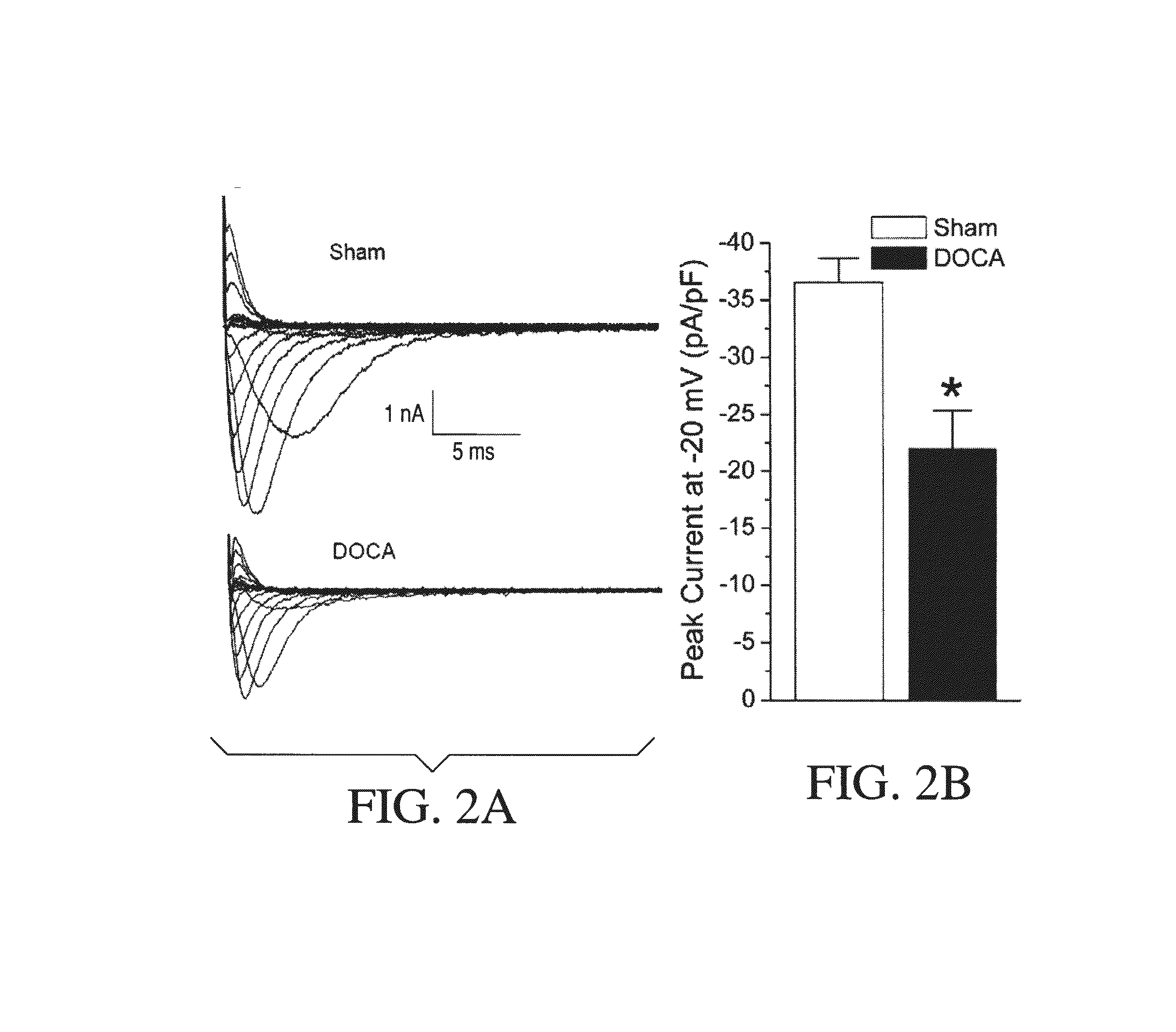
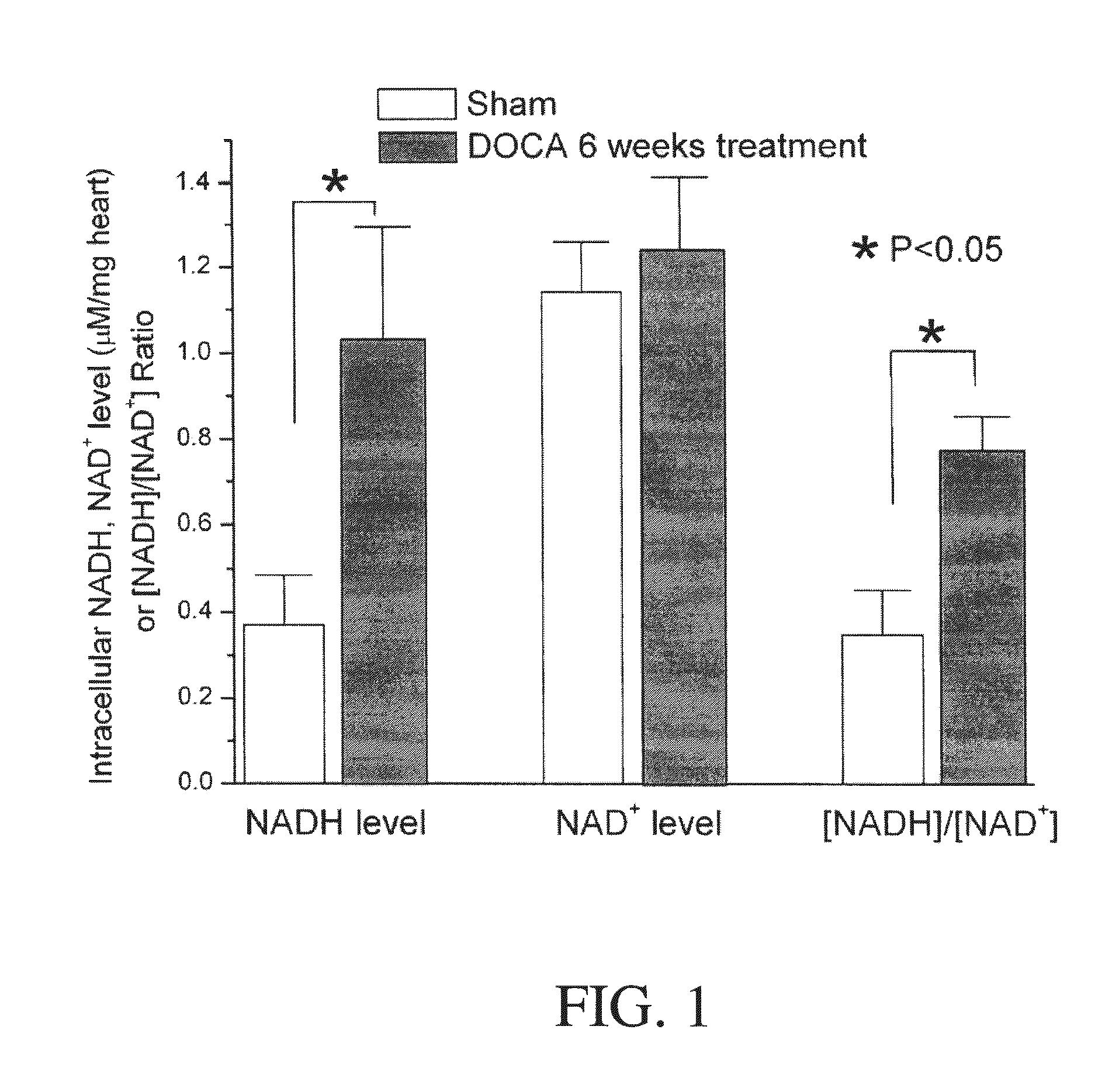
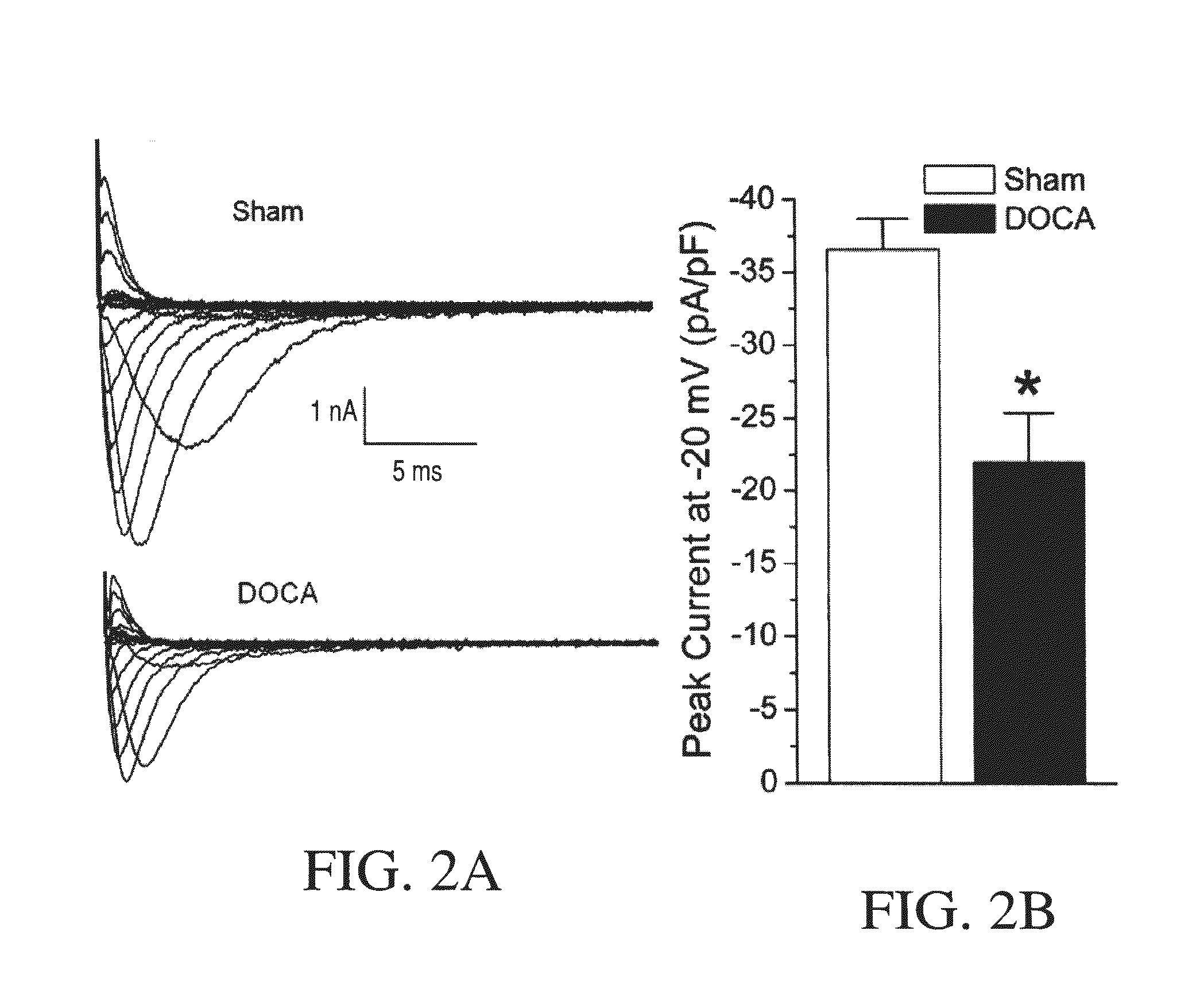
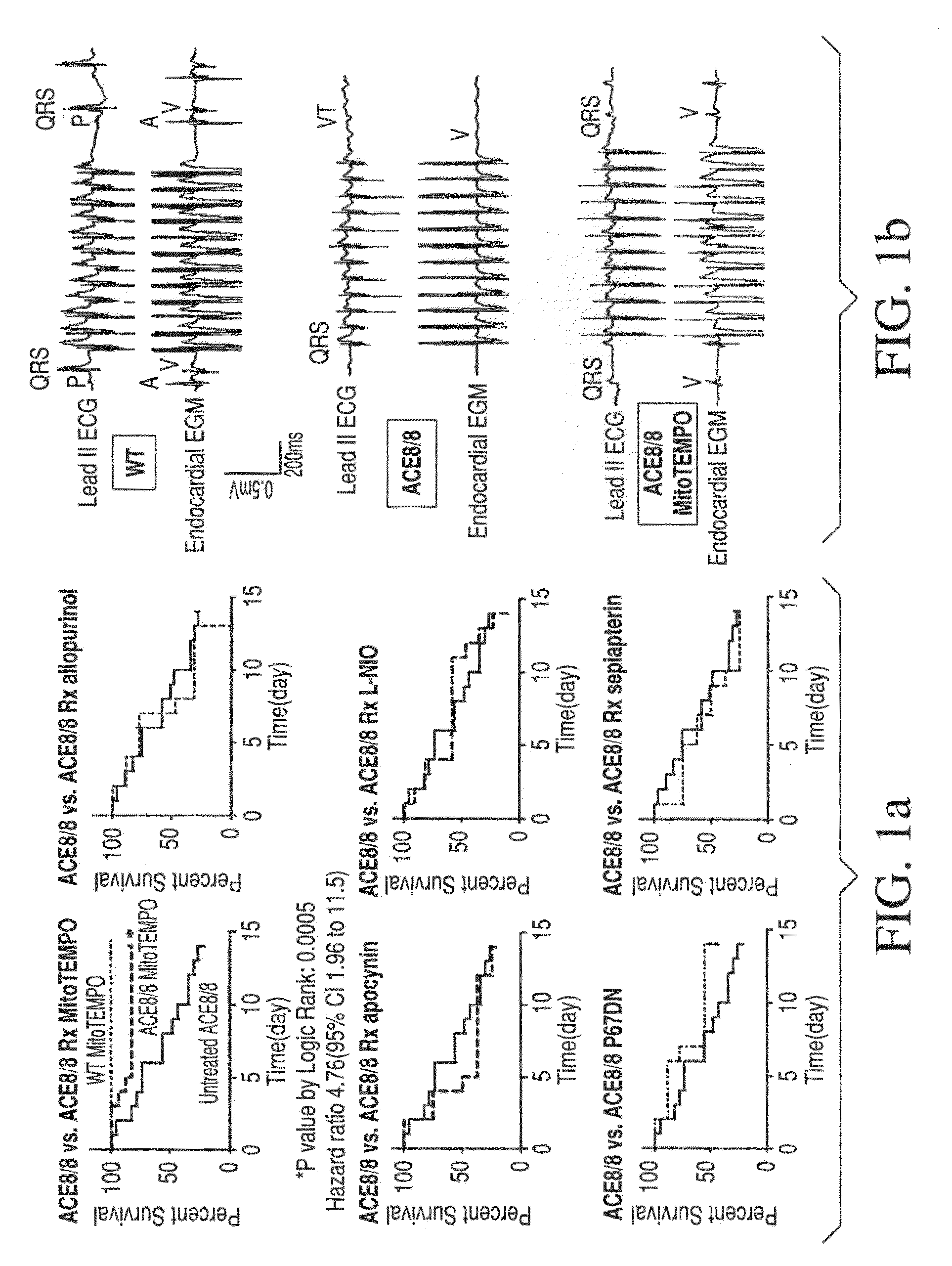
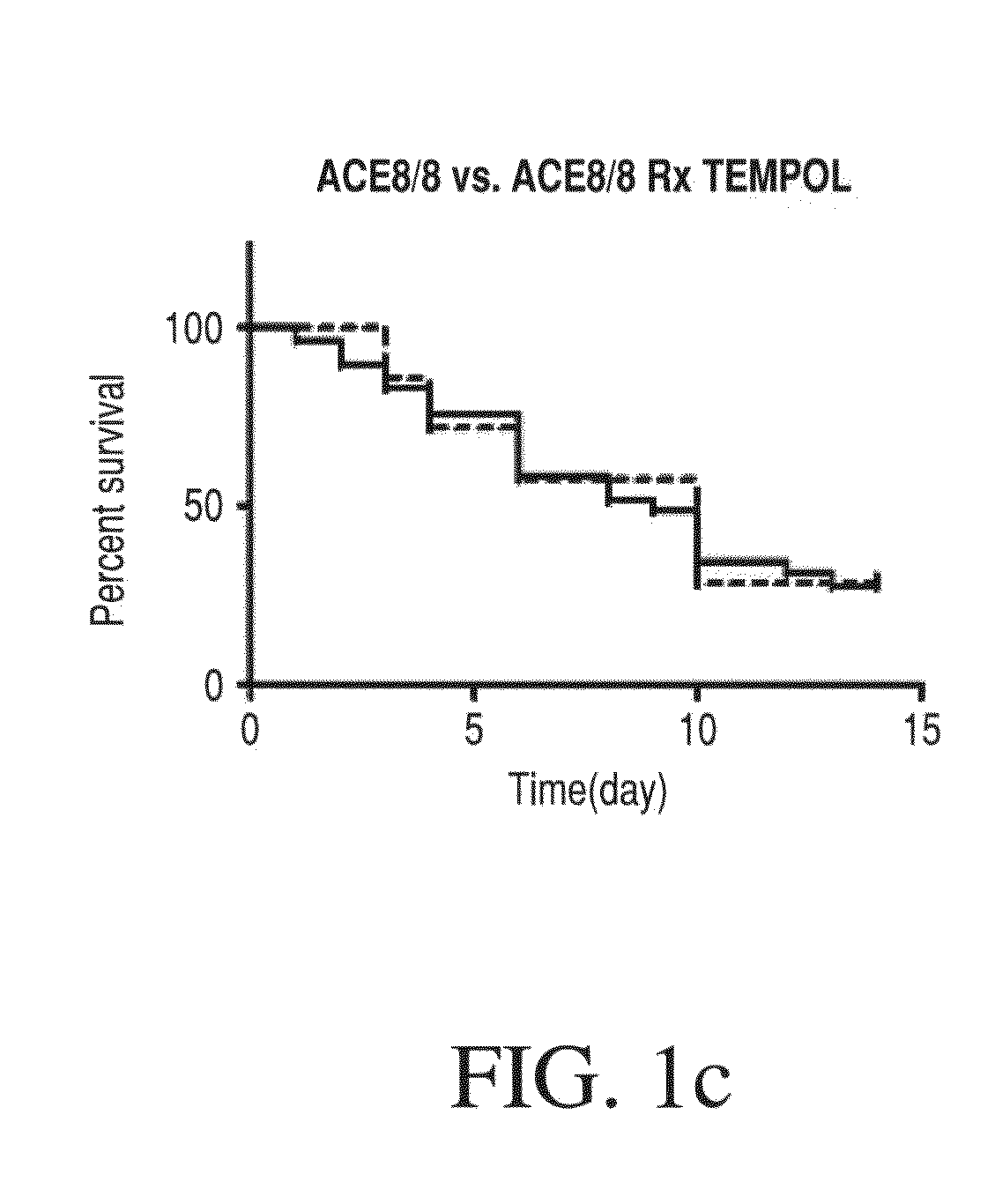
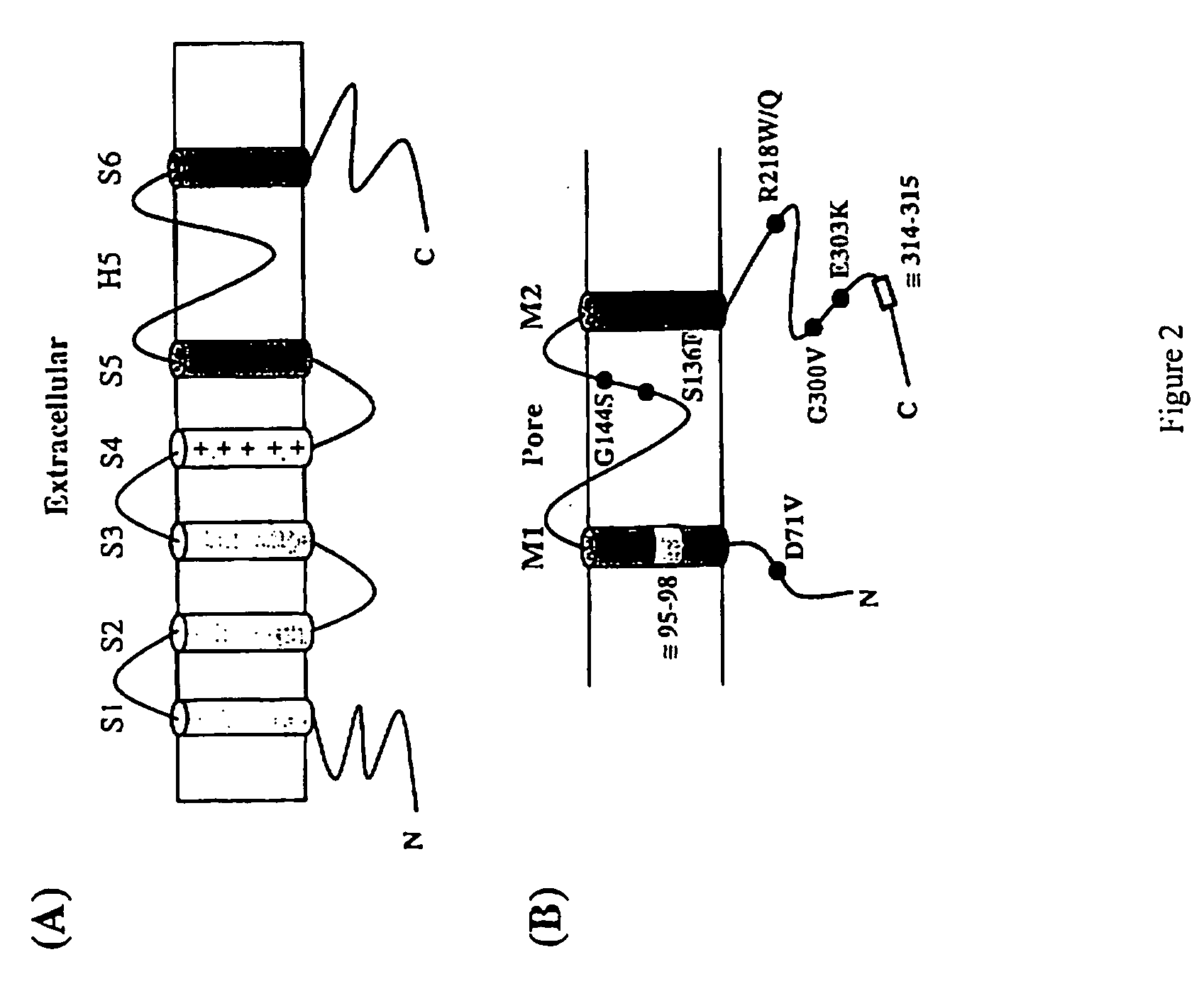
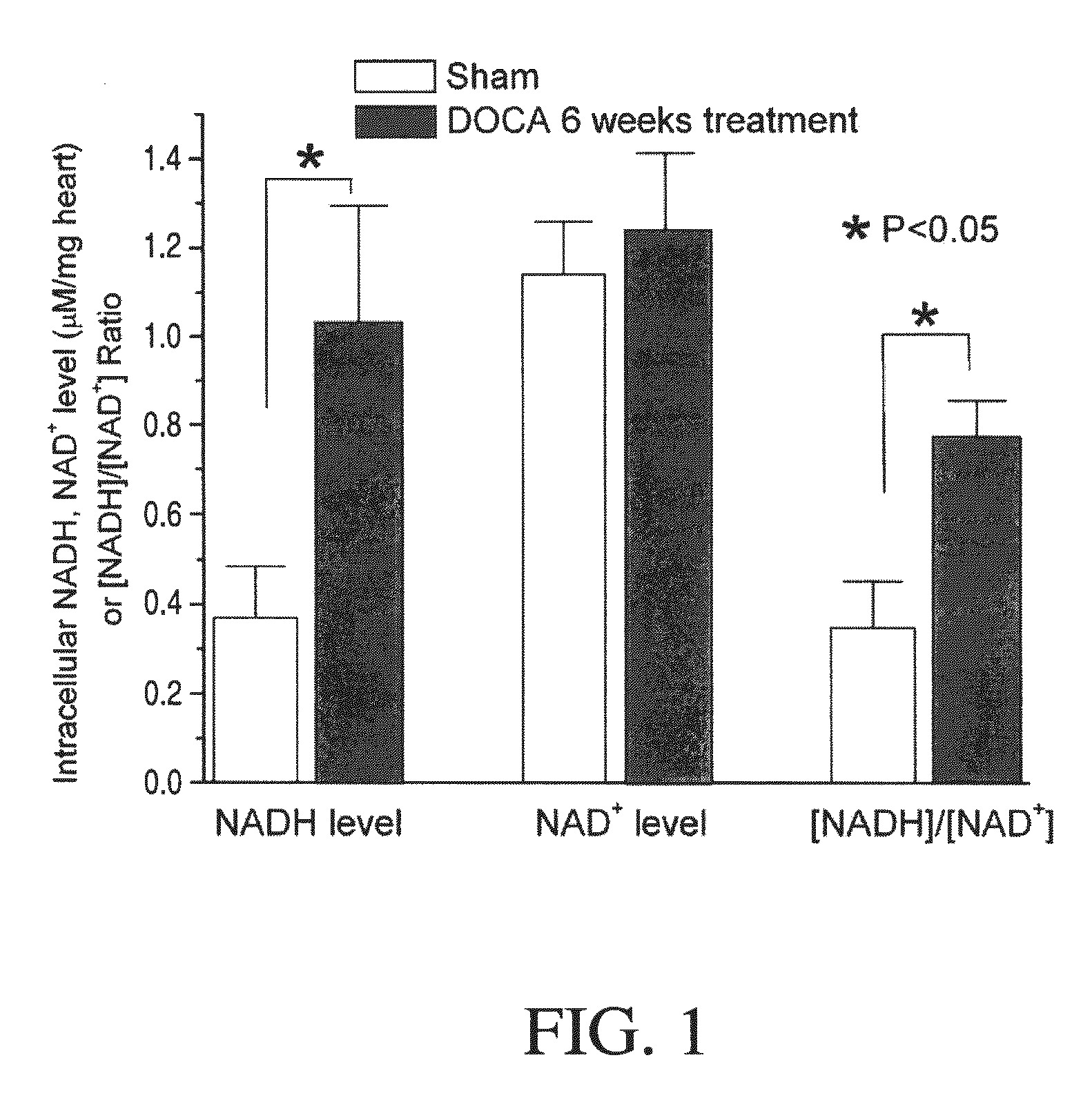
Method for Ameliorating or Preventing Arrhythmic Risk Associated with Cardiomyopathy by Improving Conduction Velocity
A method for reducing arrhythmic risk associated with cardiomyopathy by improving conduction velocity, includes administering a composition containing NAD+ or a mitochondrial targeted antioxidant to an individual or person in need thereof.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
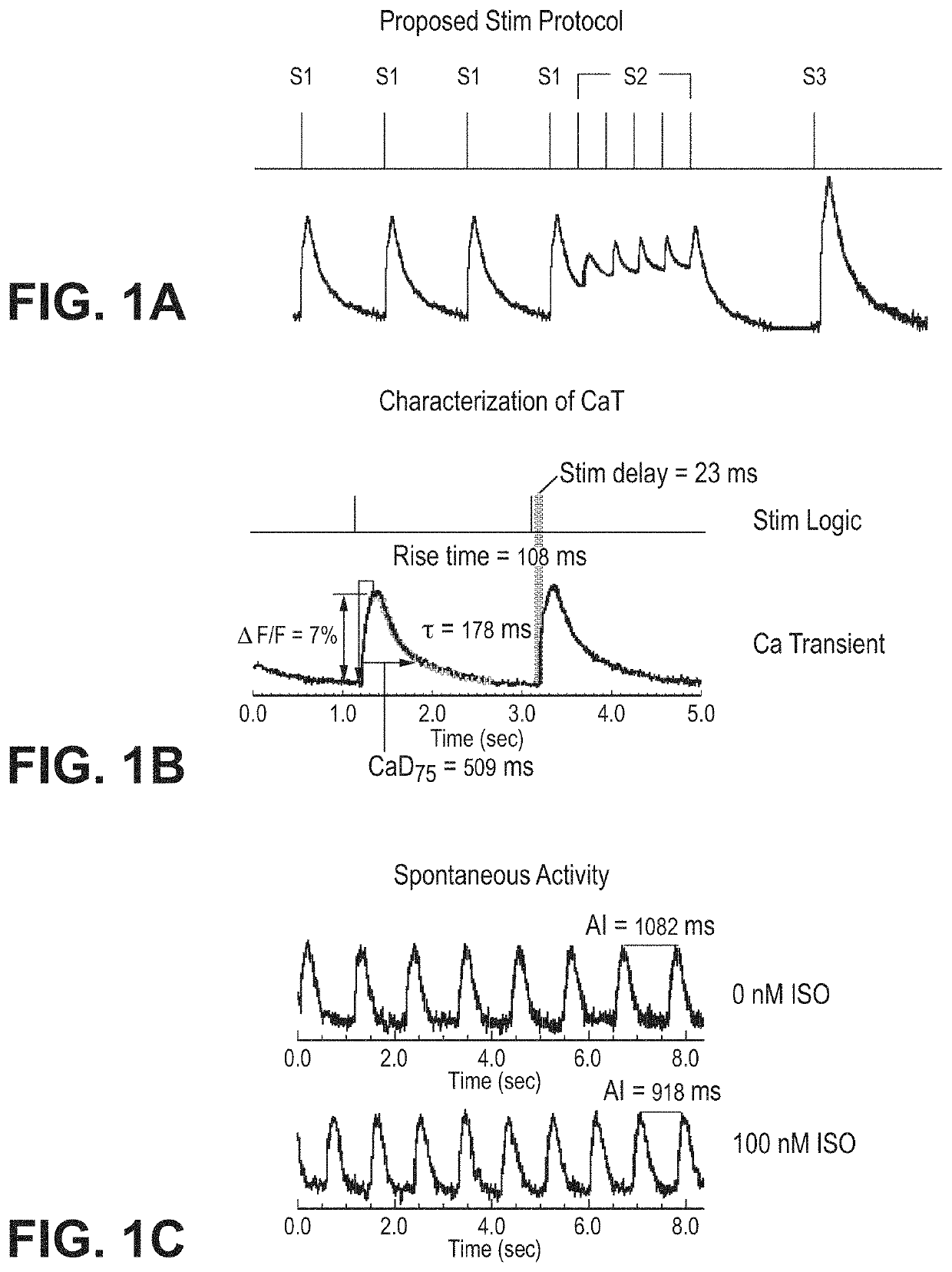
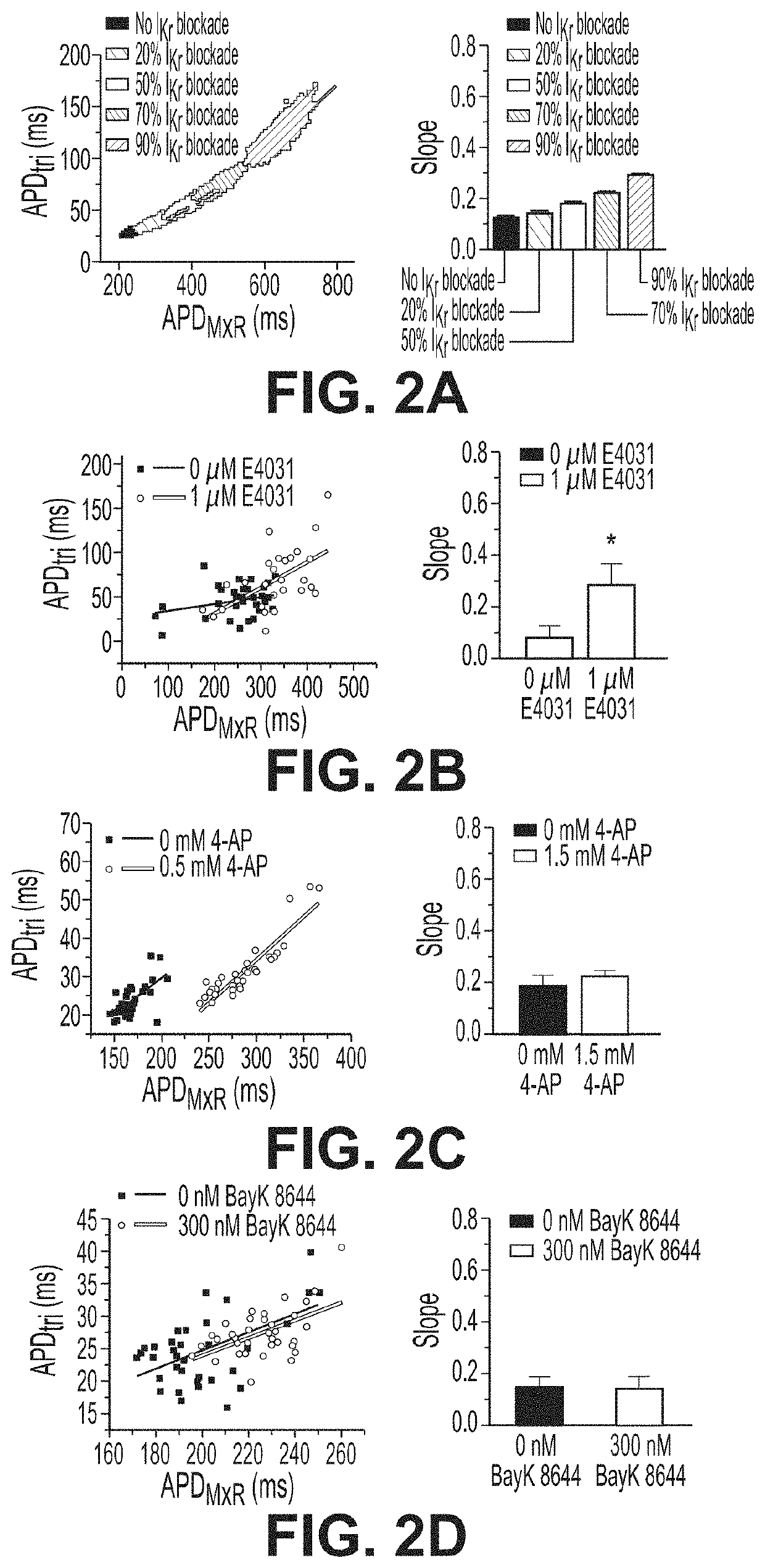
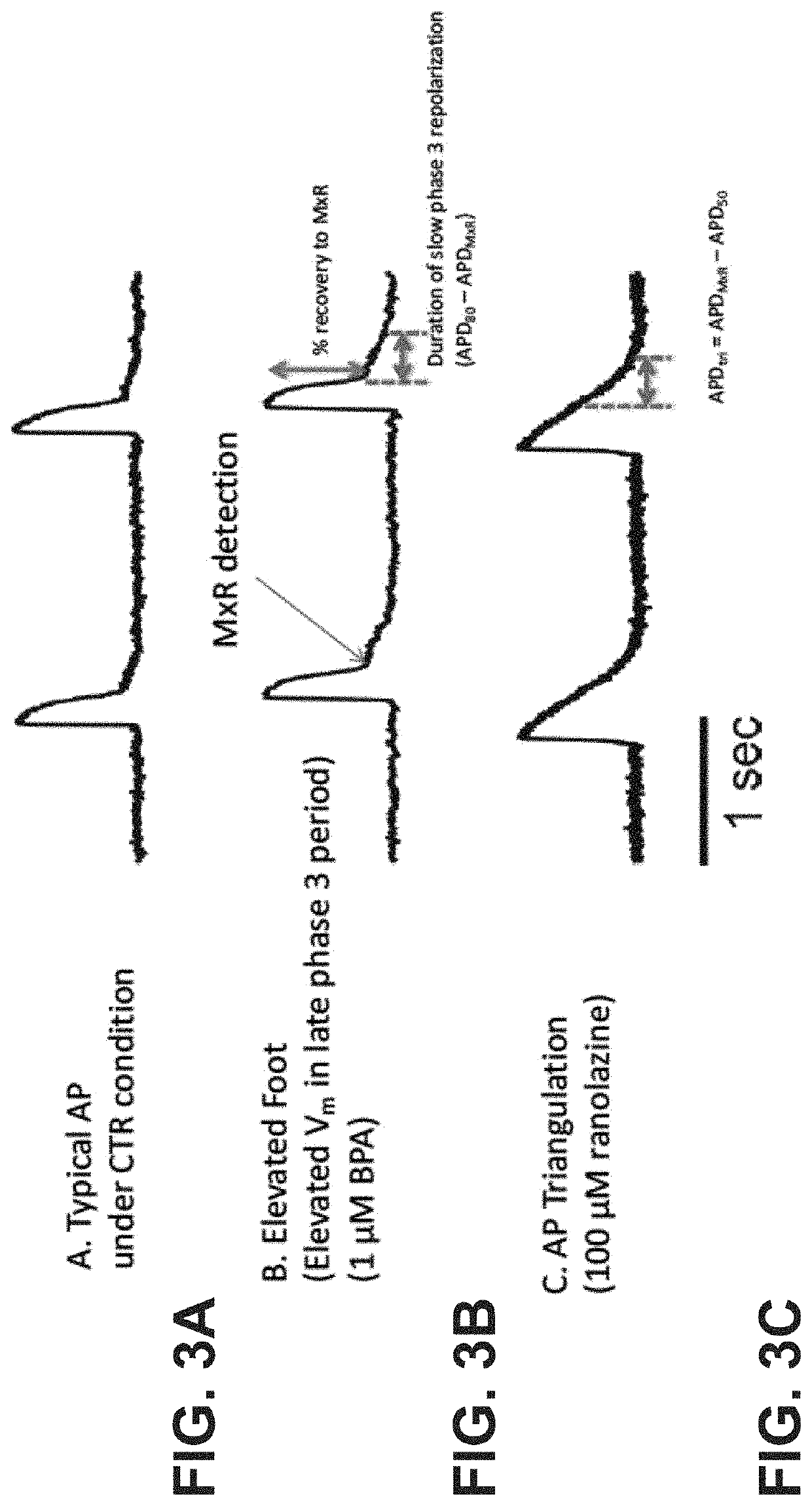
Methods for screening compounds for proarrhythmic risk and antiarrhythmic efficacy
Methods for screening compounds for their potential to induce or inhibit a cardiac arrhythmia are disclosed. The methods comprise determining the ratio of the time constant (τ) of ICa,L recovery in tissue expressing the L-type calcium channel or any subunit or combination thereof of the L-type calcium channel treated with a test compound to the ventricular repolarization time of cardiac tissue treated with a test compound. The methods further comprise determining an arrhythmic risk score for a specified dose of a test compound.
Owner:MAIN LINE HEALTH HEART CENT
Marker for arrhythmia risk
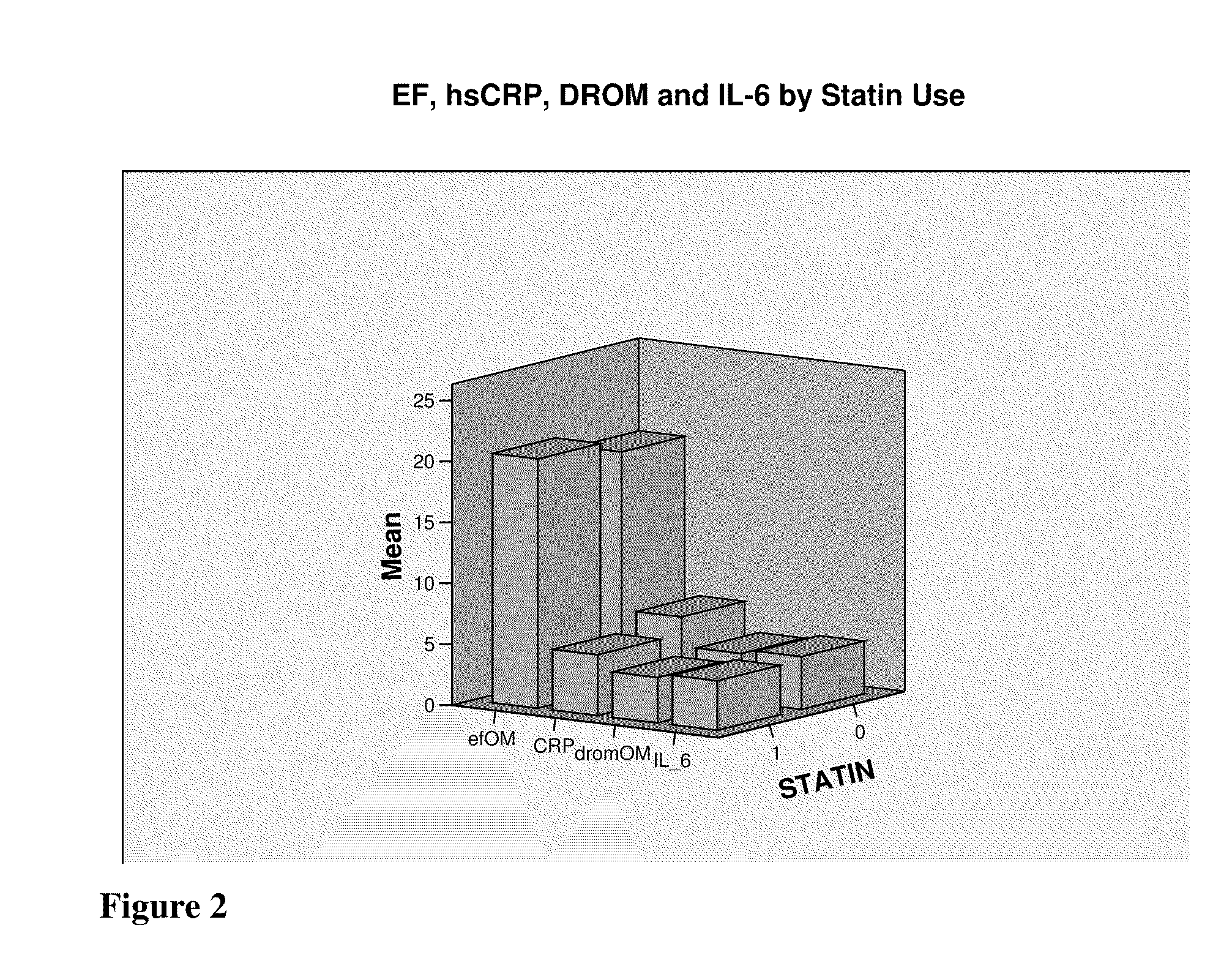
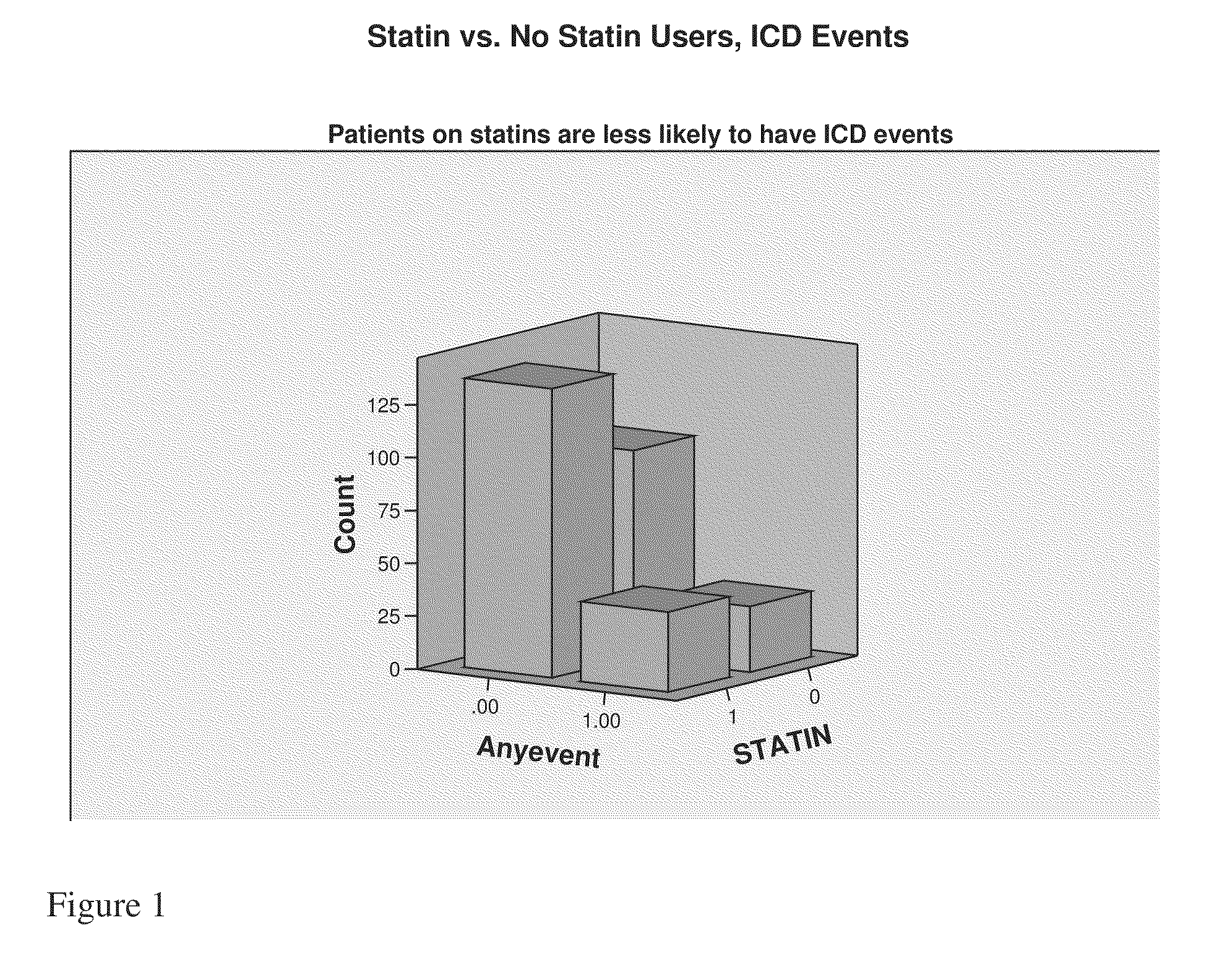
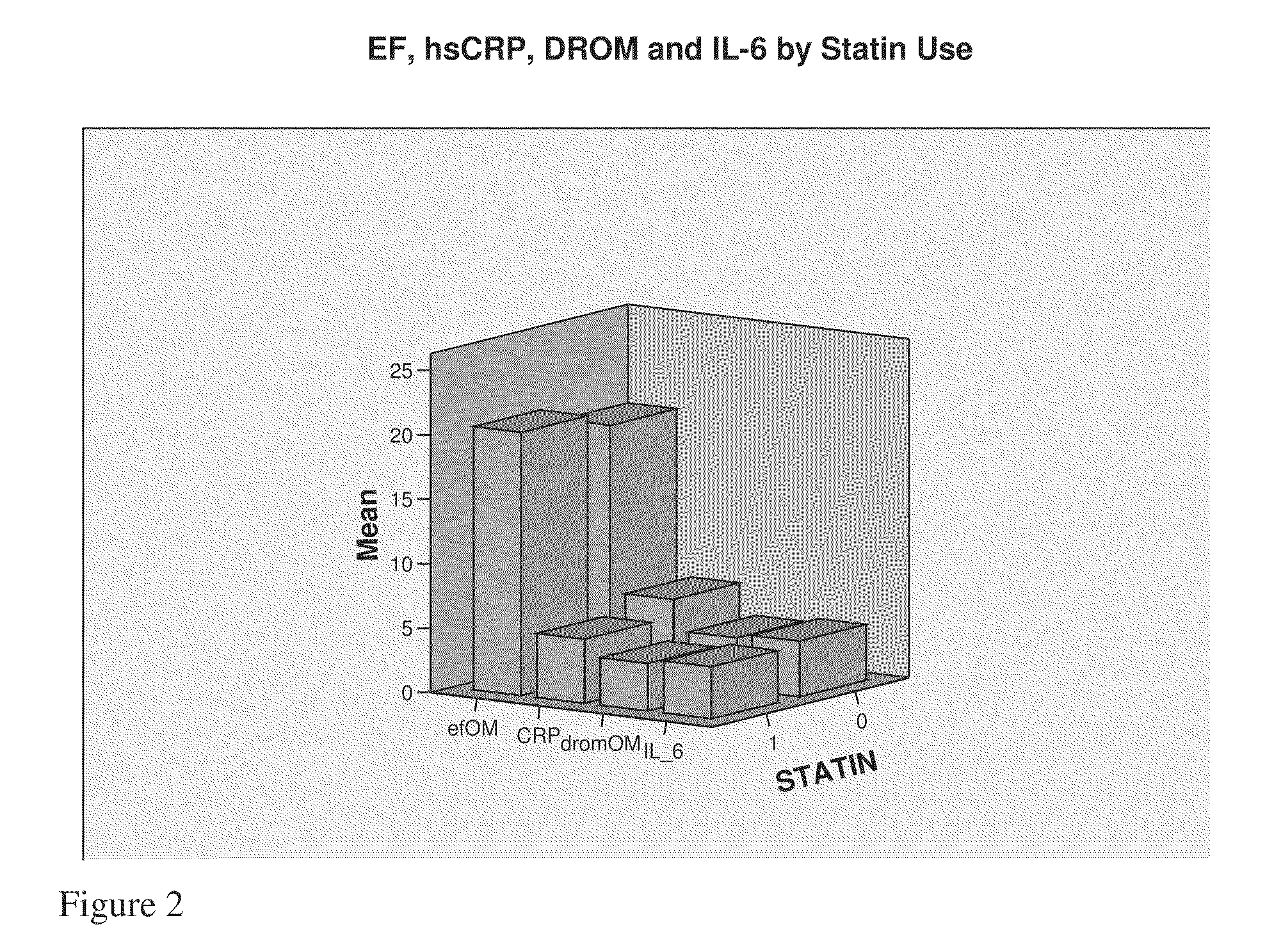
InactiveUS20100233727A1Prevent and reduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisVentricular dysrhythmiaArrhythmic risk
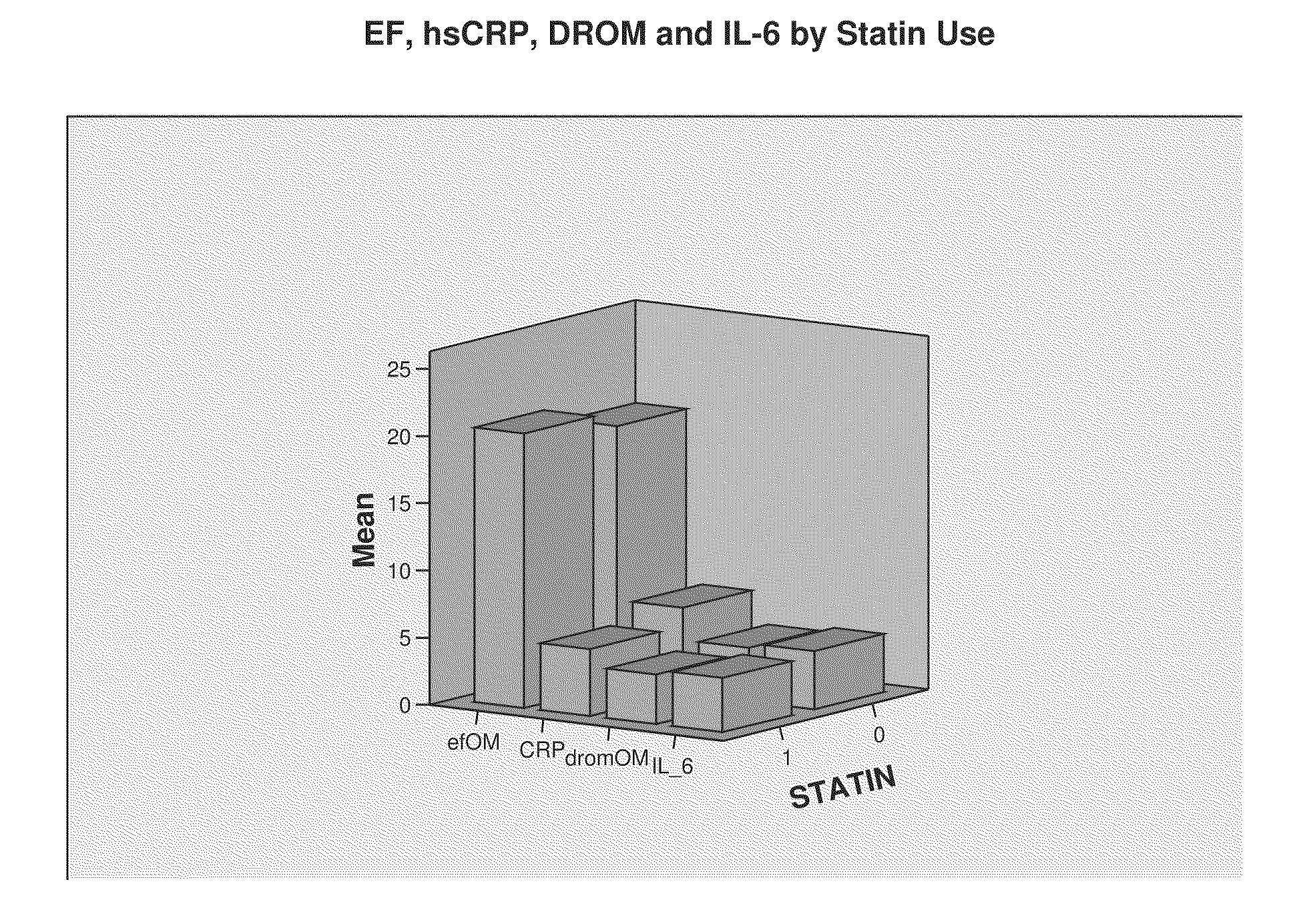
The present invention relates to markers and methods for determining risk of ventricular arrhythmia in an African American or woman patient. By using the markers of the present invention, individual with high risk of ventricular arrhythmia can properly be detected and treated. The present inventors have discovered that, in African American and women, IL-6 and / or DROMs and / or CRP have strongly positive correlation with the risk of ventricular arrhythmia.
Owner:DUDLEY JR SAMUEL C +1
Multilead ECG template-derived residua for arrhythmia risk assessment
A method and system for predicting the onset of heart arrhythmias more accurately observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and the baseline measurement is subtracted from the second set of ECG signals on a beat-to-beat basis. Afterwards, a residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the subtraction. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
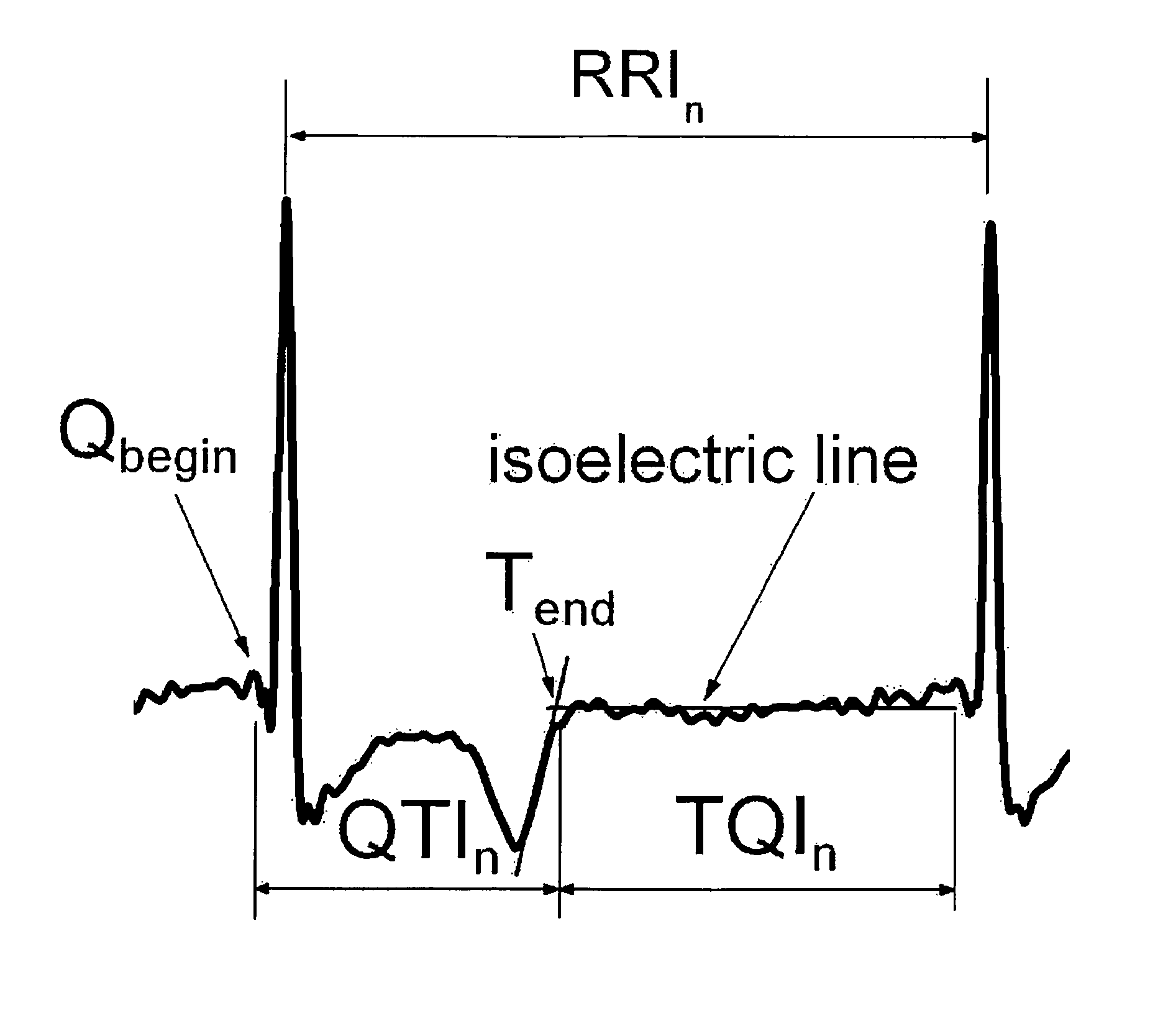
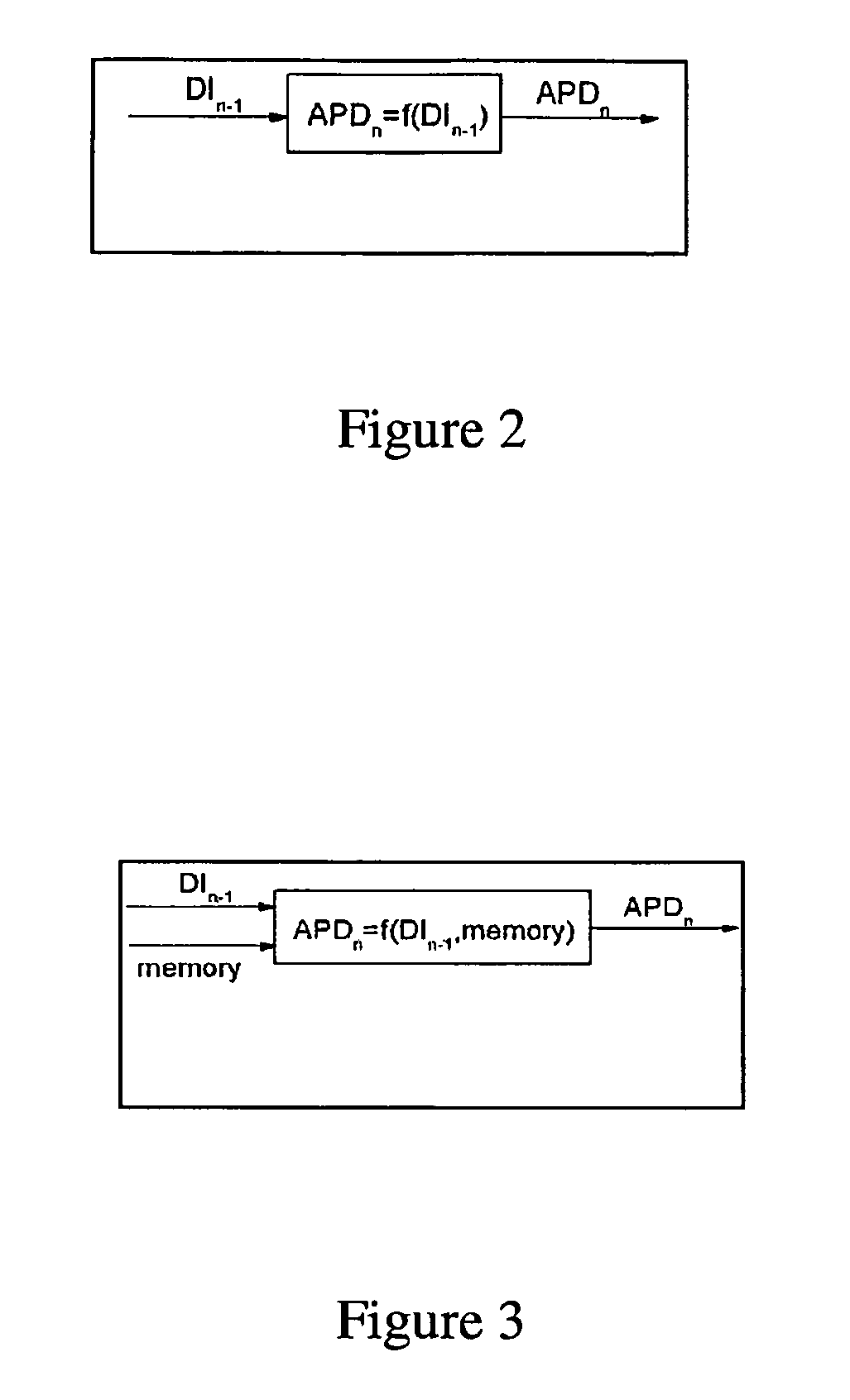
Novel methodology for arrhythmia risk stratification by assessing qt interval instability
A method of predicting ventricular arrhythmias includes receiving an electrical signal from a subject's heart for a plurality of heart beats, identifying characteristic intervals and heart beat durations of the electrical signal corresponding to each of the plurality of heart beats to provide a plurality of characteristic intervals with corresponding heart beat durations, representing dynamics of the plurality of characteristic intervals as a function of a plurality of preceding characteristic intervals and durations of corresponding heart beats over a chosen period time, assessing a stability of the function over the chosen period of time, and predicting ventricular arrhythmias based on detected instabilities in the dynamics of the characteristic intervals.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High Throughput Arrhythmia Risk Assessment Using Multilead Residua Signals
A method and system for high-throughput prediction of the onset of heart arrhythmias observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and a second baseline measurement is generated from the second set of ECG signals. A residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the baseline measurement and the second baseline measurement. The residuum signals are averaged across the leads. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals and the averaged residuum signal.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method for Ameliorating or Preventing Arrhythmic Risk Associated with Cardiomyopathy
A method for reducing arrhythmic risk associated with cardiomyopathy includes administering a composition containing NAD+ or a mitochondrial targeted antioxidant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
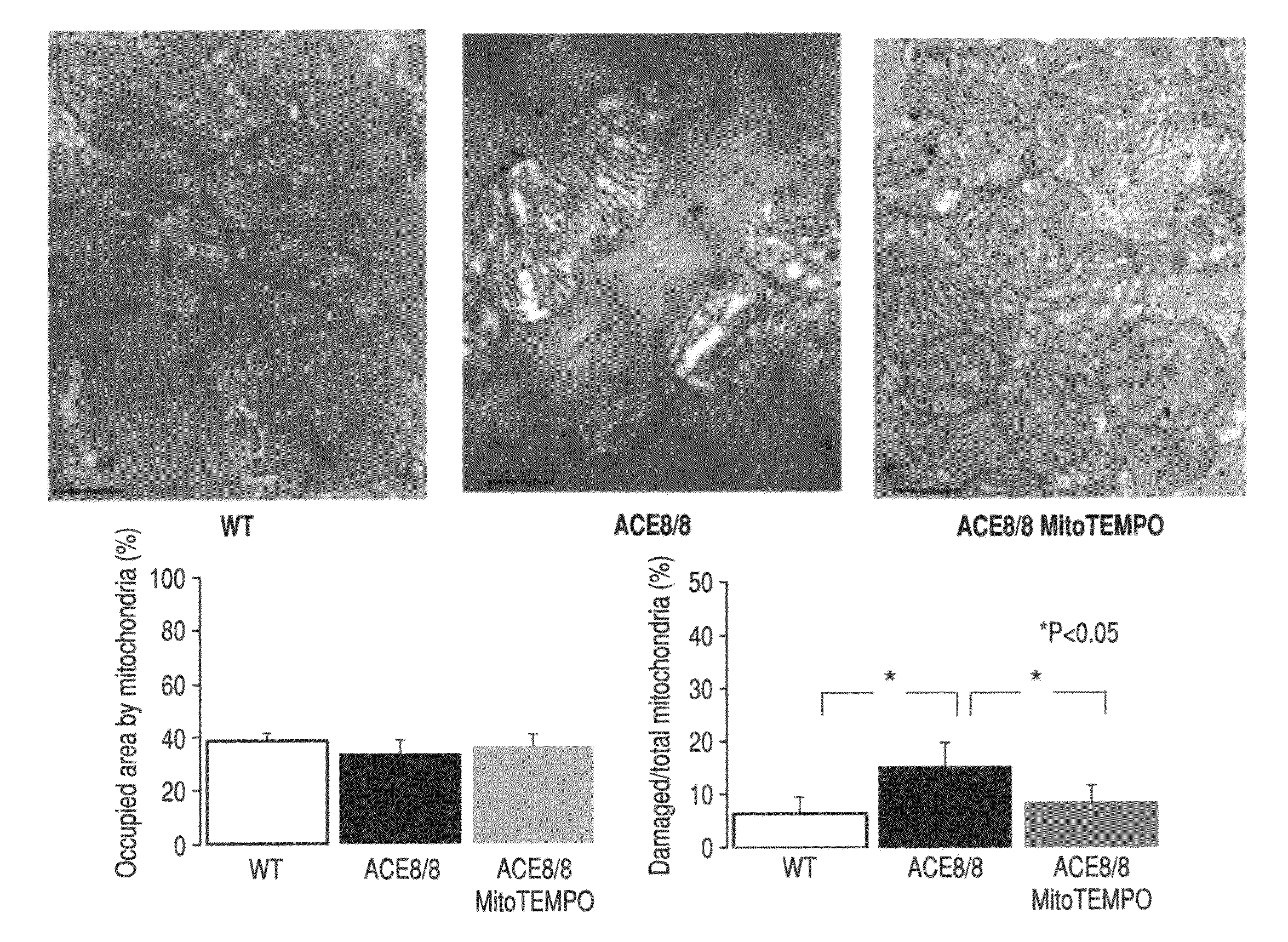
Method for modulating or controlling connexin 43(Cx43) level of a cell and reducing arrhythmic risk
A method of modulating or controlling connexin 43 (Cx43) level of a cell includes inducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in the cell.
Owner:VETERANS AFFAIRS U S DEPT OF +1
Methodology for arrhythmia risk stratification by assessing QT interval instability
A method of predicting ventricular arrhythmias includes receiving an electrical signal from a subject's heart for a plurality of heart beats, identifying characteristic intervals and heart beat durations of the electrical signal corresponding to each of the plurality of heart beats to provide a plurality of characteristic intervals with corresponding heart beat durations, representing dynamics of the plurality of characteristic intervals as a function of a plurality of preceding characteristic intervals and durations of corresponding heart beats over a chosen period time, assessing a stability of the function over the chosen period of time, and predicting ventricular arrhythmias based on detected instabilities in the dynamics of the characteristic intervals.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
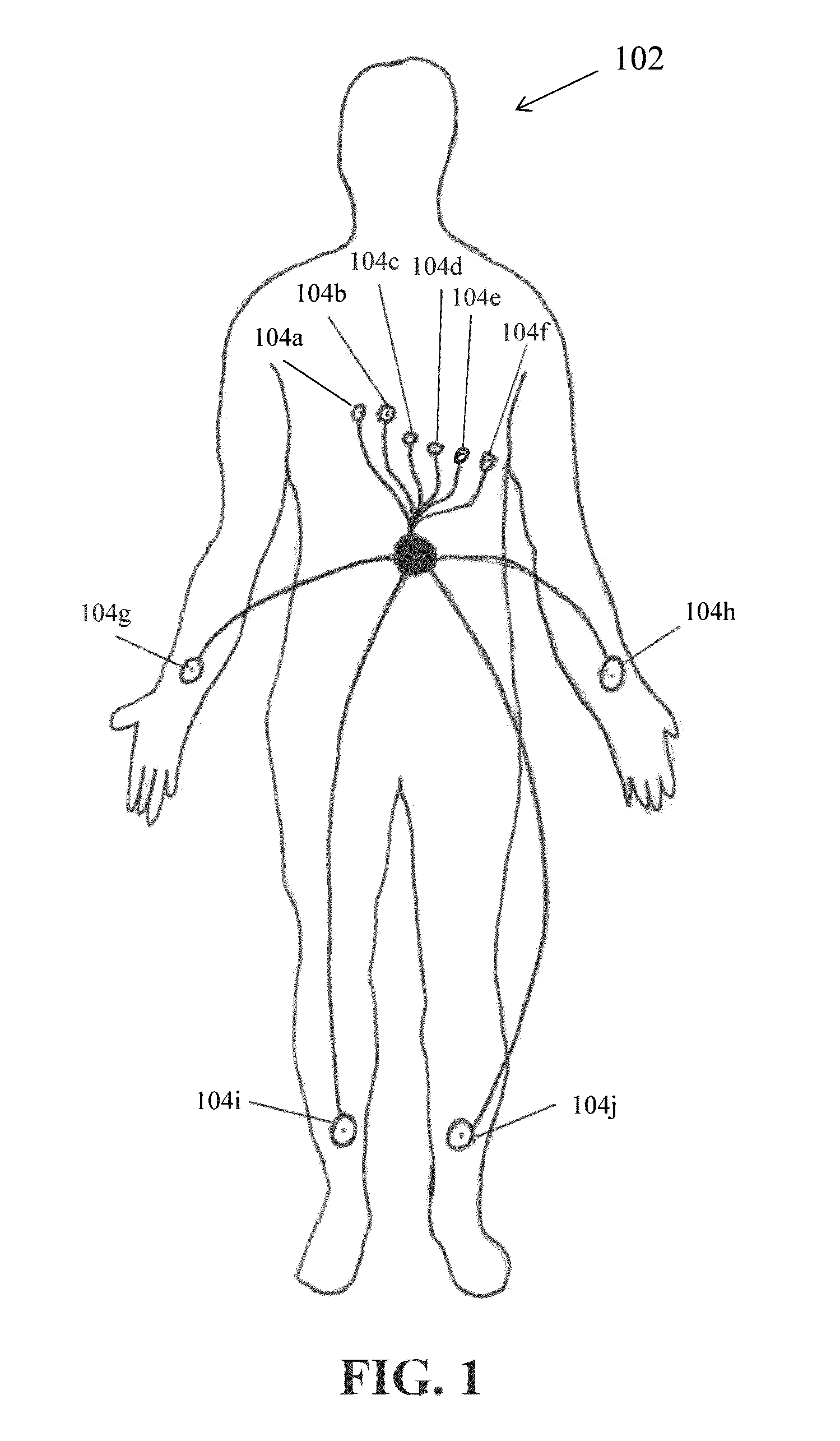
Method and device to monitor patients with kidney disease
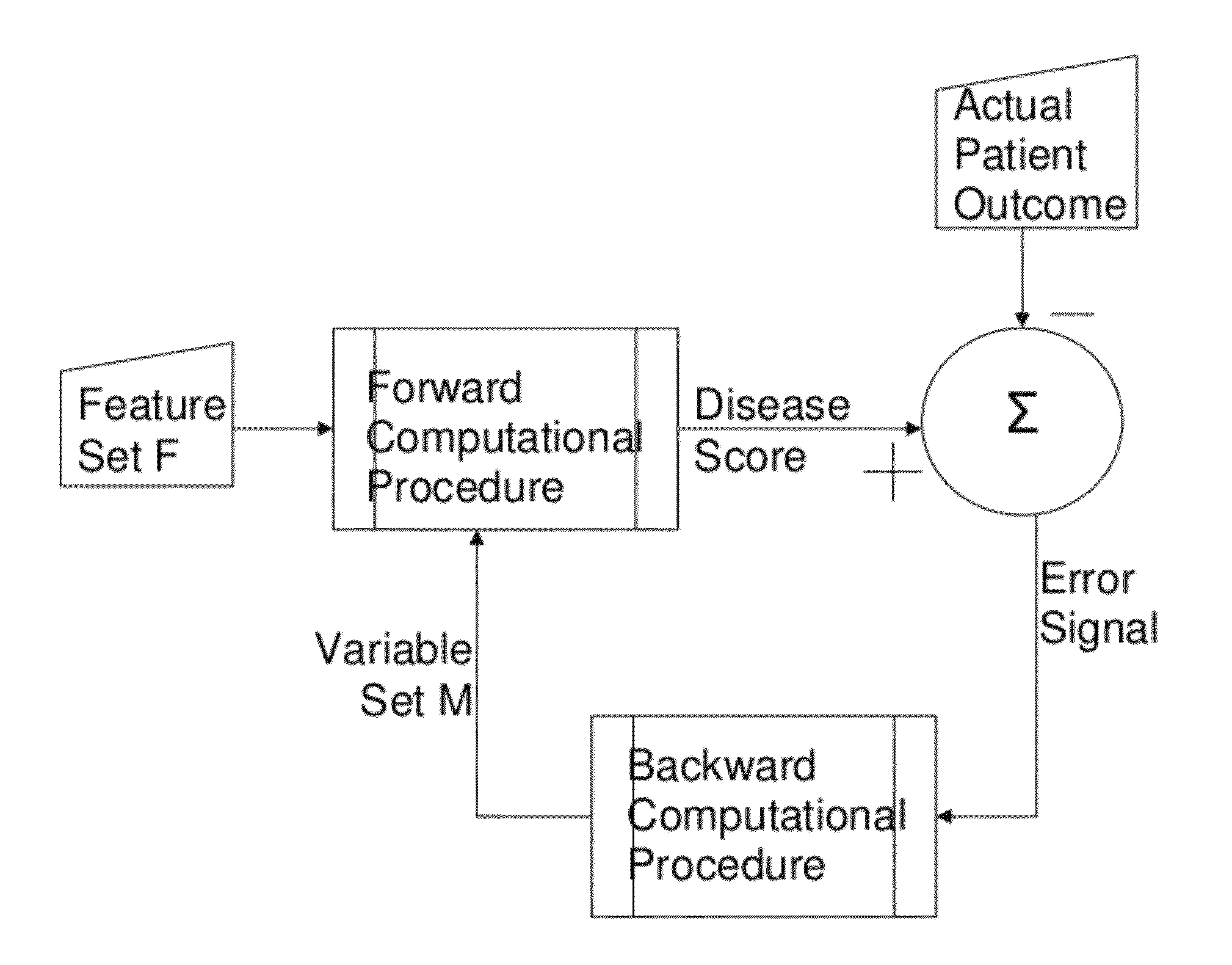
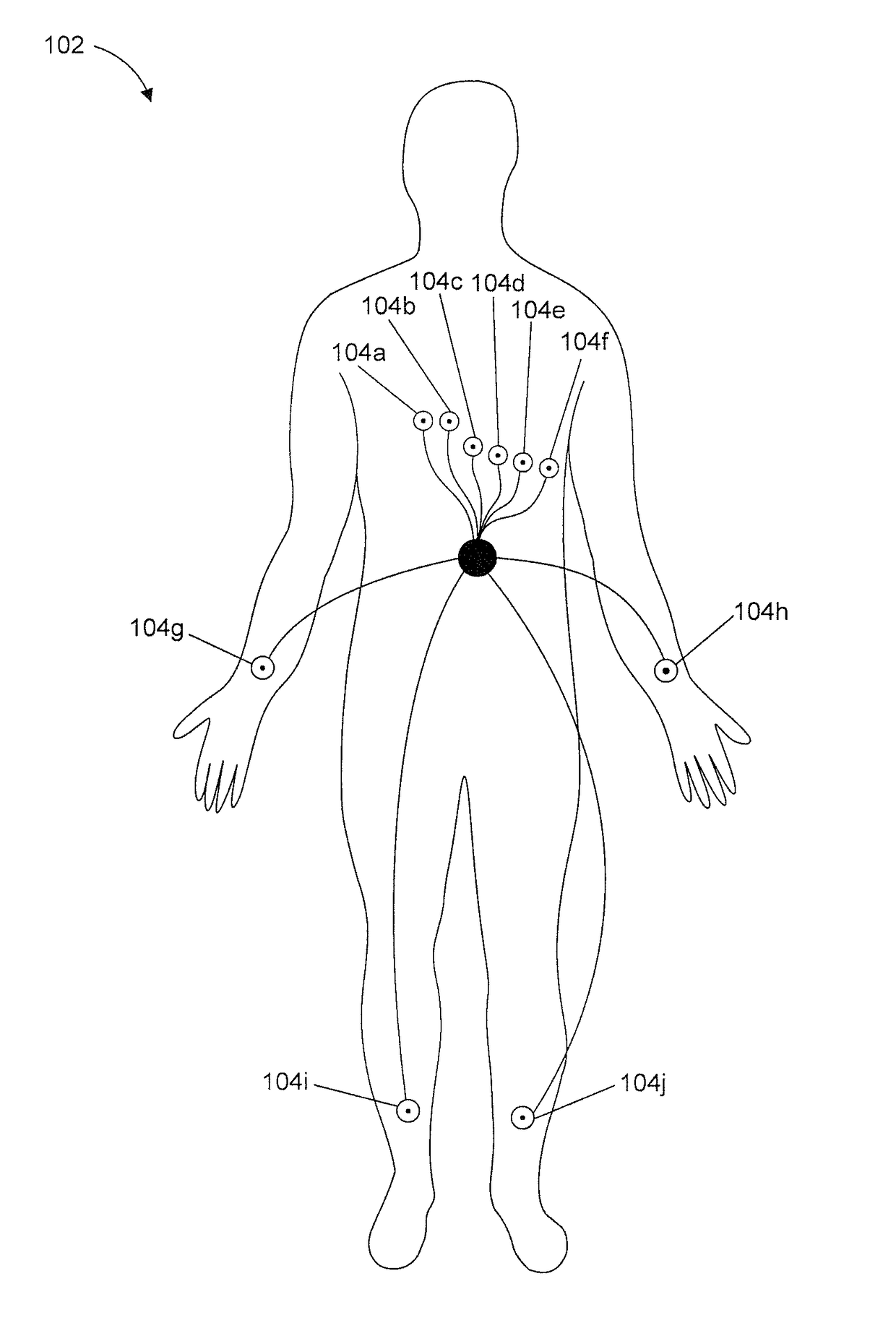
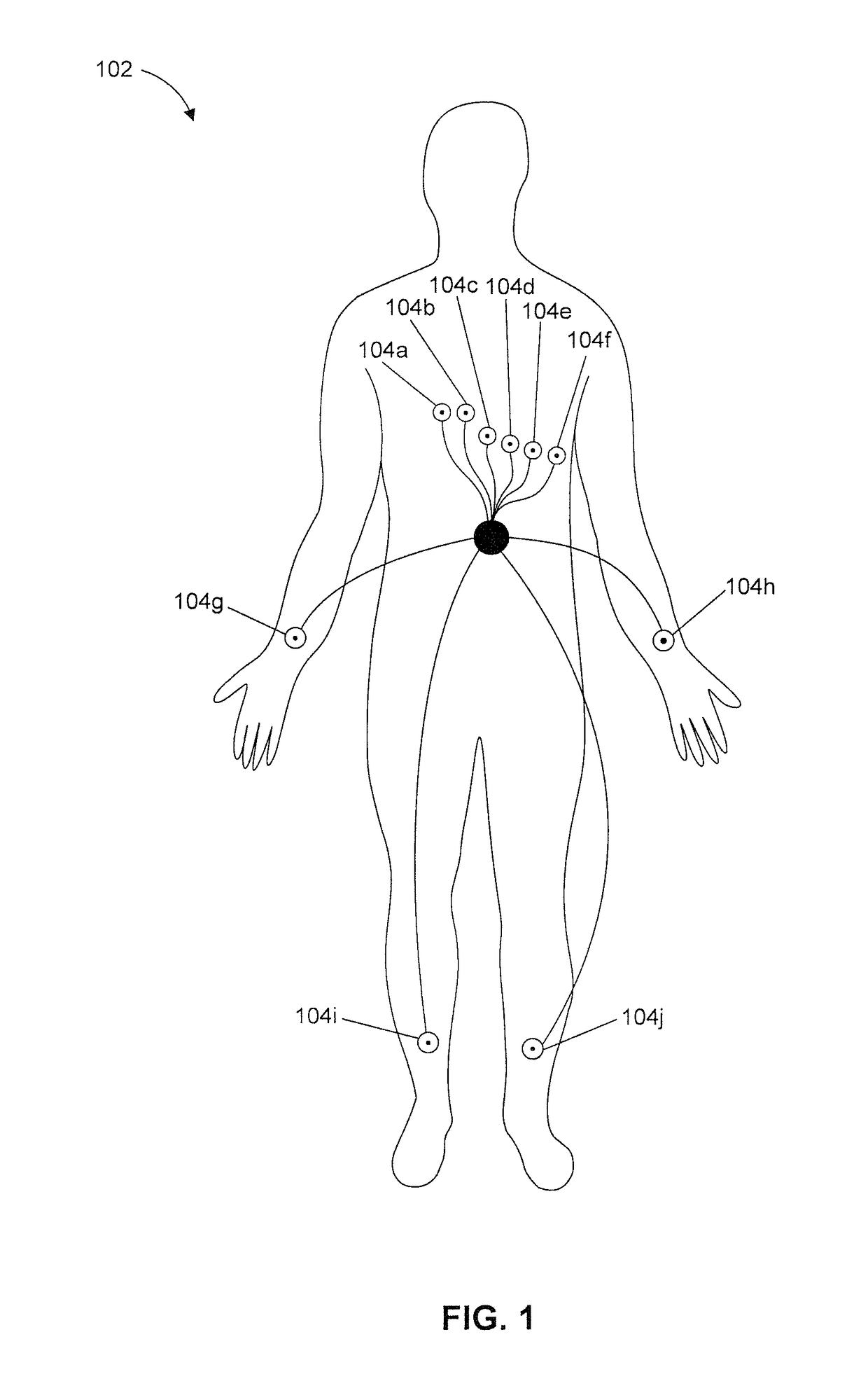
A medical monitoring device for monitoring electrical signals from the body of a subject is described. The medical monitoring device monitors electrical signals originating from a cardiac cycle of the subject and associates each cardiac cycle with a time index. The medical monitoring device applies a forward computational procedure to generate a risk score indicative of hyperkalemia, hypokalemia or arrhythmia of the subject. The medical monitoring device can adjust the forward computational procedure based upon clinical data obtained from the subject.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Marker for arrhythmia risk
InactiveUS20090092998A1Prevent and reduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisArrhythmic riskHypsarrhythmia
The present invention relates to markers and methods for determining risk of ventricular arrhythmia in an individual. By using the markers of the present invention, individual with high risk of ventricular arrhythmia can properly be detected and treated. The present inventors have discovered that IL-6 and / or DROMs have strongly positive correlation with the risk of ventricular arrhythmia.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Methods for screening compounds for proarrhythmic risk and antiarrhythmic efficacy
Methods for screening compounds for their potential to induce or inhibit a cardiac arrhythmia are disclosed. The methods comprise determining the ratio of the time constant (τ) of ICa,L recovery in tissue expressing the L-type calcium channel or any subunit or combination thereof of the L-type calcium channel treated with a test compound to the ventricular repolarization time of cardiac tissue treated with a test compound. The methods further comprise determining an arrhythmic risk score for a specified dose of a test compound.
Owner:MAIN LINE HEALTH HEART CENT
Method of determining risk of arrythmia
InactiveCN103221826AAnimal cellsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMultielectrode arrayCardiac muscle
The present invention relates to a method of determining the risk of drug induced arrhythmia using stem cell derived cardiomyocytes in a high-throughput impedance or multi-electrode array assay.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring Arrythmogenic Effects of Medications Using an Implantable Device
An implantable device and method for monitoring changes in the risk of arrhythmia induced by medications. The implantable device monitors risk of arrhythmia by analyzing an aspect of T-wave morphology to generate a metric of transmural dispersion of repolarization (“TDR”) as a proxy for the risk of arrhythmia. The implantable device generates an index of change in the risk of arrhythmia by comparing values of the metric of TDR obtained for different time periods. The implantable device generates a warning if the change in risk of arrhythmia is outside acceptable limits. The implantable device can also communicate with other devices to correlate changes in risk of arrhythmia with medications taken by the patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
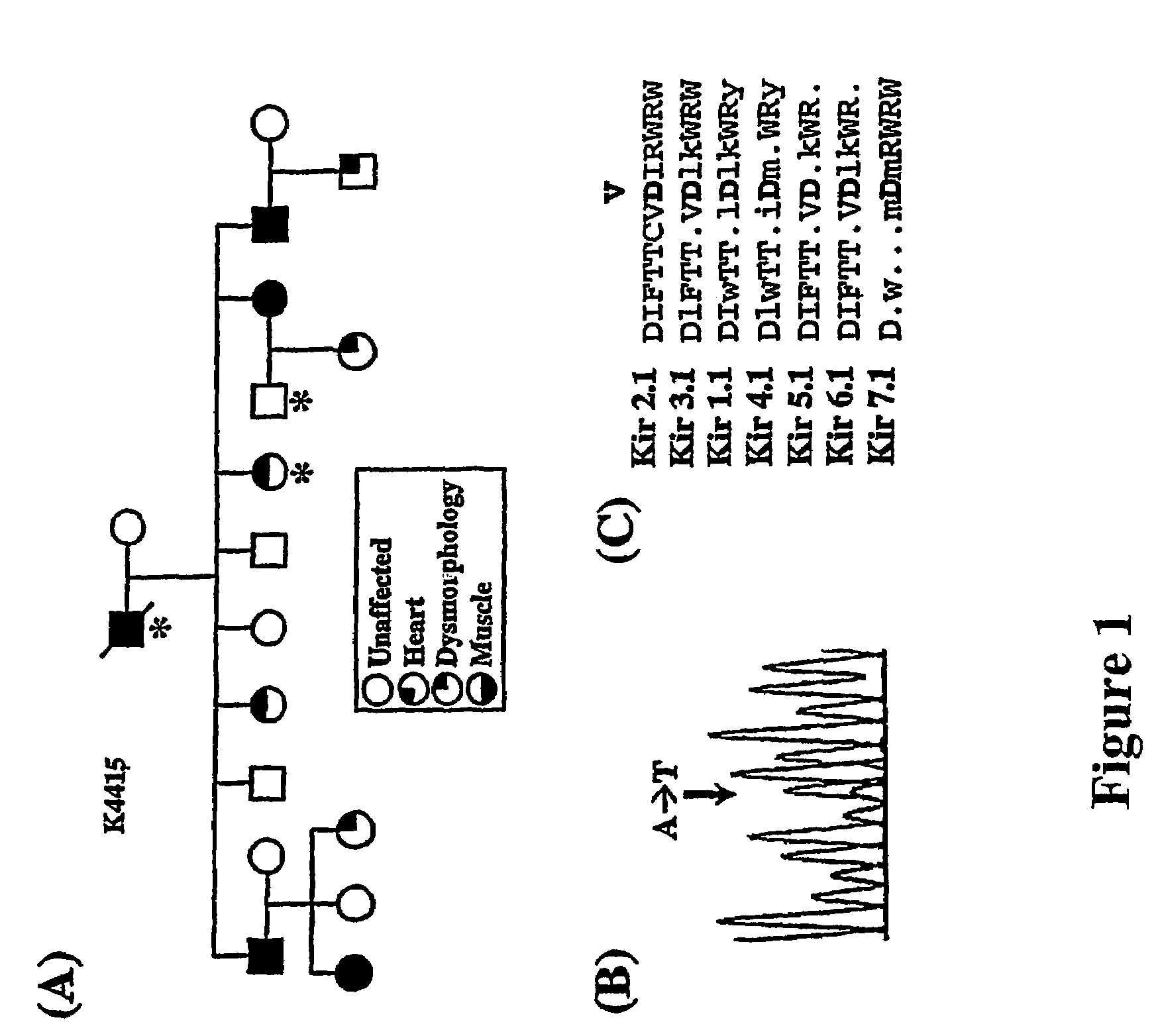
Methods for assessing risk for cardiac dysrythmia in a human subject
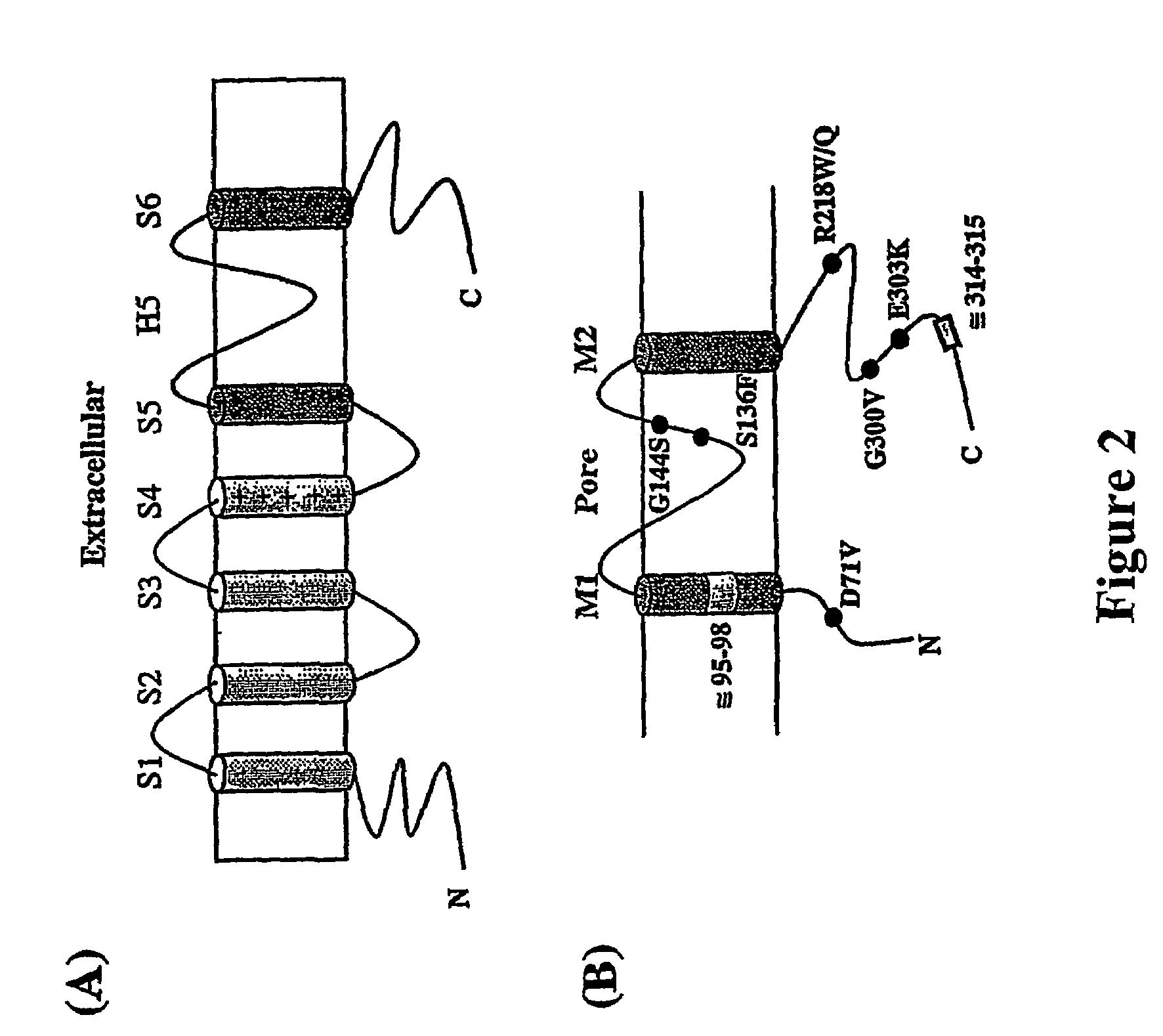
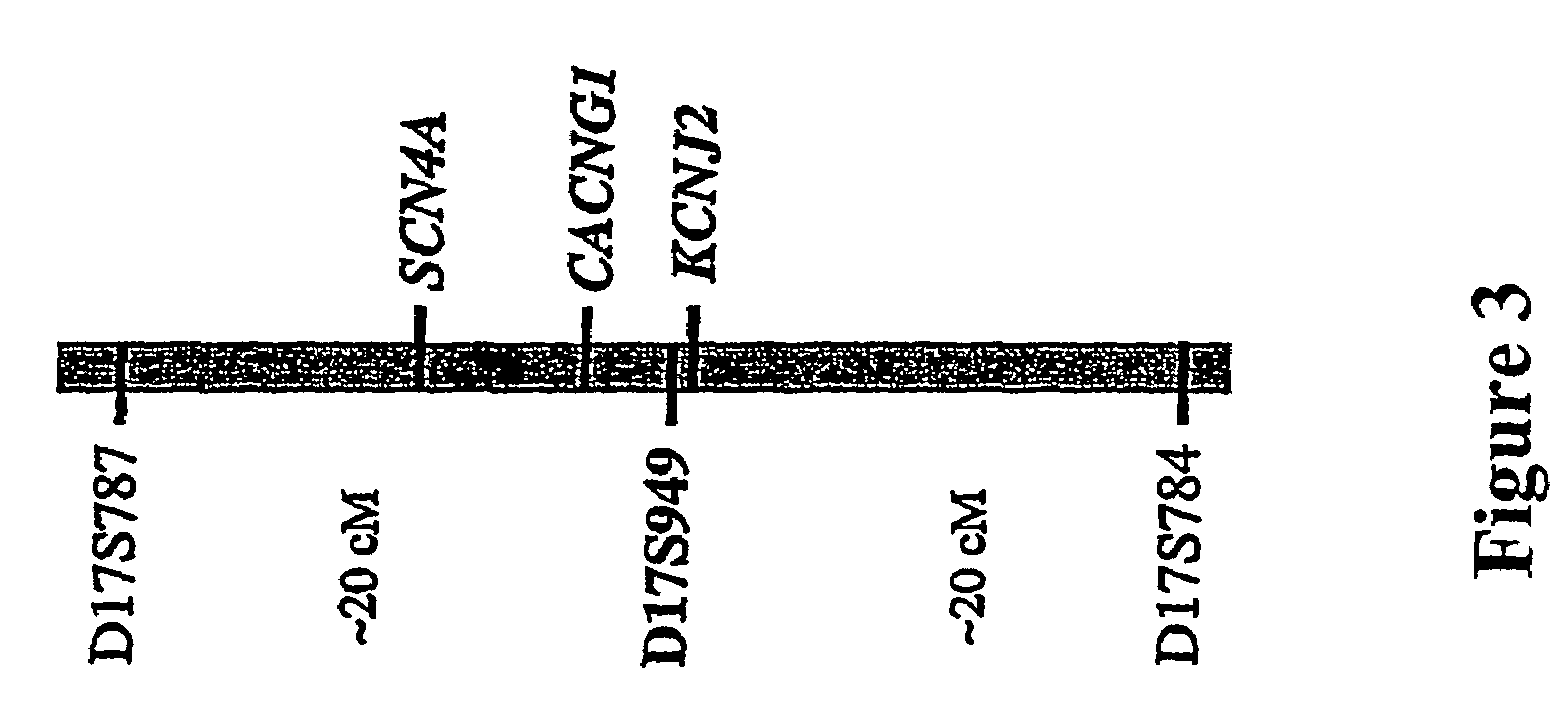
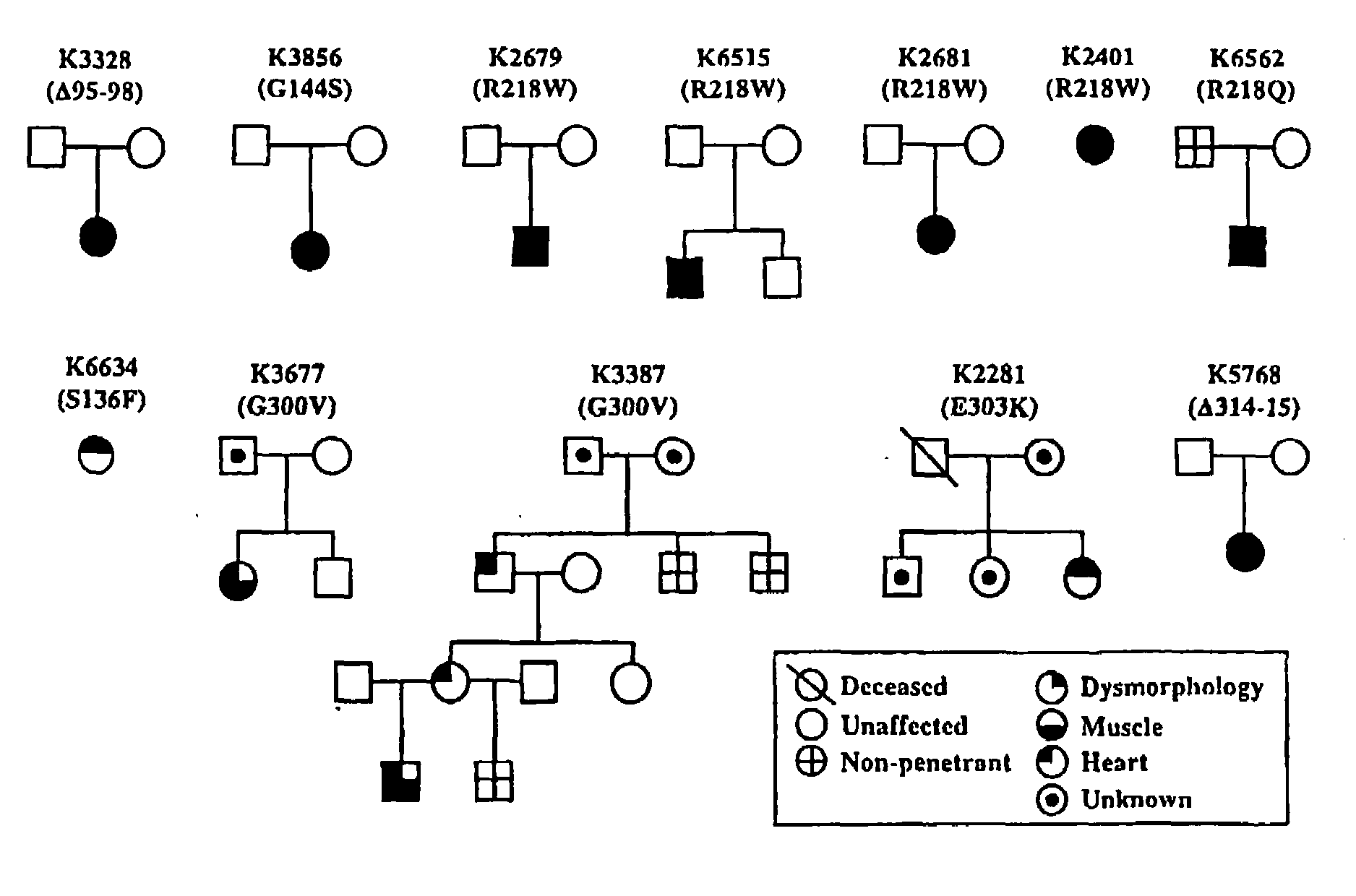
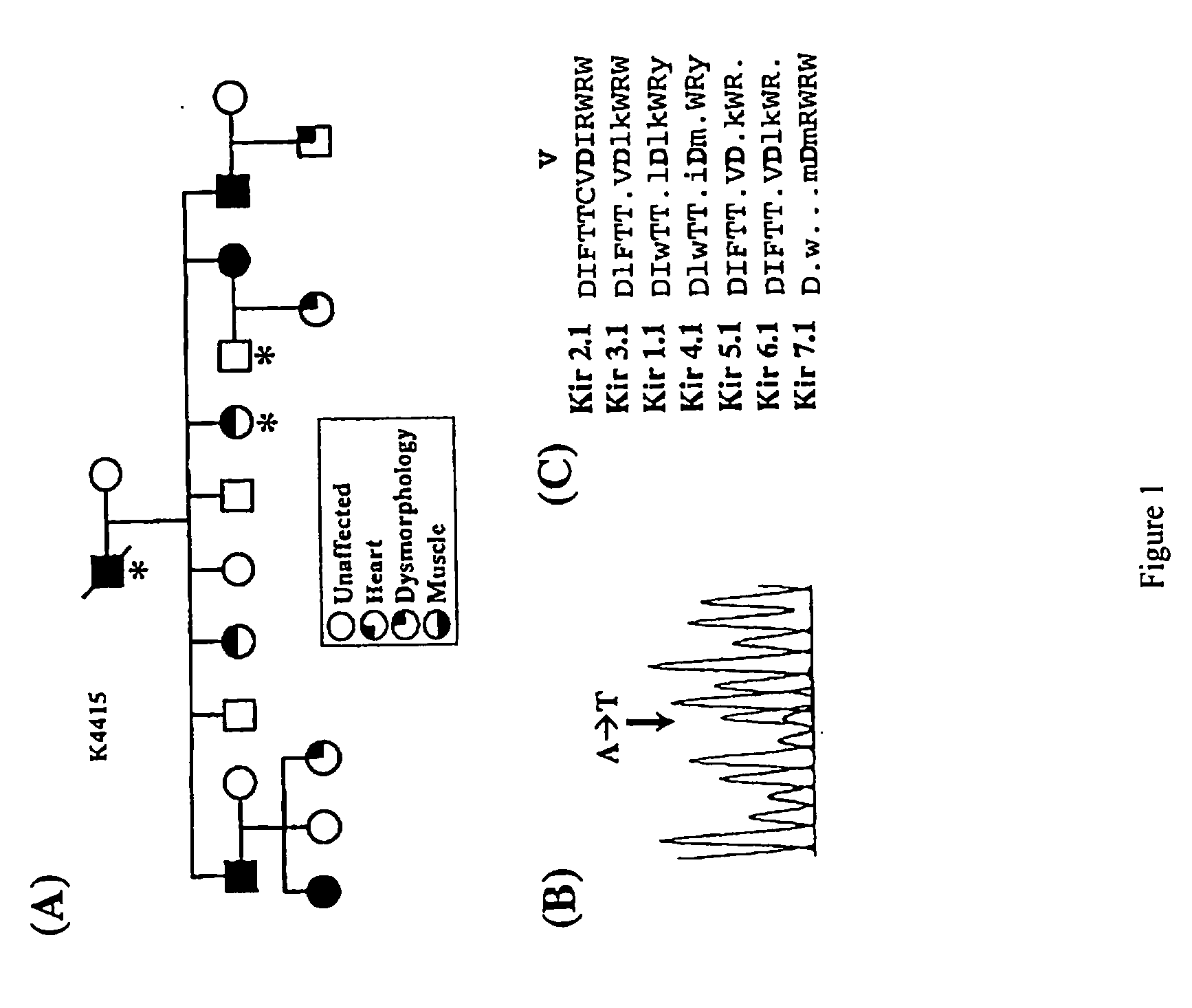
The present invention relates to methods for assessing the risk of a patient for developing a potentially fatal cardiac dysrhythmia and for diagnosing Andersen's Syndrome. A tissue sample from a patient is obtained and the DNA or proteins of the sample isolated. From the DNA and protein isolates the sequence of the KCNJ2 gene or the Kir2.1 polypeptide can be obtained. The KCNJ2 gene or the Kir2.1 can be screened for alteration as compared to the wile-type sequence. An alteration in a copy of the KCNJ2 gene or a Kir2.1 polypeptide indicates that the patient has a high risk for developing a cardiac dysrhythmia and can be diagnosed with Andersen's Syndrome. The invention also related to isolated nucleic acid molecules with one or more alterations as compared to the wild-type sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
High throughput arrhythmia risk assessment using multilead residua signals
A method and system for high-throughput prediction of the onset of heart arrhythmias observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and a second baseline measurement is generated from the second set of ECG signals. A residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the baseline measurement and the second baseline measurement. The residuum signals are averaged across the leads. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals and the averaged residuum signal.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Human in vitro cardiotoxicity model
PendingUS20220163511A1Faster pacing rateSafe exposure levelMedical simulationHealth-index calculationCardiac arrhythmiaArrhythmic risk
The Cardiac Tissue Engineered Model (TEEM) invention provides a robust in vitro model for cardiotoxicity evaluation using three-dimensional (3D) human heart microtissues to quantify dose-dependent changes in electromechanical activity, resulting in a comprehensive cardiotoxicity and arrhythmia risk assessment of test compounds. The invention also provides a predictive in vitro screening platform for pro-arrhythmic toxicity testing using human three-dimensional cardiac microtissues. The invention enables the screening of environmental and pharmaceutical compounds, chemicals, and toxicants to establish safe human exposure levels.
Owner:RHODE ISLAND HOSPIAL +1
Methods for assessing risk for cardiac dysrythmia in a human subject
The present invention relates to methods for assessing the risk of a patient for developing a potentially fatal cardiac dysrhythmia and for diagnosing Andersen's Syndrome. A tissue sample from a patient is obtained and the DNA or proteins of the sample isolated. From the DNA and protein isolates the sequence of the KCNJ2 gene or the Kir2.1 polypeptide can be obtained. The KCNJ2 gene or the Kir2.1 can be screened for alteration as compared to the wile-type sequence. An alteration in a copy of the KCNJ2 gene or a Kir2.1 polypeptide indicates that the patient has a high risk for developing a cardiac dysrhythmia and can be diagnosed with Andersen's Syndrome. The invention also related to isolated nucleic acid molecules with one or more alterations as compared to the wild-type sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method for ameliorating or preventing arrhythmic risk associated with cardiomyopathy by improving conduction velocity
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
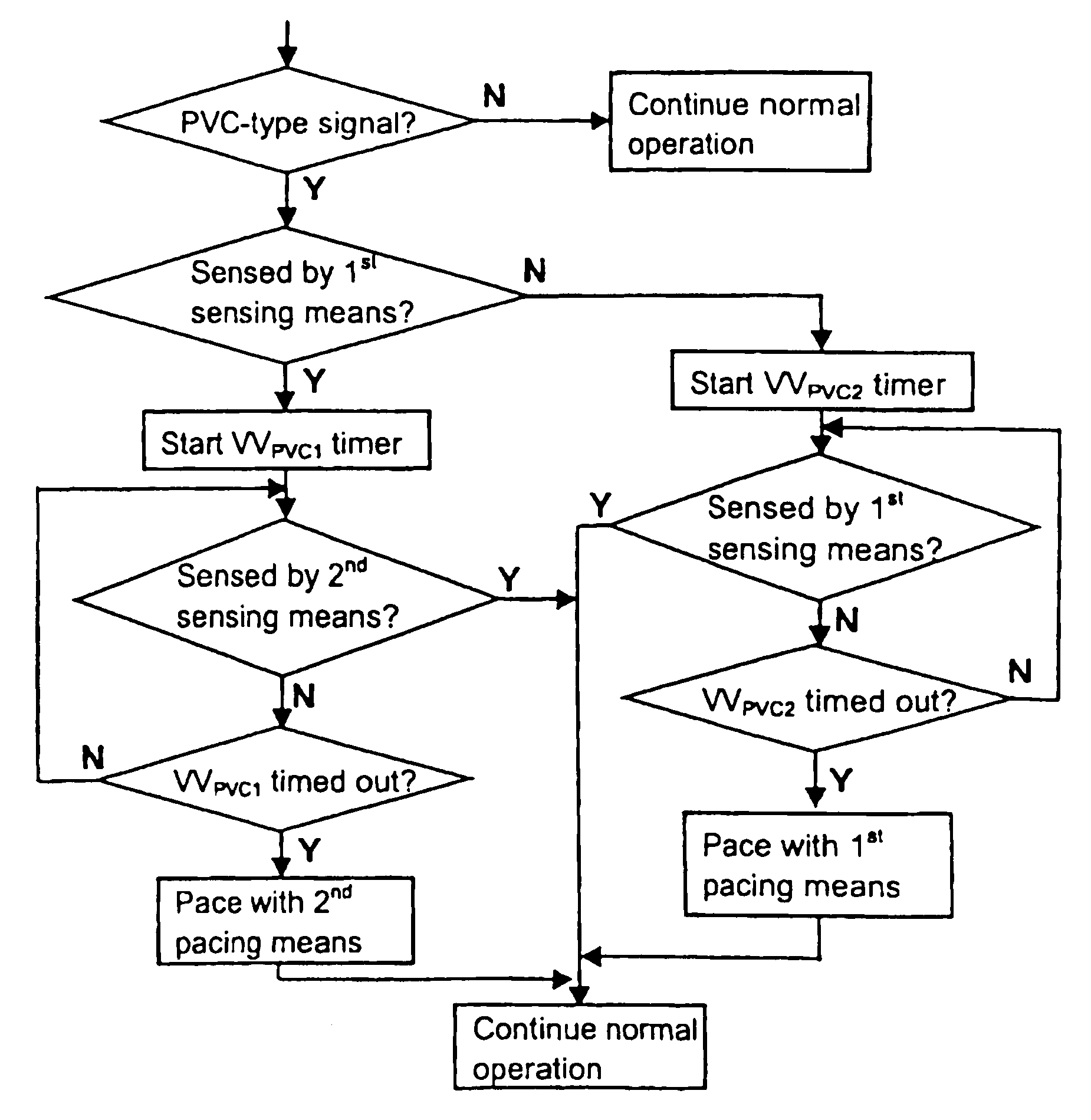
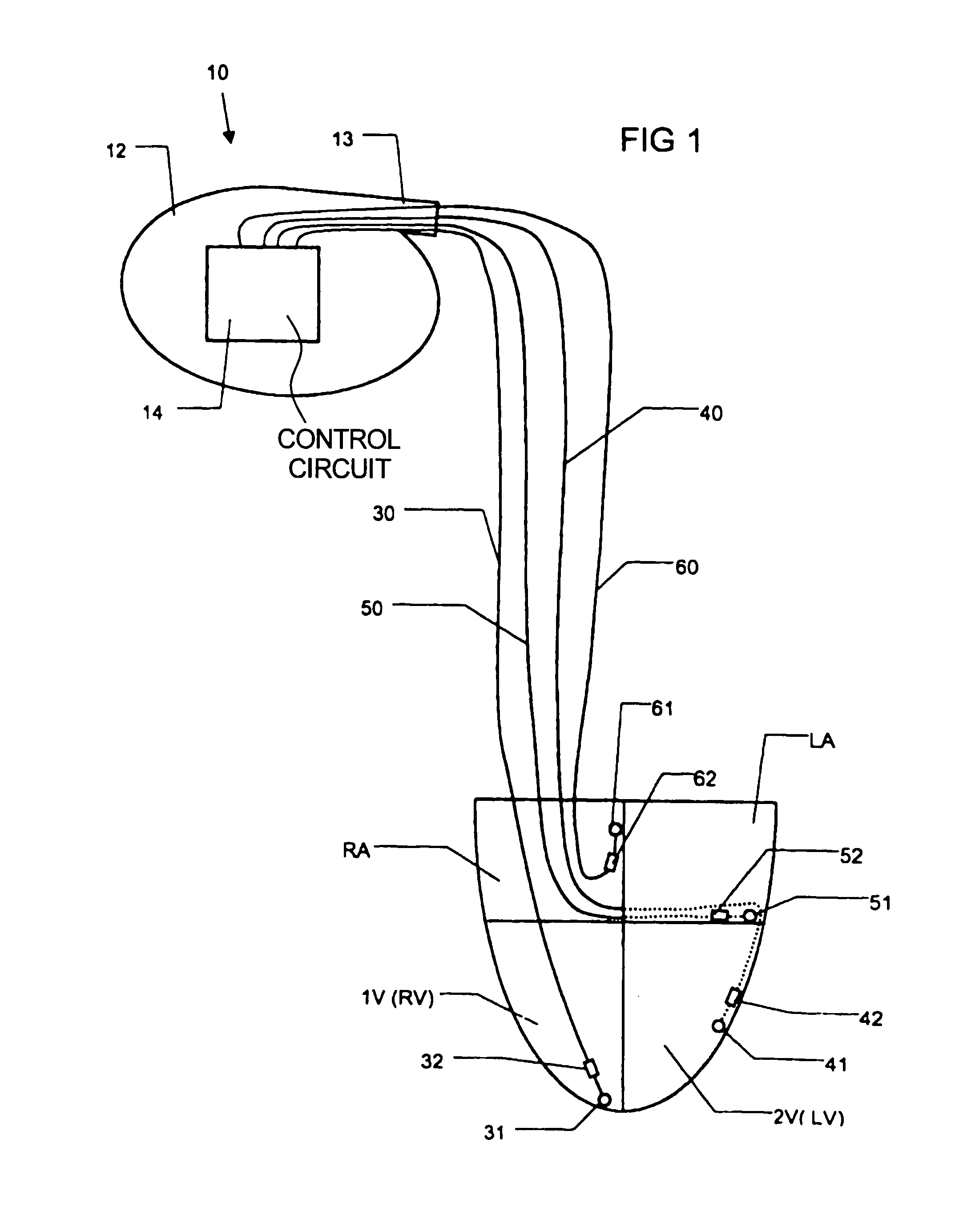
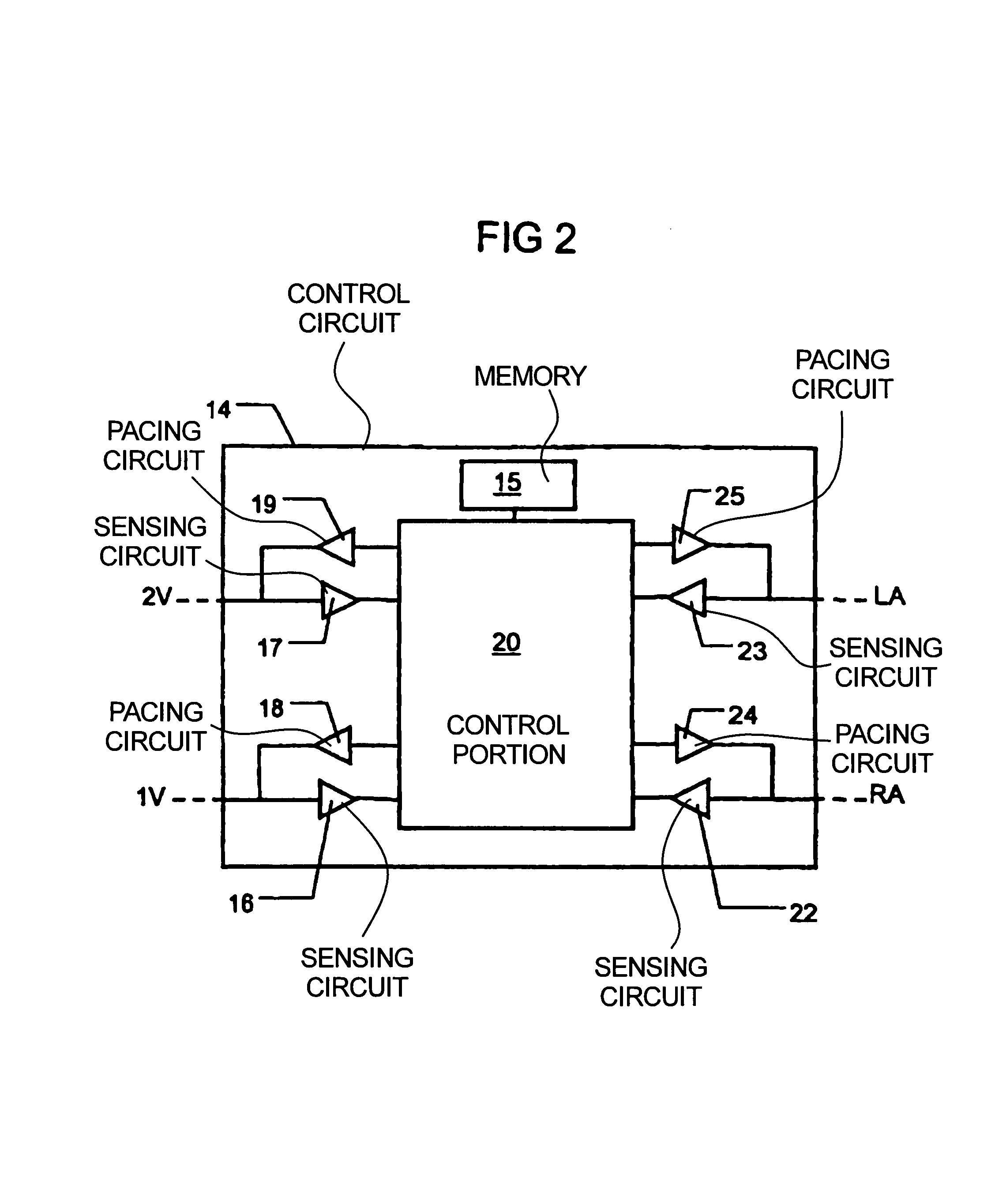
Implantable heart stimulating device, system and method
InactiveUS7181279B2Reduce riskImprove performanceHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular contractionCardiac arrhythmia
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device and system operate, within a time cycle, to deliver pacing pulses with both a first and a second pacing circuit with a first time delay between these pacing pulses. The device employs a criterion with which a signal typical for a premature ventricular contraction is detected. The device also operates with a second time delay and / or with a third time delay, and, if a predefined pacing rule is fulfilled, to deliver a pacing pulse with the second time delay or said third time delay. The risk for arrhythmia in connection with a PVC is reduced.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com