Error correction for a persistent resource allocation
a resource allocation and error correction technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve the problem that the allocation of communication resources itself can consume a large amount of resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
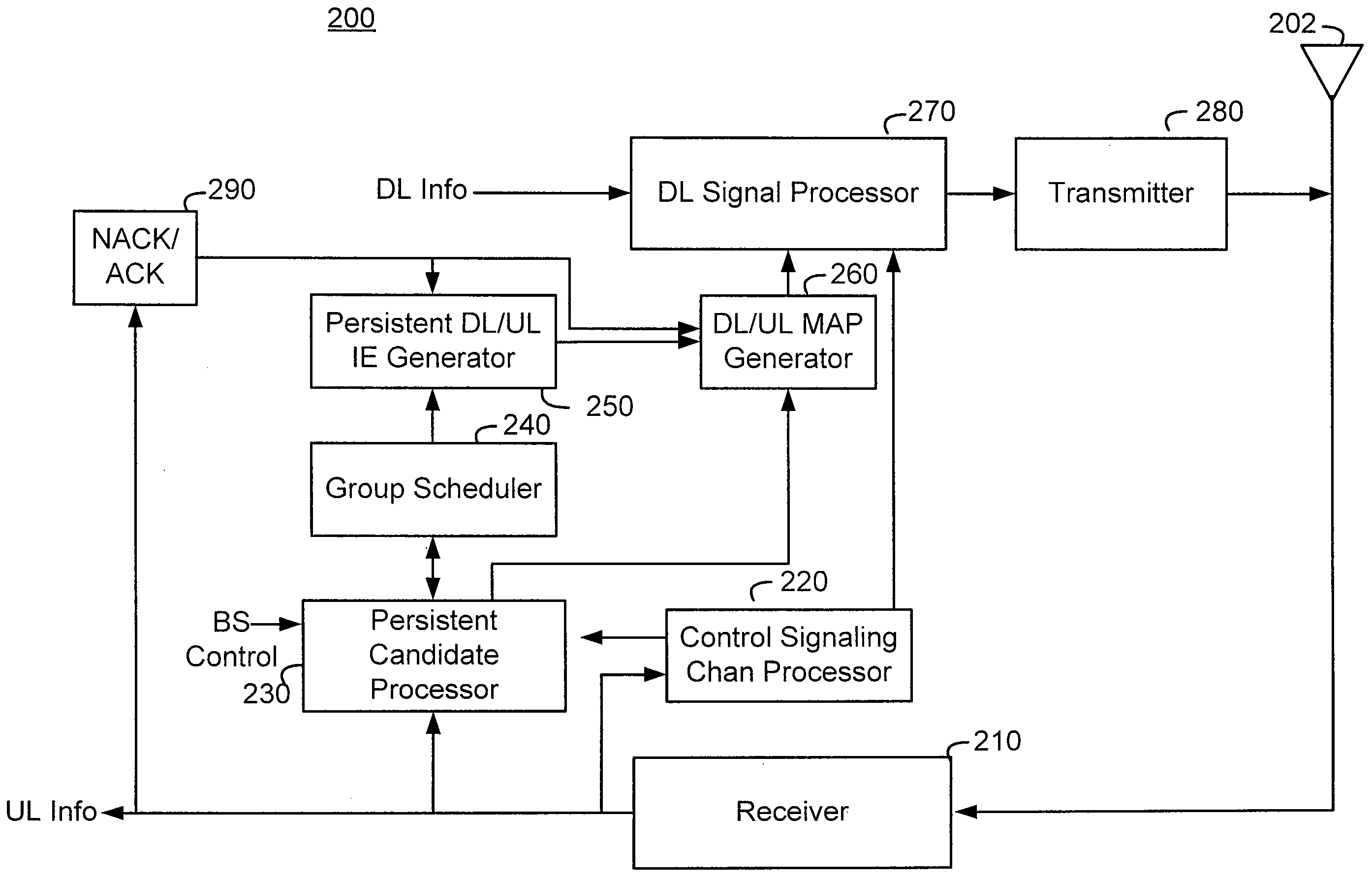
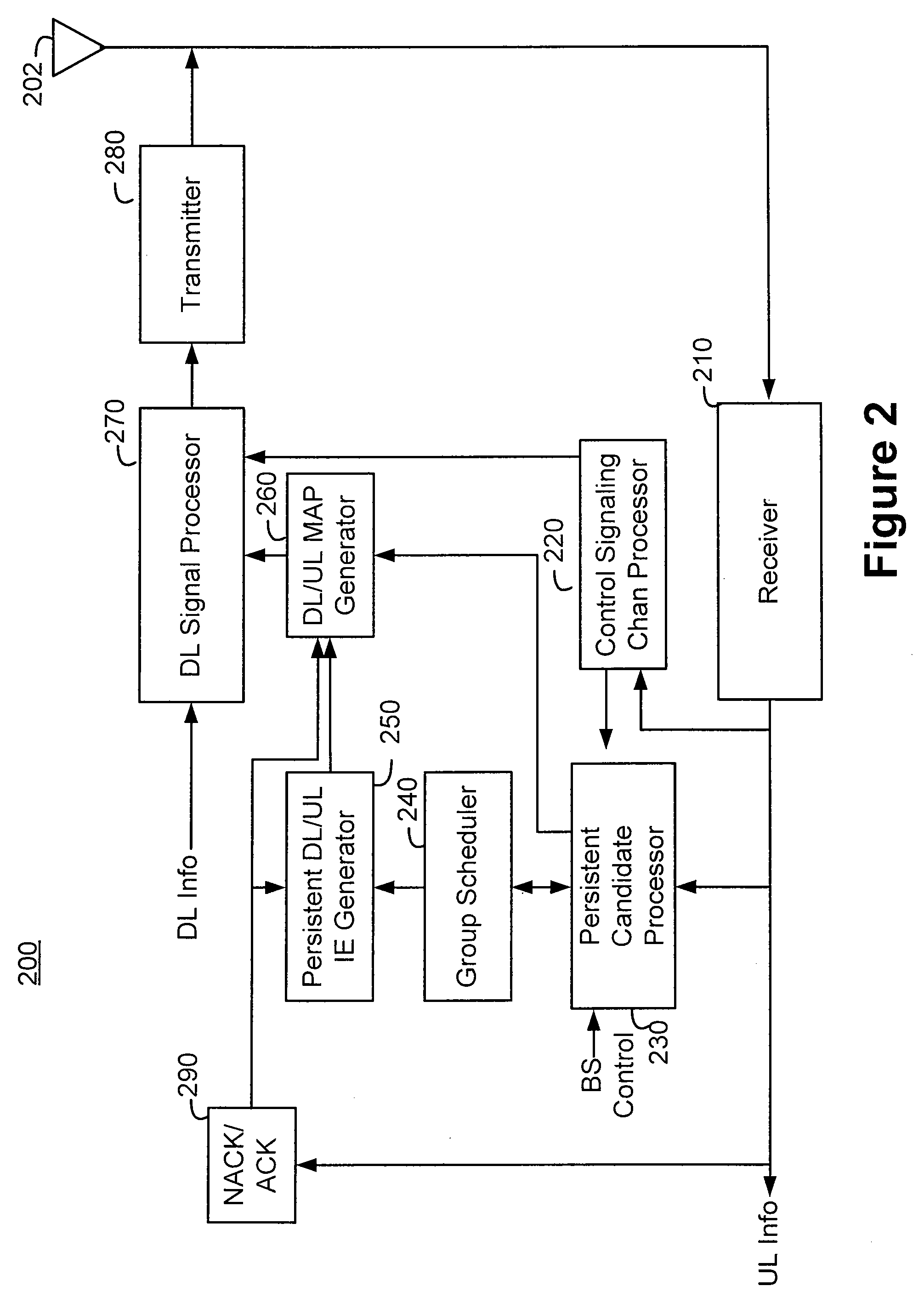
[0029]Methods and apparatus for communicating and utilizing persistent allocation of downlink or uplink resources are described herein. In this description, the communication path from the base station to the client station is referred to as a downlink (DL) and the communication path from the client station to the base station is referred to as an uplink (UL).
[0030]When the base station assigns a standard non-persistent downlink or uplink allocation for use by a client station, the allocation is valid for a predetermined frame, such as a frame in which the allocation is granted or the frame following the frame in which the allocation is granted, depending on the allocation relevancy. In contrast, when a base station assigns a persistent downlink or uplink allocation to a client station, the allocation typically remains valid for multiple future downlink or uplink frames. Thus, the client station does not need to repeat a request for uplink resources periodically over a long series o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com