Content-based replication of data between storage units
a content-based and storage unit technology, applied in the direction of database distribution/replication, instruments, transmission, etc., can solve the problems of large data transmission over the network, data may be improperly transferred, and large amount of data may be expensive to transmit over the network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]The following embodiments describe methods, devices, systems, and computer programs for replicating data across storage systems. It will be apparent, that the present embodiments may be practiced without some or all of these specific details. In other instances, well-known process operations have not been described in detail in order not to unnecessarily obscure the present embodiments.
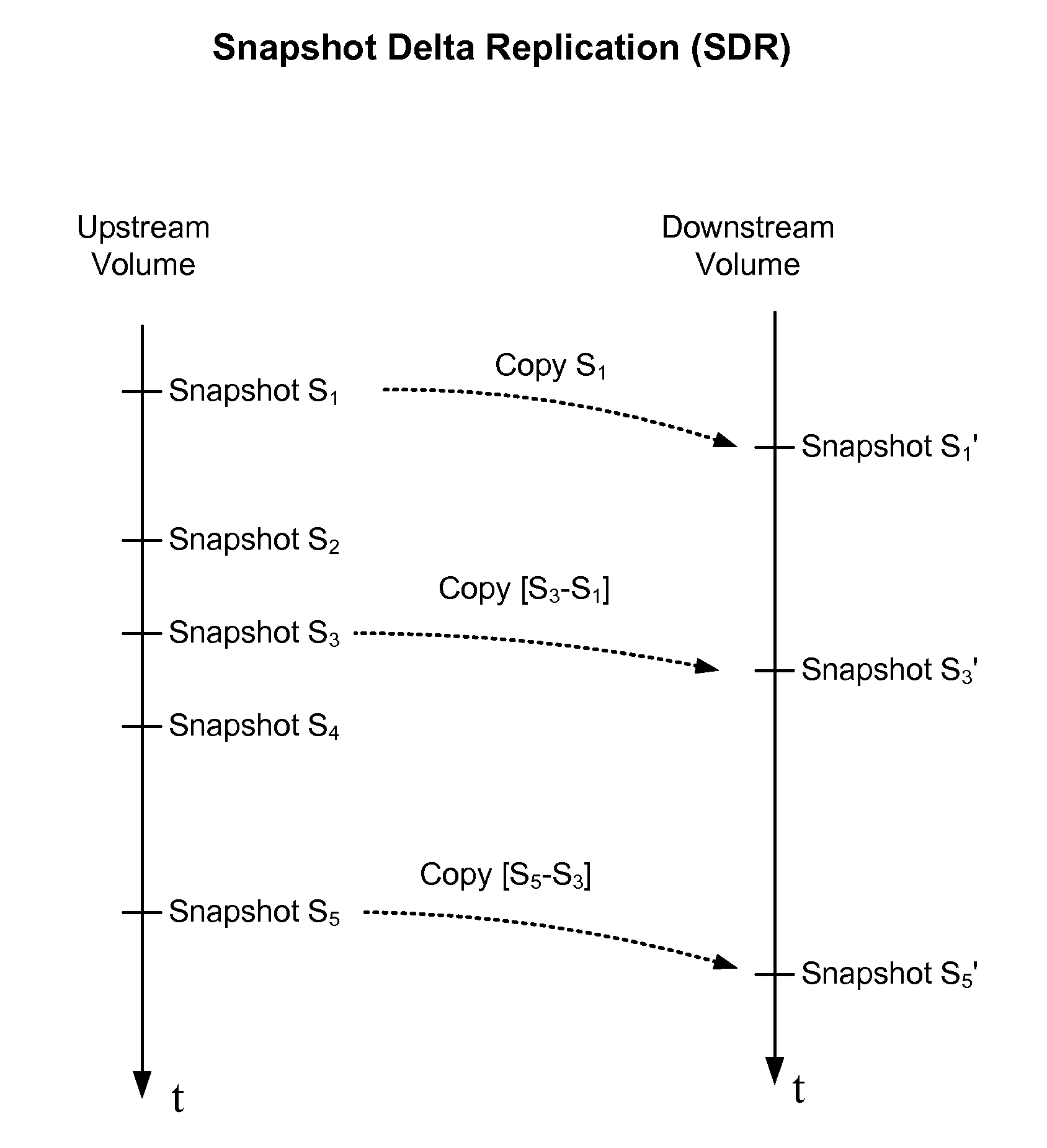
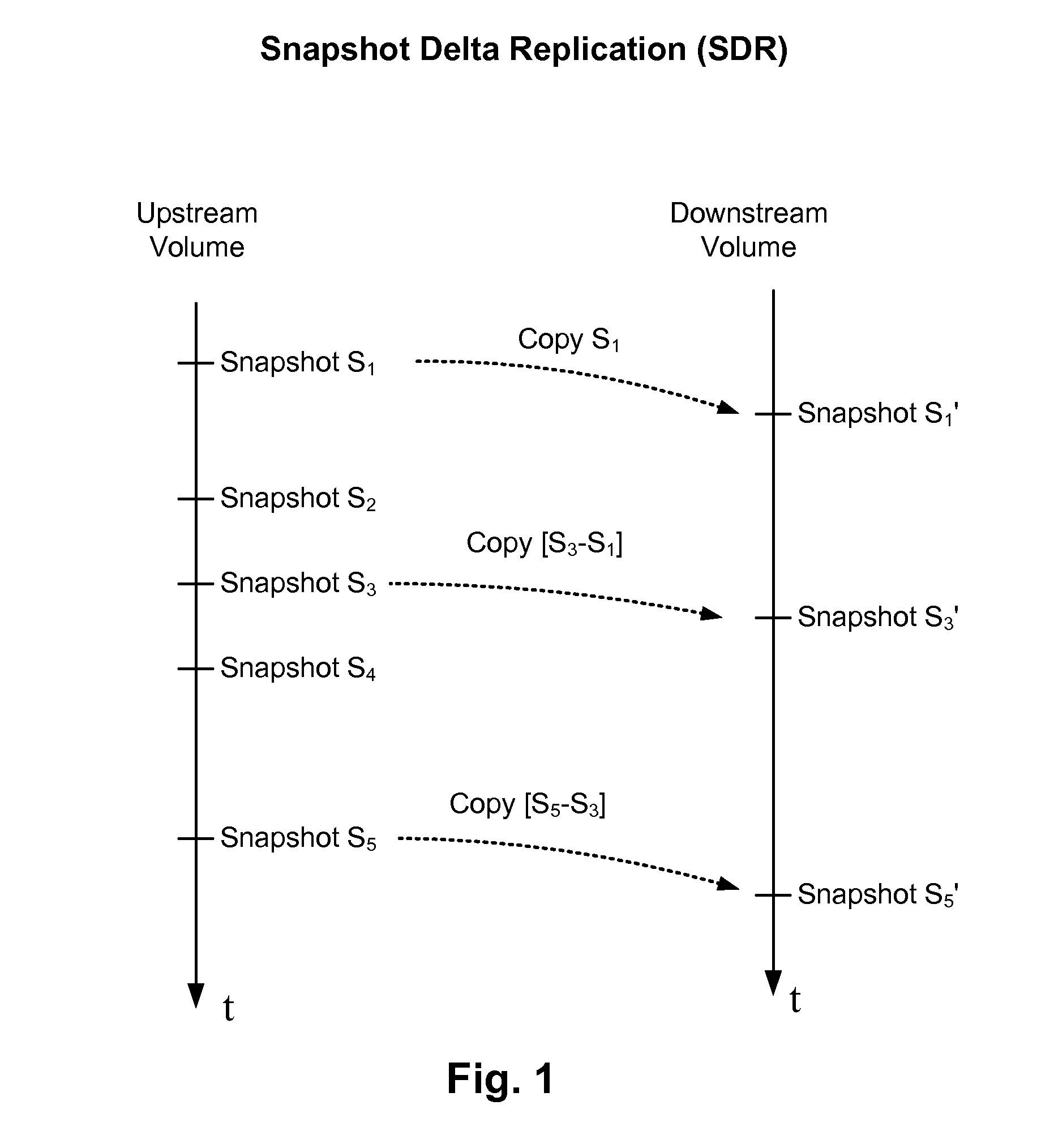
[0026]In some implementations, a Snapshot Delta Replication (SDR) method is used to replicate snapshots of data volumes in a network storage device. However, something could have gone wrong during the replication, and a check is made to determine if the replicated snapshot is correct. If the replication is not completely correct, the data would have to be resent, which may be very resource costly. In order to avoid having to replicate all the data again, a Content-Based Replication (CBR) method is used to minimize the amount of data needed to fix the replicated snapshot.
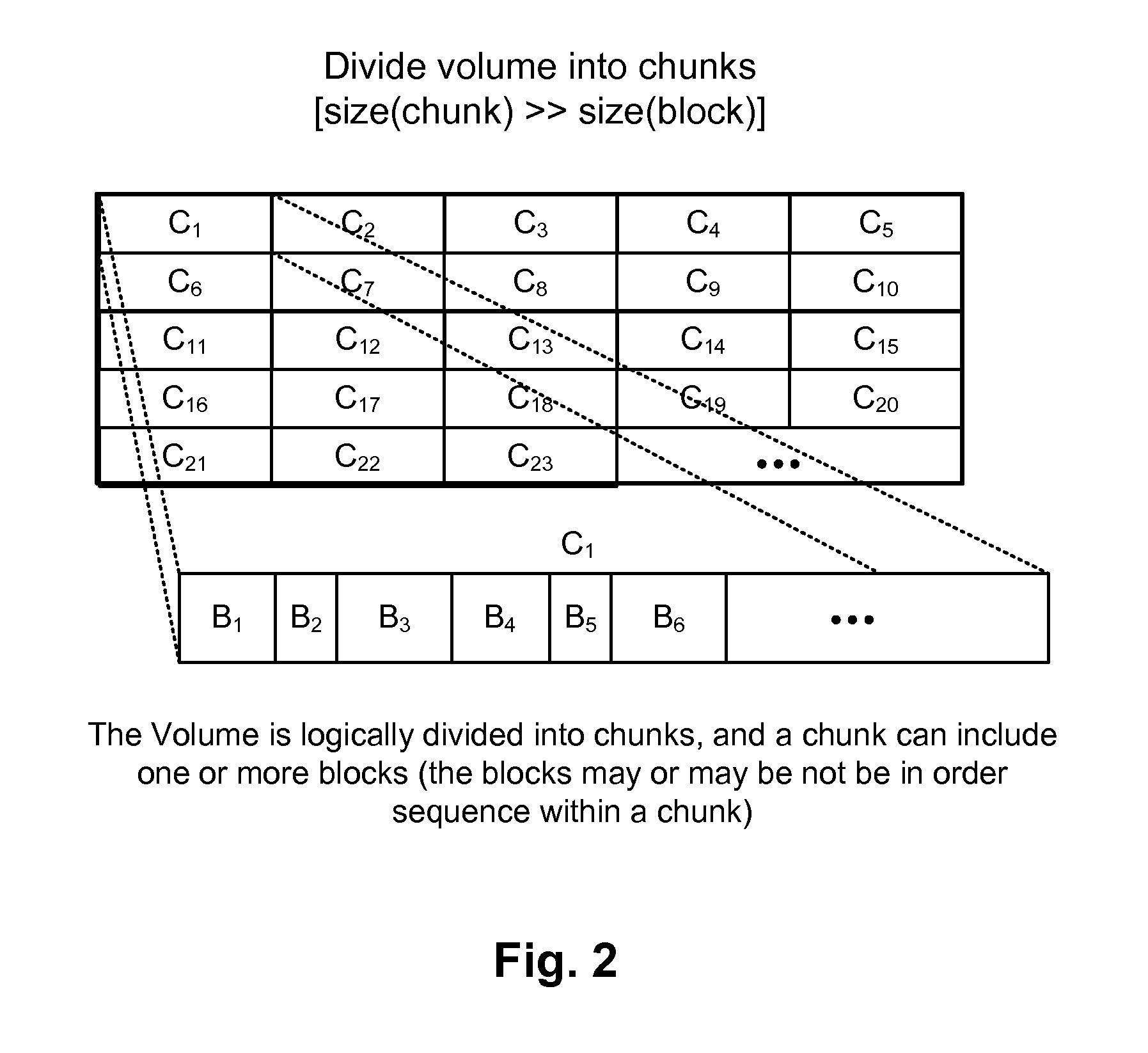
[0027]With the CBR method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com