Reactive learning for efficient dialog tree expansion
a dialog tree and active learning technology, applied in the field of dialog systems, can solve the problems of large quantity of data, lack of expertise and training data, time and cost of building such systems,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
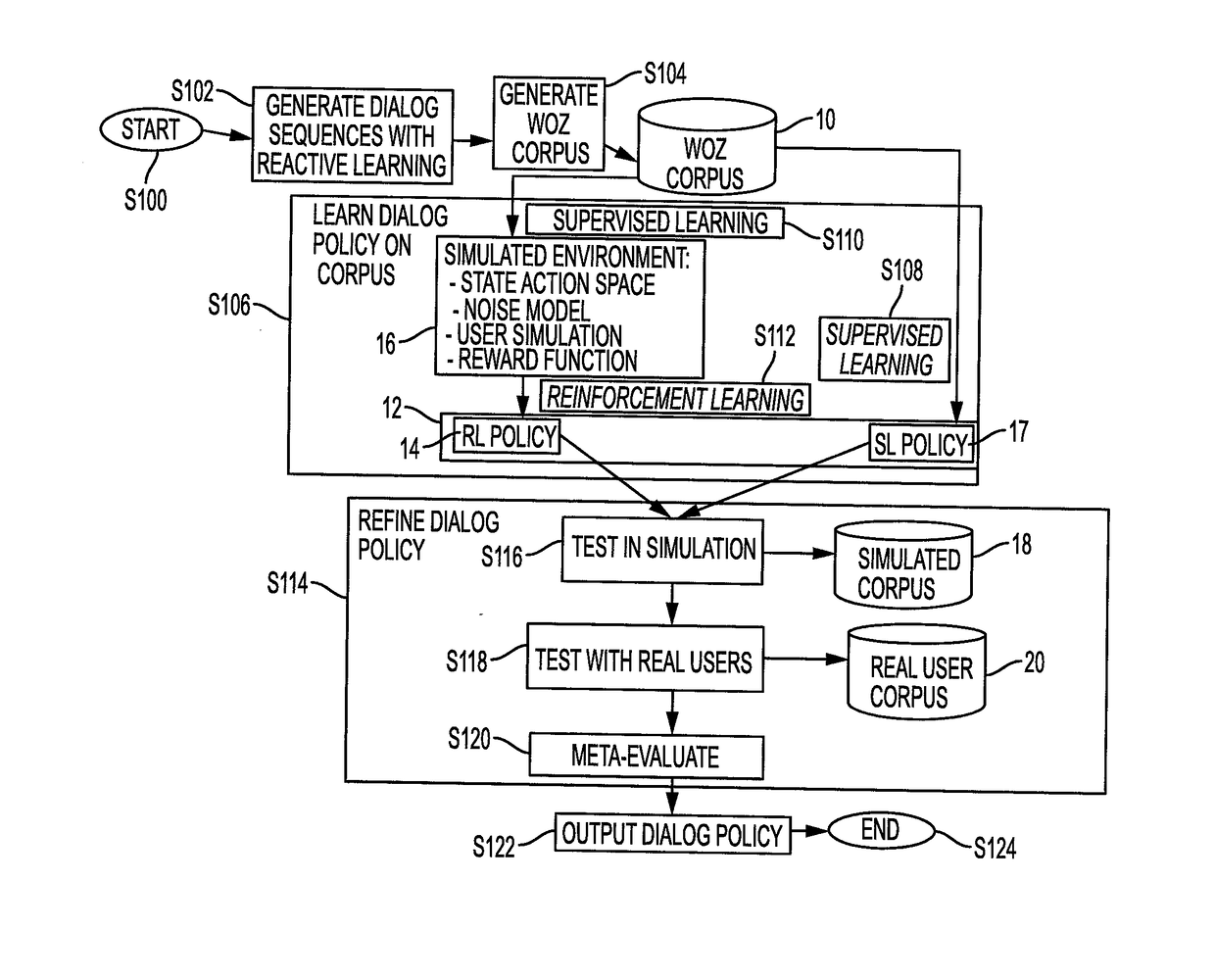
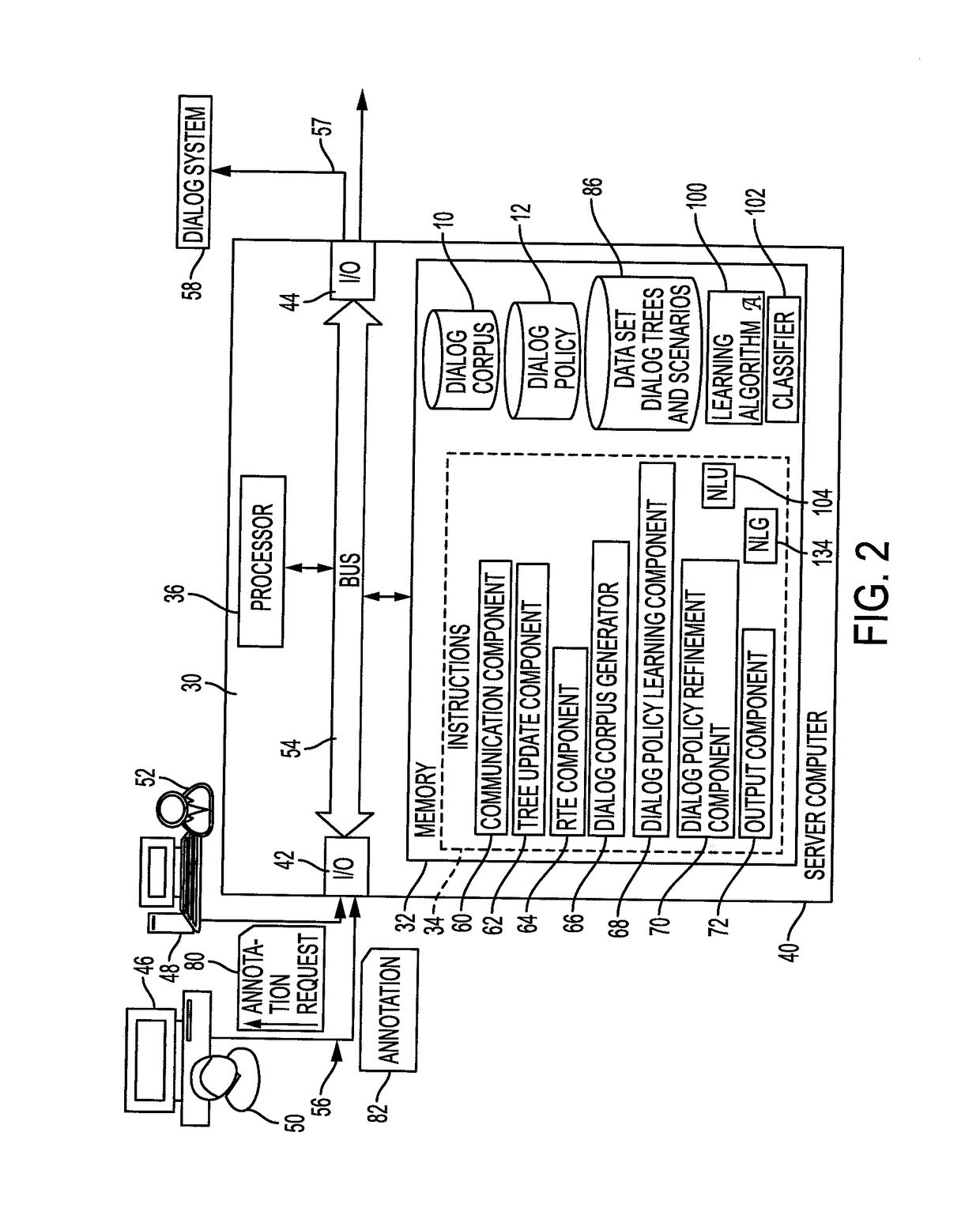
[0025]Aspects of the exemplary embodiment relate to a system and method for generating a dialog corpus through efficient tree expansion, based on reactive learning, which can reduce the time taken in preparing simulations, provide easy ways to collect data in realistic conditions, and facilitate the building of new autonomous and task-oriented dialog systems.
[0026]The dialog corpus can be used, for example, to generate a dialog policy for question-answering, conducting transactions, or diagnosis, or other conversational systems. The system and method are able to produce usable data for dialog policy learning independently of the chosen policy learning model.
[0027]Dialog data production is achieved in the exemplary method through a reactive learning formulation using a Wizard of Oz (WOZ) approach in which a human simulates a virtual agent for conducting a dialog with client. An efficient method is described herein for producing valuable dialog data in order to initialize a policy lea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com