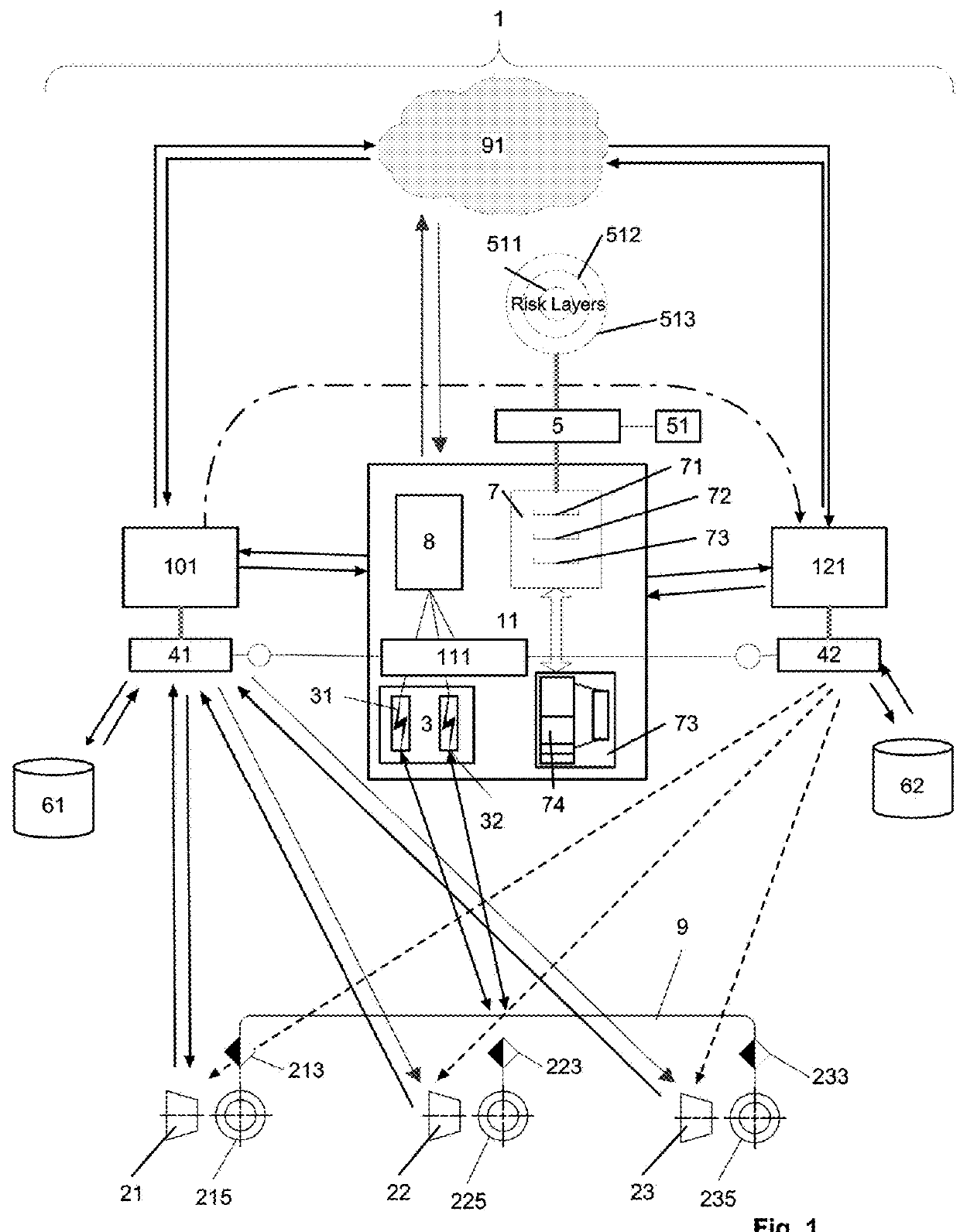
[0016]In still another embodied variant, the assembly module of the switching device comprises means for processing risk-related component data and for providing data as to the likelihood of said risk exposure for one or a plurality of the pooled risk exposure components, in particular, based on risk-related component data, and wherein the receipt and preconditioned storage of payments from risk exposure components for the pooling of their risks can be dynamically determined based on the total risk and / or the likelihood of risk exposure of the pooled risk exposure components. This embodied variant has, inter alia, the advantage that the operation of the first and / or second resource-pooling system can be dynamically adjusted to changing conditions in relation to the pooled risk, as, for example, a change of the environmental conditions or risk distribution, or the like, of the pooled risk components. A further advantage is that the system does not require any manual adjustments, when it is operated in different environments, places or countries, because the size of the payments of the risk exposure components is directly related to the total pooled risk.
[0017]In one embodied variant, the assembly module of the switching device comprises means for processing risk-related component data and for providing information as to the likelihood of said risk exposure for one or a plurality of the pooled risk exposure components, in particular, based on risk-related component data, and wherein the receipt and preconditioned storage of payments to the resource pooling system for the transfer of its risk can be dynamically determined based on the total risk and / or the likelihood of risk exposure of the pooled risk exposure components. This embodied variant has, inter alia, the advantage that the operation of the primary and / or secondary risk-transfer unit can be dynamically adjusted to changing conditions of the pooled risk, as, for example, changes of the environmental conditions or risk distribution, or the like, of the pooled risk components. A further advantage is the fact that the system does not require any manual adjustments, when it is operated in different environments, places or countries, because the size of the payments of the risk exposure components is directly related to the total pooled risk.
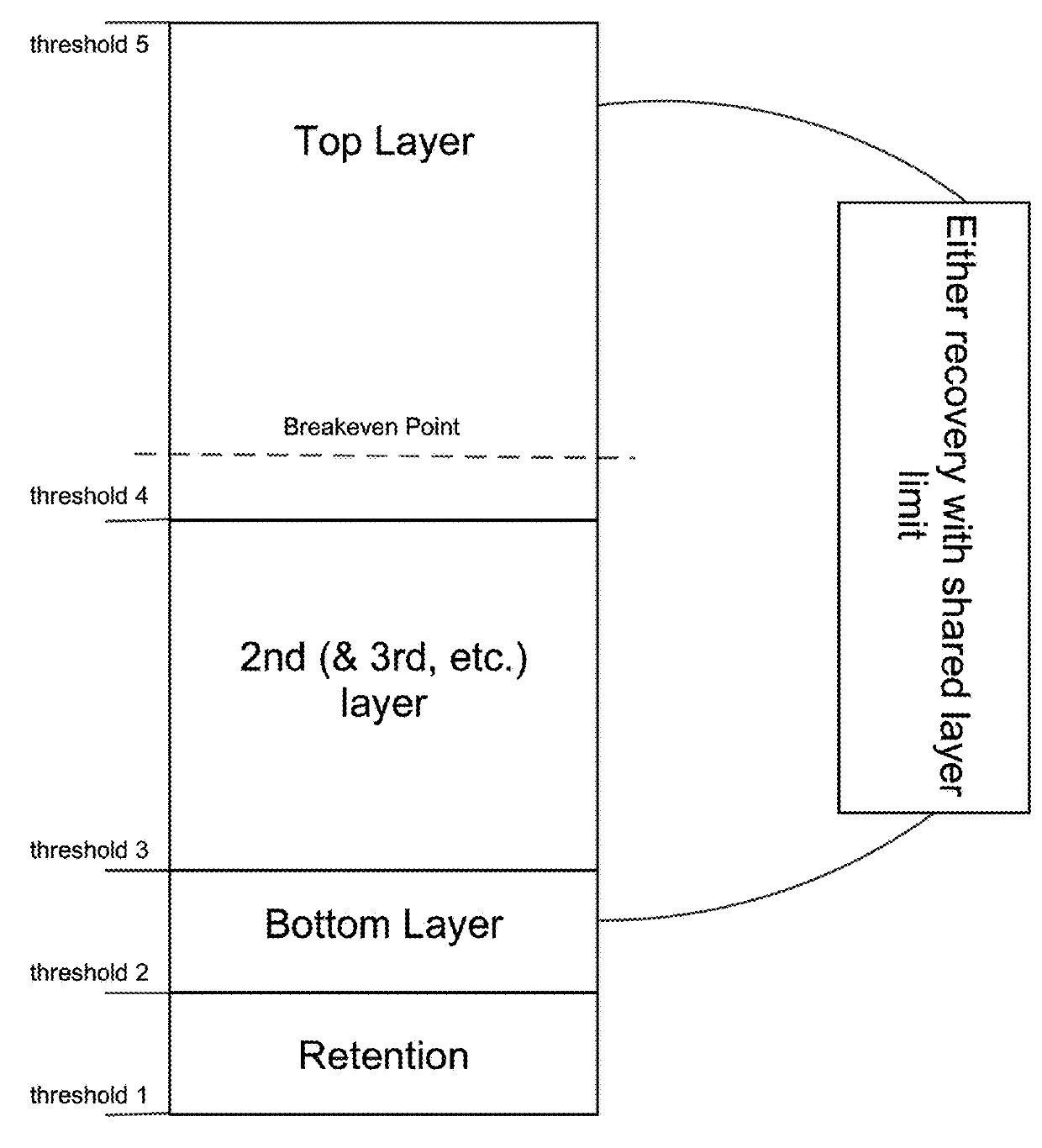
[0018]In one embodied variant, the number of pooled risk exposure components is dynamically adjusted by means of the resource-pooling system to a range where non-covariant, occurring risks covered by the resource-pooling system affect only a relatively small proportion of the total pooled risk exposure components at any given time. Analogously, in the variant with two resource-pooling systems the second resource pooling system can, e.g., dynamically adjust the number of pooled risk shares transferred from first resource pooling systems to a range where non-covariant, occurring risks covered by the second resource-pooling system affect only a relatively small proportion of the total pooled risk transfers from first resource pooling systems at any given time. This variant has, inter alia, the advantage that the operational and financial stability of the system can be improved.
[0019]In one embodied variant, the risk event triggers are dynamically adjusted by means of an operating module based on time-correlated incidence data for one or a plurality of risk events. This embodied variant has, inter alia, the advantage that improvements in capturing risk events or avoiding the occurrence of such events, e.g. by improved forecasting systems etc., can be dynamically captured by the system and dynamically affect the overall operation of the system based on the total risk of the pooled risk exposure components.
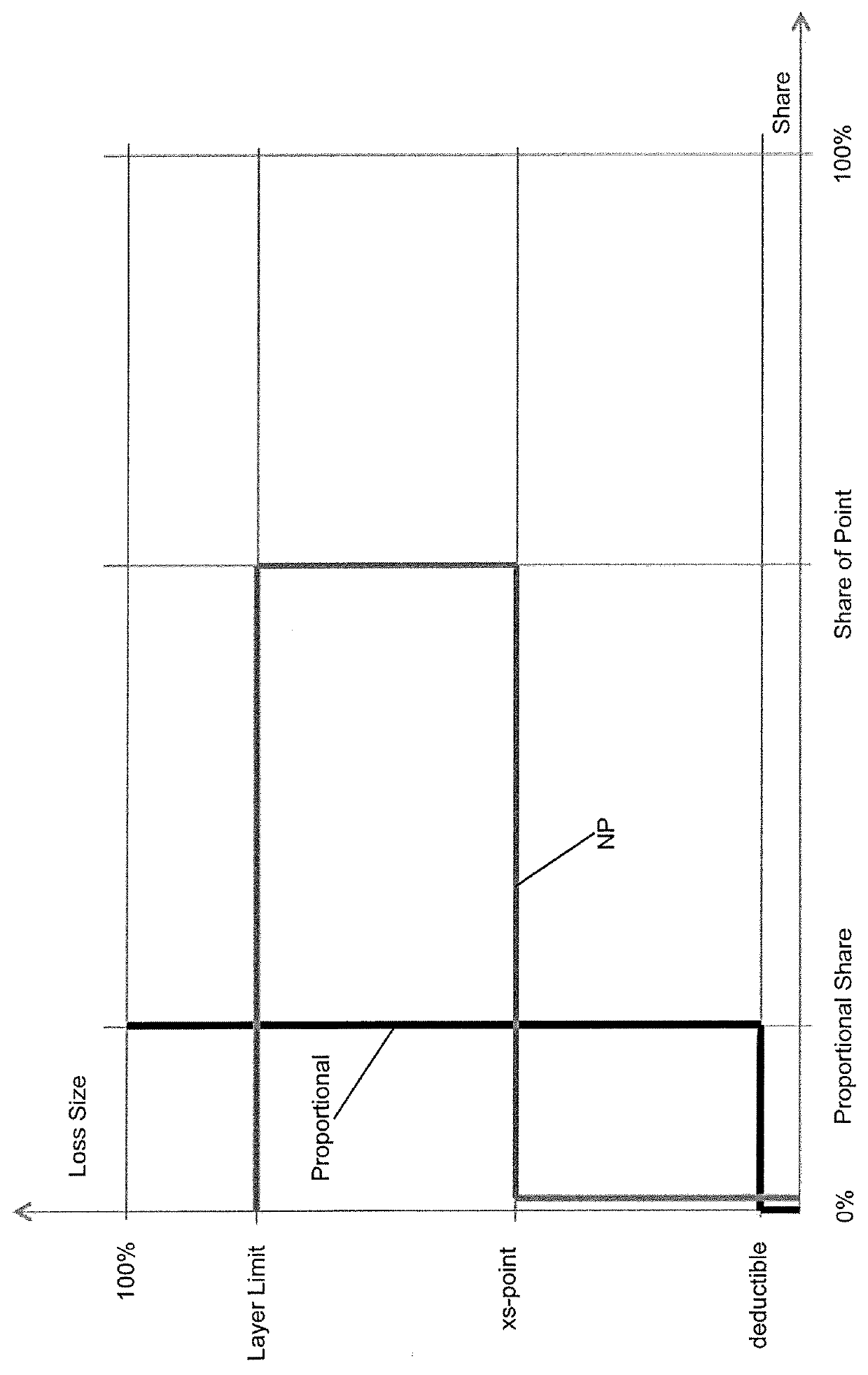
[0020]In another embodied variant, upon each triggering of an occurrence, where parameters indicating a risk event are measured, by means of at least one risk event trigger, a total parametric payment is allocated with the triggering, and wherein the total allocated payment is transferrable upon a triggering of the occurrence. The predefined total payments can, e.g., be leveled to any appropriate lump sum, such as, for example, a predefined value, or any other sum related to the total transferred risk and the amount of the periodic payments of the risk exposure component. This variant, inter alia, has the advantage that the parametric payments or the payments of predefined amounts, which, as in the embodied variant, may also depend on a first, second, third or a plurality of trigger levels, i.e. the different stages of triggers, and allow for an adjusted payment of the total sum that can, e.g., be dependent on the stage of the occurrence of a risk event, as triggered by the system.
[0021]In one embodied variant, a periodic payment transfer from the risk exposure components to the resource pooling system via a plurality of payment receiving modules is requested by means of a monitoring module of the resource-pooling system, wherein the risk transfer or protection for the risk exposure components is interrupted by the monitoring module, when the periodic transfer is no longer detectable by means of the monitoring module. As a variant, the request for periodic payment transfer can be interrupted automatically or waived by means of the monitoring module, when the occurrence of indicators for a risk event is triggered in the data flow pathway of a risk exposure component. These embodied variants have, inter alia, the advantage that the system allows for further automation of the monitoring operation, especially of its operation with regard to the pooled resources.
 Login to view more
Login to view more  Login to view more
Login to view more