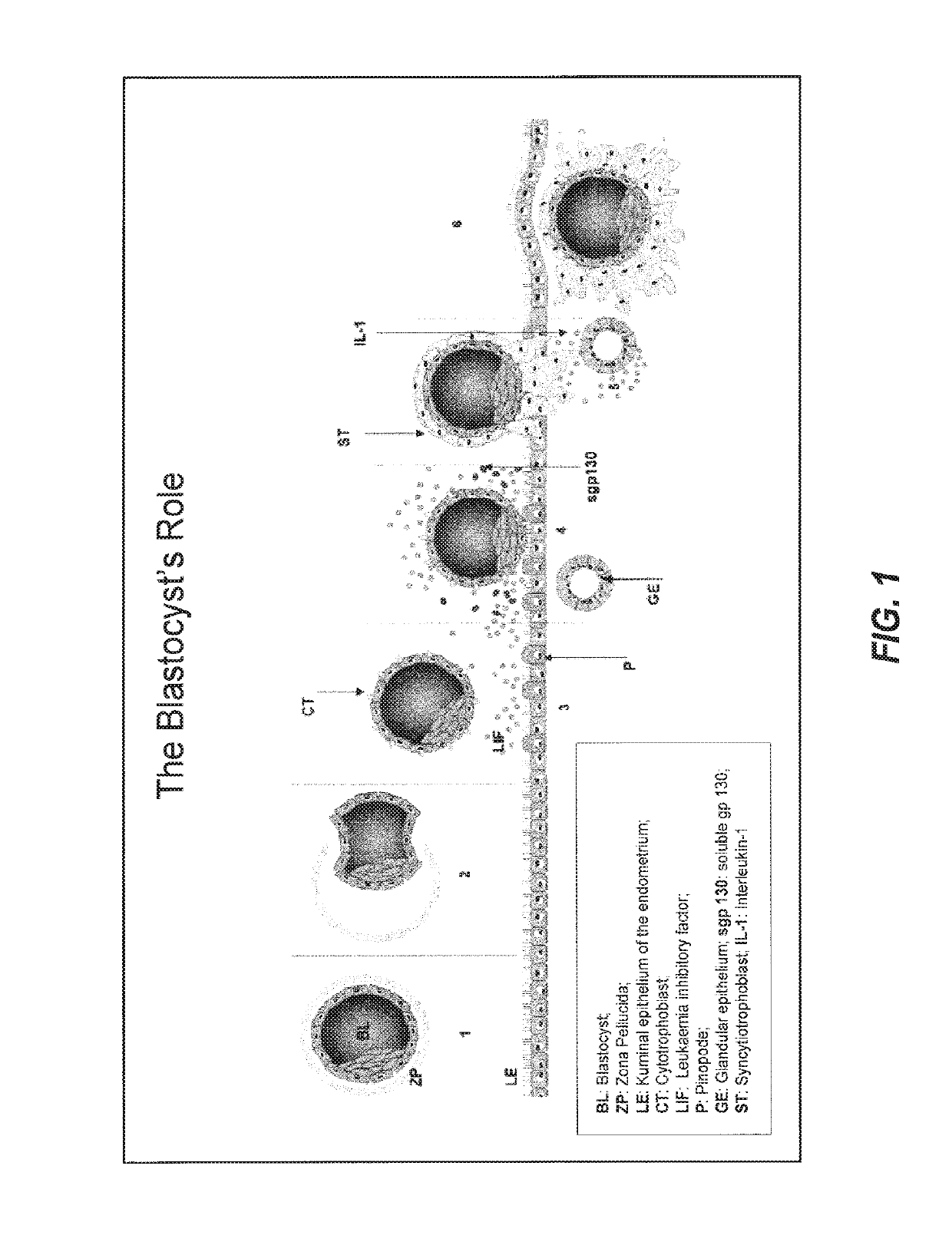
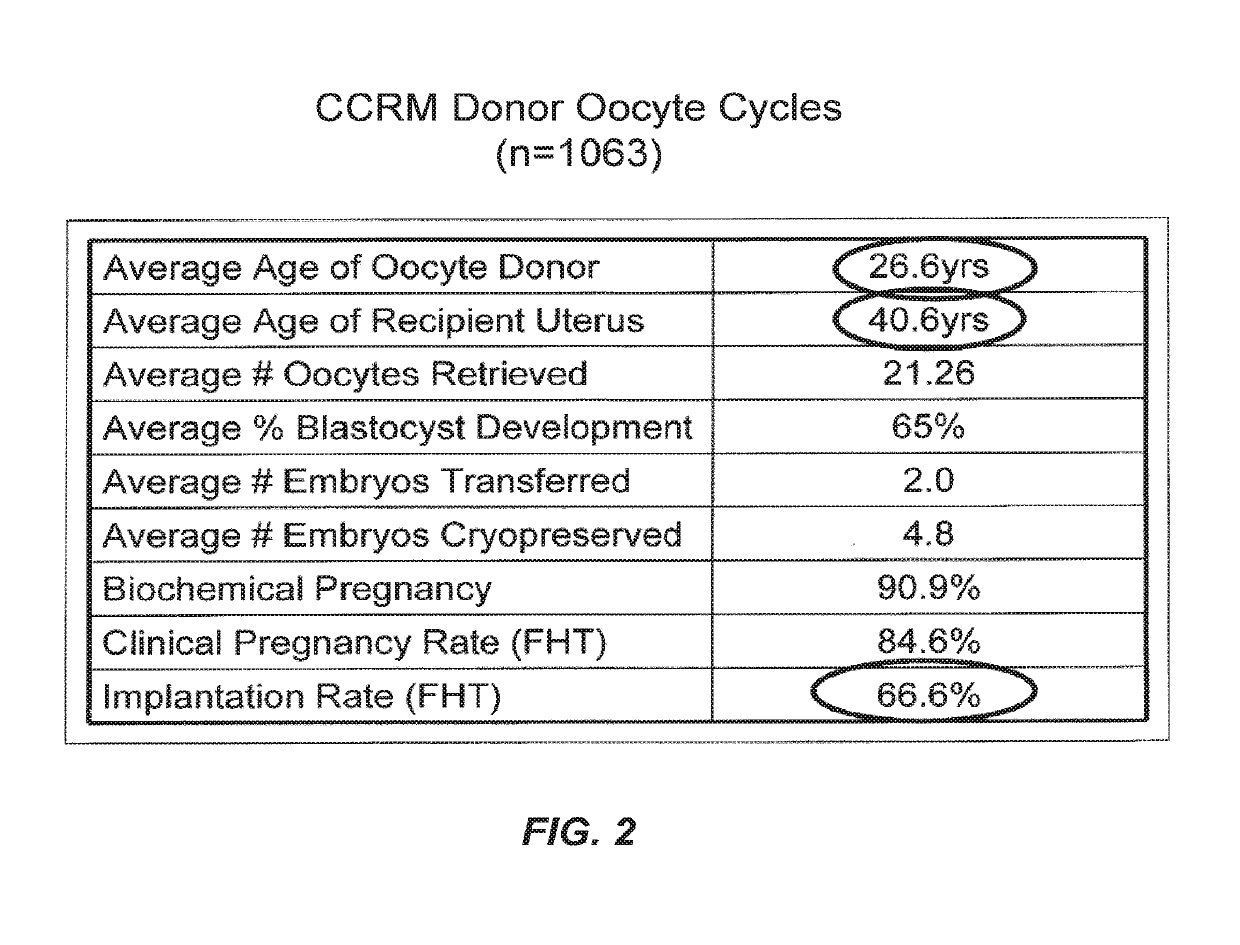
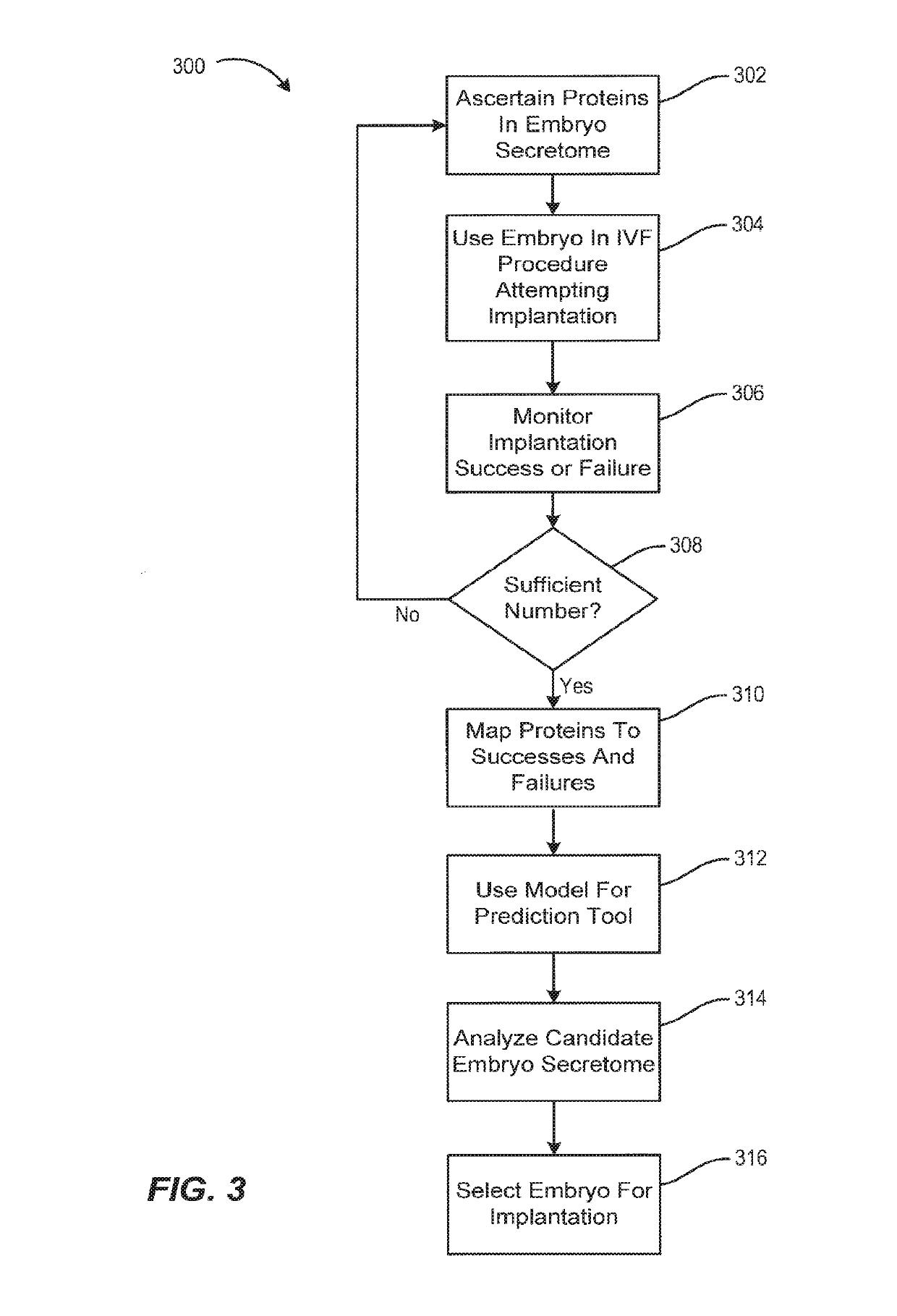
Secretome profile-facilitated in vitro fertilization
a secretome profile and in vitro fertilization technology, applied in the field can solve the problems of higher pregnancy rate, complicated and complex process, spontaneous abortion, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing the pregnancy success rate of in vitro fertilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Secretome Profiling of Human Embryos Using Mass Spectrometry
[0038]The following nonlimiting example teaches by way of illustration, not by limitation, secretome profiling of a human embryo using mass spectrometry (MS). Human cleavage-stage embryos were cultured in 10 μL drops of G1 supplemented with 2.5 mg / mL recombinant albumin under oil at 37° C., 6% CO2, 5% O2 for 24 hours. The embryos were washed twice in G2 culture media and further cultured in 10 μL drops of G2 supplemented with 2.5 mg / mL recombinant albumin under oil at 37° C., 6% CO2, 5% O2 for 48 hours with a fresh drop of G2 media added after 24 hours. Spent media samples of blastocysts were transferred into 0.65 mL Eppendorf tubes. Control groups comprised media cultured and collected under the same conditions but without embryos.
[0039]Micro-drops of spent media were depleted of human serum albumin (HSA) using Cibracron Blue Activated SwellGel Discs (Themo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, Ill.). The proteins in the spent medi...
example 2
Secretome Profiling to Predict Implantation Potential of a Human Embryo
[0045]The following nonlimiting example teaches by way of illustration, not by limitation, the fabrication and employment of a customized immunoassay test kit for secretome profiling of a human embryo Immunoassay test kit fabrication occurs by modifying the well surfaces of a 96-well microtiter plate. Each separate well of the microtiter plate is incubated with an unlabelled capture antibody that recognizes one specific protein from the secretome panel. Custom capture antibodies are purchased from Rockland Immunochemicals, Inc. After incubation for 12 hours at 4° C., capture antibodies passively adsorb to the well surface. Subsequently, all wells of the 96-well plate are washed three times with a buffer comprising 1× phosphate buffer saline and 0.1% Tween-20 (PBST), blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 1 hour at ambient temperature and washed three times with PB ST.
[0046]Human cleavage-stage embryos are...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com