Wire bar, method of manufacturing wire bar, and image forming apparatus
a wire bar and wire bar technology, applied in the field of image forming technique, to achieve the effect of preventing deviation of wire wounds, stable scraping of liquids, and improving development accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
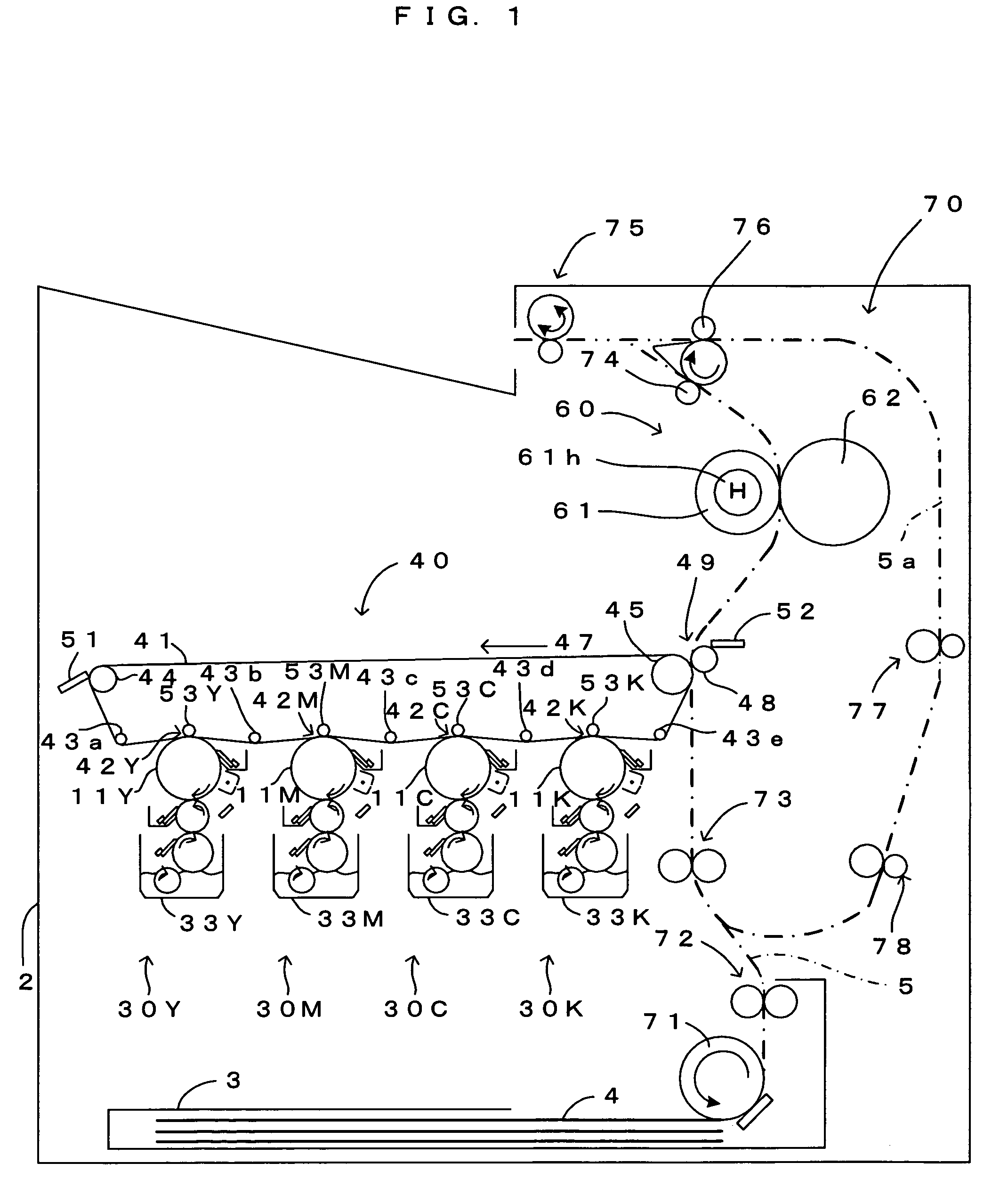
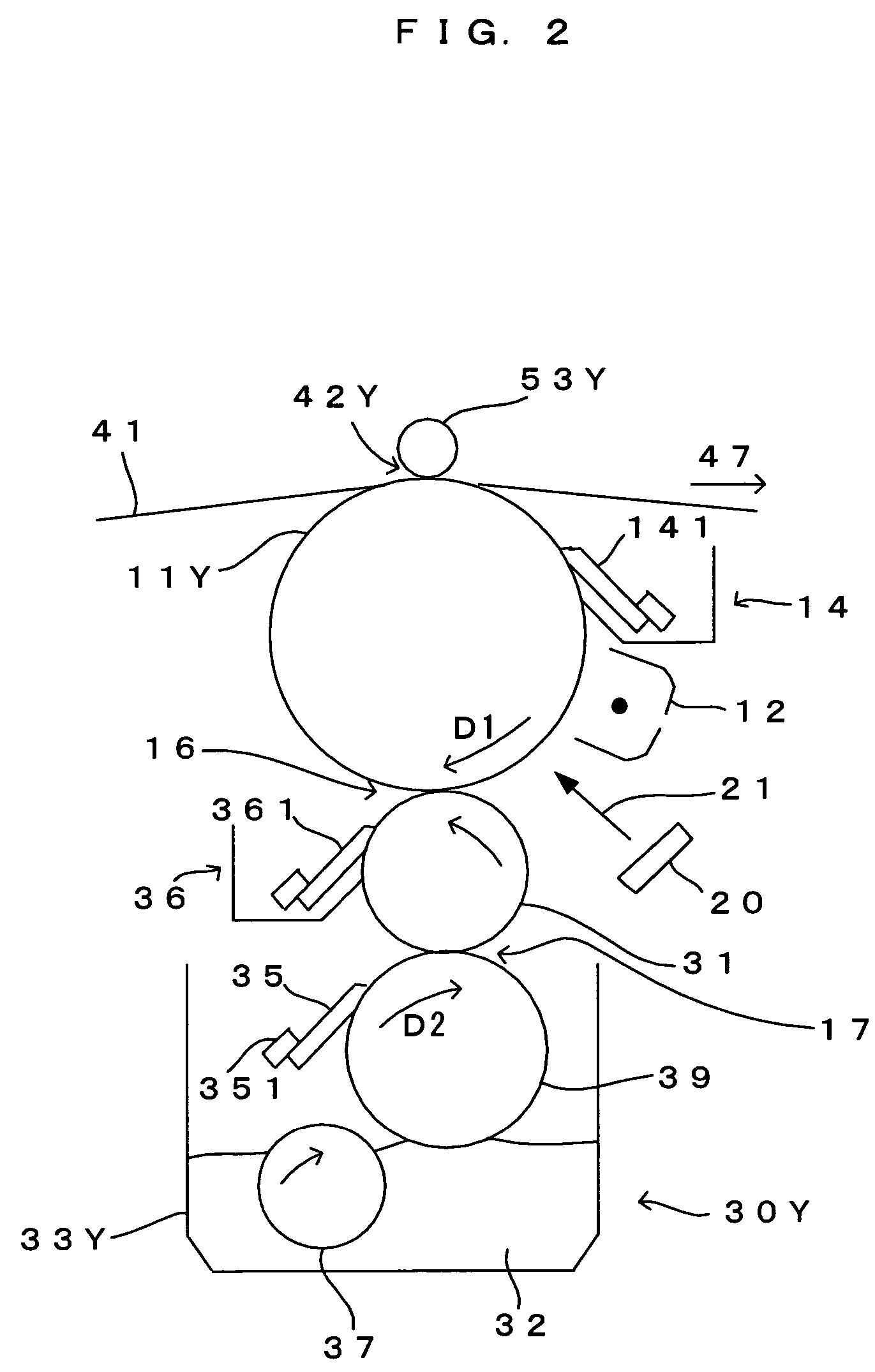
[0050]FIG. 1 is a drawing which shows the internal structure of a printer, a first embodiment of an image forming apparatus according to the invention. FIG. 2 is an enlarged view of an essential part in FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is a block diagram which shows the electric structure of the printer. This image forming apparatus is a color printer of the so-called tandem type, and photosensitive members 11Y, 11M, 11C and 11K for the four colors of yellow (Y), magenta (M), cyan (C) and black (K) are disposed as the “latent image carrier” of the invention parallel to each other inside a main apparatus section 2. A liquid development method is implemented in this printer, to thereby superimpose toner images carried on the photosensitive members 11Y, 11M, 11C and 11K upon each other and form a full color image, or form a monochrome image using a black (K) toner image alone. In this printer, as a print command signal containing an image signal is fed to a main controller 100 from an external appar...
second embodiment
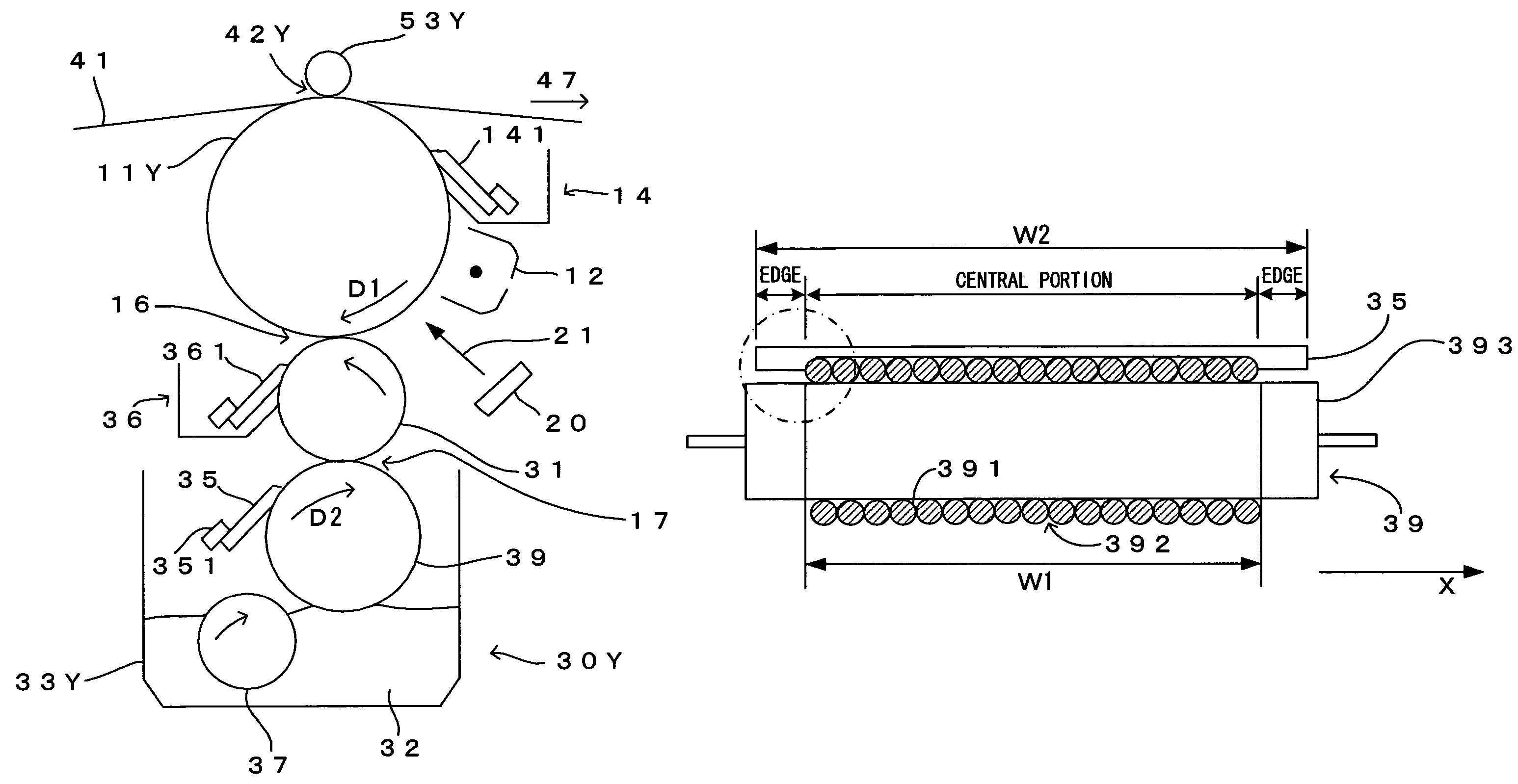
[0086]FIG. 8 is an enlarged schematic diagram of a wire bar and a regulator blade in the second embodiment of the image forming apparatus according to the invention. A major difference of the second embodiment from the first embodiment is that concaves 353 corresponding to the coating area are formed in a central portion of a regulator blade 35b, and other structures are similar to those in the first embodiment. The second embodiment will now be described in detail, focusing mainly on the difference from the first embodiment. The structures and the operations which are the same as those according to the first embodiment will not be described.
[0087]The regulator blade 35b according to the second embodiment is made of urethane rubber which serves as an elastic member. There are the concaves 353 in the central portion of the regulator blade 35b and there are steps HK at the boundaries between the ends and the central portion of the regulator blade 35b. The regulator blade 35b is dispos...
third embodiment
[0088]FIG. 9 is an enlarged schematic diagram of a wire bar and a regulator blade in the third embodiment of the image forming apparatus according to the invention. A major difference of the third embodiment from the first embodiment is that the width W2 of a regulator blade 35c is wider than the width W3 of the wire bar 39, and other structures are similar to those in the first embodiment. The third embodiment will now be described in detail, focusing mainly on the difference from the first embodiment. The structures and the operations which are the same as those according to the first embodiment will not be described.
[0089]In the third embodiment, along the X-direction, the width W2 of the regulator blade 35c is wider than the width W3 of the wire bar 39 (metal core 393), and the both edges of the regulator blade 35c are respectively located on the outer side to the both edges of the wire bar 39 (metal core 393). Since the both edges of the regulator blade 35 are respectively loca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com