Driving circuit with impedence calibration
a driving circuit and impedence technology, applied in the direction of pulse generators, electrical apparatus, electric pulse generators, etc., can solve the problems of inability to apply the tail current source connection reference ground, still suffer from an over-large power consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of less power consumption and the same performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
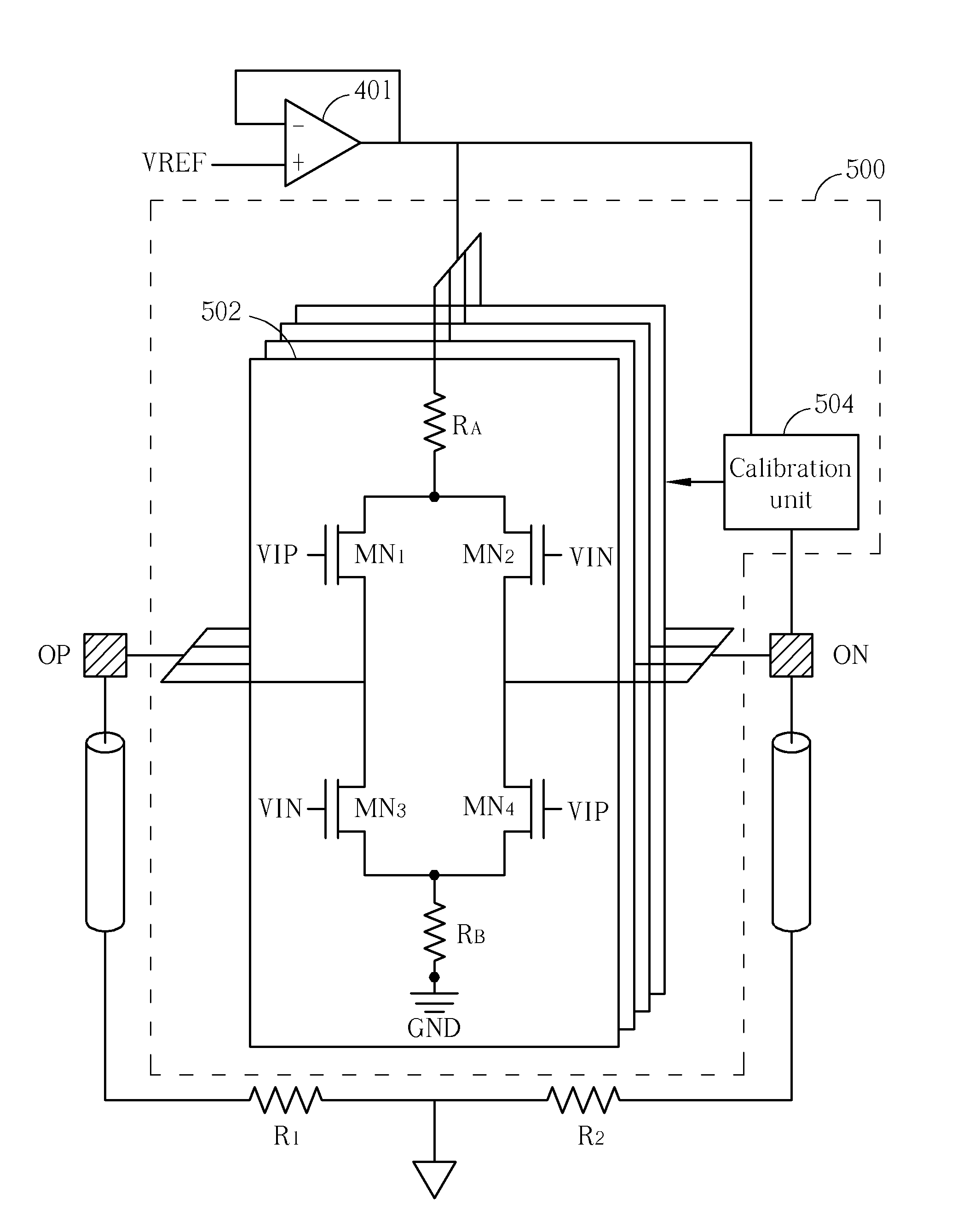
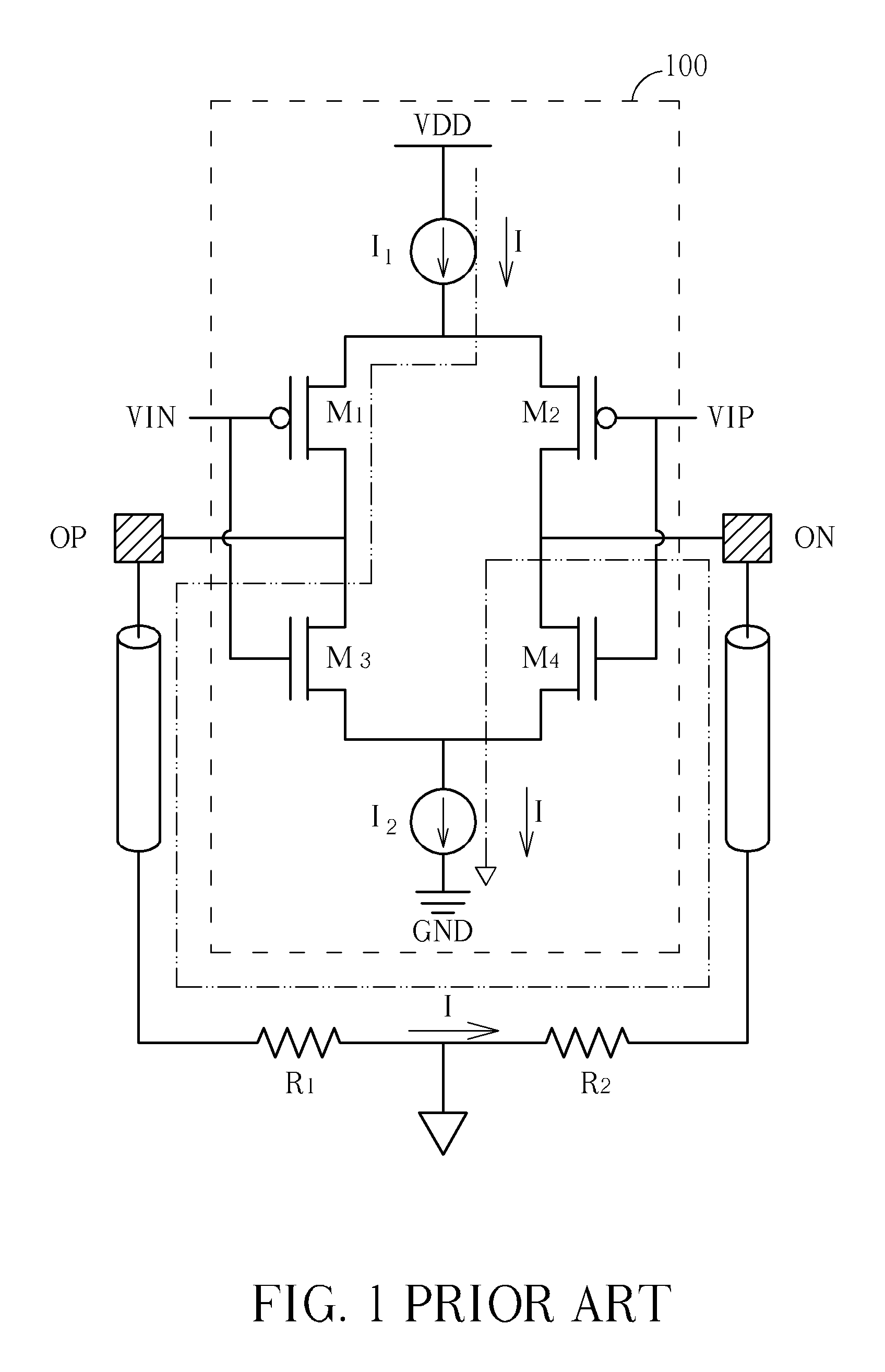
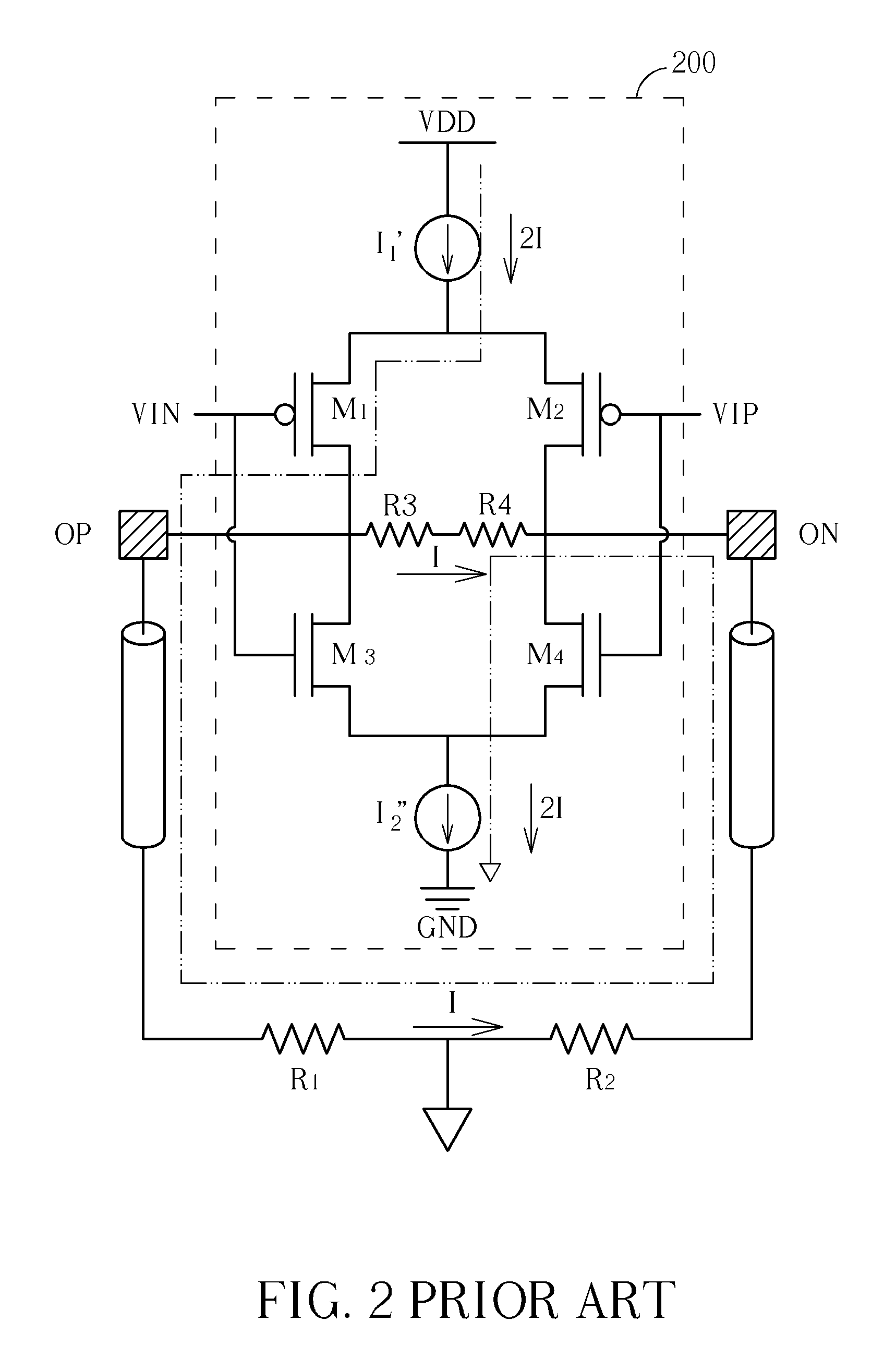
[0016]Please refer to FIG. 4, which shows a driving unit (e.g., an LDVS driver) according to an embodiment of the present invention. The exemplary driving unit 400 includes, but is not limited to, a first bias component RA, a second bias component Re, a first metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor MN1, a second MOS transistor MN2, a third MOS transistor MN3, and a fourth MOS transistor MN4, where the first, second, third, and fourth MOS transistors MN1-MN4 have the same conductive type. By way of example, rather than limitation, the first and second bias components RA and RB are implemented using resistors, and the first, second, third, and fourth MOS transistors are N-channel metal-oxide-silicon (NMOS) transistors for a lower threshold voltage. However, this is for illustrative purposes only. Any driving circuit that follows the exemplary circuit architecture shown in FIG. 4 to configure interconnections of implemented bias components and MOS transistors falls within the scope ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com