Optimum modulator bias systems and methods in coherent optical transmitters
a modulator and bias technology, applied in the field of optical communication systems and methods, can solve the problems of not necessarily optimum points, inability to generate correct constellations, and added unnecessary costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
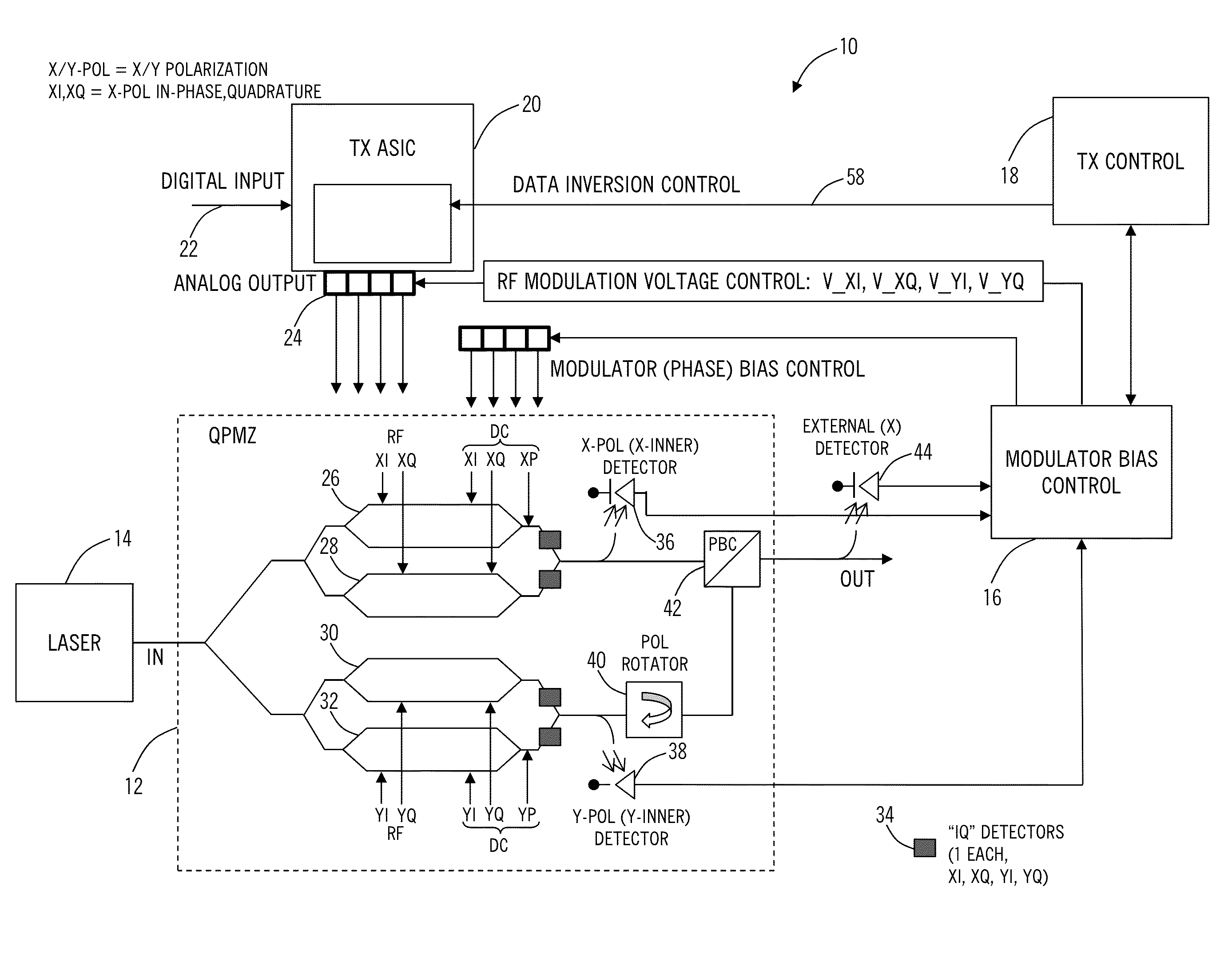
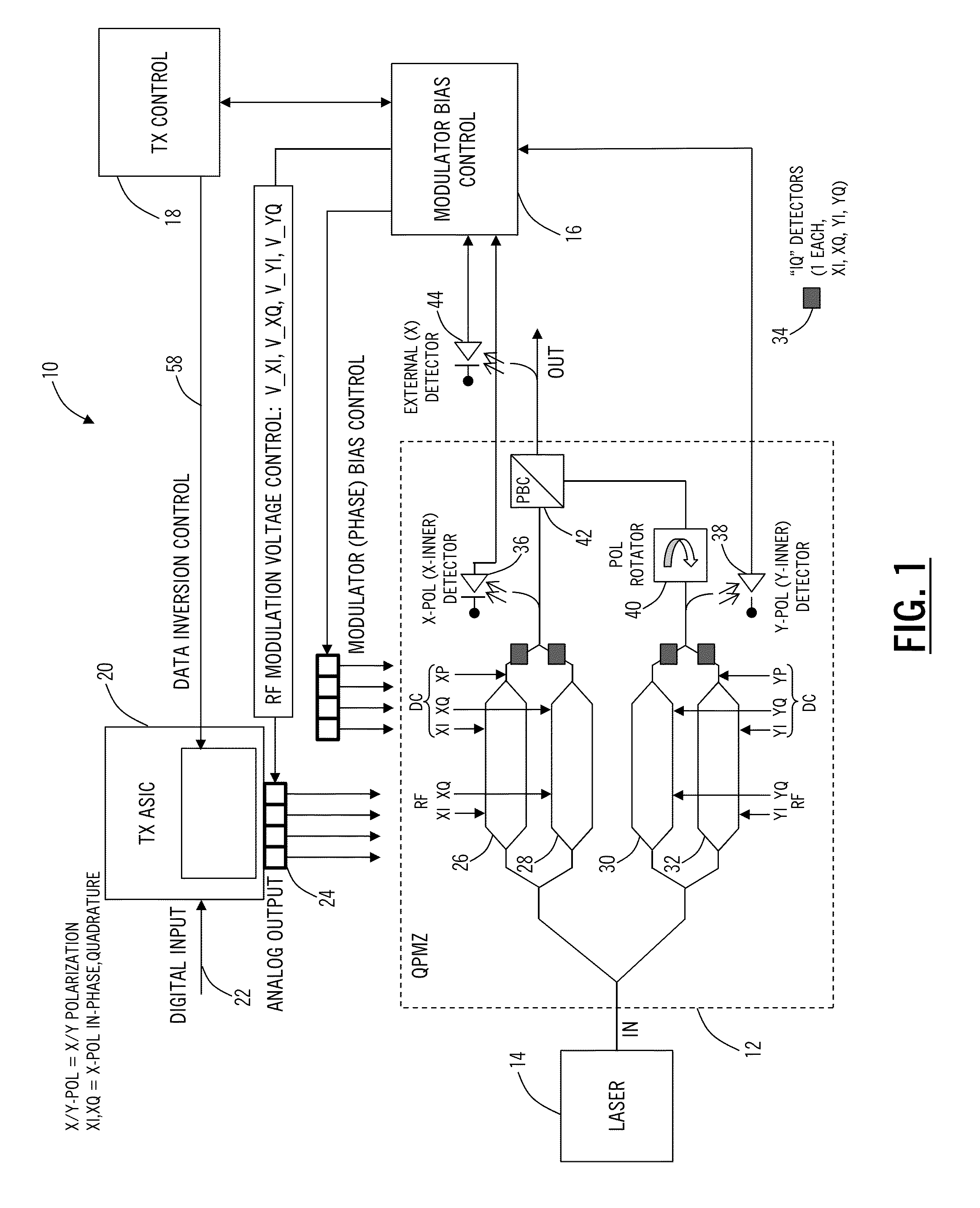
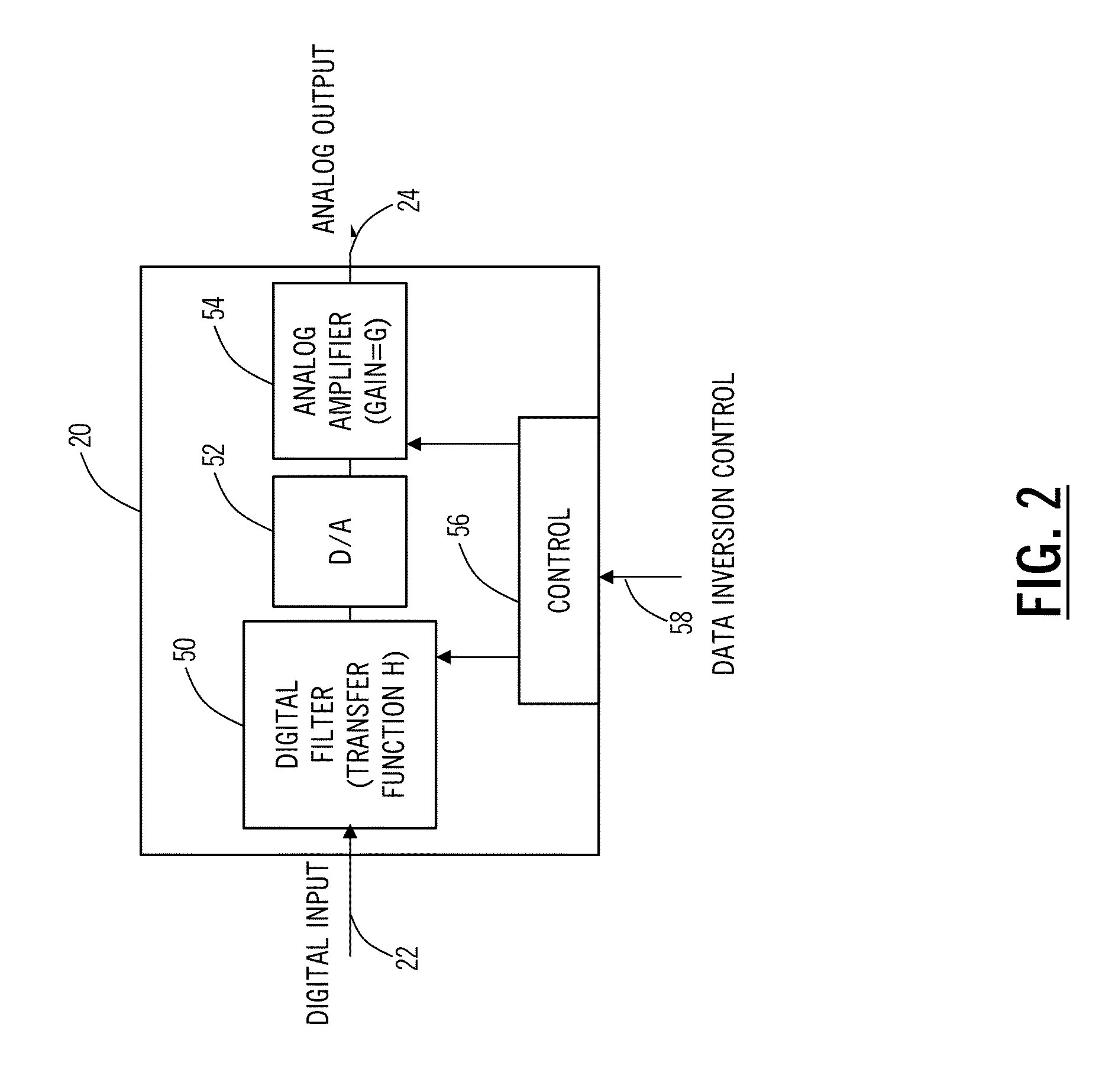
[0016]In various exemplary embodiments, the present disclosure relates to optimum modulator bias systems and methods in coherent optical transmitters. The optimum modulator bias systems and methods solve the problem of generating the correct constellation using the (bias points) with the minimum phase adjustment range. The optimum modulator bias systems and methods include a coherent optical transmitter with control of four (XI, XQ, YI, YQ) quadrature data signals via a transmitter (Tx) application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), with a modulator bias controller which implements an algorithm to find the optimum bias points. The optimum bias points yield a correct constellation with minimum phase / bias adjustment. An algorithm is used to find the optimum bias solution using fast, simple method, adjusting only one quadrature at a time and exploiting a control feature of the Tx ASIC. This algorithm is significantly simpler than a generalized search, is a local algorithm, and uses on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com