Method for plating using nested plating buses and semiconductor device having the same
a plating bus and bus technology, applied in the direction of conductive pattern reinforcement, electrical apparatus construction details, association of printed circuit non-printed electric components, etc., can solve the problems of restriction in routing electrical connections from the vias, single layer substrates, and the most expensive individual cost components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
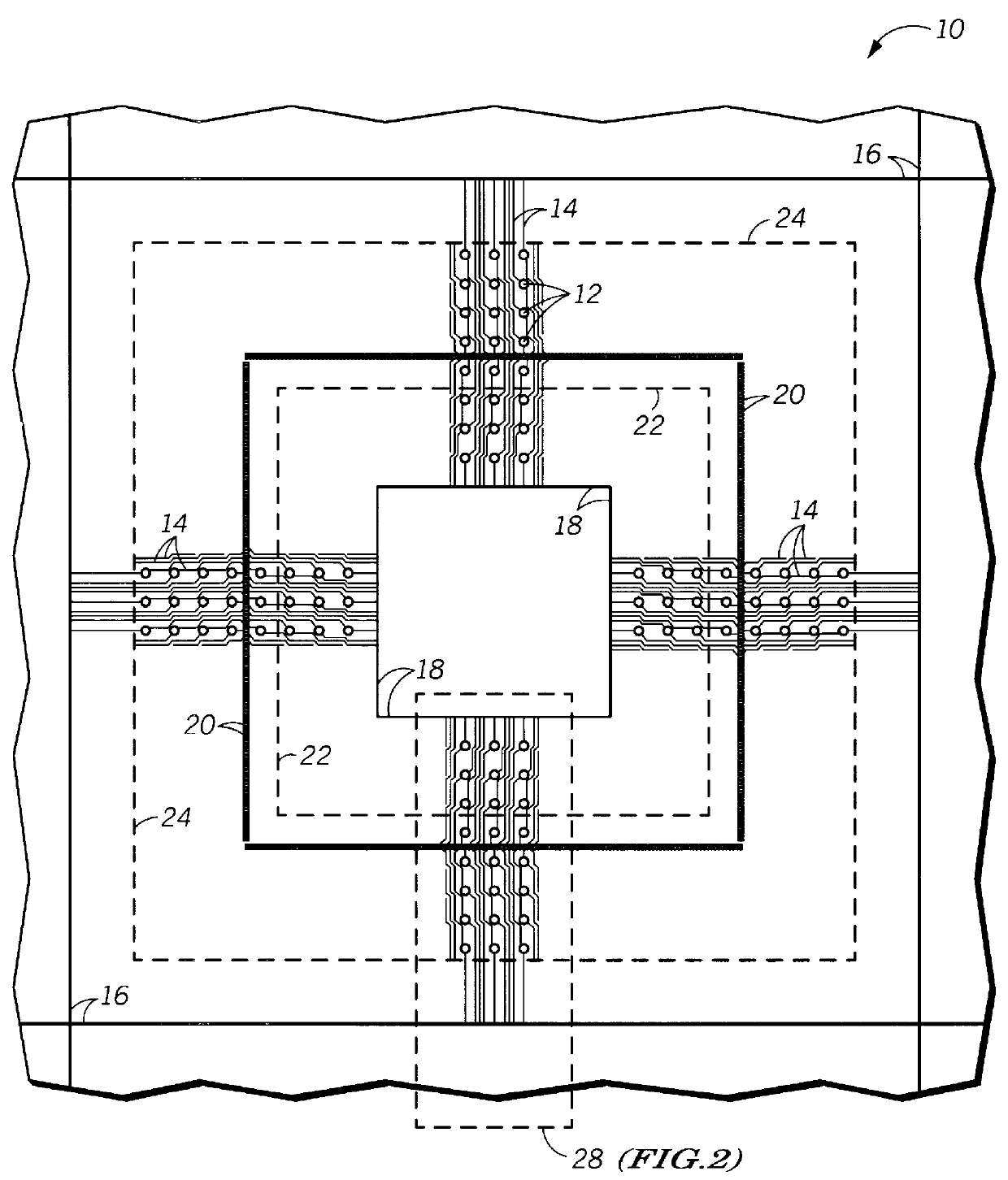
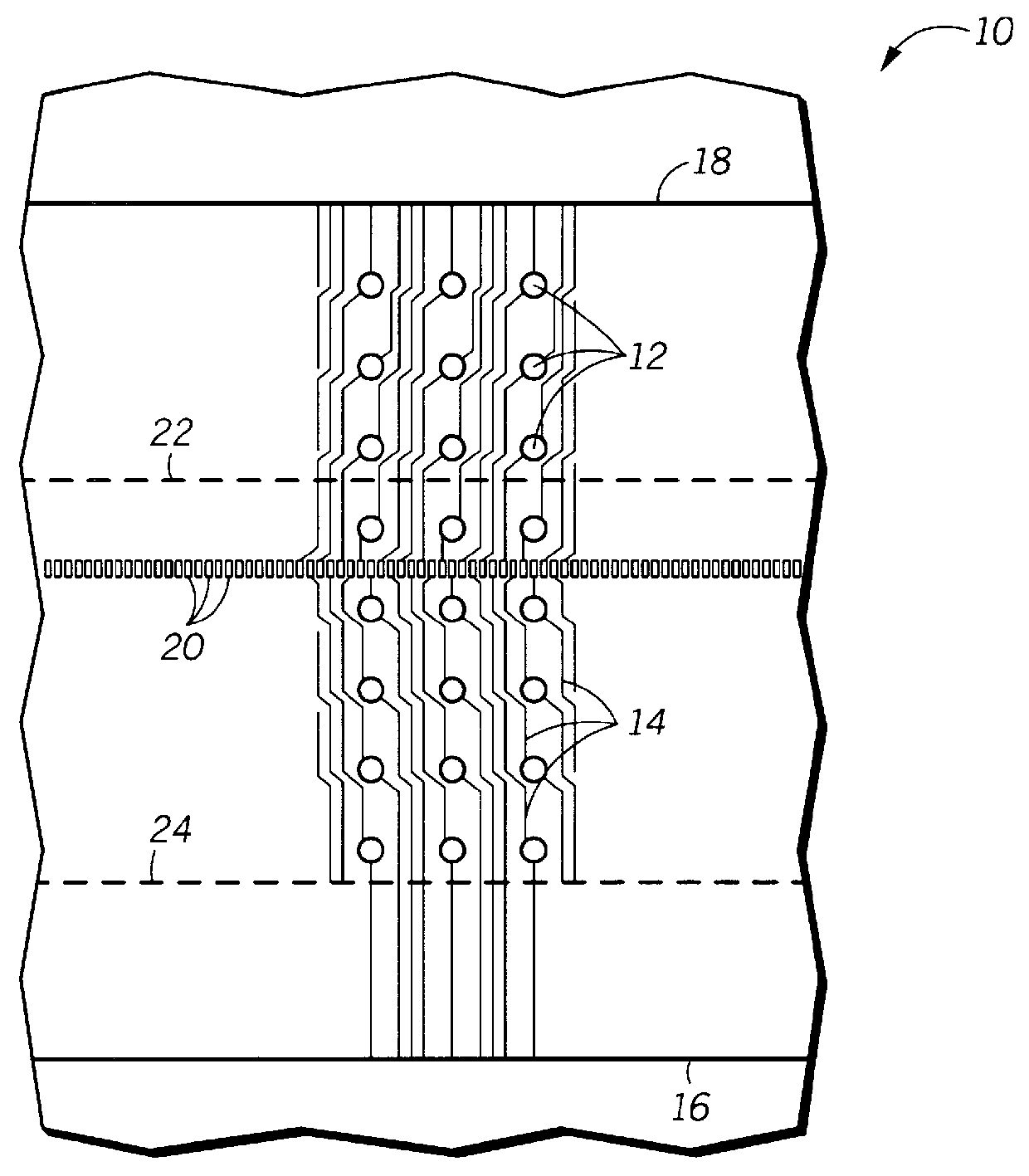
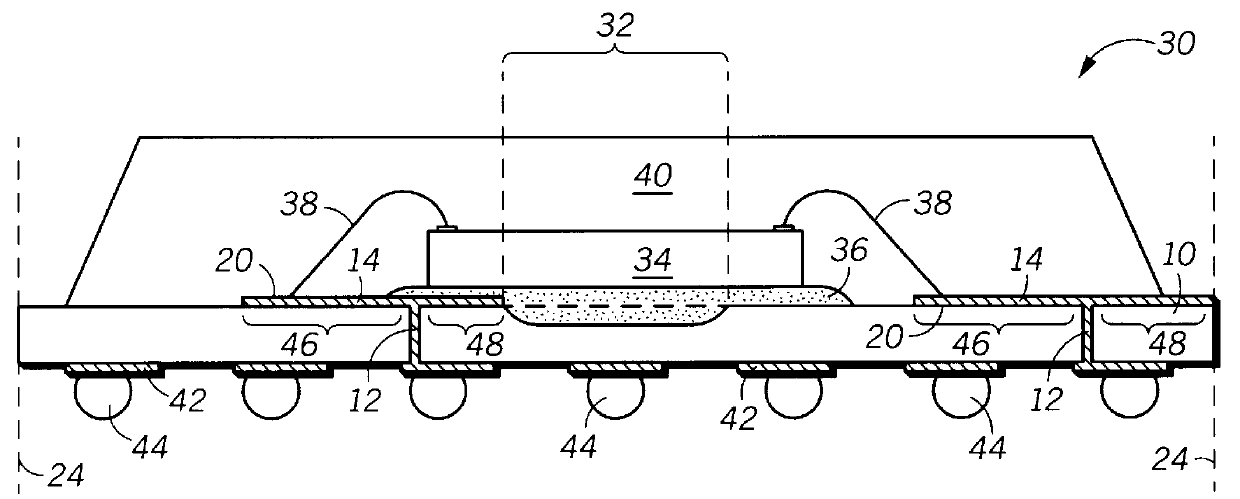
The present invention increases the maximum possible I / O count for a given substrate size by allowing a nested plating bus to complement the existing external plating bus. In addition, the use of the nested plating bus reduces or eliminates the need for bottom side electrical routing which should improve package reliability and electrical performance by increasing the distance between discrete conductive traces, vias and solder pads on the bottom side of the substrate.
These and other features, and advantages, of the present invention will be more clearly understood from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It is important to point out that the illustrations may not necessarily be drawn to scale, and that there may be other embodiments of the present invention which are not specifically illustrated. Also, like reference numerals may be used throughout the various views, indicating identical, corresponding, or similar elements.
FIG. 1 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com