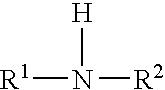
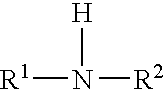
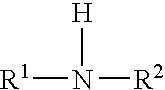
Lubricant containing molybdenum compound and secondary diarylamine
a technology of molybdenum compound and diarylamine, which is applied in the direction of lubricant composition, liquid carbonaceous fuel, additives, etc., can solve the problems of demanding environment of lubricating oil used in automobiles or trucks, and achieve low treatment level, reduce the overall cost of the entire additive package, and supplemental oxidation protection and frictional properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0060]The following example shows the antioxidant synergism that exist,; when molybdenum naphthenate and a diphenylamine are formulated into an SAE Grade 5W-30 type motor oil. The example also shows that this antioxidant behavior is unique when compared to other metals.
[0061]A variety of oil soluble metals and one diphenylamine type antioxidant were blended into an SAE Grade 5W-30 type motor oil as shown in Table 1. The only additional antioxidant in these blends was the zinc dialkyldithiophosphate. The oxidation stability of these oils was measured by pressurized differential scanning calorimetry (PDSC) as described by J. A. Walker and W. Tsang in “Characterization of Lubrication Oils by Diffrential Scanning Calorimetry”, SAE Technical Paper Series, 801383 (Oct. 20-23, 1980). Oil samples were treated with an iron (III) acetylacetonate catalyst (55 ppm Fe) and 2 milligrams (mg) were analyzed in an open aluminum hermetic pan. The DSC cell was pressurized with 500 psi air and programm...
example 2
[0068]Molybdenum naphthenate and alkylated diphenylamine, Naugalube 680, from Uniroyal Chemical Company; were blended into an SAE Grade 5W-30 type motor oil as shown in Table II. The only additional antioxidant in these blends was the zinc dialkyldithiophosphate. The oxidation stability of these oils was measured by pressurized differential scanning calorimetry (PDSC) as described in Example 1. These oils were also subjected to the following hot oil oxidation test: Into 25 grams (g) of each motor oil was blended 0.8 g of a catalyst mixture containing 5.55 wt % iron (III) naphthenate (6 wt % Fe content) and 94.45 wt % xylenes. Dry air was blown through the oil at rates of 10 Liters (L) / hour (h) while maintaining the temperature at 160° C. for a period of 72 hours. The oil was cooled and the percent change in viscosity between the new oil and the oxidized oil was determined at 40° C. A lower percent change in viscosity for an oil is an indication of less oil degradation and thus bette...
example 3
[0070]The following example shows that other classes of amines, e.g., certain substituted amines, disubstituted phenylene diamines, and alkyl amines, are not effective or minimally effective at controlling oxidation when used in combination with molybdenum carboxylates.
[0071]Molybdenum naphthenate and a variety of amines, were blended into an SAE Grade 5W-30 type motor oil (formulated crankcase oil as described in Example 2) as shown in Table III and as further described below. The only additional antioxidant in these blends was the zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate. The oxidation stability of these oils was measured by pressurized differential scanning calorimetry (PDSC) as described in Example 1. These oils were also subjected to the hot oil oxidation test described in Example 2.
[0072]Both the hot oil oxidation test results (small percentage changes in viscosity) and the PDSC test results (prolonged oxidation induction times) show that the combination of molybdenum naphthenate and alky...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com