Face recognition method based on random sampling
A random sampling and face recognition technology, applied to computer components, character and pattern recognition, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as no discriminant information and too small zero space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
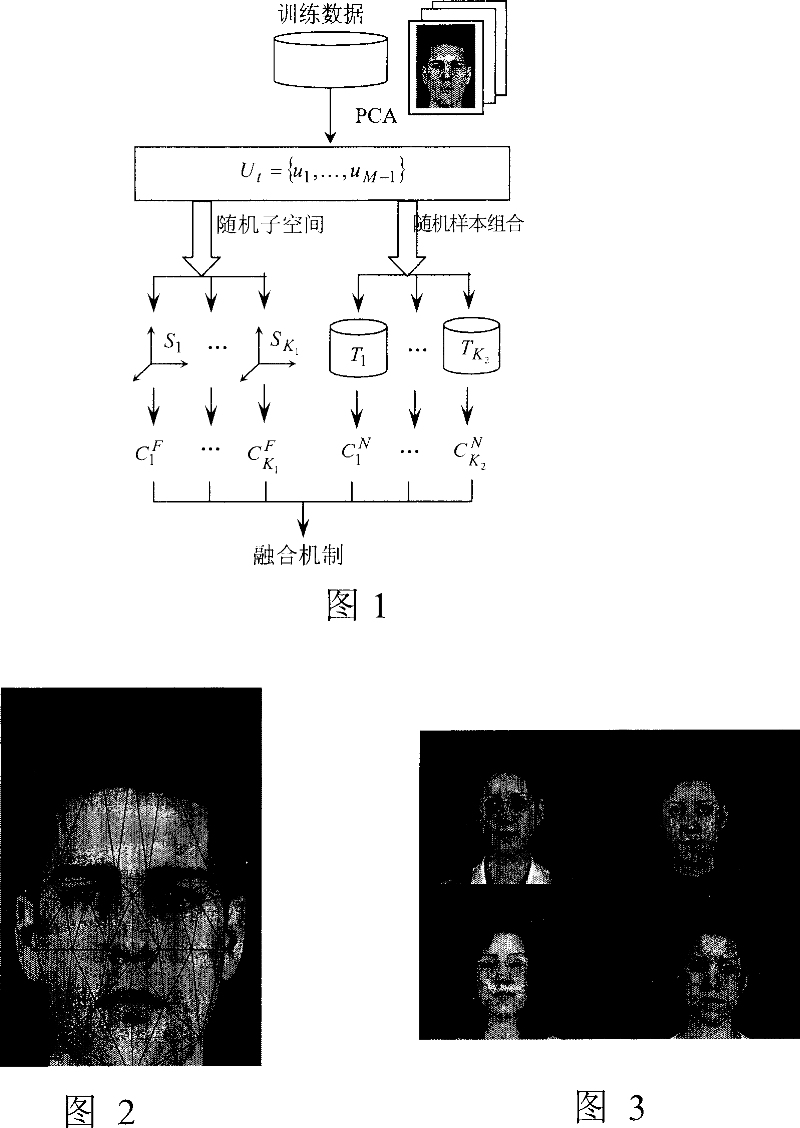
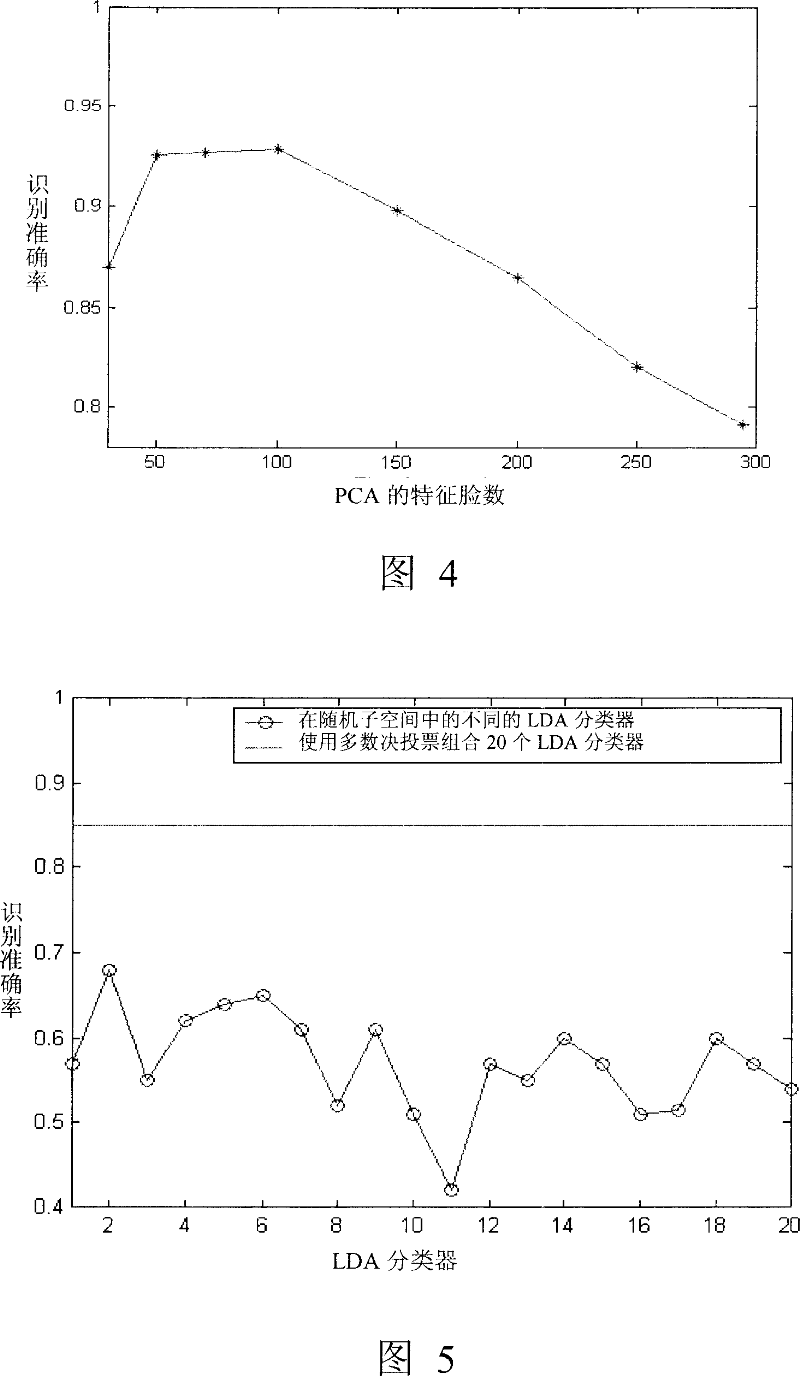
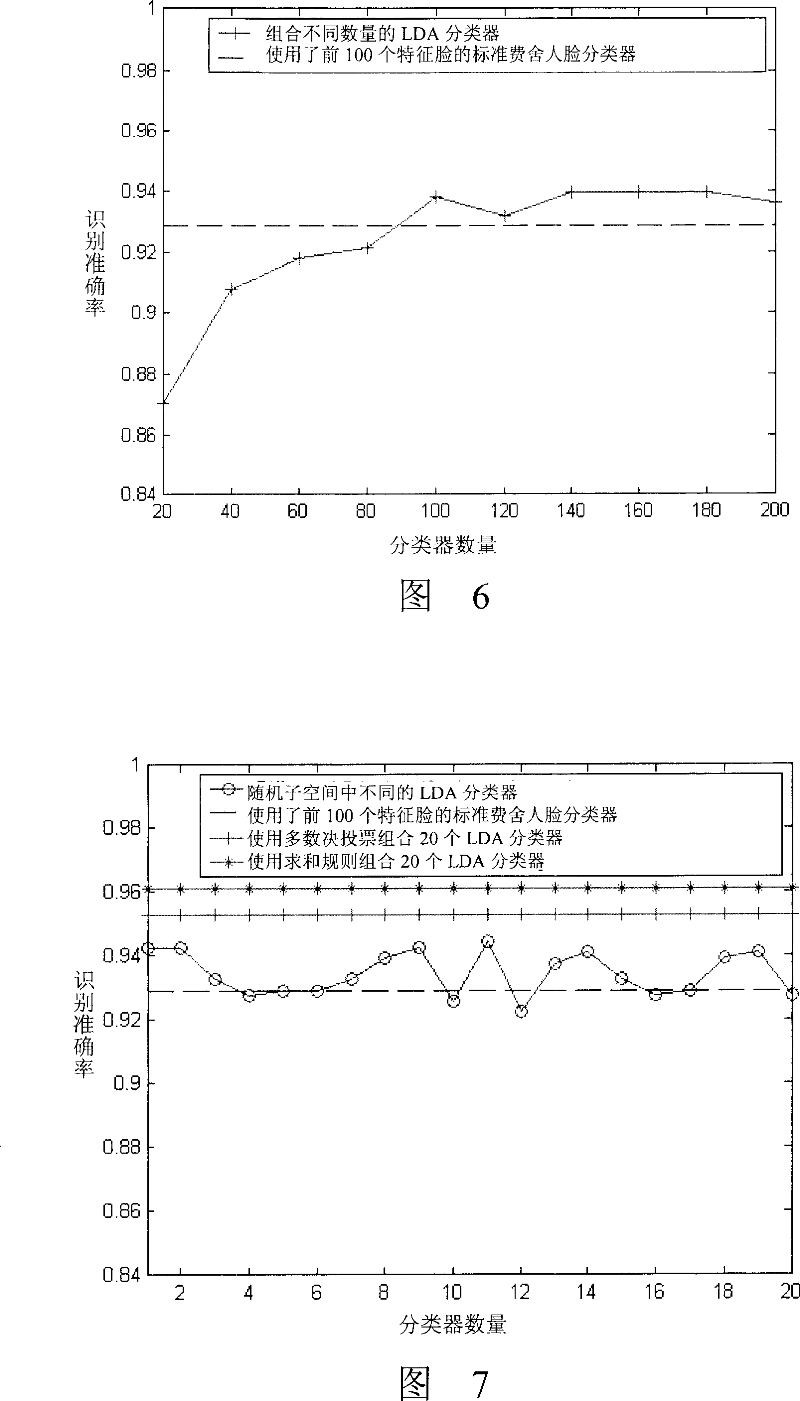
[0057]Although the dimensionality of the image space is high, only part of the space (subspace) includes discriminative information. These subspaces are spanned by eigenvectors corresponding to nonzero eigenvalues in covariance C. The covariance matrix calculated from M training samples has at most M-1 eigenvectors corresponding to non-zero eigenvalues. In the remaining eigenvectors corresponding to zero eigenvalues, all training samples have zero projections and contain no discriminative information. Therefore, the two LDA algorithms in the present invention firstly project the high-dimensional image data to the M-1 dimensional PCA subspace, and then perform random sampling. Of course, it is also possible to directly perform random sampling on the original data without performing PCA processing.
[0058] Random subspace and random sample combination...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com