Synchronous mirror delay (SMD) circuit and method including a ring oscillator for timing coarse and fine delay intervals
A delay circuit, fine delay technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, automatic power control, signal generation/distribution, etc., can solve the problem of SMD power consumption and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
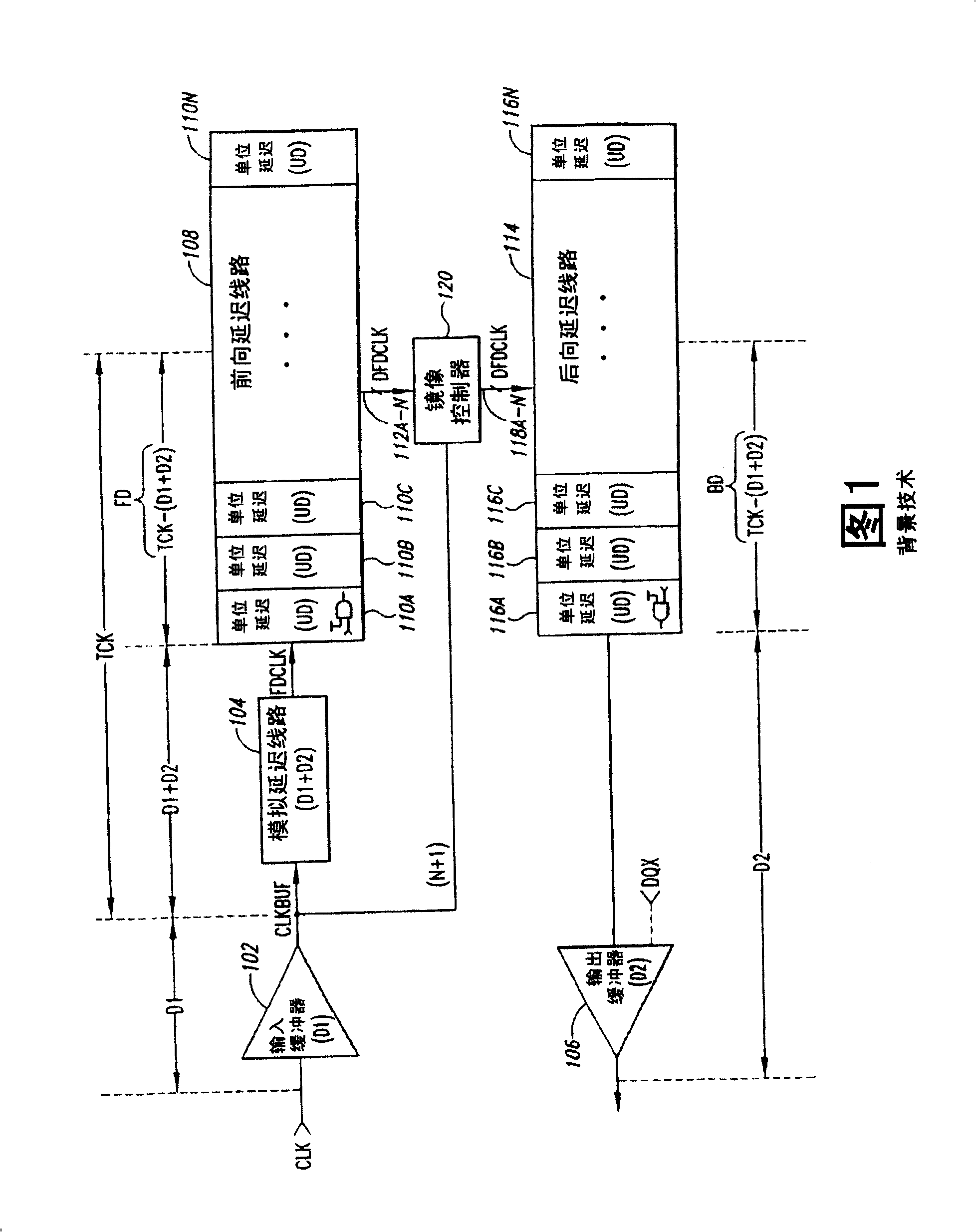
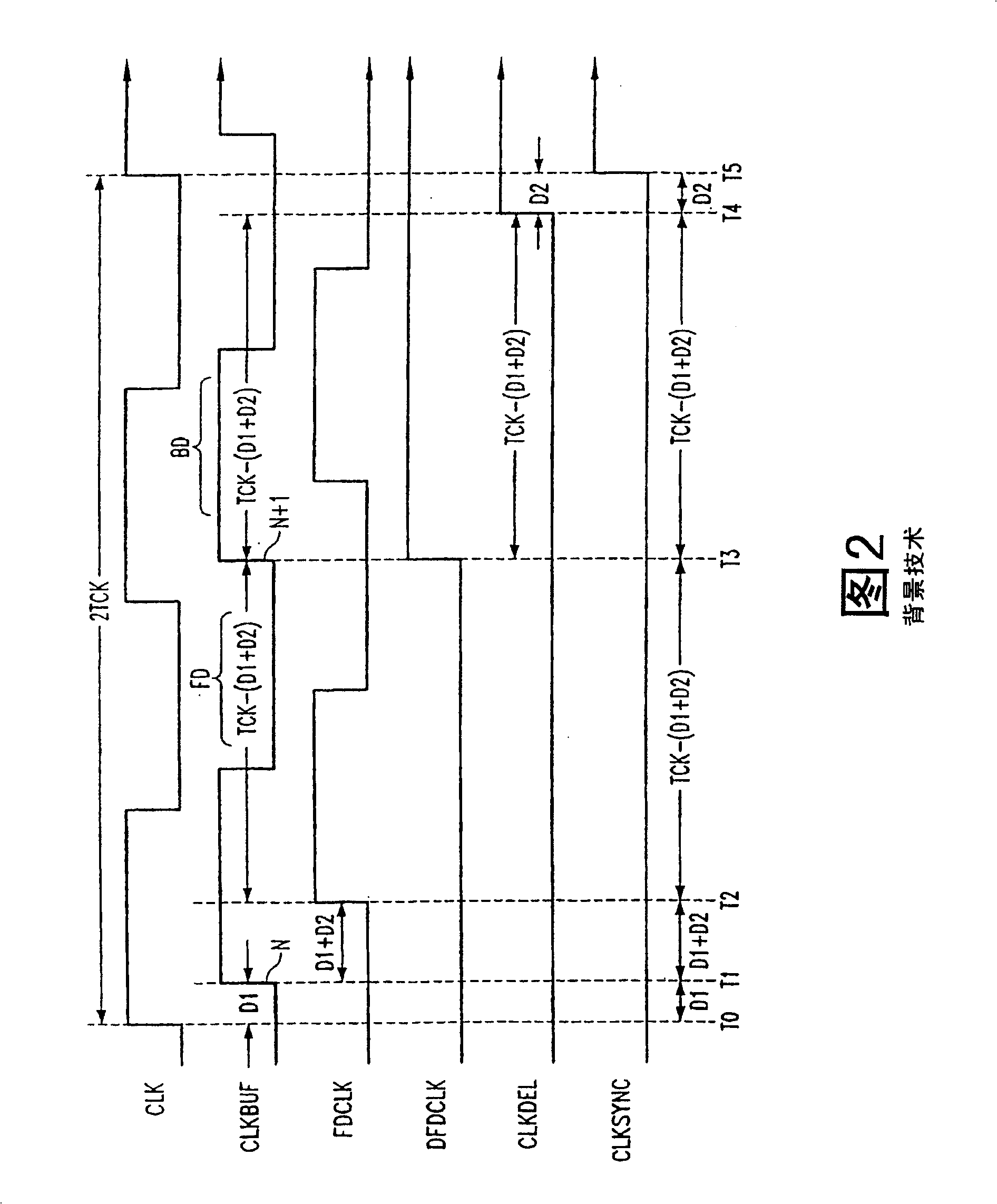
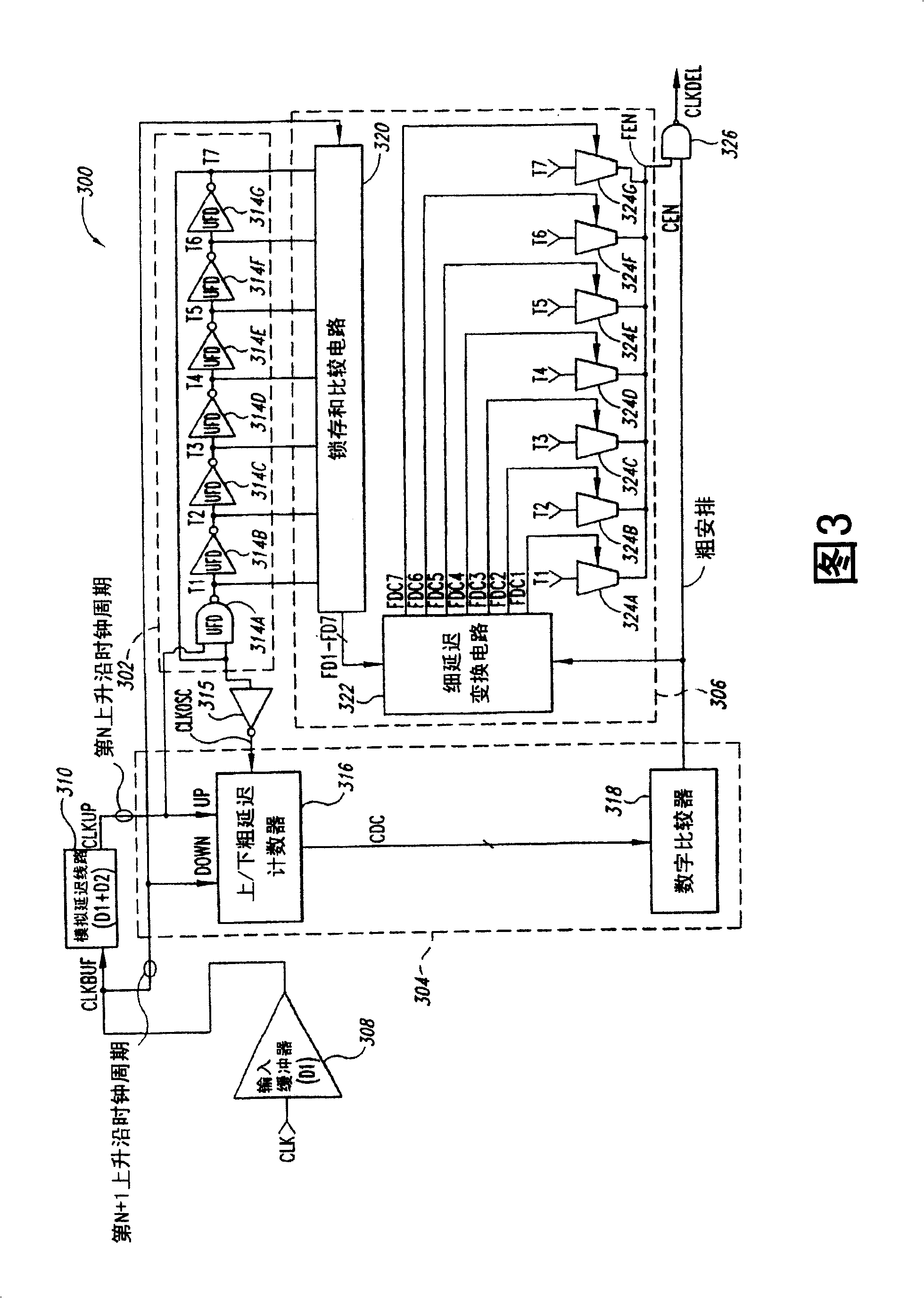
[0024] FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram of the rising edge portion of the SMD 300, in which the SMD 300 removes the relatively large and high-power forward and backward delay lines 108 included in the conventional SMD 100 described in FIG. 1, and replaces it A ring oscillator 302 is included. The ring oscillator 302 provides a clock to the coarse delay circuit 304 to define a coarse delay CD, and is utilized by the fine delay circuit 306 to define a fine delay FD. During operation, the SMD 300 adjusts the values of the coarse and fine delays CD and FD to generate a delayed clock signal CLKDEL that is synchronized with the external clock signal CLK (for example, has a desired delay relative to the external clock signal), as will be described in more detail below . In the following description, specific details are explained to provide a thorough understanding of the present invention. However, it is obvious to a person of ordinary skill in the art that the present invention c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com