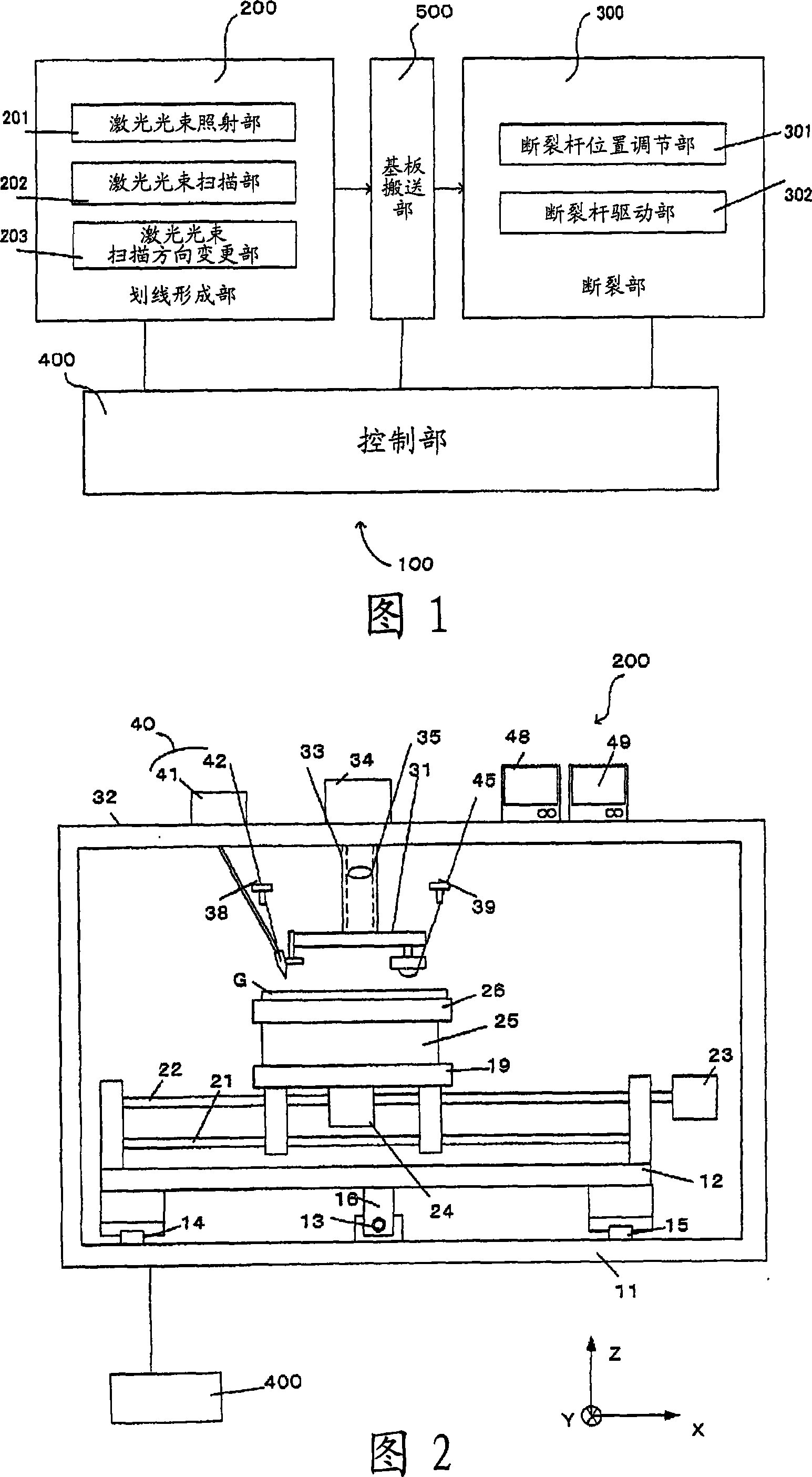
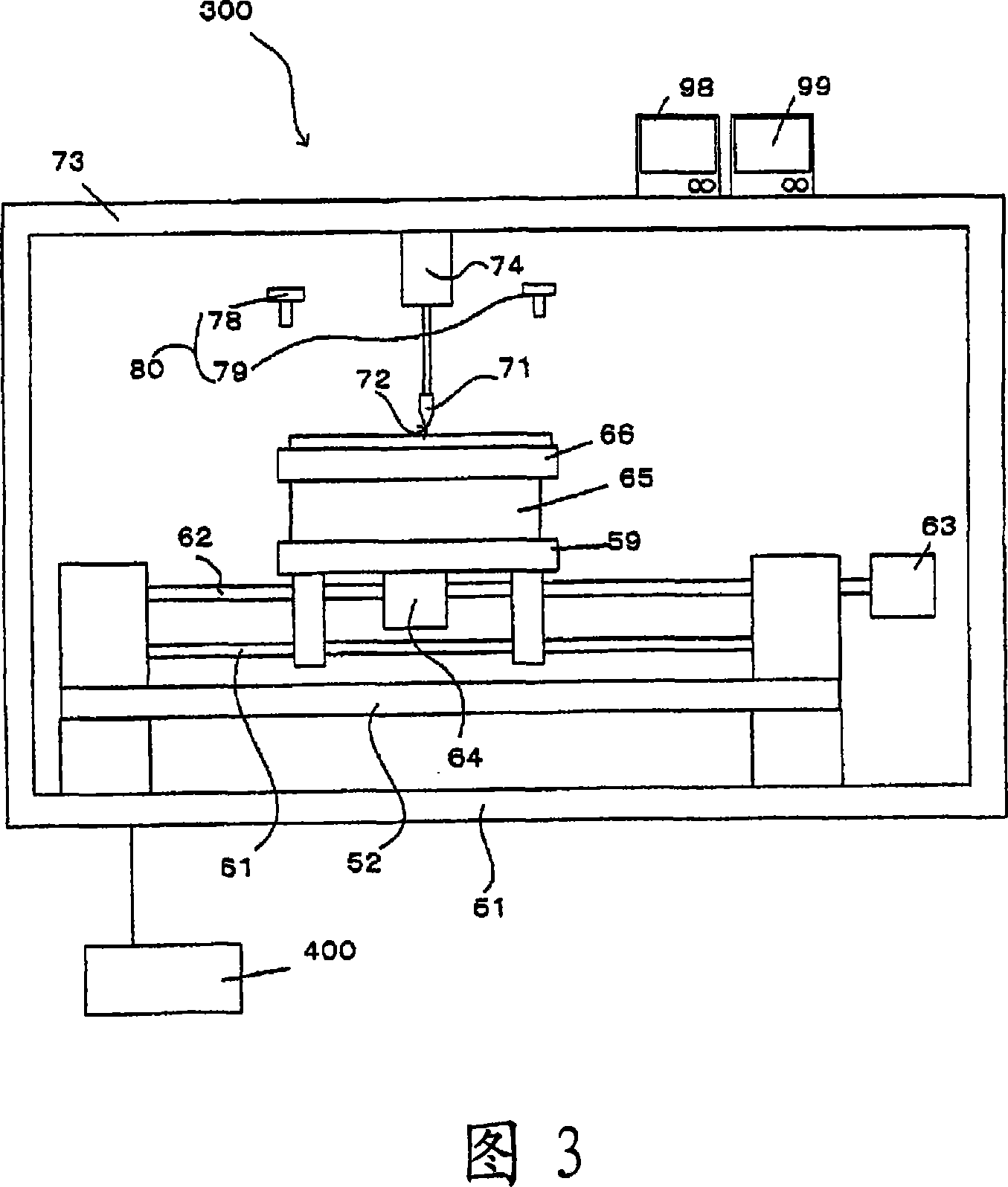
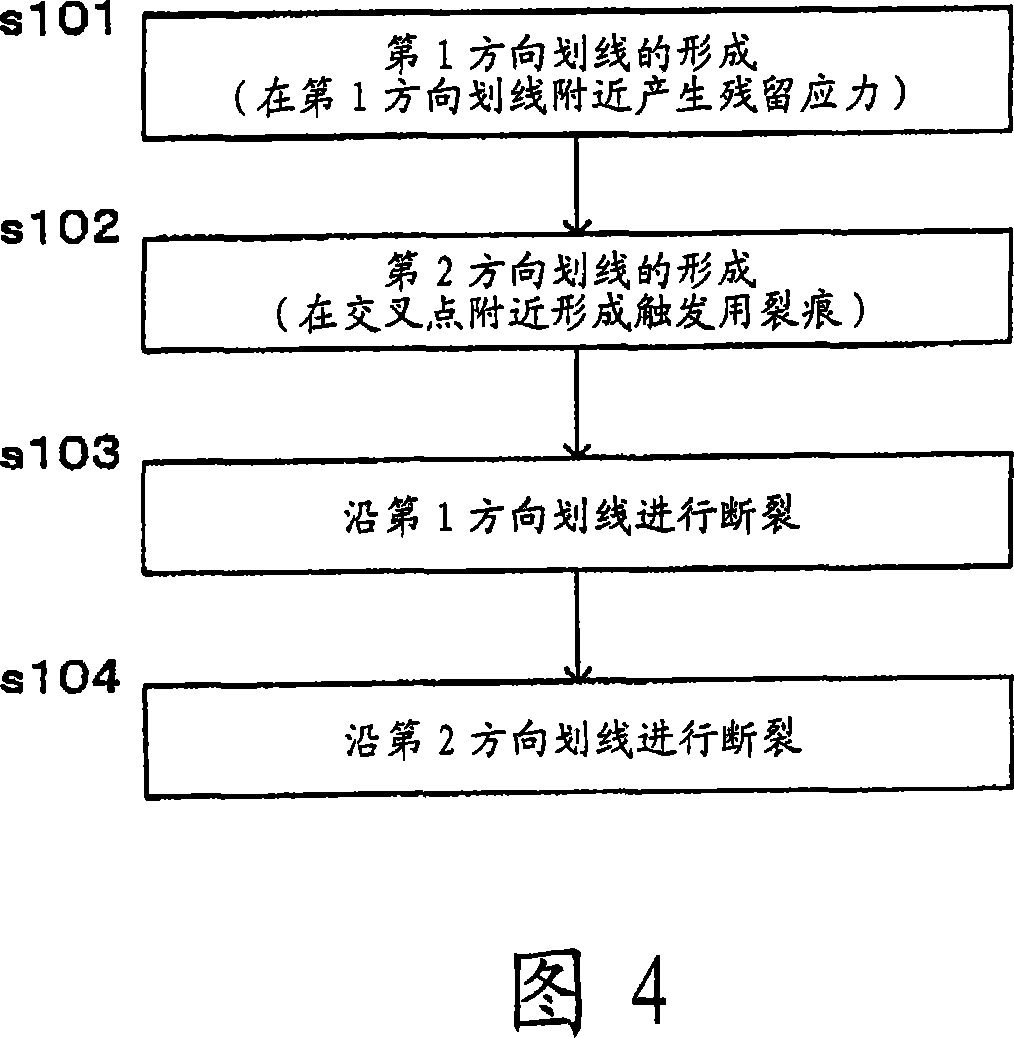
Method for cutting brittle material substrate and substrate cutting system
A brittle material substrate and substrate technology, which is applied in the processing of insulating substrates/layers, nonlinear optics, stone processing equipment, etc. The effect of simplifying the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0113] In the case of carrying out the cutting method of the present invention as described above, it is necessary to form a trigger crack for breaking on the mother substrate when the scribing step is performed. Hereinafter, based on the experimental data, the presence or absence of the occurrence of the trigger crack for fracture will be described.
[0114] 7 shows the moving speed of the laser beam (row direction data in FIG. 7 ) when the scribing process (first scribing) is performed in the first direction, and the scribing process (second scribing) is performed in the second direction, respectively. ) data on the visible crack generation range when the laser beam moving speed (the column direction data in FIG. 7 ) is changed. The moving speeds of the laser beams for both the first scribe line and the second scribe line were changed within a range of 90 to 160 mm / s.
[0115] The material of the substrate used at this time was soda glass, and its thickness was 2.8 mm. The...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com