Method of papermaking
A white water and aqueous solution technology, used in papermaking, papermaking, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as affecting product paper hue, corroding pipe metal materials, etc., to reduce COD in drainage, high deodorization effect, and simplify the effect of chemical treatment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
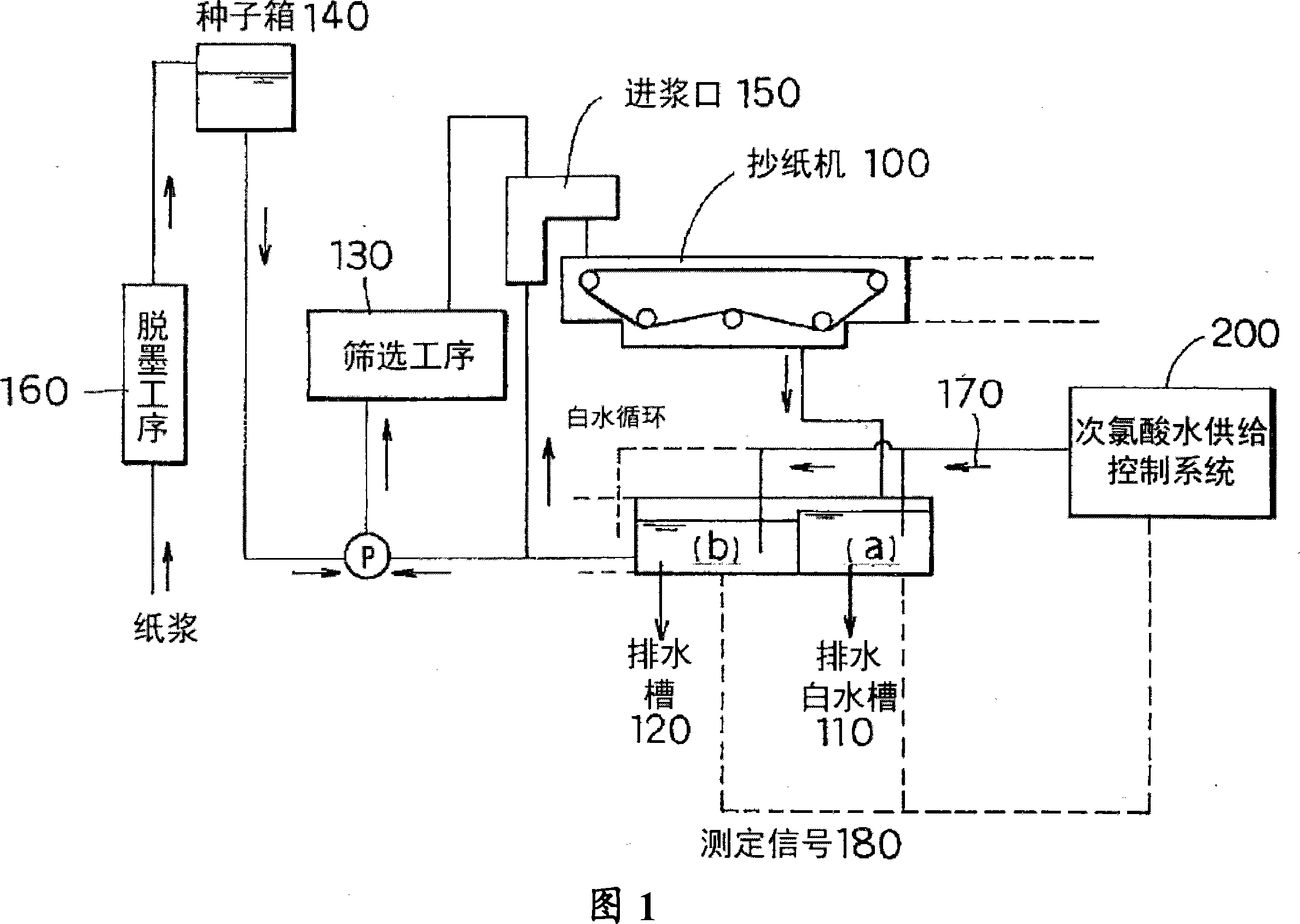
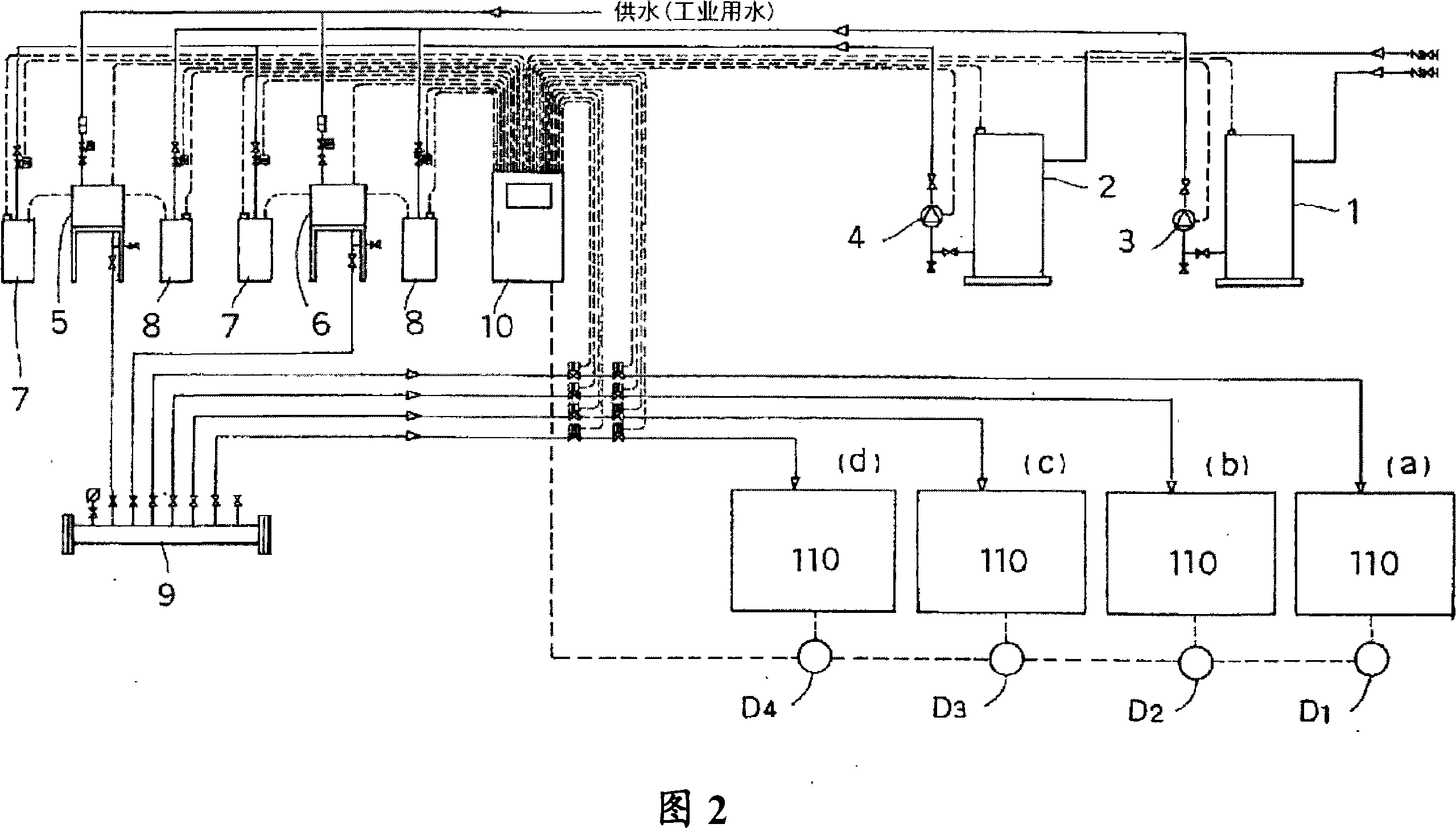
[0044] FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a wet end environment control system of a white water circulation line in a papermaking process using a waste paper raw material. The white water after papermaking in the paper machine 100 is first sent to the white water tank 110 , where slime treatment is performed, a part of it is recycled to the pulp inlet 150 , and the other part is sent to the drainage tank 120 . On the other hand, the pulp raw material is sent from the deinking process tank 160 to the seed box 140 , passes through the screening tank 130 , is sent to the pulp inlet 150 , and finally reaches the paper machine 100 . Here, only one white water tank 110 on one paper machine 100 is shown, but usually four paper machines 100 are connected in series, and each paper machine is provided with each white water tank 110 (a), (b) ), (c), (d) slots.
[0045] From the hypochlorous acid water supply system 200, predetermined hypochlorous acid water is continuously supplied to the...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Type of waste paper used: Office waste paper recovered from the office (premium waste paper and medium waste paper were mixed together) were used, and the following bleaching treatment was performed before papermaking.
[0052] Analysis evaluation / Brightness: JIS-P8123 (Hunter whiteness test method)
[0053] Remaining ink amount: Using a microscope (10 times) and an image analyzer (LA-525 manufactured by Pias), the area of the ink in a certain field of view was expressed as a ratio (%).
[0054] The office waste paper is thrown into the pulper for disintegration. The conditions of the pulper were a pulp concentration of 4.5%, a temperature of 26°C, and a NaOH of 1.0%. Next, the waste paper pulp was dewatered in the screw press until the pulp concentration became 18%, and the waste paper pulp was retained in the aging tower for 12 hours. Next, the pulp was diluted to a concentration of 3.5%, and the pulp was extracted from the maturing tower, dedusted by a Jonson scr...
Embodiment 3
[0063]The absolute dry mass of 80.0 g of kraft pulp after alkali oxygen bleaching (brightness is 47.2%, kappa value is 9.9) is put into a plastic bag, and the pulp concentration is adjusted to 10% with ion-exchanged water, and then pH4. 5. The 10000ppm sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution was soaked for 60 minutes at room temperature for initial bleaching. After diluting the obtained pulp with ion-exchanged water to 3%, dehydration and washing were performed with a Buchner funnel. The pulp was placed in a plastic bag, and the pulp concentration was adjusted to 10% with ion-exchanged water, then an aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution of pH 5 and 3000 ppm was added, and the mixture was treated at room temperature for 90 minutes to perform second-stage bleaching. After diluting the obtained pulp with ion-exchanged water to adjust the pulp concentration to 3%, a pulp mat was formed with a Buchner funnel, and the pulp was dewatered with a pulper to obtain (30.0% concentration) pul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap