Anti-CD19 antibodies and uses in oncology
A technology of antibodies and human antibodies, applied in the direction of antibodies, chemical instruments and methods, peptides, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be evaluated by efficacy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0460] 6.2 Example 1: Expression of human CD19 in transgenic mice
[0461] The transgenic hCD19TG mice described herein or other transgenic animals expressing human CD19 can be used to evaluate different treatment regimens comprising human, humanized or chimeric anti-CD19 antibodies, e.g. or change over time. Efficacy in human patients with different treatment regimens can be predicted using two indicators, namely: B cell depletion in certain body fluids and / or tissues and monoclonal human or humanized anti-CD19 antibodies Ability to bind to B cells. In particular embodiments, therapeutic regimens that are effective in human CD19 transgenic mice and compositions and methods of the invention can be used to treat B-cell malignancies in humans.
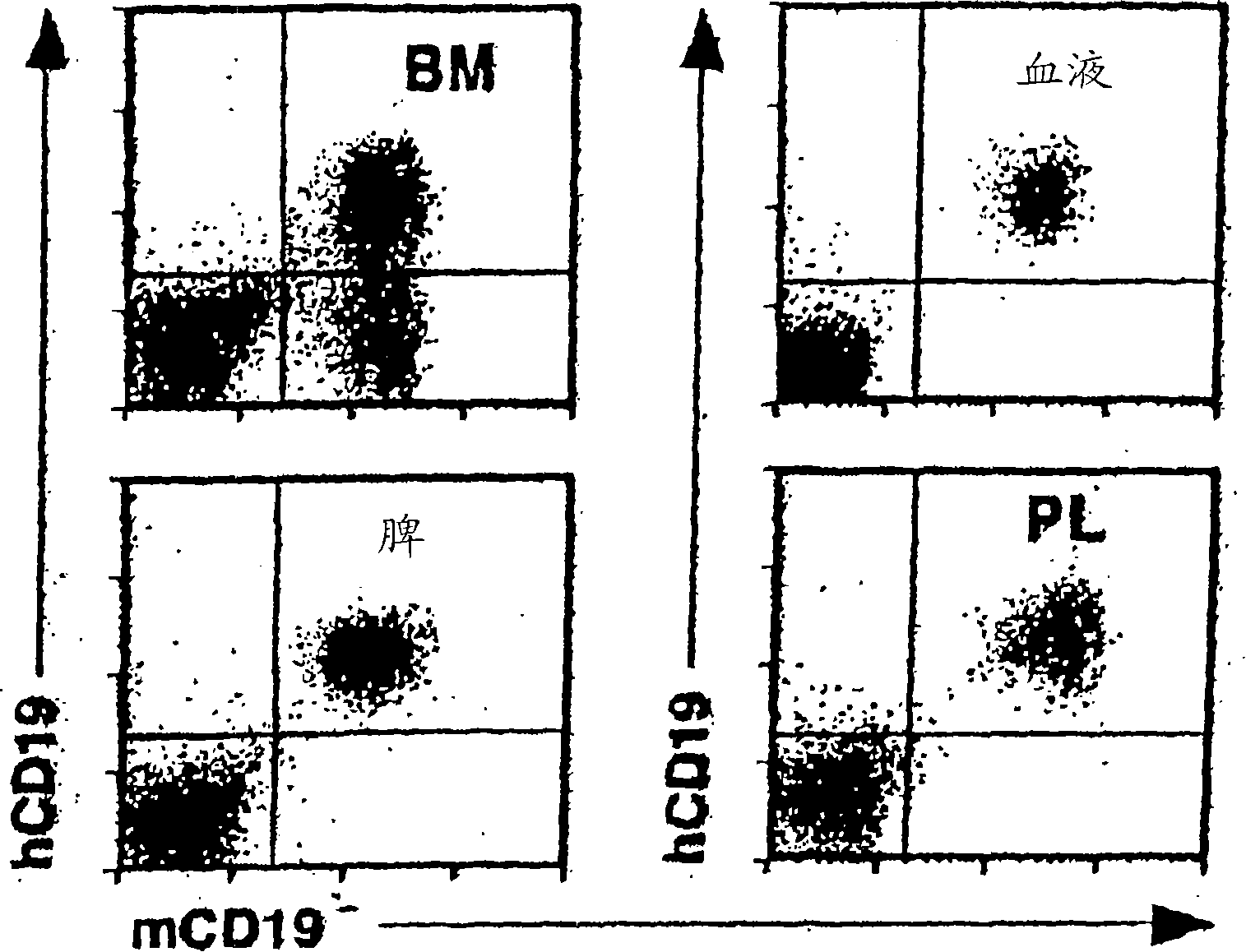
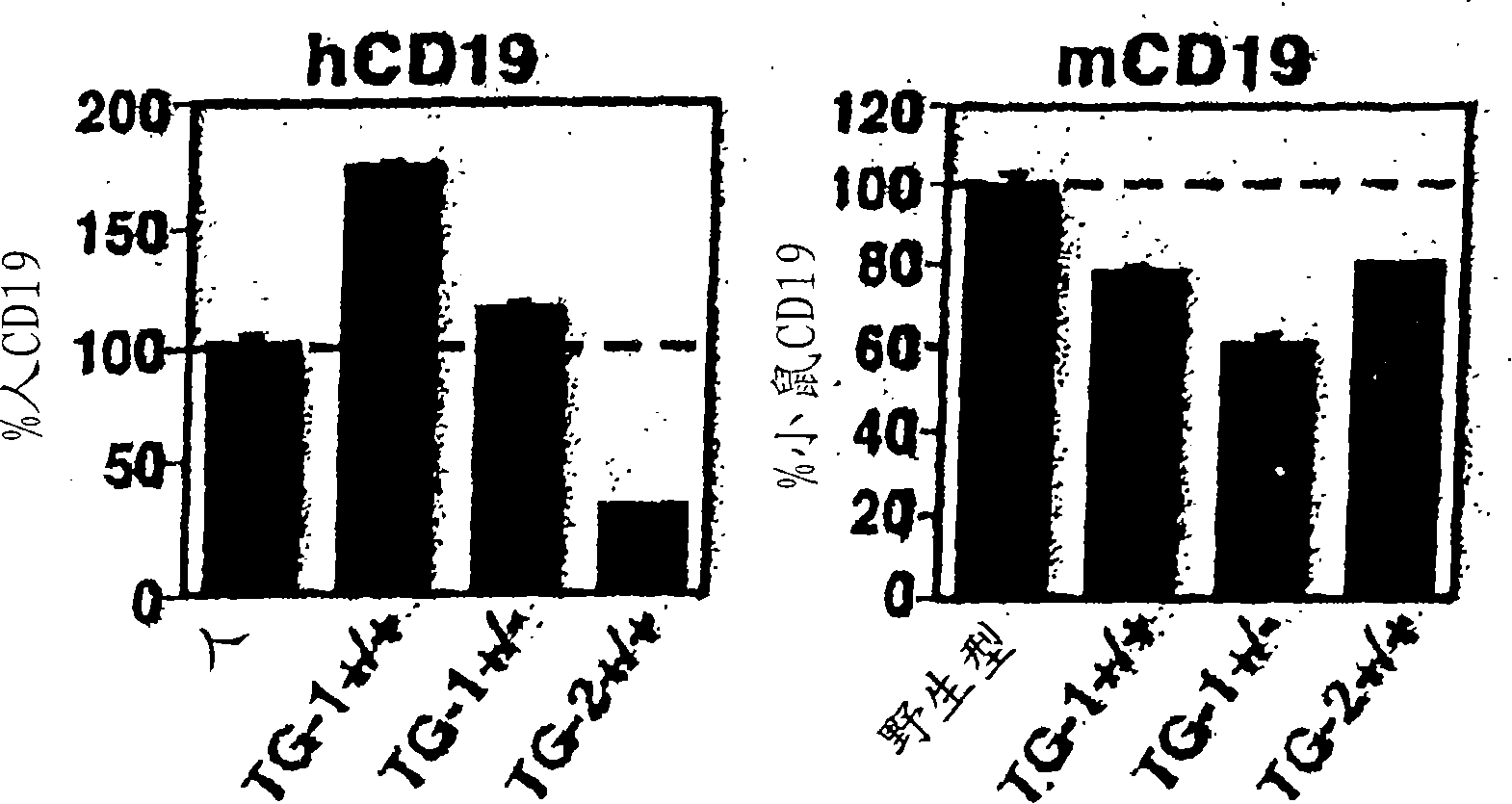
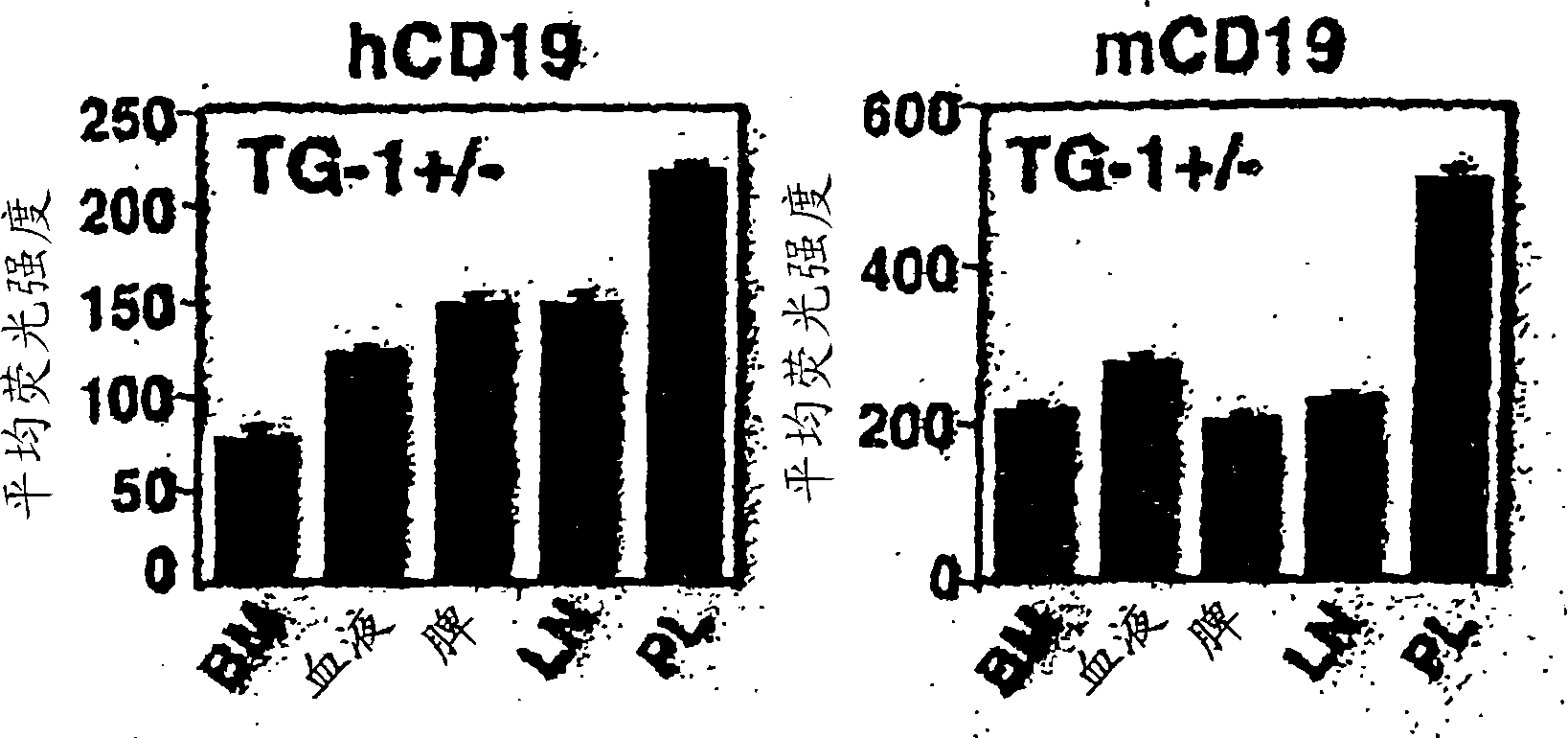
[0462] In order to determine whether human CD19 in transgenic mice (hemizygous TG-1 + / - ) B cells were extracted from the bone marrow, blood, spleen and peritoneal fluid of these mice. Expression of human CD19 and mouse CD19 was asse...
Embodiment 2
[0471] 6.3 Example 2: Anti-CD19 antibody depletion of B cells in vivo
[0472] Mouse anti-CD19 antibody, which binds to human CD19, was evaluated for its in vivo depletion of hCD19TG (TG-1 + / - ) capacity of blood, spleen and lymph node B cells. Each antibody was administered to mice at an amount of 250 or 50 μg / mouse, a single dose approximately 10 to 50 times lower than the dose of 375 mg / m in four doses of anti-CD20 therapy in humans (Maloney et al., J Clin. Oncol, 15:3266-74 (1997) and McLaughlin et al., 12:1763-9 (1998)).
[0473] exist Figure 2A Results are shown in block diagrams of B cells after 7 days of CD19 or paired isotype control (CTL) treatment with HB12a, HB12b or FMC63 anti-CD19 antibody or control. Separate blocks were provided for lymph node, spleen and blood tissues for each anti-CD19 antibody or control. Percentage of channel lymphocyte depletion over 7 days indicated in each block, indicating TG-1 depletion from TG-1 as determined by immunofluorescenc...
Embodiment 3
[0512] 6.4 Example 3: Tissue B cell depletion is FCγR dependent
[0513] The following assay was used to determine whether B cell depletion by anti-CD19 antibodies was dependent on FCγR expression. Mice expressing hCD19 and expressing some FcγRs were generated by cross-breeding hCD19tg with mice lacking expression of some FcγRs. Such mice are used in assays to determine the ability of anti-CD19 antibodies to deplete B cells through pathways involving FcyR expression, eg, ADCC. Accordingly, anti-CD19 antibodies identified in these assays can be used to prepare chimeric, human or humanized anti-CD19 antibodies using the methods described above in Section 5.1. Such antibodies can in turn be used in the compositions and methods of the invention to treat B cell malignancies in humans.
[0514] The innate immune system mediates B cell depletion following anti-CD20 antibody treatment through an FcγR-dependent process. Mouse effector cells express four distinct FcyR types: IgG, hig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com