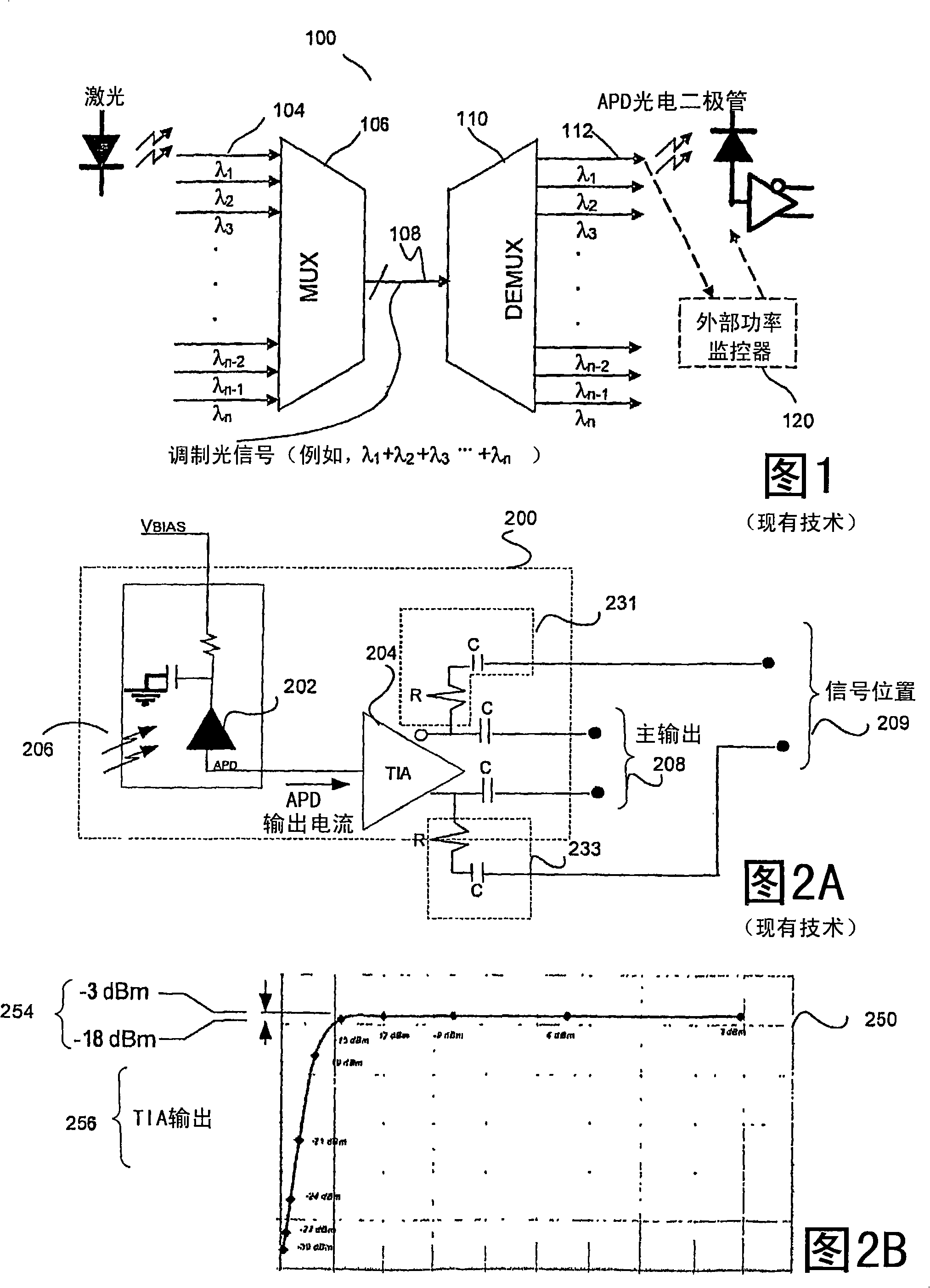
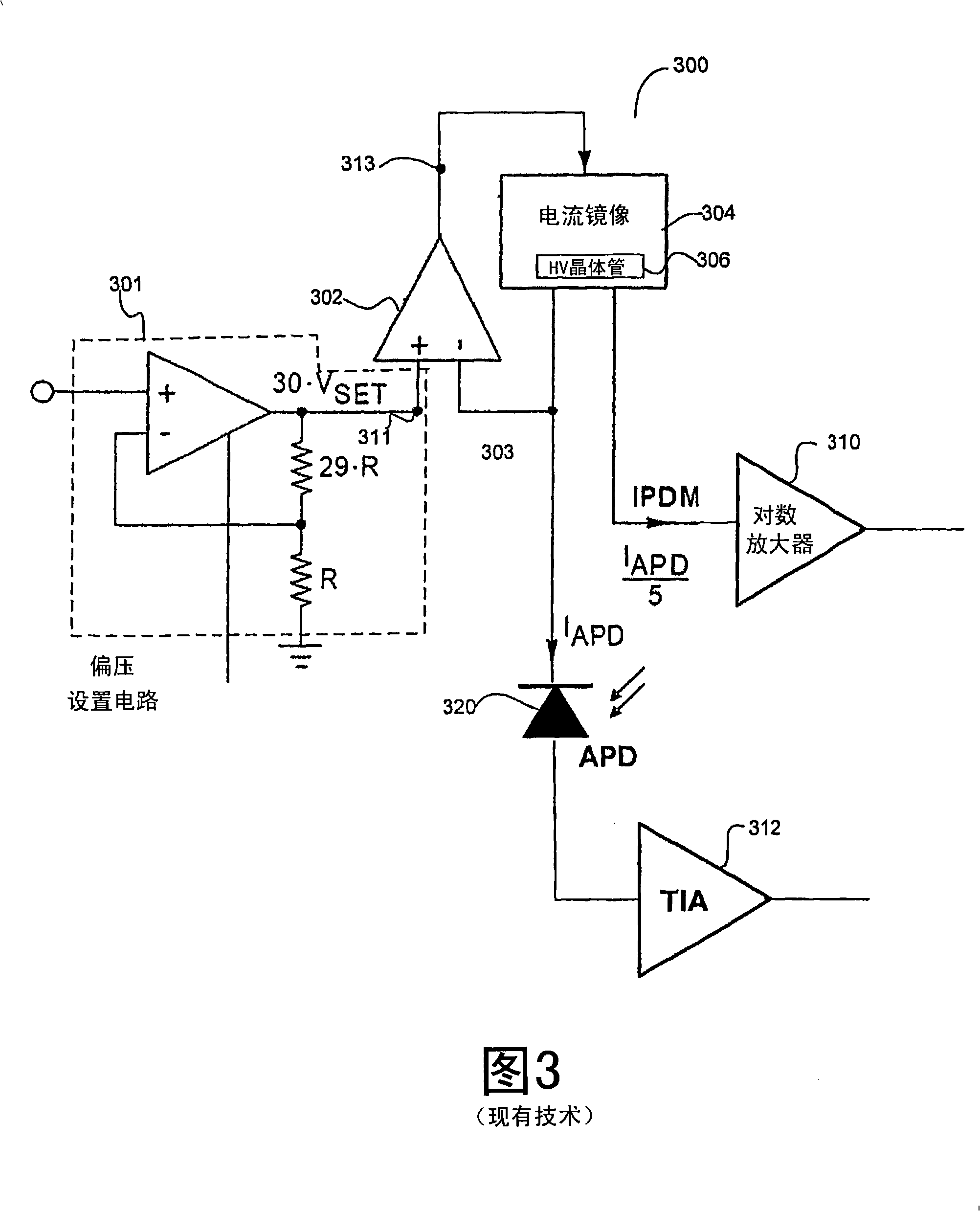
In-situ power monitor having an extended range to stabilize gain of avalanche photodiodes across temperature variations
A temperature change, avalanche photoelectric technology, applied in discharge tubes, electromagnetic transceivers, photometry, etc., can solve problems such as power monitoring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
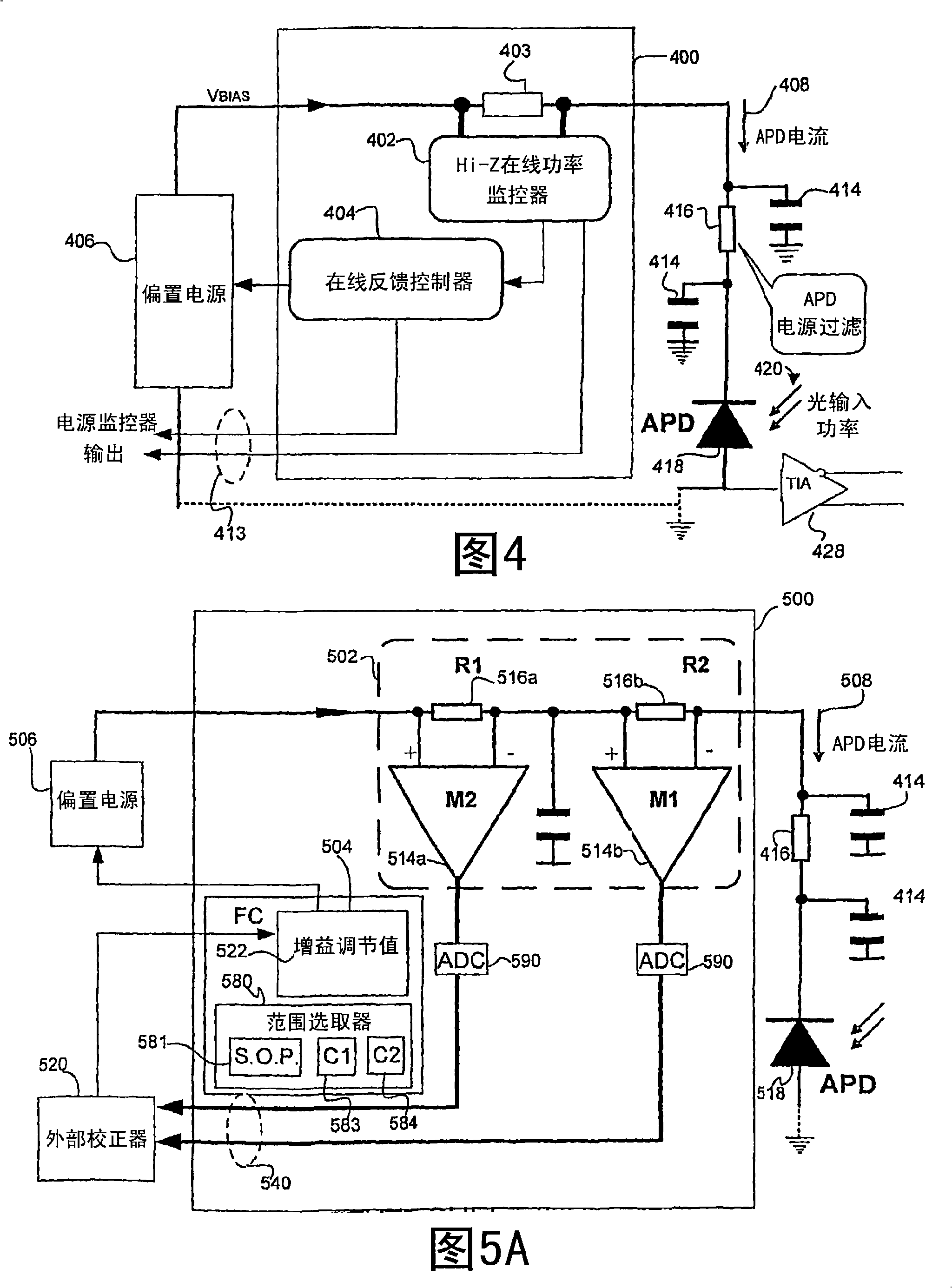
[0027] Fig. 4 is a block diagram of an apparatus for online monitoring of input optical power according to at least one embodiment of the present invention. Device 400 includes an online power monitor 402 for monitoring optical signal 420 . A sense current 408 flowing from a bias source ("bias supply") 406 provides an adjustable bias voltage. In one embodiment, the optical signal detector is APD 418 . Sometimes, resistor 416 and / or capacitor 414 filter current 408 to reduce noise effects, for example. In order to detect and monitor the current 408 , the device 400 also includes a passive element 403 which can replace 416 .
[0028]Note that the current 408 passing through the APD can be expressed by the formula (1): I(APD_current)=Ip×APD(responsitivity)×APD(gain), in the formula (1), Ip represents the luminous flux flowing into the APD 418, and APD(responsitivity) represents The responsivity of the APD 418, APD(gain) represents the gain (or multiplication) of the APD. Note...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com