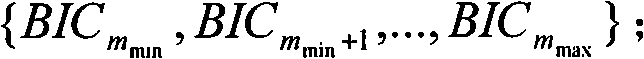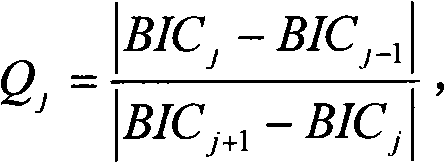Supervision-free Markov random field image segmentation method
An image segmentation and random field technology, which is applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not fully considering pixel gray level difference and positional relationship, etc., so as to reduce misclassification, improve anti-noise performance, and misclassify Effect of Classification Rate Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further described now in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
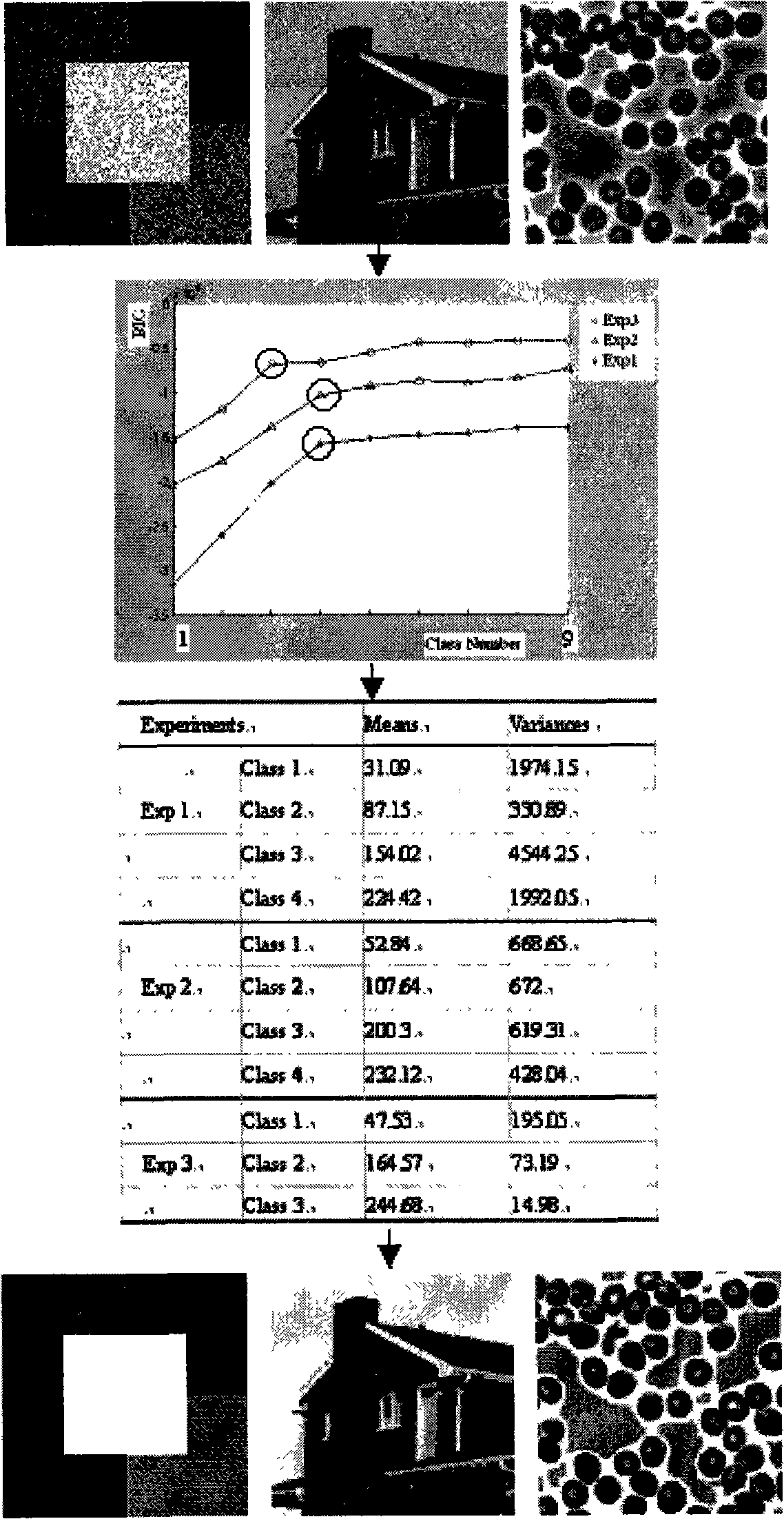
[0034] The present invention uses three images as an implementation example, including an artificially synthesized noise image, a standard image with noise added, and a real blood cell image. The result is shown in Figure 2. The experimental steps are as follows:
[0035] 1) First, for the original images A, B, and C, as shown in the first column in Figure 2, determine that the range of possible classification numbers for each image is 1 to 9;
[0036] 2) For A, B, and C, the K-means method is used to segment 1 to 9 categories, and each image obtains 9 initial segmentation results;
[0037] 3) For each of the 9 segmentation results of A, B, and C, calculate the BIC value under each segmentation result, and obtain the BIC value of each image { BIC m min , BIC ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com