Ocean bottom seismic structure resistivity detection mainly using vertical magnetic field component of naturally changing electromagnetic field of globe
A technology of vertical component and resistivity, which is applied in the field of shallow stratum structure on the seabed, and can solve the problem of expensive containers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
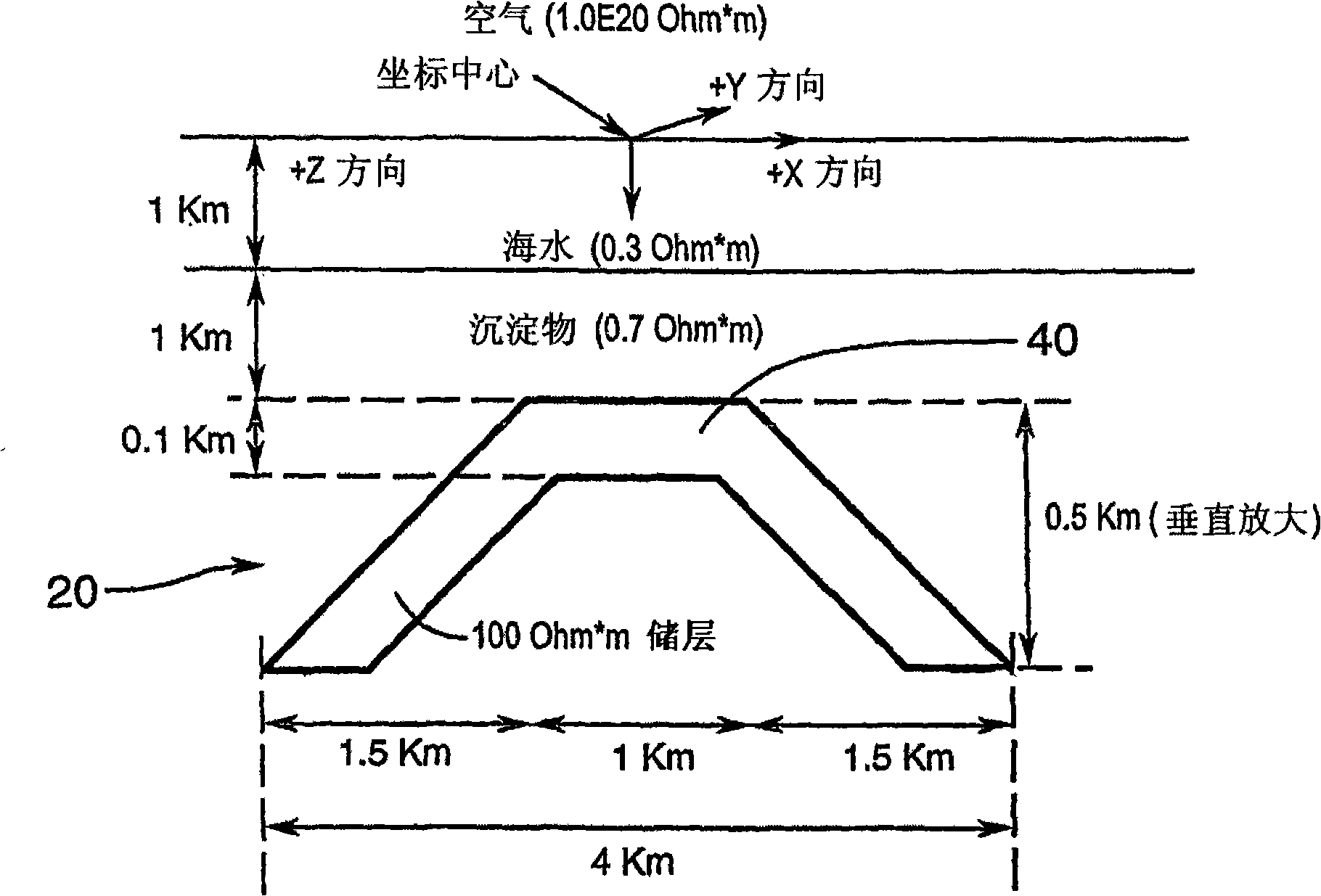
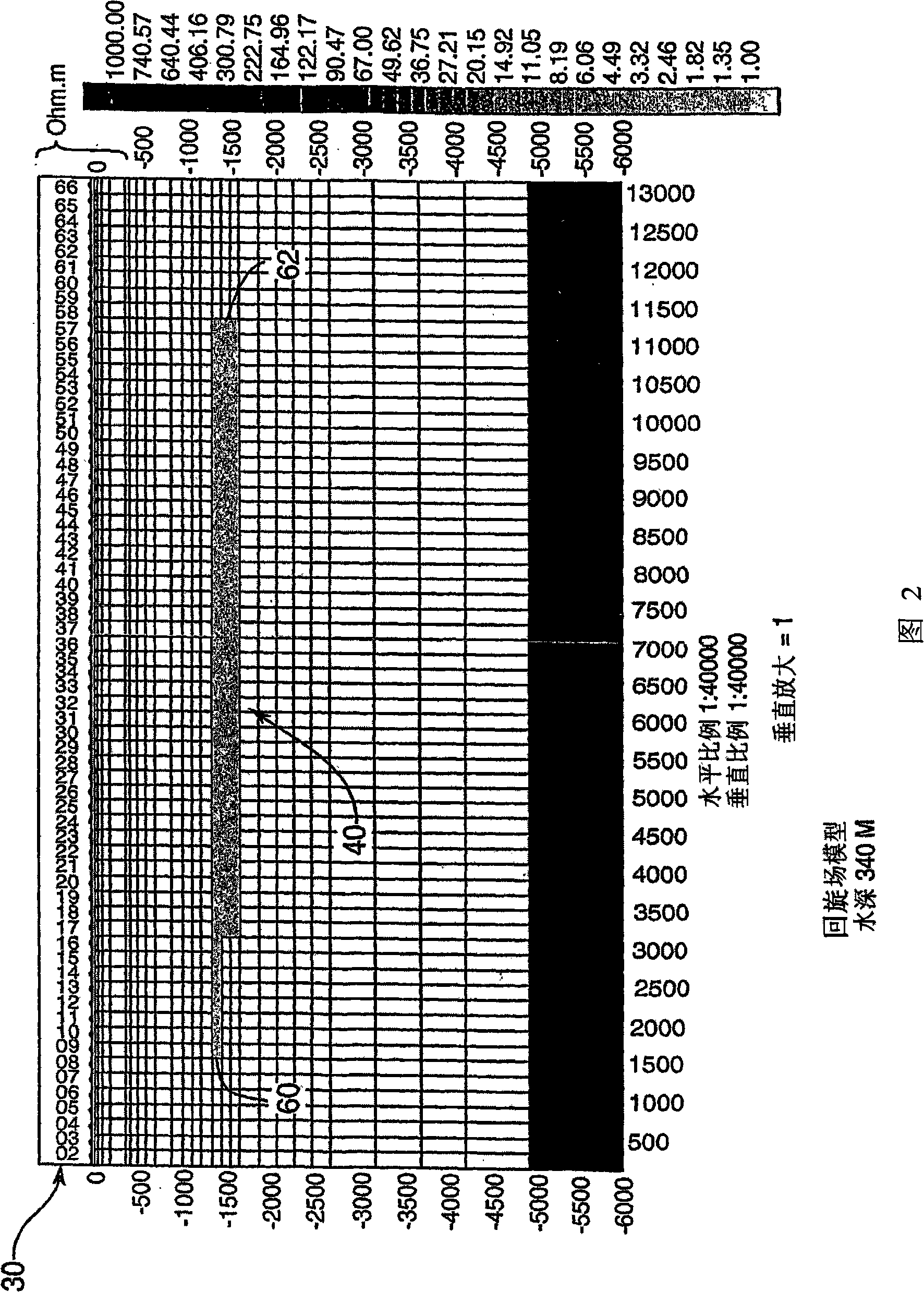
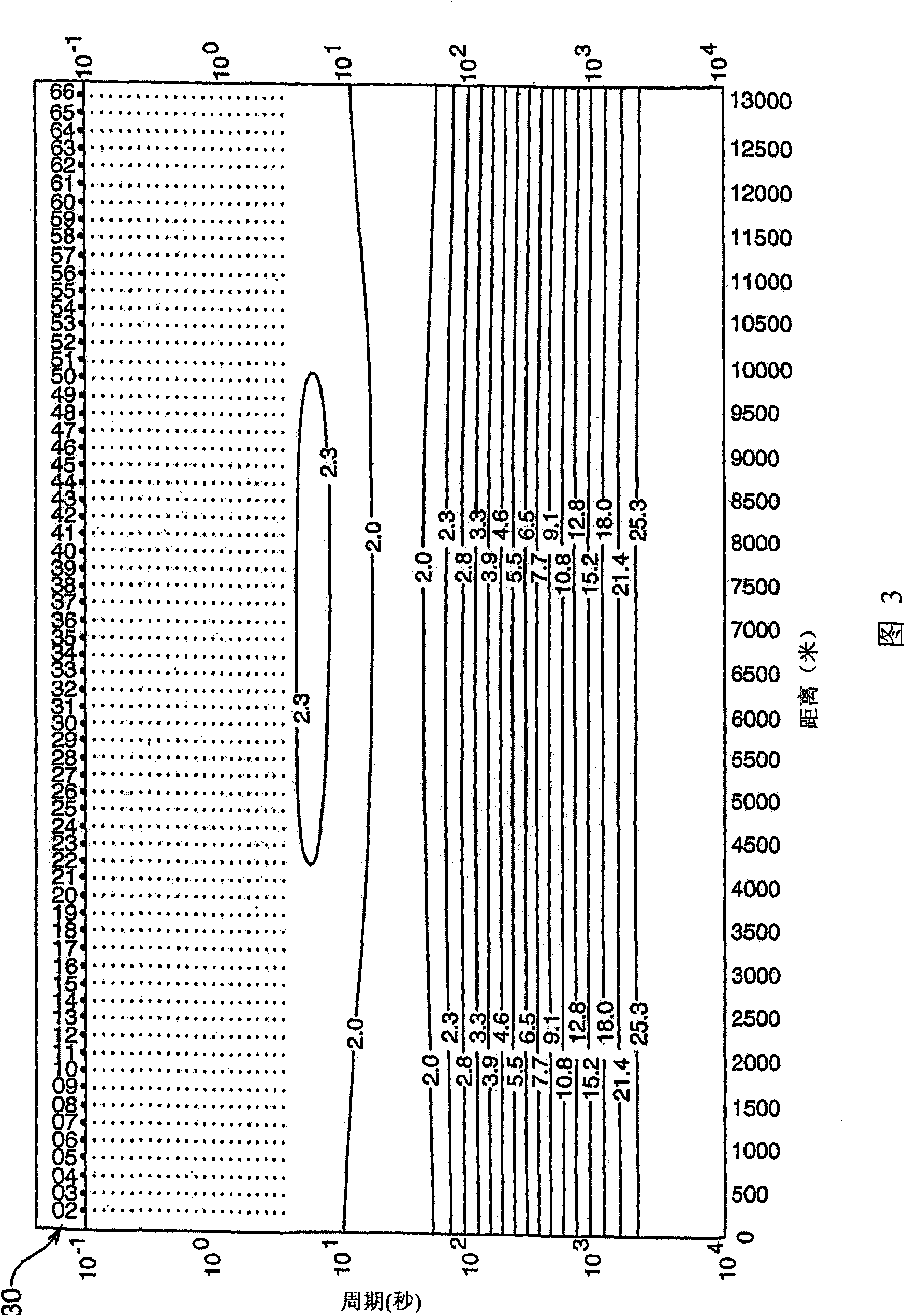
[0060] According to a first preferred embodiment of the invention, the vertical component Hz of the magnetic field is measured simultaneously at multiple points on the seabed from a natural source (as opposed to an artificial or controlled source) which is appropriate for the structure under study. location. From the physics of the problem it follows that in the absence of noise the magnitude of the vertical component "Hz" of the magnetic field (i.e. the magnitude of the unreferenced sign) is only non-zero at or near the resistivity boundary 50, as Figure 7 The variation in |Hz| (vertical axis) across the resistivity boundary 32 is shown in (from McNeill et al., 1991). Here, "|Hz|" is a mathematical definition representing the amplitude of the vertical magnetic field in Hz. if we imagine in Figure 7 Another such boundary at some distance to the left or right, then the object of interest is a model of the lateral extension of a hydrocarbon-laden, reactive shallow substratum...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com