Refrigerator
A technology for refrigerators and cold rooms, applied in the field of refrigerators, which can solve the problems of reduced cooling performance, uneconomical performance, and lack of reliable defrosting of coolers for cold rooms, achieving reliable defrosting and saving power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment
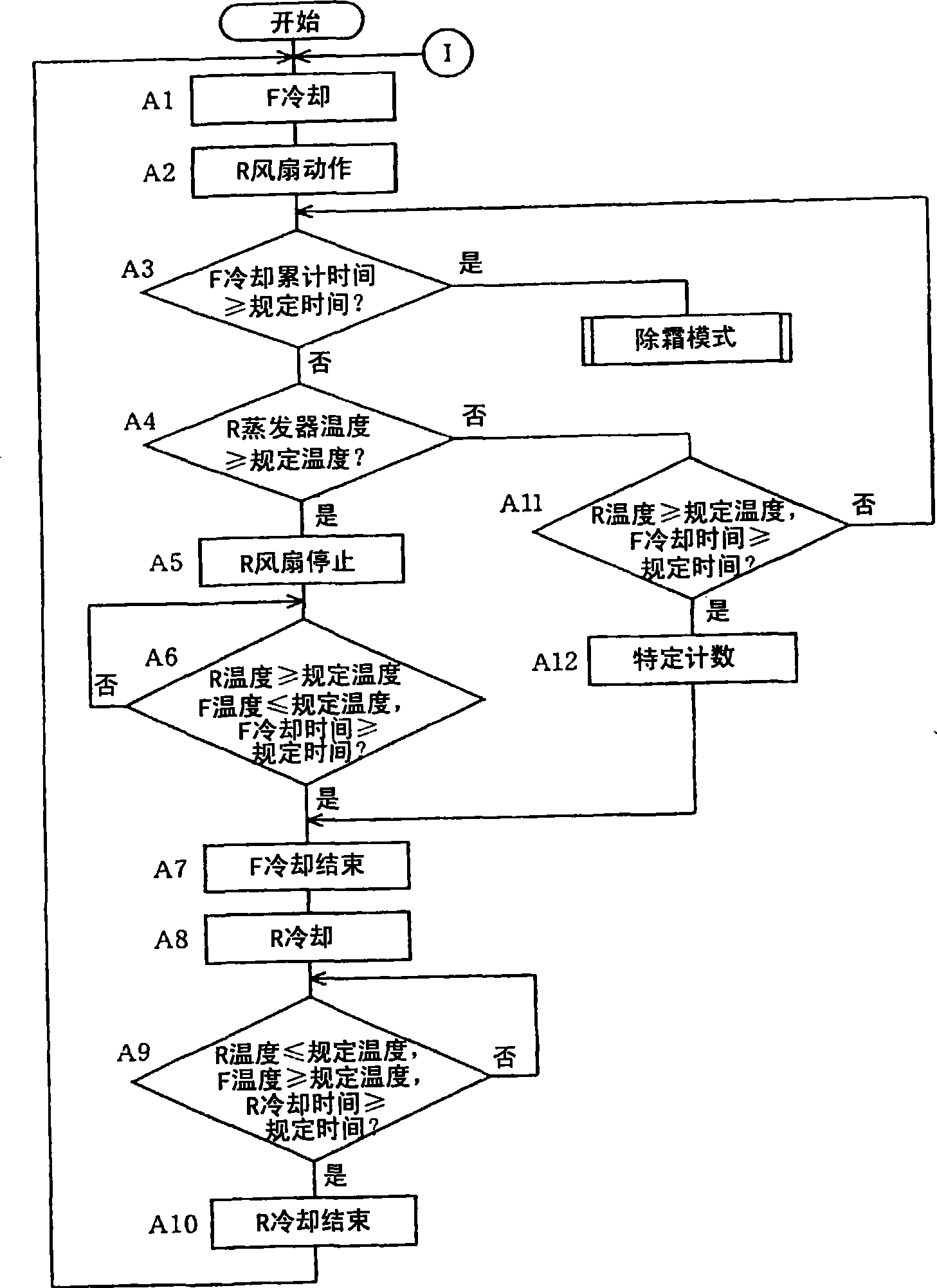
[0098] exist Figure 8 to Figure 11 In the second embodiment shown, the specific conditions, the operation timing and the stop timing of the refrigerator defrosting heater 26 for refrigerator compartments are changed from those of the first embodiment.
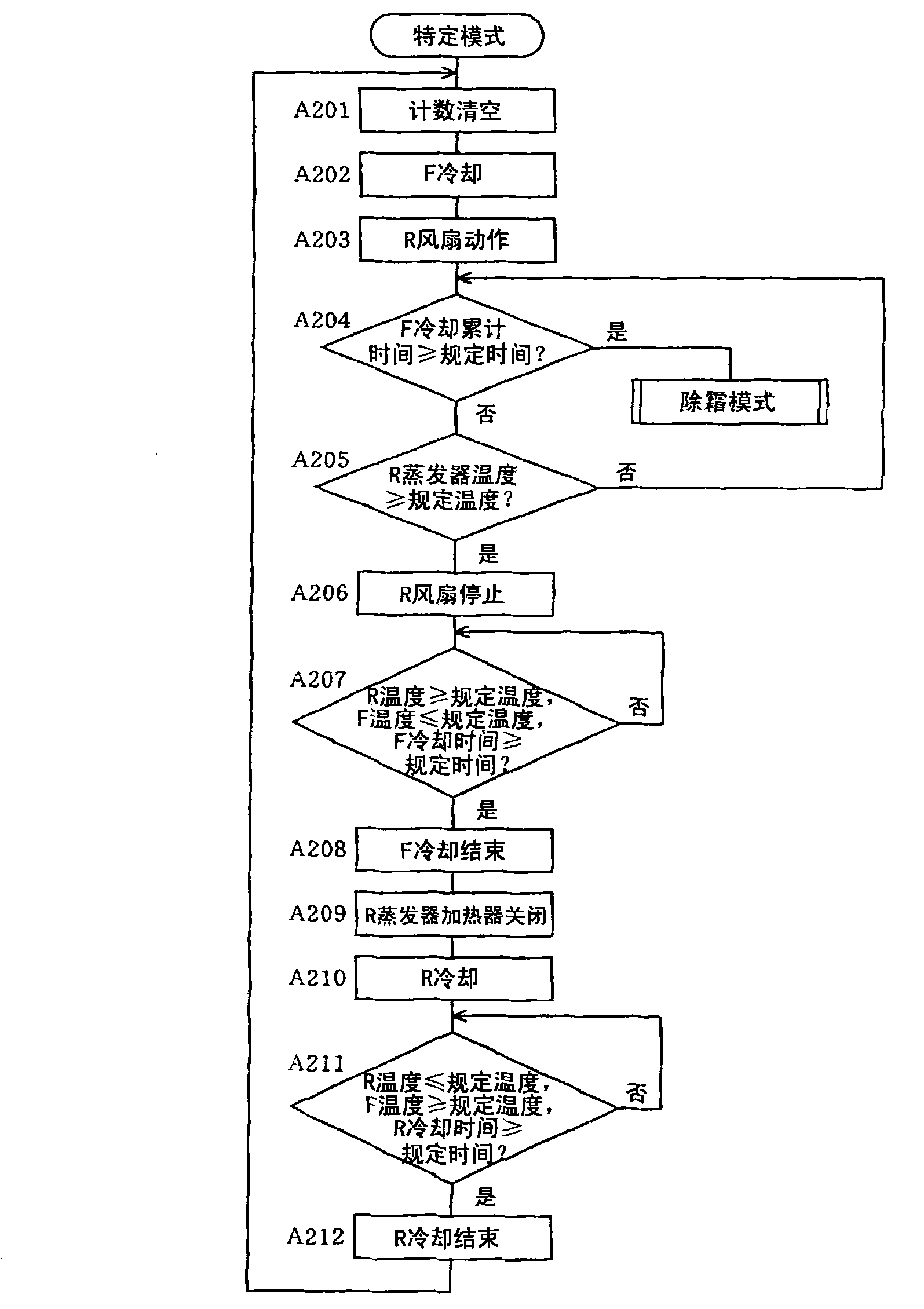
[0099] Specifically, first, if Figure 8 As shown, when "R fan operation" is executed after "F cooling" is executed, the execution of "F cooling" (freezing mode) and "R cooling" (refrigerating mode) is regarded as one cycle. The number of times is counted (step B1).
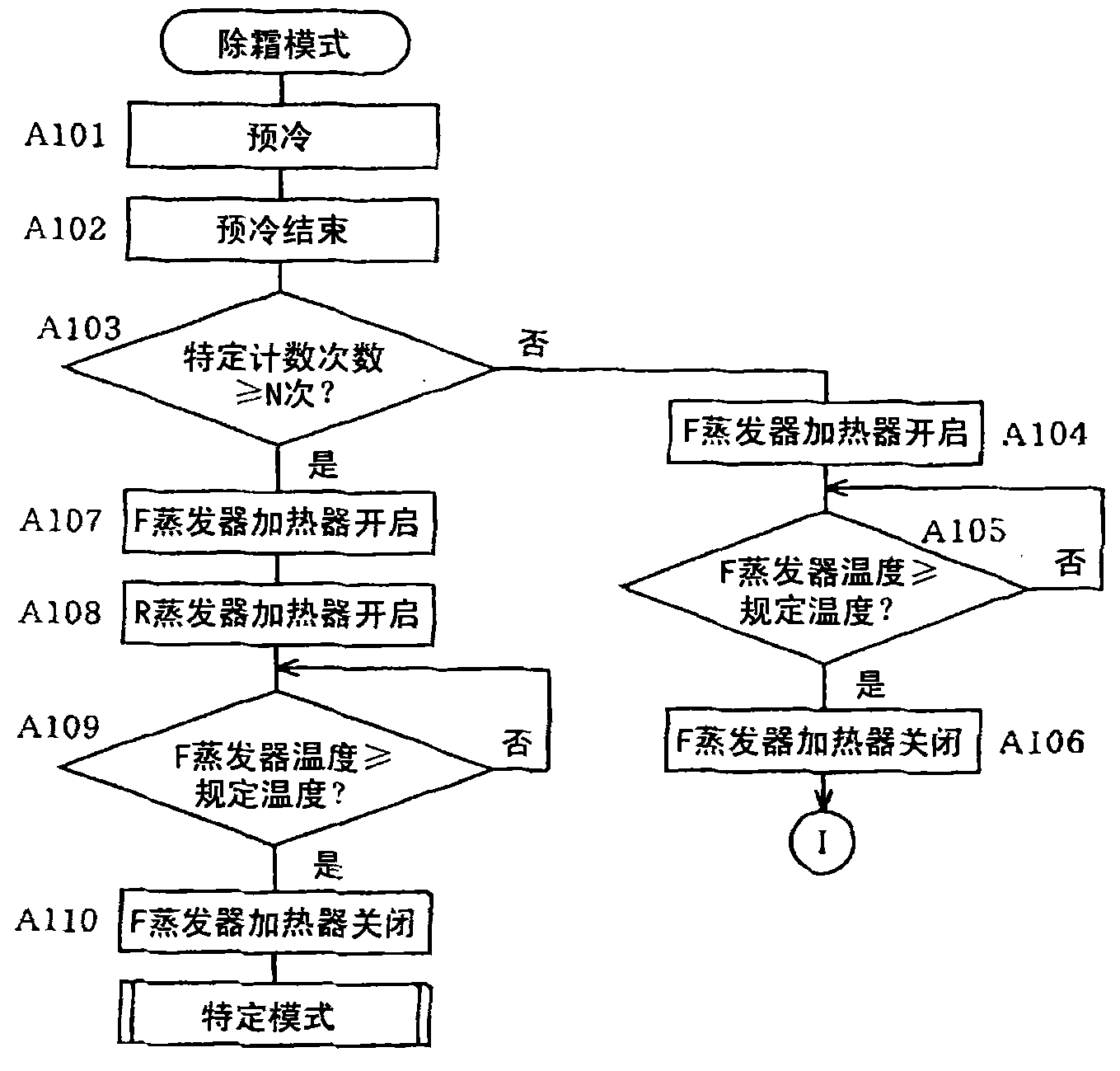
[0100] and, if Figure 9 As shown, in the defrosting mode, in step A103, if it is judged that the number of times counted in step A12 is not more than the prescribed N times (NO), then whether the number of cycles counted in step B1 is the prescribed N' Determination of times (for example, 20 times) or more (step B101), in this step B101, if it is judged that it is not N' times or more (NO), the process proceeds to step A104.
[0101] On the other hand, in st...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0114] exist Figure 12 to Figure 15 In the third embodiment shown, the specific conditions, the operation timing and the stop timing of the refrigerator defrosting heater 26 for refrigerator compartments are changed from those in the first embodiment.
[0115] Specifically, first as Figure 12 As shown, when the "R fan operation" after "F cooling" is executed, the counting of the temperature rise time of the R evaporator (cooler 20 for refrigerating room) is simultaneously started (step C1).
[0116] And, in step A4, if it is judged that the "R evaporator temperature" detected by the cooler temperature sensor 28 for the refrigerating room has become more than a predetermined temperature (defrosting end temperature) (YES), the R fan is stopped, and the R fan is stopped. Counting of the temperature rise time of the evaporator (step C2). Then, it is judged whether the temperature rise time of the R evaporator counted so far is longer than a predetermined time (for example, 30 ...
no. 4 Embodiment
[0126] exist Figure 16 and Figure 17 In the fourth embodiment shown, the specific conditions, the operation timing and the stop timing of the refrigerator defrosting heater 26 for refrigerator compartments are changed from those in the first embodiment.
[0127] Specifically, first, if Figure 16 As shown, after executing "F cooling" (step A1), it is judged whether or not the number of specific counts is predetermined N"" times (for example, 3 times) (step D1). At this time, if it is judged not to be the prescribed N"" times (NO), then proceed to step A4 through step A2 (R fan operation), but if it is judged to be the prescribed N"" times (YES), then the R fan After operating and operating the R evaporator heater (step D2), clear the counted number of times judged in step D1 (step D3), and proceed to step A4.
[0128] In step A4, if it is judged that "R evaporator temperature" is above the predetermined temperature (defrosting end temperature) (YES), stop the R fan and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com