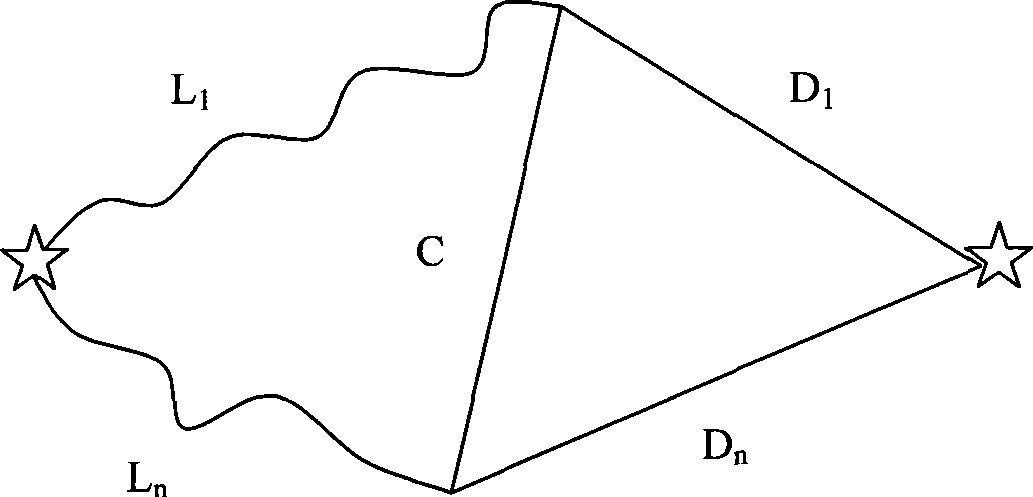
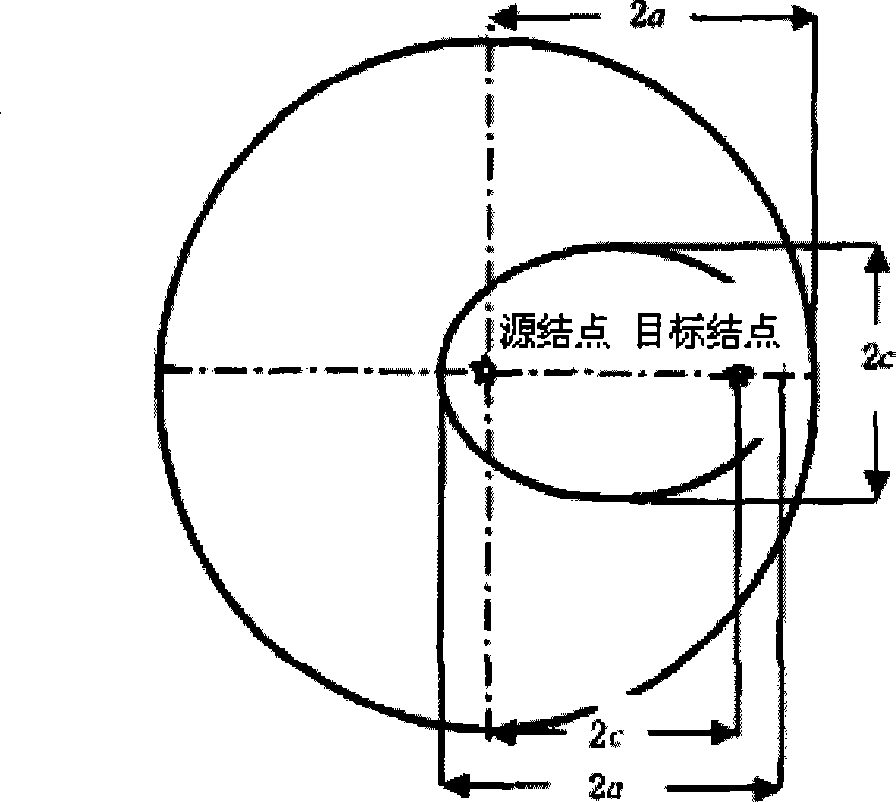
Linear optimal shortest path search method
A shortest path and path technology, applied in the shortest path search field of linear optimization, can solve the problem of not considering the direction or position of the target node, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of nodes and improving the speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
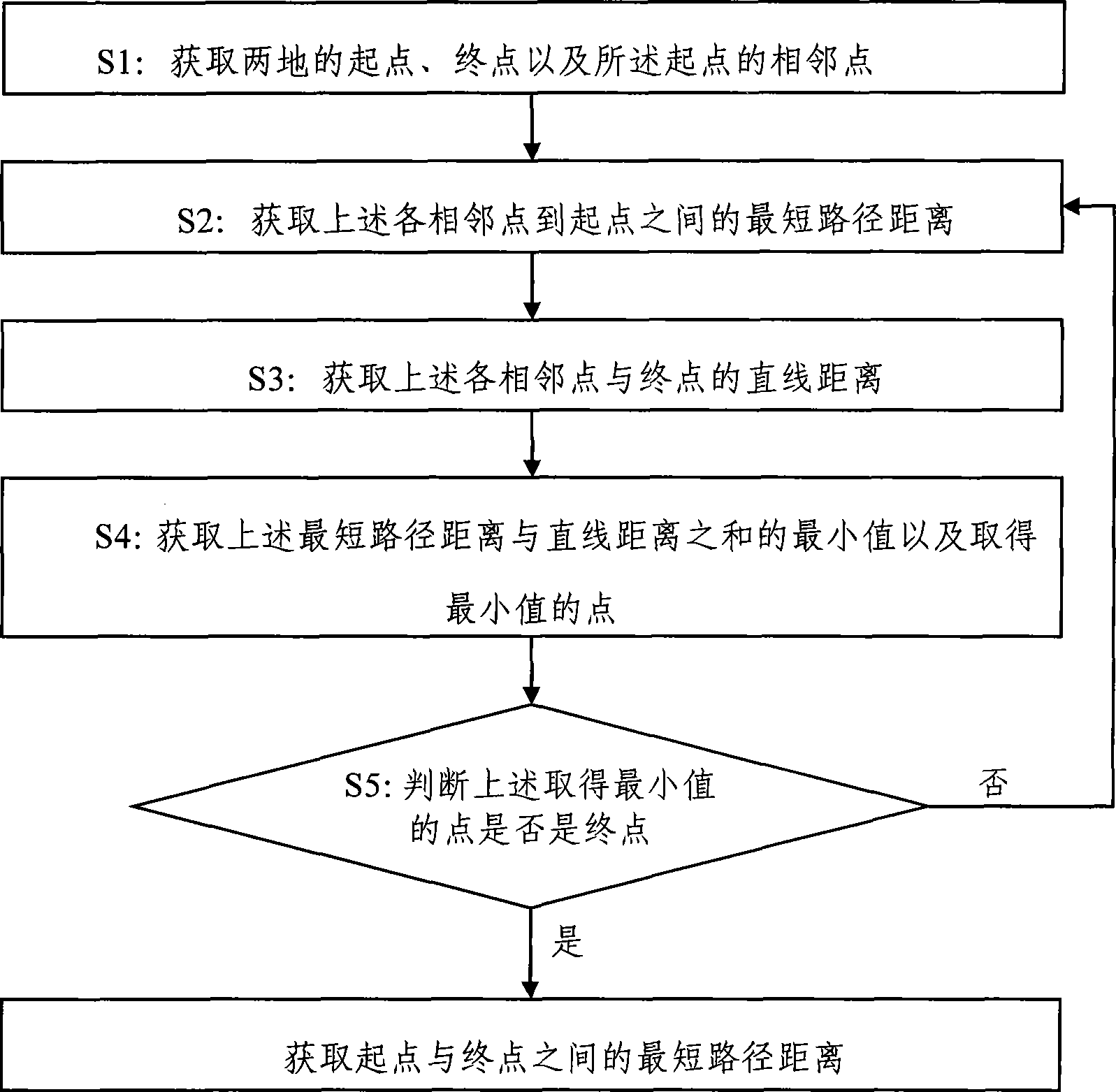
[0029] The present invention provides a method for obtaining the shortest path between two places. The method includes steps: S1, obtaining the starting point, the ending point, and the adjacent points of the starting point of the two places; S2, obtaining the distance between the adjacent point and the starting point. S3, obtain the straight-line distance between the above-mentioned adjacent points and the end point; S4, obtain the minimum value of the sum of the above-mentioned shortest path distance and the straight-line distance and the point where the minimum value is obtained; S5, judge the above-mentioned minimum value Whether the point is the end point, if yes, then obtain the path distance from the above starting point to the end point via the point that obtains the minimum value as the shortest path distance between the start ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com