Card reader and card reading method thereof
A card reader and card reading technology, which is applied in the field of smart card applications, can solve the problem of incompatibility of universal card readers and smart cards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
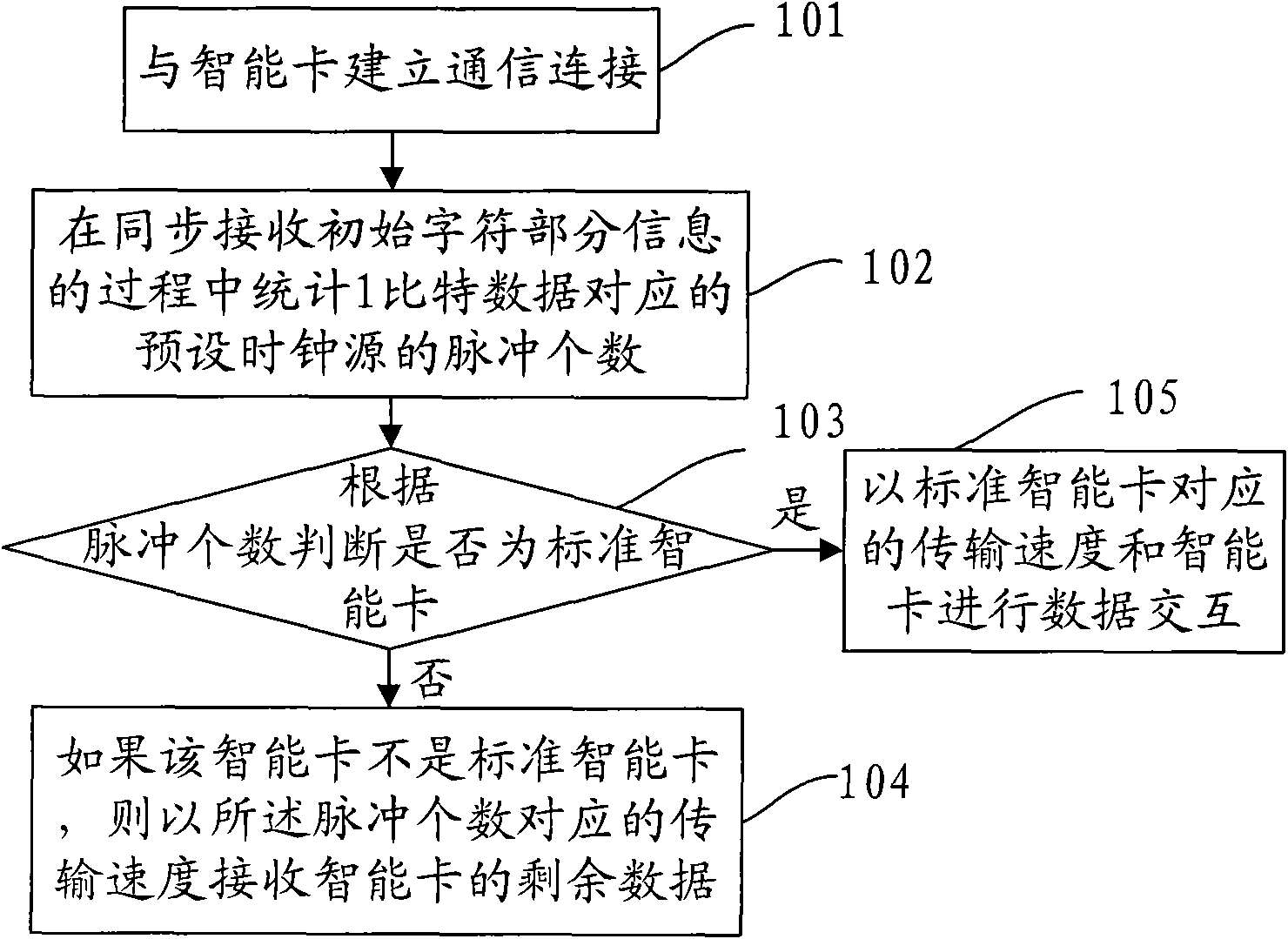
[0046] This embodiment provides a card reading method of a card reader, such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0047] 301. The card reader establishes a communication connection with the CPU card (smart card), such as mechanically connecting the smart card to the card reader through contacts;
[0048] 302. The CPU card returns an answer to reset (ATR) to the card reader;
[0049] 303. Regardless of whether the CPU card is a forward contract card (0x3B) or a reverse contract card (0x3F), its specific performance on the TTL signal is respectively Figure 4 and Figure 5 , so the first bit ( Figure 4 and Figure 5 The Start bit in) must be a complete low level. Therefore, in this embodiment, the number of pulses corresponding to 1-bit data can be counted in the following manner:
[0050] Therefore, in this process, when the first falling edge of the initial character of the reset response data returned by the smart card is detected, the number of pulses of the s...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This embodiment provides a card reading method of a card reader, such as Figure 8 As shown, the method includes:
[0082] 801. The card reader establishes a communication connection with the CPU card (smart card), such as mechanically connecting the smart card to the card reader through contacts;
[0083] 802. The CPU card returns an answer to reset (ATR) to the card reader;
[0084] 803. Regardless of whether the CPU card is a forward contract card (0x3B) or a reverse contract card (0x3F), its performance on the TTL signal is Figure 4 and Figure 5 , so the first bit of the initial character of the reset response data returned by the CPU card ( Figure 4 and Figure 5 The Start bit in ) must be a complete low level, and then the first bit b0 and the second bit b1 are both complete high levels. Therefore, in this embodiment, the number of pulses corresponding to 1-bit data can be counted in the following manner:
[0085] Therefore, this process starts to count t...
Embodiment 3
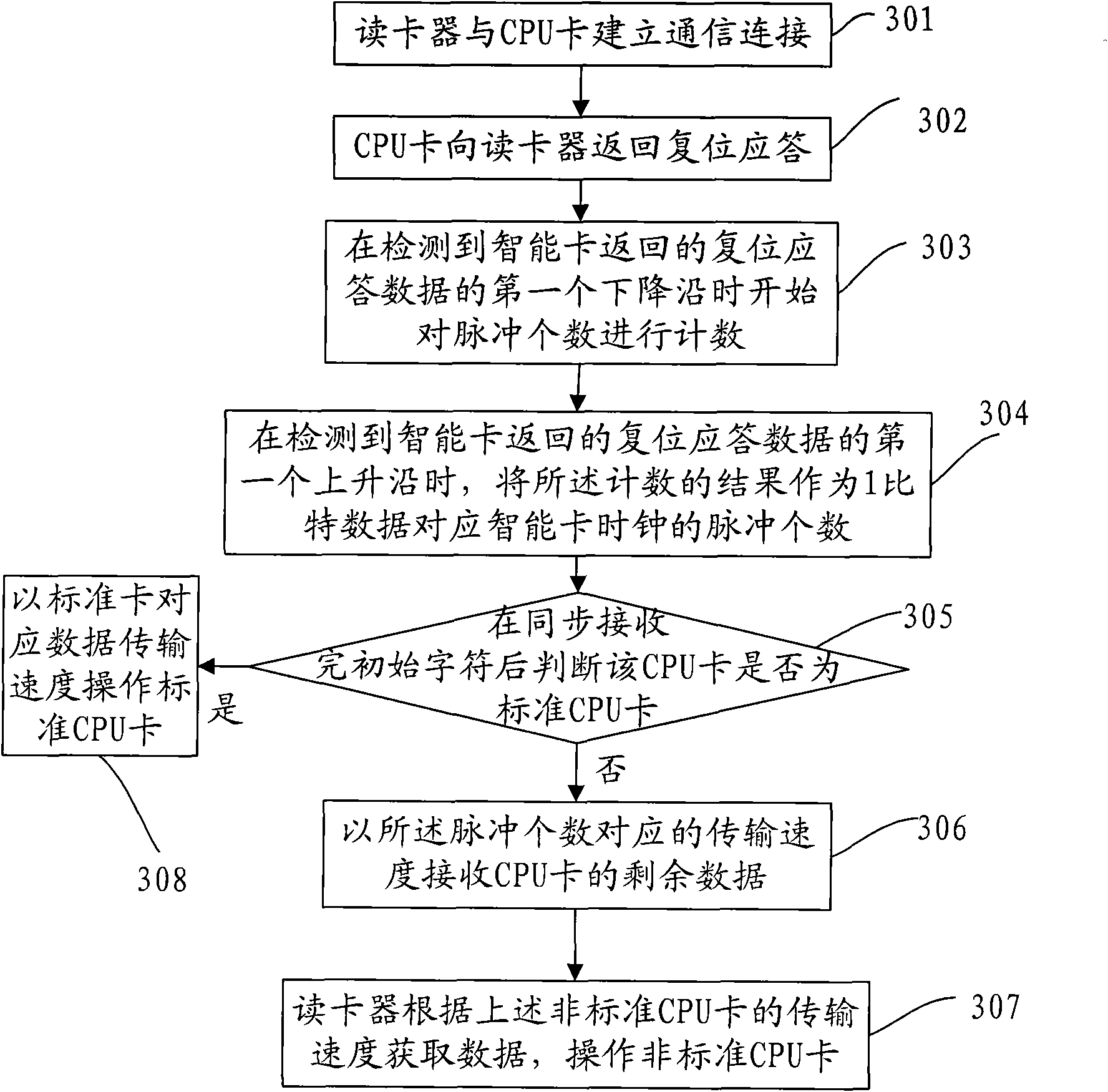
[0107] This embodiment provides a card reading method of a card reader, such as Figure 10 As shown, the method includes:
[0108] 1001. The card reader establishes a communication connection with the CPU card (smart card), such as mechanically connecting the smart card to the card reader through contacts;
[0109] 1002. The CPU card returns an answer to reset (ATR) to the card reader;
[0110] 1003. Regardless of whether the CPU card is a forward contract card (0x3B) or a reverse contract card (0x3F), its performance on the TTL signal is Figure 4 and Figure 5 , so the first bit of the initial character of the reset response data returned by the CPU card ( Figure 4 and Figure 5 The Start bit in ) must be a complete low level, and then the first bit b0 and the second bit b1 are both complete high levels. Therefore, in this embodiment, the following method can be used to count the number of pulses of 1 bit data corresponding to the smart card clock:
[0111] This proce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com