Double-stator conical adjustable air gap permanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor, double stator technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve problems such as the reduction of motor efficiency, and achieve the effects of wide speed expansion range, simple field weakening method, and good adjustment performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
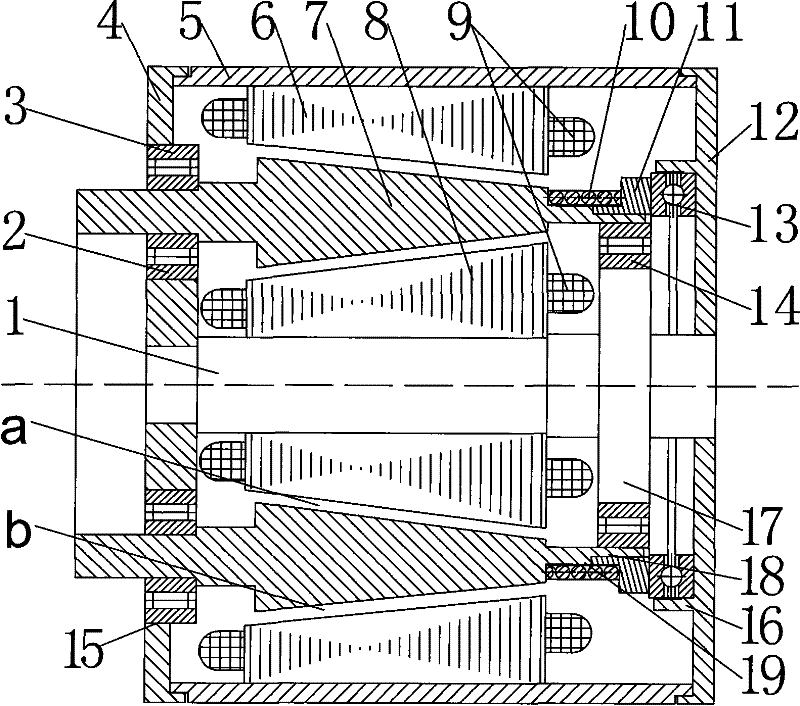
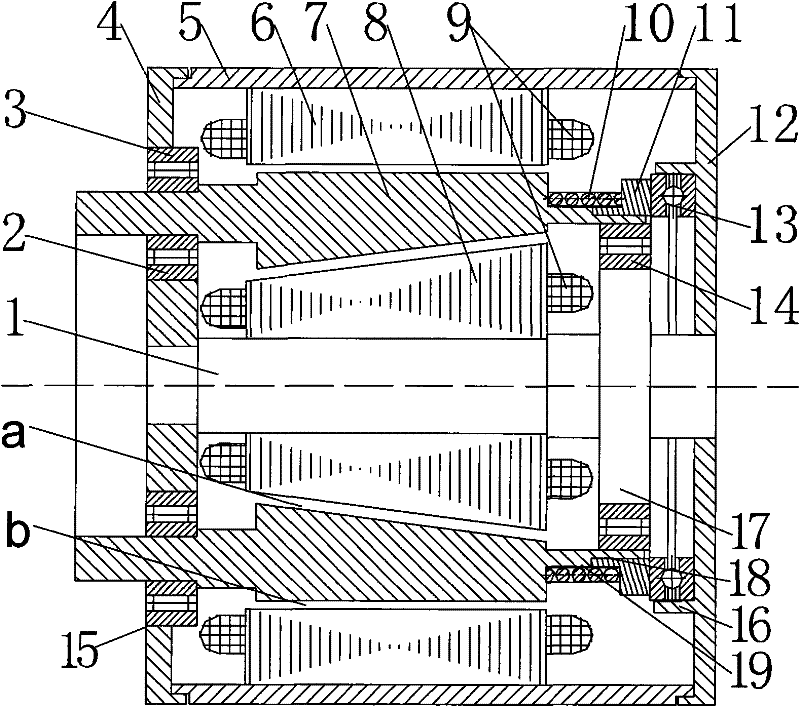
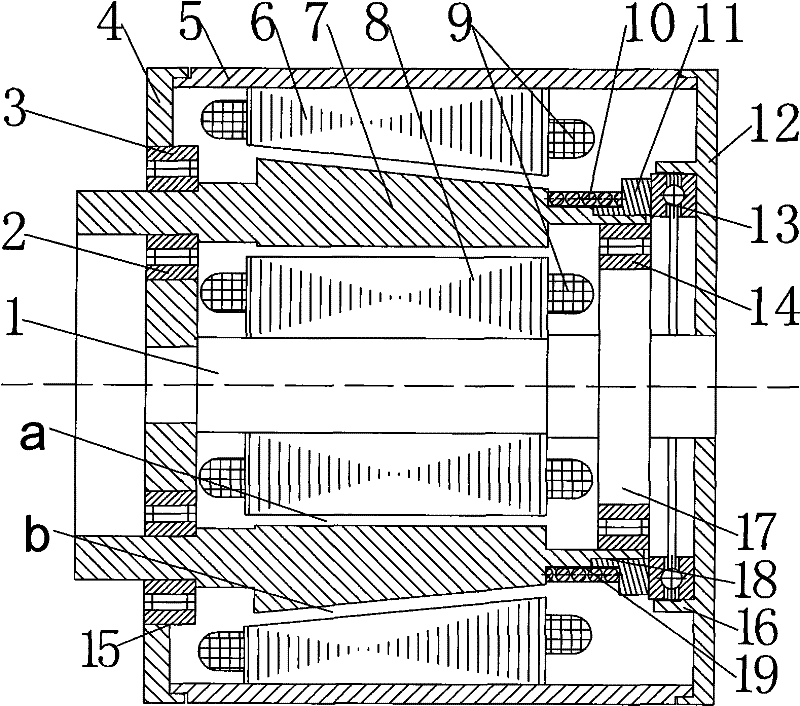
[0007] Specific implementation mode 1: Combination figure 1 , figure 2 or image 3 To illustrate this embodiment, this embodiment includes a stator, a rotor, a support frame, and two rotor slides; the stator includes an outer stator core 6, an inner stator core 8 and a stator winding 9. The stator windings 9 are respectively arranged on the outer stator core 6 and the inner stator. On the sub core 8, the outer stator core 6, the rotor 7 and the inner stator core 8 are fixed on the support frame. The outer stator core 6, the rotor 7 and the inner stator core 8 are coaxially sleeved together from the outside to the inside. An equal inner air gap a is provided between the surface and the inner surface of the rotor 7; an equal outer air gap b is provided between the outer surface of the rotor 7 and the inner surface of the outer stator core 6, the outer surface of the inner stator core 8 and the inner surface of the rotor 7 The outer surface of the rotor 7 and the inner surface of...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Specific implementation manner two: combination figure 1 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the outer surface of the inner stator core 8, the inner surface of the rotor 7, the outer surface of the rotor 7 and the inner surface of the outer stator core 6 are all cones. The specific embodiment one is the same. Both the inner and outer stator cores produce axial magnetic pull and torque on the rotor. Through the control of the stator winding 9 current, the appropriate axial displacement of the rotor 7 can be obtained, the air gap is enlarged, the air gap magnetic field is weakened, and the weak magnetic field is realized. At the same time, the stator winding 9 current is controlled to increase the air gap. In this case, sufficient output torque can be obtained.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0009] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 2 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the outer surface of the inner stator core 8 and the inner surface of the rotor 7 are both tapered, and the outer surface of the rotor 7 and the inner surface of the outer stator core 6 are both cylindrical; The magnetic pulling force is only produced by the action of the inner stator core 8 on the rotor 7, and the torque is produced by the inner stator core 8 and the outer stator core 6 together. The other composition and connection relationship are the same as in the first embodiment. By controlling the current of the stator winding 9 in the inner stator core 8, a suitable axial displacement of the rotor can be obtained to increase the air gap, thereby weakening the air gap magnetic field and realizing weak magnetic field expansion, and at the same time the stator winding of the outer stator core 6 9 Current con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com