Dynamic pointer disambiguation
A pointer, dynamic technology, used in program control design, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
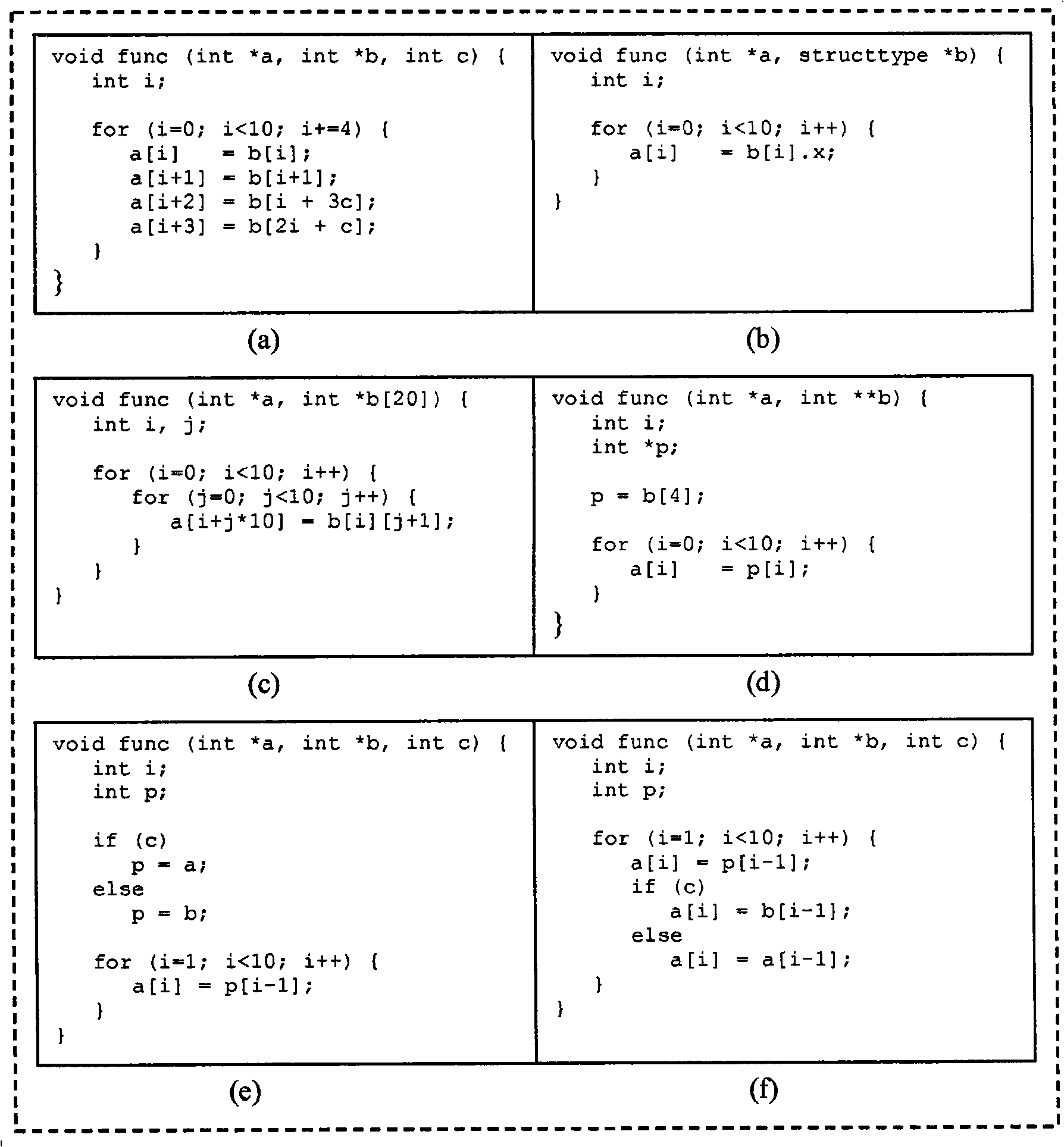
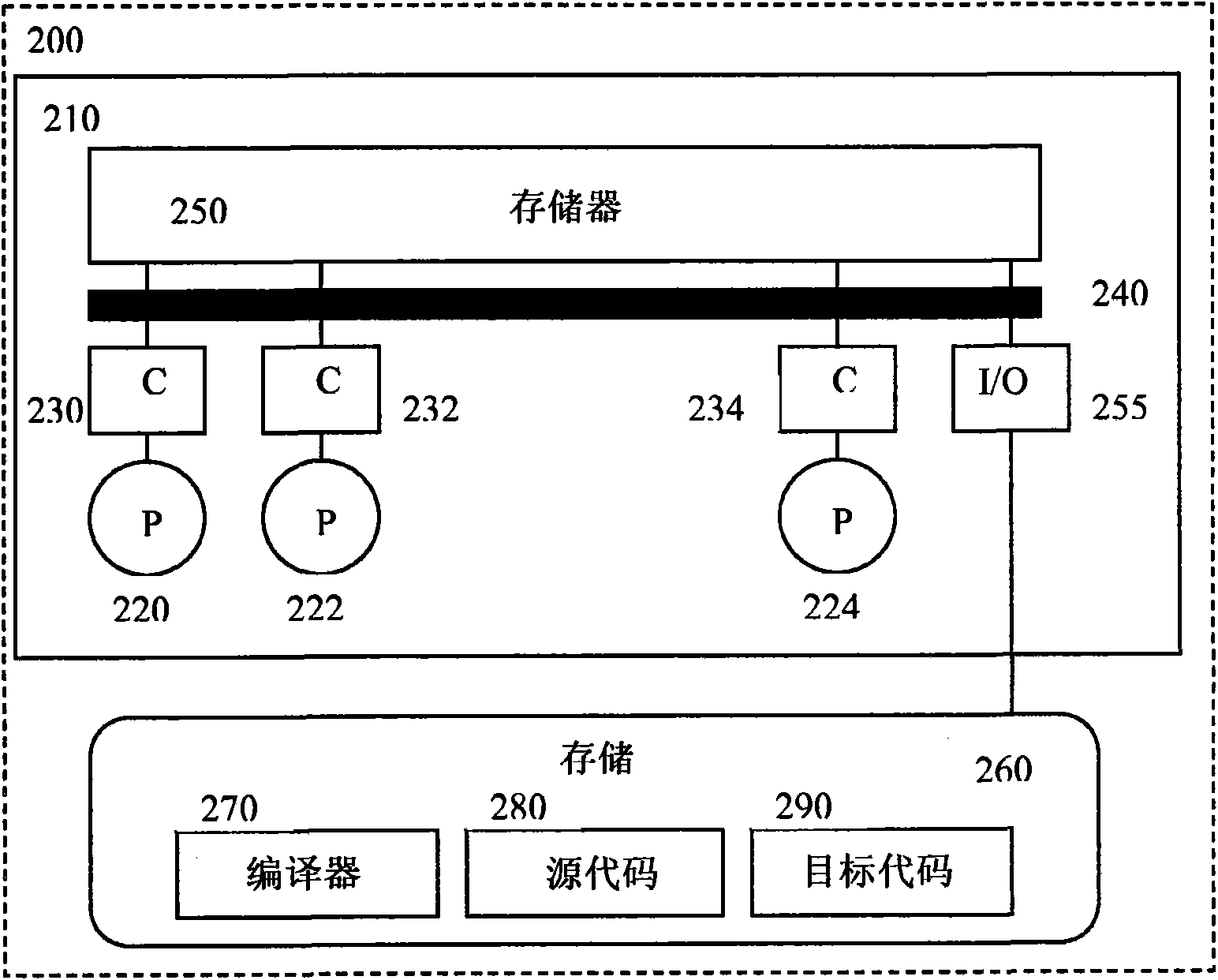
[0046] Dynamic pointer disambiguation techniques can produce faster dependency testing code than known techniques, and are useful for more complex code in high-level languages such as C and C++ (other languages are not excluded) (for example, using Structure - that is, struct-multidimensional pointers in the C programming language, and some control flow dependency issues) for analysis.
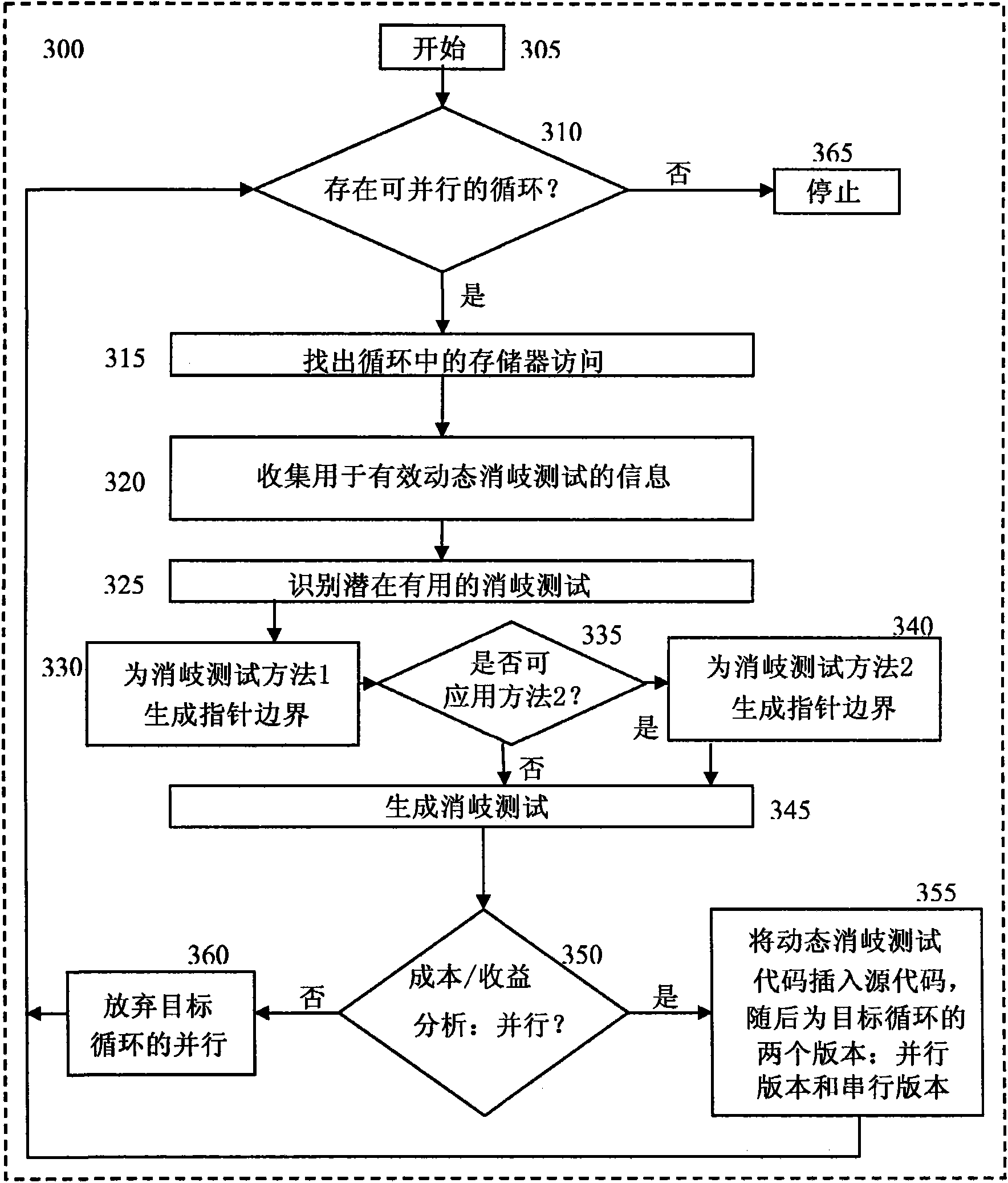
[0047] A method for generating dependency testing code to determine whether pointer accesses may overlap may include: (1) performing static analysis on a segment of code preceding code to be parallelized in order to (a) reduce the number of dependency tests that must be performed the amount of code, and (b) collect the information needed to test the code for dependencies; (2) use one of two published techniques to determine the memory intervals (i.e., the lowest and highest memory locations) that a pointer can access; and (3) Dependency test code is generated to ensure that memory interval...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com