Luminance compensation method using multiwire interpolated lens
A brightness compensation and lens technology, which is applied to color TV parts, TV system parts, TVs, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of hardware memory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
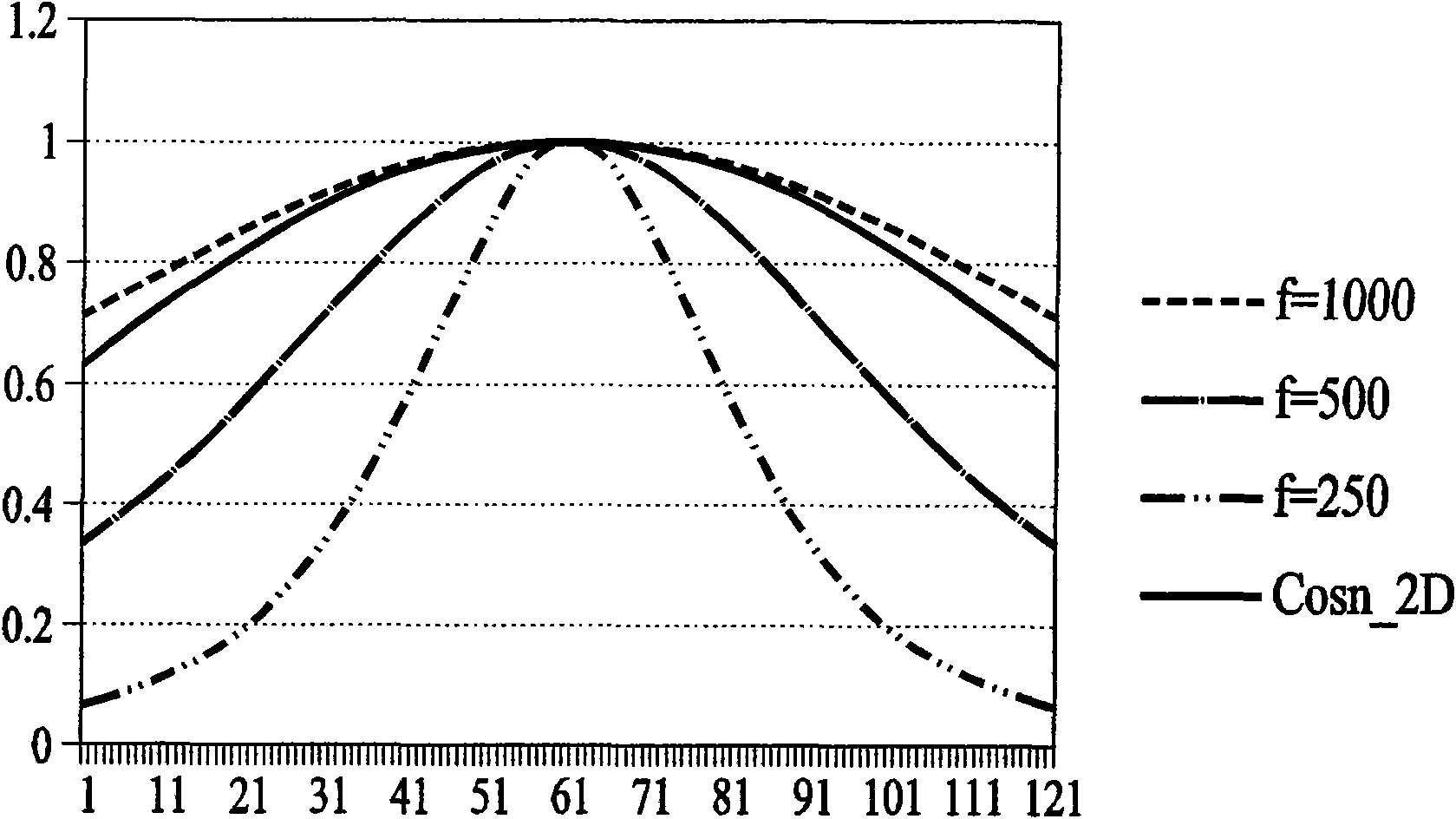
[0047] Embodiment 1: How polynomials describe brightness changes
[0048] If the hardware of the lens brightness compensation method using multi-line interpolation in the present invention supports the calculation of radical operation, the radial distance from the brightness compensation target point P to the center of the mirror can be used as a variable to establish a certain direction The polynomial equation of the line is used to approximate the brightness attenuation curve in this direction, and the approach of the polynomial can be obtained by the existing complex variable regression or the Levenberg Marquardt nonlinear least square method.
[0049] The correction value of the same radius distance on the line can be obtained from the polynomial equation of the line in a certain direction The compensation value of the brightness compensation target point P (coordinates are Px, Py) is obtained by the same interpolation method:
[0050] P = ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: The implementation mode of establishing the brightness change curve by looking up the table
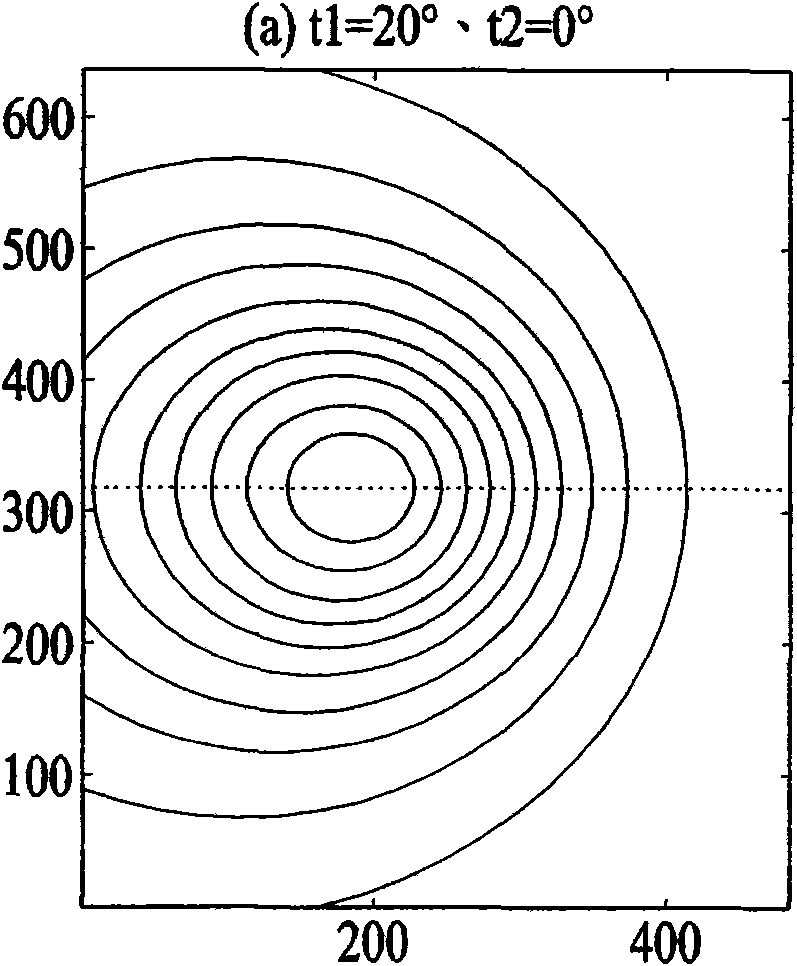
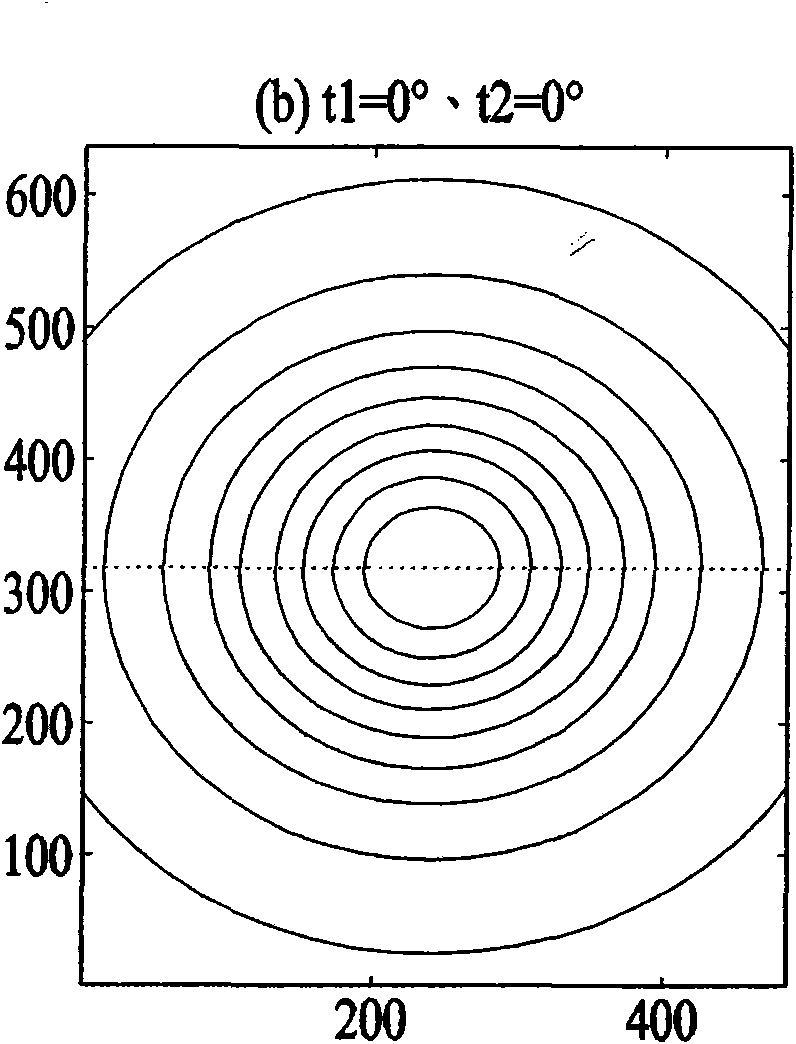
[0058] will be like Figure 5A The sampling points on the displayed direction line are stored in a look-up table, and the memory usage is different from that of the first embodiment, but it can describe the brightness change of the direction line in a simple and efficient way of looking up a table, and only the interpolation method is required for correction. Get the correction value for this line.
[0059] According to one of the preferred embodiments, wherein such as Figure 5A The calculation of the interpolation weight uses the distance formula from a point to a straight line, and the square of the radius distance is used to replace the square root of the original radius distance in the interpolation method, which can save the hardware circuit of the square root calculation. The calculation formula of the compensation value is as follows:
[0060] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com