Monoacyl-diacyl lipase, and coding gene and application thereof
A mono- and di-acyl lipase and gene technology, applied in the field of biology, can solve the problems of low enzyme activity, limited application, and small number of mono- and di-acyl lipases, and achieve high enzyme activity and reduce the cost of separation and purification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Preparation of Penicillium arcuates cDNA
[0026] 1.1 Extraction of total RNA from Penicillium arcuatens
[0027] (1) Take an appropriate amount of arctic Penicillium filaments, absorb the water with filter paper, grind with liquid nitrogen, add 1 ml of Trizol reagent (Invitrogen), shake on a shaker for 5 min, and let stand for 1 min at room temperature;
[0028] (2) add 0.2ml of chloroform, shake for 15 seconds, and let stand for 2min;
[0029] (3) 4℃, 12000rpm, 15min;
[0030] (4) Aspirate the supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol, and precipitate at -20°C for 30min;
[0031] (5) 4℃, 12000rpm, 15min;
[0032] (6) Pour off the supernatant, wash the precipitate with 1 ml of 75% ethanol, 7500rpm, 4°C, 5min;
[0033] (7) Repeat (6) step once;
[0034] (8) pour off the supernatant and dry for 10min;
[0035] (9) adding an appropriate amount of DEPC water to dissolve to obtain total RNA;
[0036] 1.2 Preparation of the first strand of Penicillium ...
Embodiment 2
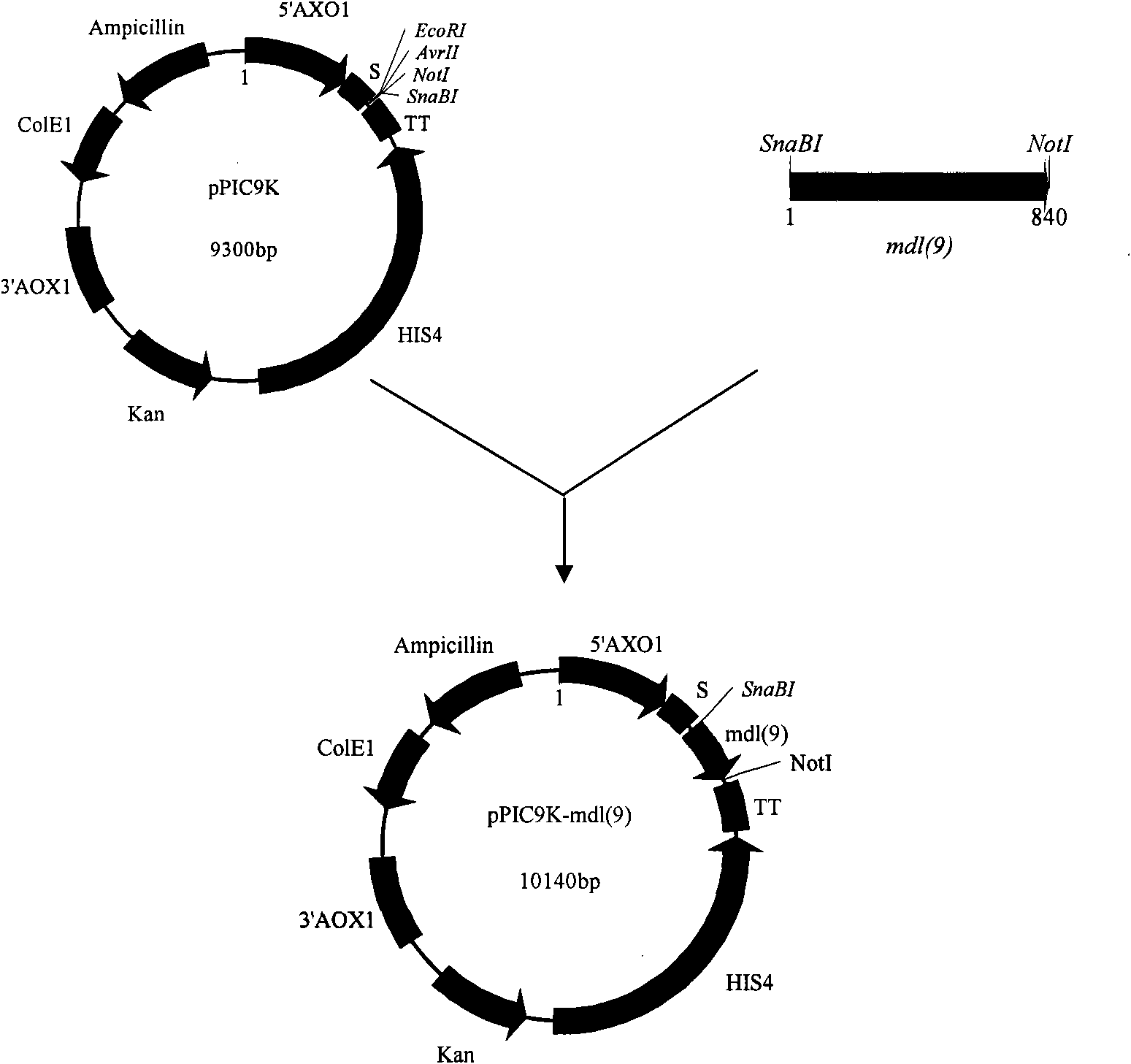
[0045] Embodiment 2 Penicillium arcus mono-diacyl lipase gene mdl (9) primer design
[0046] 2.1 Primer design
[0047] According to the sequence of the mdl gene in GenBank (GenBank accession number is AF288219), the following pair of primers were designed and synthesized:
[0048] FW(P1): 5'-GACC GATGTTTCGACCAGCGAACT-3'
[0049] REV (P2): 5'-ATTT TTAAACCCTCTTGAATGGCA-3'
[0050] SnaBI and NotI restriction sites are designed at both ends of P1 and P2 respectively (see the italicized and underlined part in the above sequence)
[0051] 2.2 Penicillium arcuum mono-diacyl lipase gene mdl (9) PCR amplification
[0052] Using P1 and P2 primers, using Penicillium arcuatus (purchased from the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3.4515) cDNA as a template, the PCR reaction system is:
[0053] Template DNA (10μg / μl) 1μl
[0054] 10×Buffer 2μl
[0055] dNTP (2.5mmol / μl) 0.5μl
[0056] primer (P1) (10pmol / μl) 0.8μl
[0057] primer (P2) (10pmol / μl) 0.8...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3 mono-diacyl lipase gene mdl (9) Secretory expression in Pichia pastoris GS115
[0071] 3.1 Preparation of Pichia pastoris GS115 (Invitrogen) Electroporation Competent Cells and Electroporation Transformation
[0072] (1) Pick a fresh single colony and put it in 5ml YPD liquid medium, cultivate it at 30°C and 250rpm for 12-14 hours;
[0073] (2) Inoculate 0.1% of the inoculum into a 2-liter Erlenmeyer flask containing 500 ml of YPD medium, and cultivate at 30° C. and 250 rpm for 12-14 hours to make OD600=1.3-1.5;
[0074] (3) Centrifuge at 1500 rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C to collect the cells;
[0075] (4) Wash the cells twice with 500-250ml ice-cold sterile water;
[0076] (5) Wash the cells once with 20ml of ice-cold 1M sorbitol solution;
[0077] (6) Resuspend the cells with 1ml of ice-cold 1M sorbitol solution to a final volume of about 1.5ml, and dispense 80μl into small centrifuge tubes;
[0078] 3.2 Electric shock transformation of Pichia pastoris y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com