Herbicide-resistant sunflower plants with multiple herbicide resistant alleles of AHASL1 and methods of use
An allele, sunflower technology, applied in the field of agriculture, can solve the problems of undescribed imidazolinone specific resistance and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0190] Example 1: Phenotypic interactions of imidazolinone resistance mutations in sunflower AHASL1
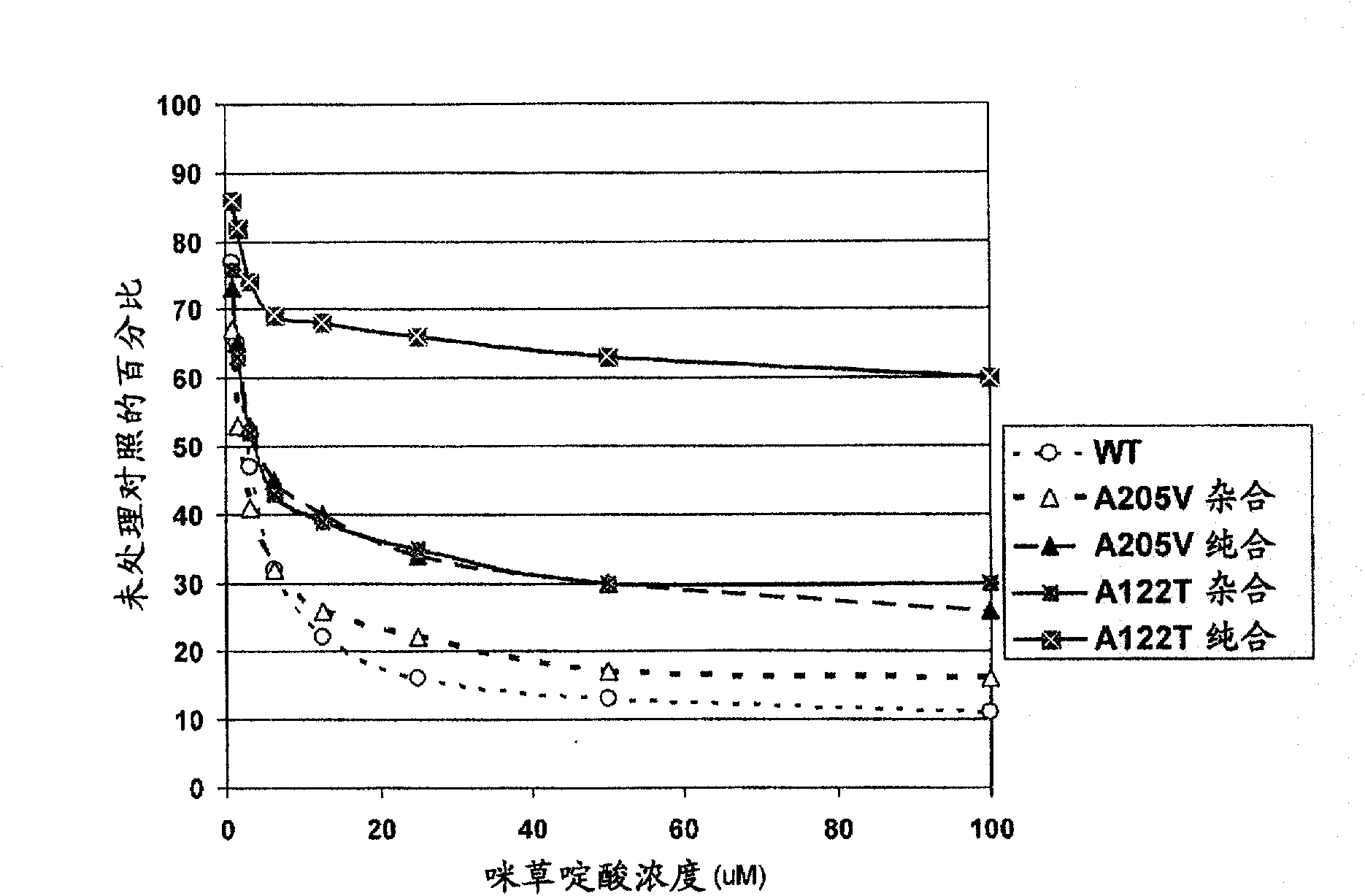
[0191] GM40 and GM1606 are mutant derived lines of sunflower that show a high level of tolerance to imidazolinones due to a point mutation at codon 122 of AHASL1 (Arabidopsis nomenclature) (WO2007005581 and Jul. 1, 2005 filed U.S. Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 60 / 695952). This demonstrates that the A122T mutation and derivative lines and hybrids homozygous for this mutation show better tolerance to imazamox than the known commercially available Clearfield sunflower homozygous for the A205V mutation on AHASL1 (WO2007005581) . Both mutants exhibit an incompletely dominant, sensitive allele relative to the wild type, as do many other examples in the literature. The present invention is based on the discovery that the A122T mutation exhibits near complete dominance over A205V for resistance to imidazolinones over the herbicide application range of 0.5X to 6X commerci...
Embodiment 2
[0195] Example 2: Response of homozygous A122T / A122T and A205V / A205V and heterozygous A122T / A205V events to imazapyr at the whole plant level
[0196] This experiment was performed to quantify and compare imazapyr in sunflower hybrids carrying the A122T and A205V mutations in homozygous (A122T / A122T or A205V / A205V) and heterozygous (A122T / A205V) states on different genetic backgrounds and at the whole plant level sensitivity.
[0197] Material
[0198] Seeds of different sunflower lines (Table 1) were obtained under field conditions.
[0199] Table 1. Sunflower materials utilized, their families, and types of mutation events.
[0200] the code
family lineage
Line (L) or Hybrid (H)
mutation event
L1
L
A205V
L2
L
A205V
H1
L1x L2
H
A205V
L3
cmsGM40
L
A122T
L4
L
A122T
H2
L3x L4
H
A122T
L5
BTK 47
L
Sensitive
H...
Embodiment 3
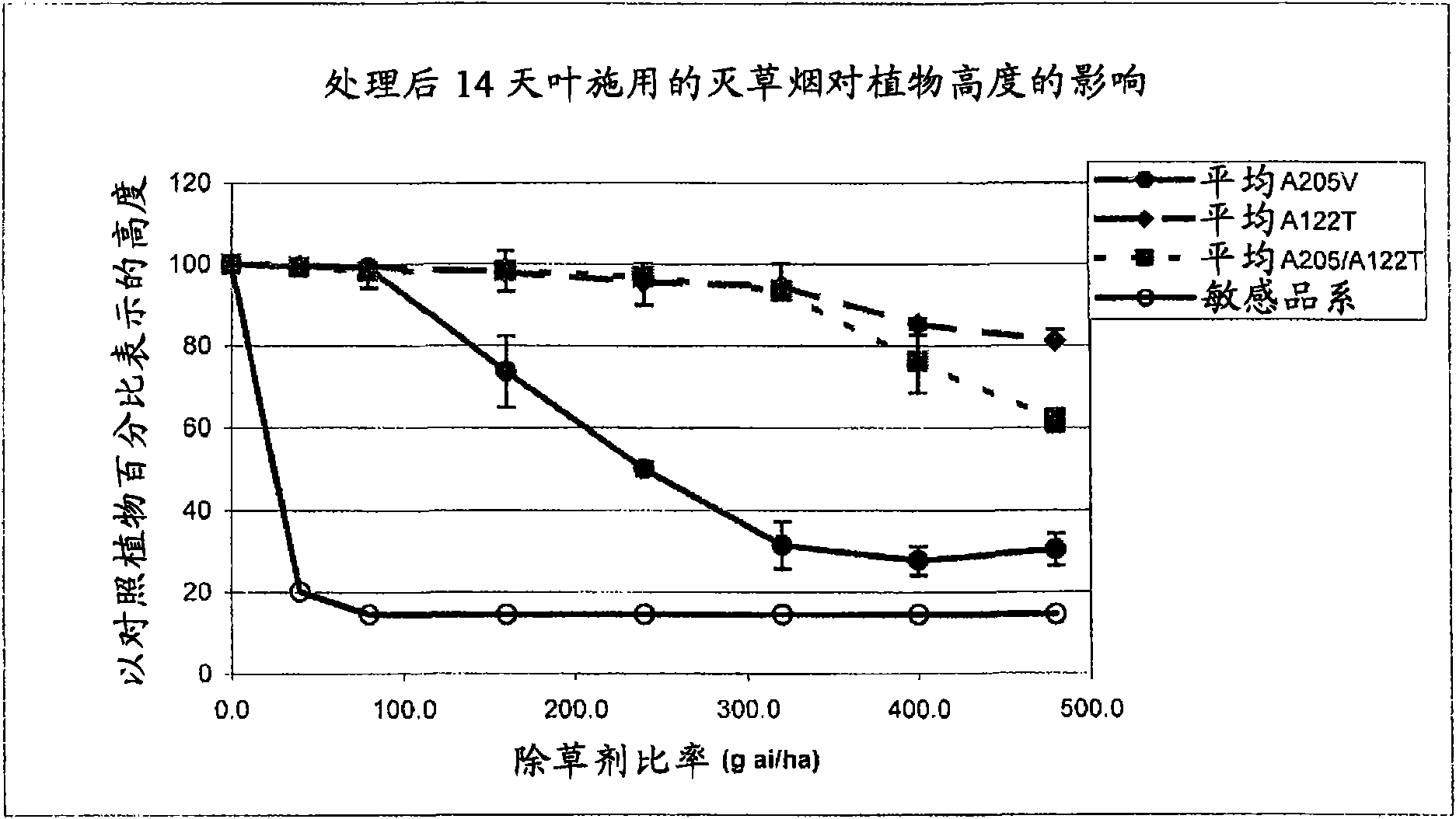
[0235] Example 3: Herbicide tolerance of A122T and A205V homozygous and heterozygous lines and two mutant heterozygous lines (A122T / A205V) under field conditions
[0236] This experiment was carried out under field conditions to compare the difference between the mutants carrying the A122T and A205V mutations in homozygous (A122T / A122T or A205V / A205V), heterozygous (A122T / - or A205V / -) and double stacked heterozygous (A122T / A205V) states. Herbicide tolerance of genotyped sunflower hybrids and lines.
[0237] Material
[0238] The sunflower materials used are listed in Table 5.
[0239] Table 5: Item List
[0240]
material type
mutation event
join
sex
product
project
illustrate
item
head
make up
Number
WT x IMI Restoration System
A205V
hybrid
bastard
1-hybrid
1
WT x IMI Restoration System
A205V
hybrid
bastard...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com