Granularity centering measuring method utilizing CCD (charge coupled device) or CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) as photoelectric detector
A photodetector, particle size technology, used in measuring devices, particle size analysis, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the complexity and cost of instruments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
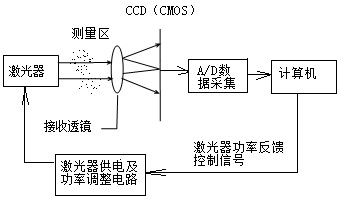
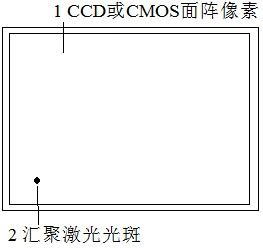
[0025] Depend on image 3 As shown, the area array CCD or CMOS is used as the multi-element photodetector, and the laser uses an adjustable power laser. The laser power supply and power adjustment circuit are connected to the laser. Output signal, control the laser power supply and power adjustment circuit to adjust the laser power according to the signal of CCD or CMOS, when the maximum output signal of all pixels of CCD or CMOS reaches slightly lower than saturation, such as reaching 95% of the saturation signal, stop adjusting the laser The computer records the output signal of CCD or CMOS, and according to the size of the output signal of each pixel of the recorded CCD or CMOS, determine the pixel point with the largest output signal as the position of the converging laser point, and use this as the spatial distribution of particle scattering light energy The central point is used as the basis for the following theoretical calculations, such as Figure 4 shown. Then add...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Depend on Figure 5 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the laser power is not automatically adjusted by the computer according to the signal size measured by the CCD or CMOS, but the operator manually adjusts the laser power to the most appropriate size. Adjusting the laser power manually can simplify the structure of the instrument, especially suitable for occasions requiring low-cost instruments.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com