Pixel structure
A pixel structure and pixel electrode technology, applied in optics, instruments, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced aperture ratio and reduced display quality of liquid crystal display devices, so that the aperture ratio will not be reduced, and the uneven brightness of the picture can be improved. Effects of Different Pixel Gate-Drain Parasitic Capacitance Cgd Different Problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
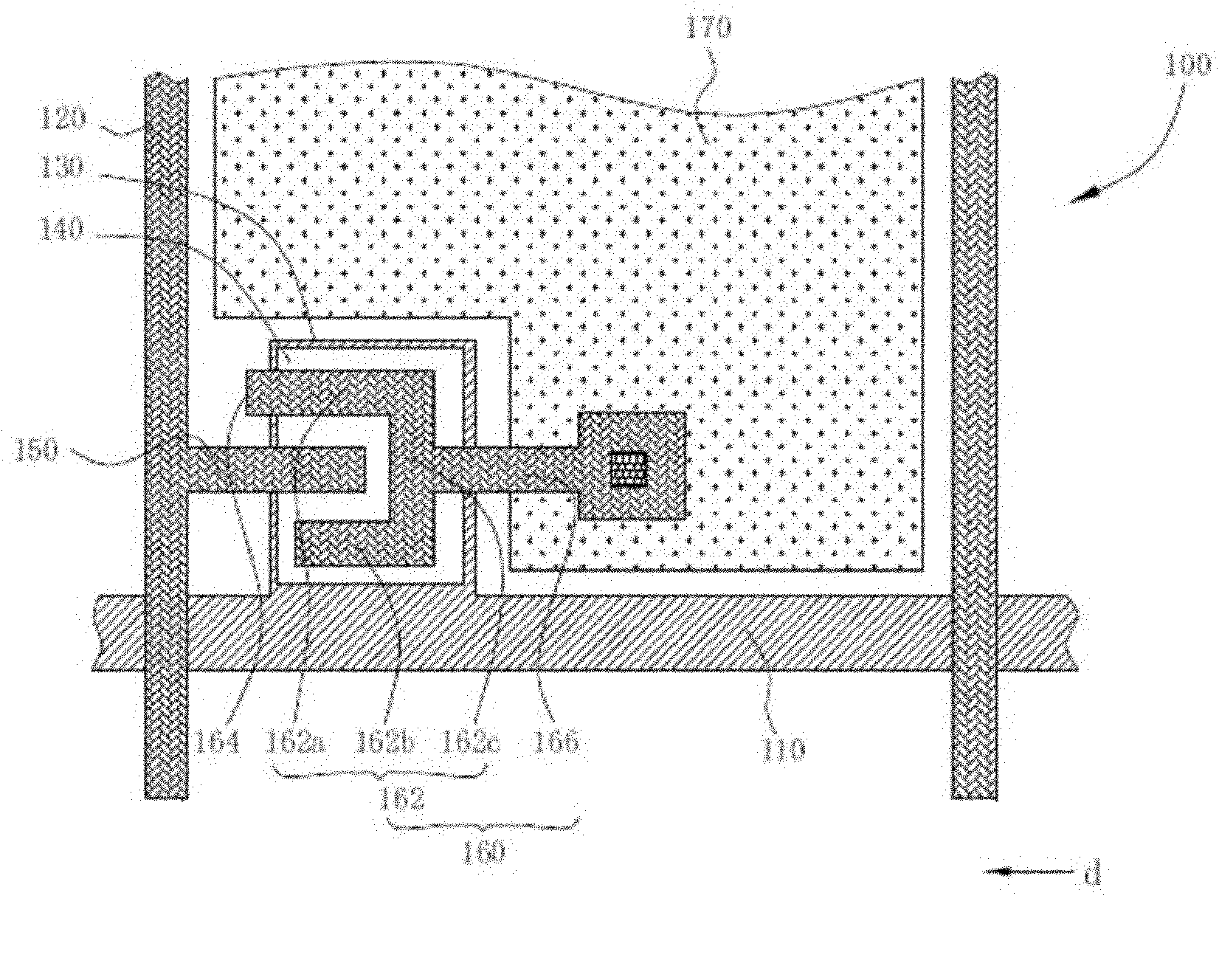
[0036] figure 2 is a partial top view schematic diagram of the pixel structure of the first embodiment of the present invention, please refer to figure 2 The pixel structure 200 includes a scan line 210 , a data line 220 , a gate 230 , a semiconductor layer 240 , a source 250 , a drain 260 and a pixel electrode 270 . The scan lines 210 and the data lines 220 intersect each other and are electrically insulated. The gate 230 and the scan line 210 are the first metal layer, and the gate 230 is electrically connected to the scan line 210 . The semiconductor layer 240 is located above the gate 230 . The data line 220 , the source 250 and the drain 260 are the second metal layer, and the source 250 is electrically connected to the data line 220 , and both the source 250 and the drain 260 are at least partially located on the gate 230 . In this embodiment, the gate 230 , the semiconductor layer 240 , the source 250 and the drain 260 can form a thin film transistor (not shown). ...
no. 2 example
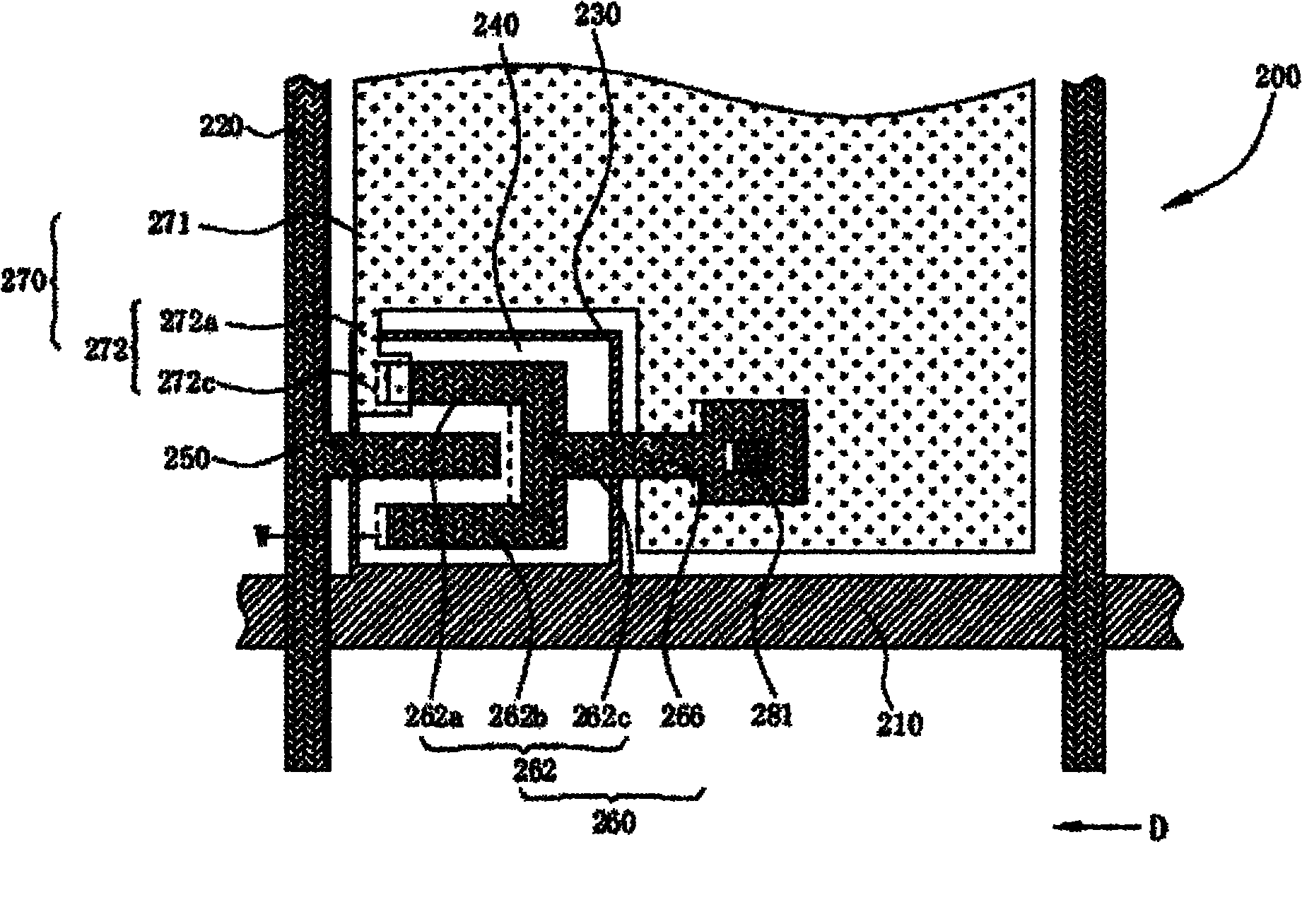
[0046] image 3 is a partial top view diagram of the pixel structure of the second embodiment of the present invention, image 3 The pixel structure and figure 2 The pixel structure is similar, so the same reference numerals represent the same components. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is the design of the drain 360 of the pixel structure 300 .
[0047] Specifically, the difference between the drain 360 of this embodiment and the drain 260 of the first embodiment is that the width W1 of the first branch 362a of the comb-shaped portion 362 is not equal to the width W3 of the connecting portion, and the relationship is satisfied: W1 is substantially 1.4 times of W3. When the width W1 of the first branch 362a and the width W3 of the connecting portion satisfy this relationship, it can be obtained that the variation of the parasitic capacitance between the gate 230 and the extension branch 272c is equal to the variation of the parasitic capacit...
no. 3 example
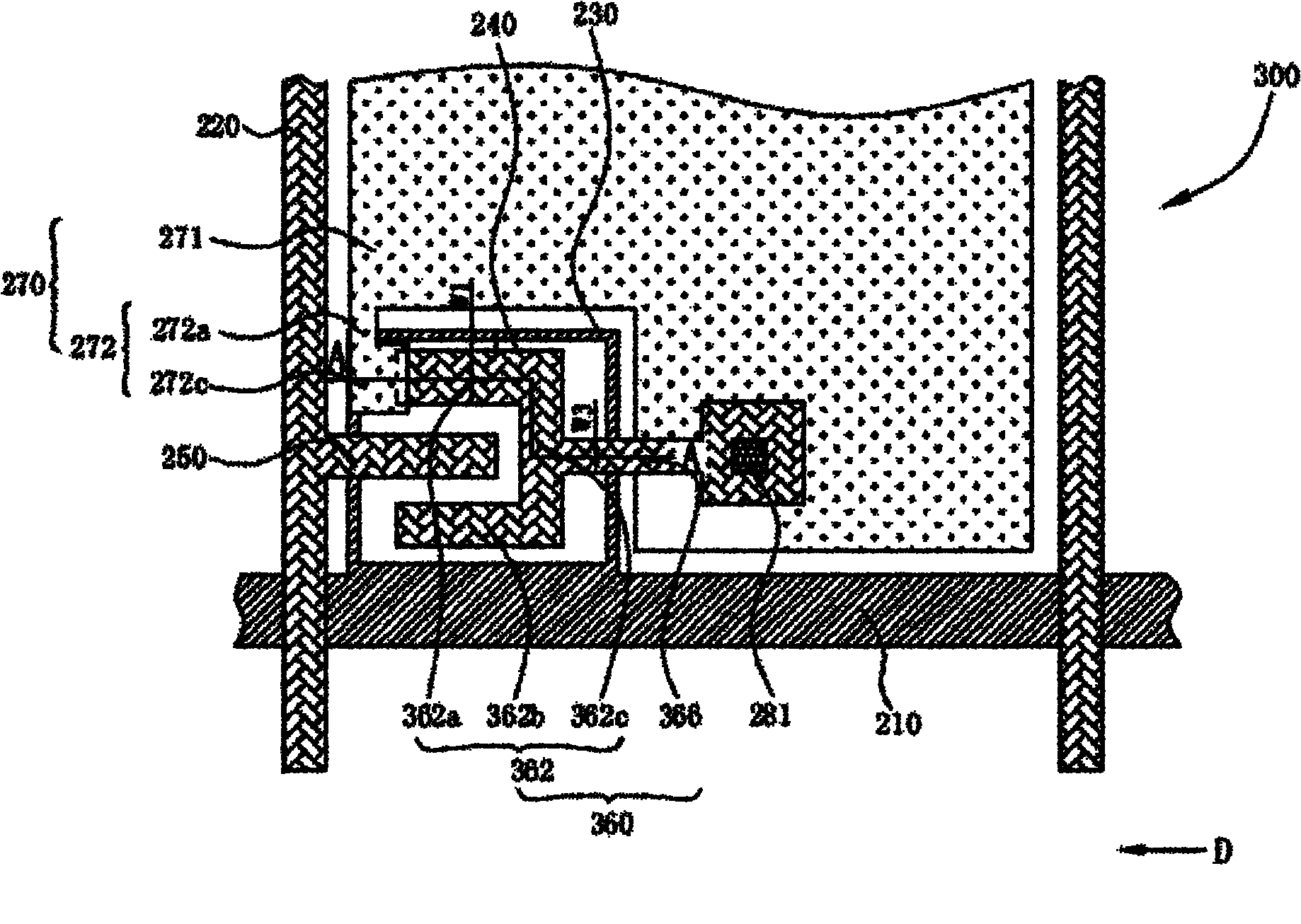
[0056] Figure 5 is a schematic partial top view of the pixel structure of the third embodiment of the present invention, Figure 5 The pixel structure and figure 2 The pixel structure is similar, so the same reference numerals represent the same components. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is the design of the pixel electrode 470 of the pixel structure 400 .
[0057] Specifically, the difference between the pixel electrode 470 of this embodiment and the pixel electrode 270 of the second embodiment is that the width W4 of the extension branch 472c of the pixel electrode 470 is smaller than the width W1 of the first branch 262a, and the overlapping portion of the extension branch 472c is completely placed Inside the first branch 262a, that is, the first branch 262a completely covers the extension branch 472c in the region of the overlapping portion. Likewise, the design of this embodiment can improve the difference in gate-drain parasitic capa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com