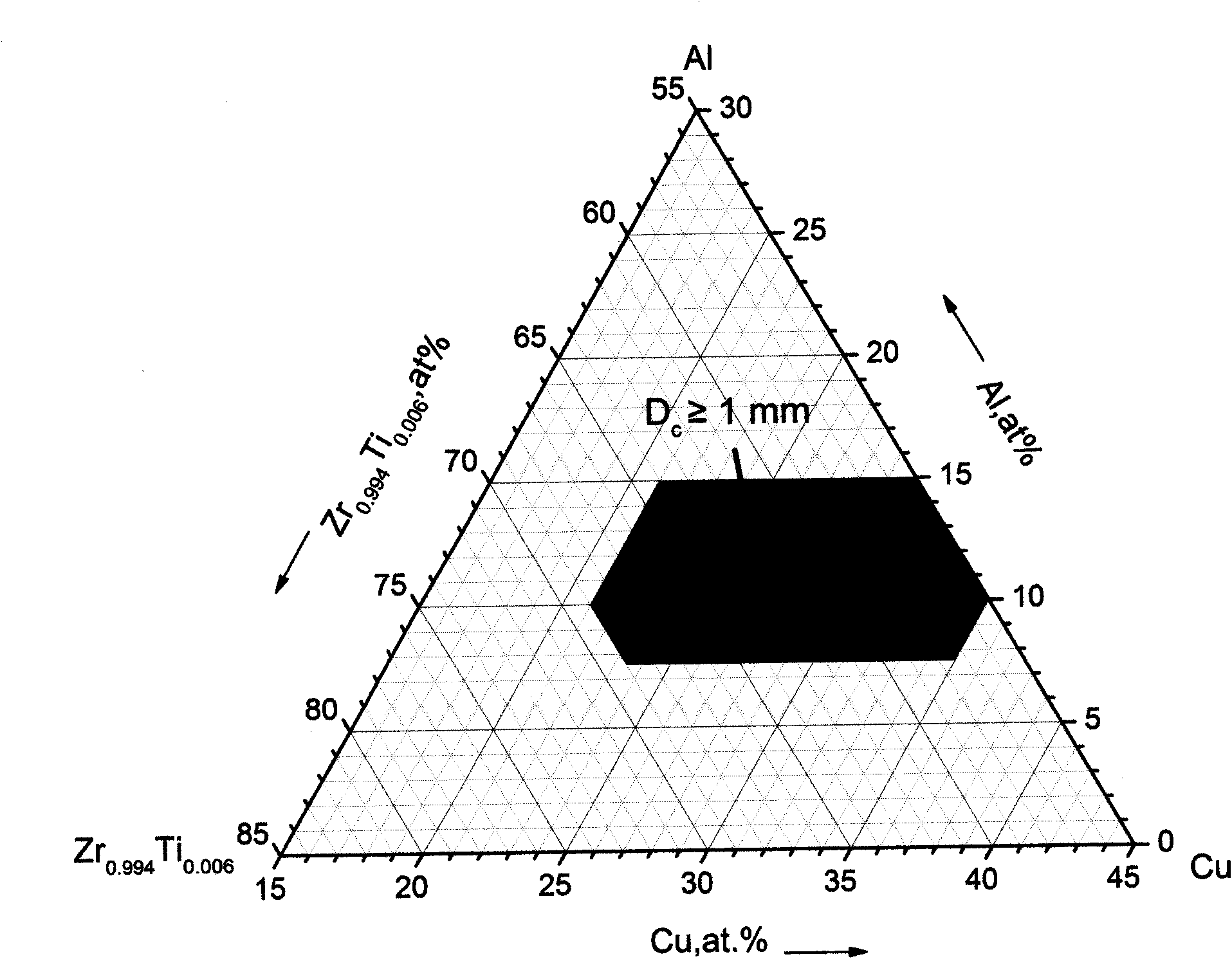
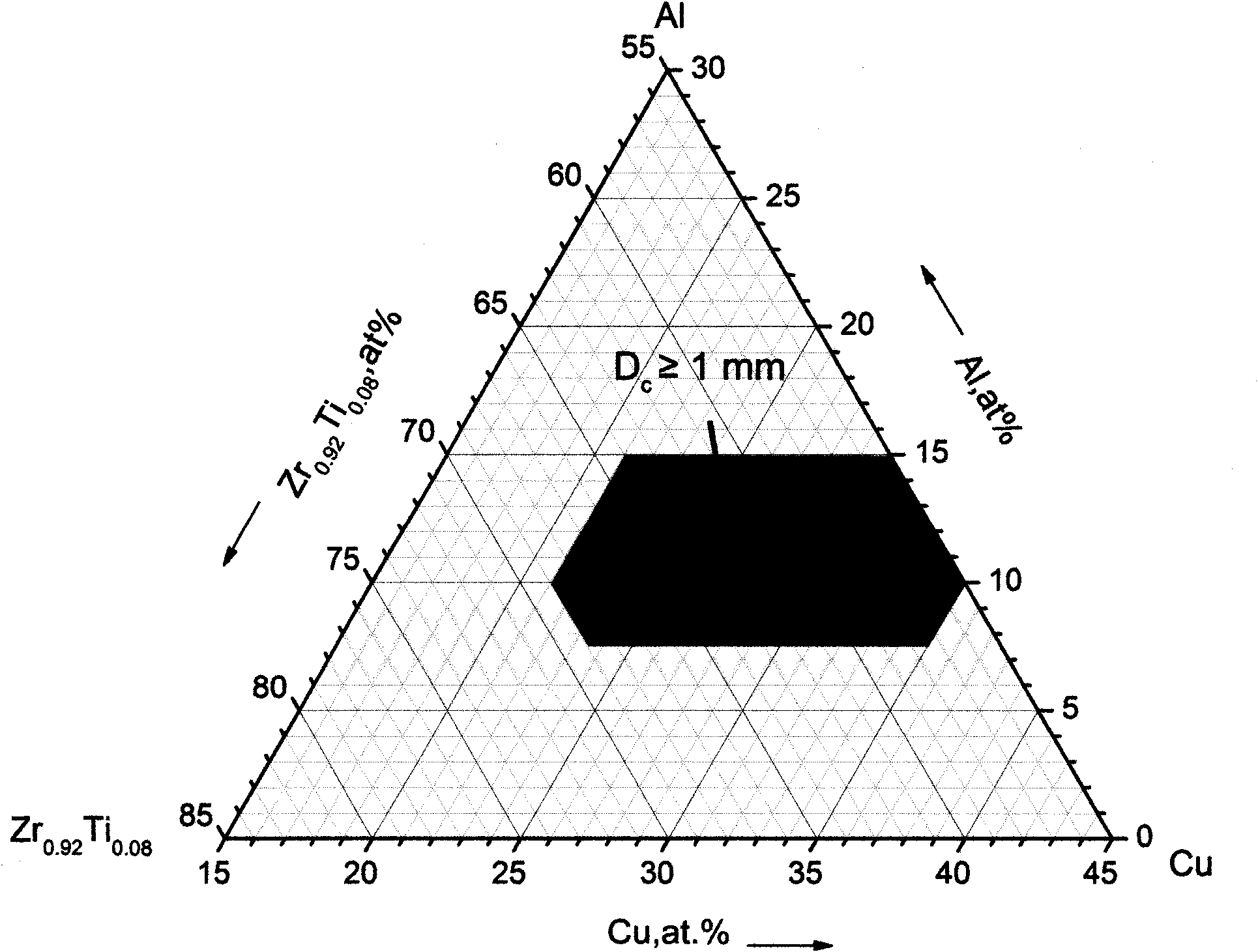
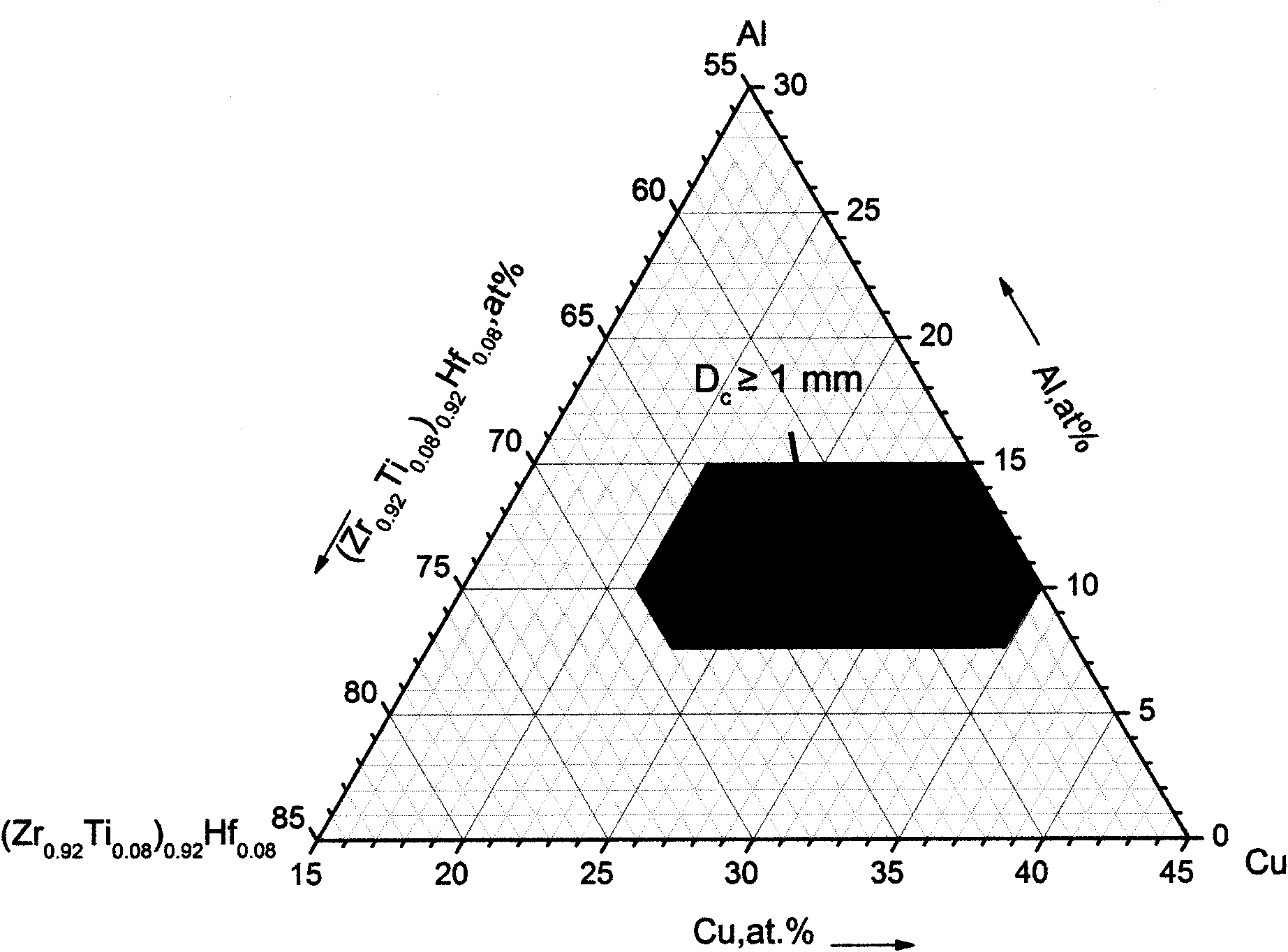
Nickel-free zirconium alloy with amorphous structure easily formed by pouring melt copper mould
A technology of amorphous and zirconium alloys, applied in the field of amorphous alloys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Casting Zr 60.9 Ti 2.1 Cu 25 Al 12 Alloy rods (nominal composition is atomic percentage, the same below)
[0039] Using commercially available pure metal Zr, Ti, Cu, Al elements such as rods, blocks, ingots, plates and other bulk materials (purity higher than 99.5%, weight percentage) as the starting material, arc in a titanium-purified argon atmosphere Smelted into quaternary master alloy ingots. The master alloy ingot needs to be smelted several times to ensure the uniformity of the composition. Take 55 grams of master alloy material and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible, heat it in an electric arc furnace to above the melting point, turn over the water-cooled copper crucible after melting, and pour the melt into a copper mold. The geometric shape of the inner cavity of the copper mold is φ10mm×110mm (different diameters and lengths or other geometric shapes can be selected according to needs). After the melt is cooled, a round rod with a dia...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Casting Zr 61.6 Ti 4.4 Cu 24 Al 10 Alloy bar
[0041] Using commercially available pure metal Zr, Ti, Cu, Al elements such as rods, blocks, ingots, plates and other bulk materials (purity higher than 99.5%, weight percentage) as the starting material, arc in a titanium-purified argon atmosphere Smelted into quaternary master alloy ingots. The master alloy ingot needs to be smelted several times to ensure the uniformity of the composition. Take 40 grams of master alloy material and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible, heat it in an electric arc furnace to above the melting point, turn over the water-cooled copper crucible after melting, and pour the melt into a copper mold. The geometric shape of the inner cavity of the copper mold is φ8mm×110mm (different diameters and lengths or other geometric shapes can be selected according to needs). After the melt is cooled, a round rod with a diameter of 8 mm and a length of 70 mm is formed. The cross-sec...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Casting Zr 58.46 Ti 2.02 f 2.52 Cu 25 Al 12 Alloy bar
[0043] Commercially available pure metal Zr, Ti, Cu, Al, Hf elements such as rods, blocks, ingots, plates and other bulk materials (purity higher than 99.5% by weight) are used as starting materials, in an argon atmosphere purified by titanium The lower electric arc is smelted into a five-element master alloy ingot. The master alloy ingot needs to be smelted several times to ensure the uniformity of the composition. Take 55 grams of master alloy material and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible, heat it in an electric arc furnace to above the melting point, turn over the water-cooled copper crucible after melting, and pour the melt into a copper mold. The geometric shape of the inner cavity of the copper mold is φ10mm×110mm (different diameters and lengths or other geometric shapes can be selected according to needs). After the melt is cooled, a round rod with a diameter of 10 mm and a lengt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com