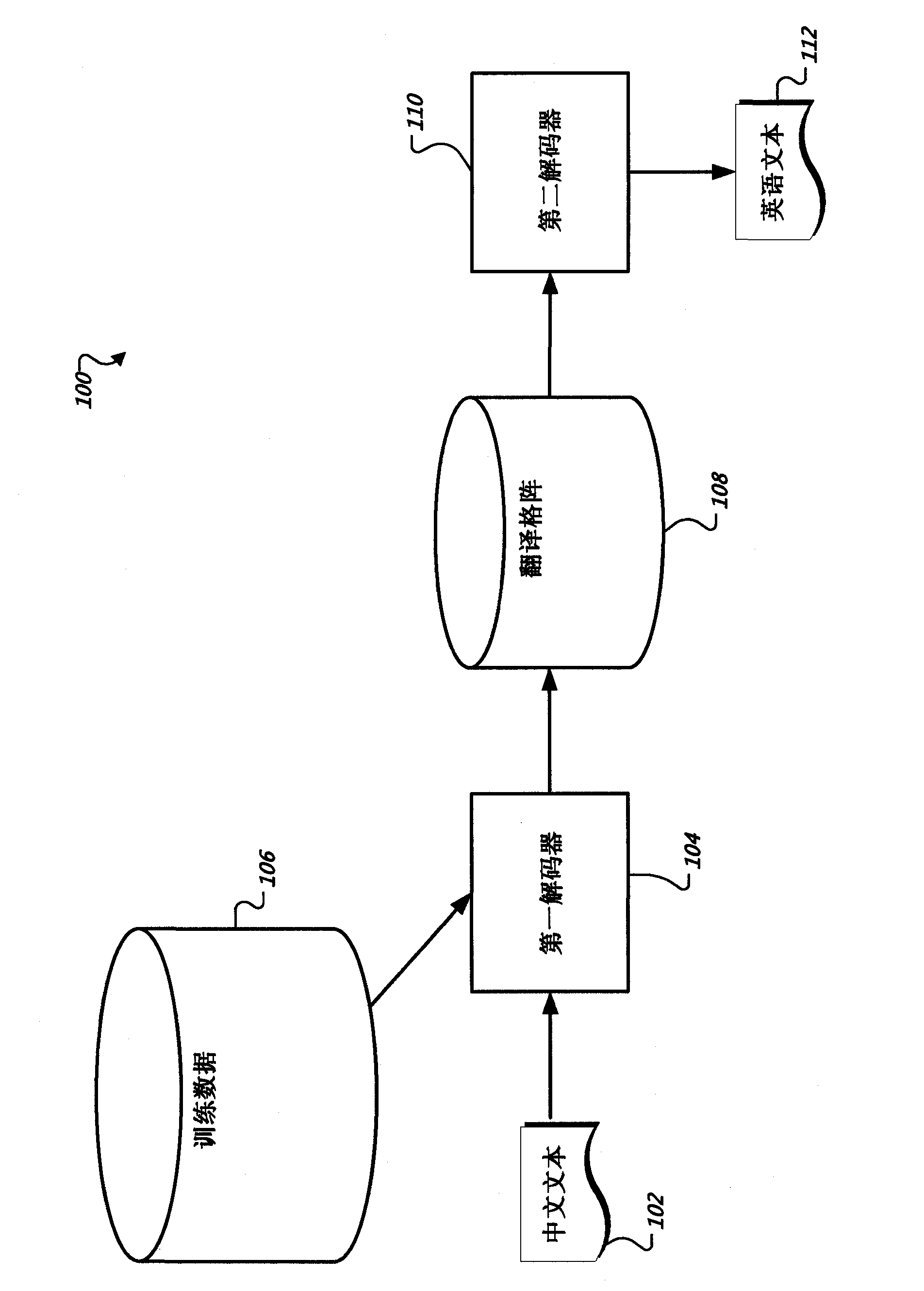
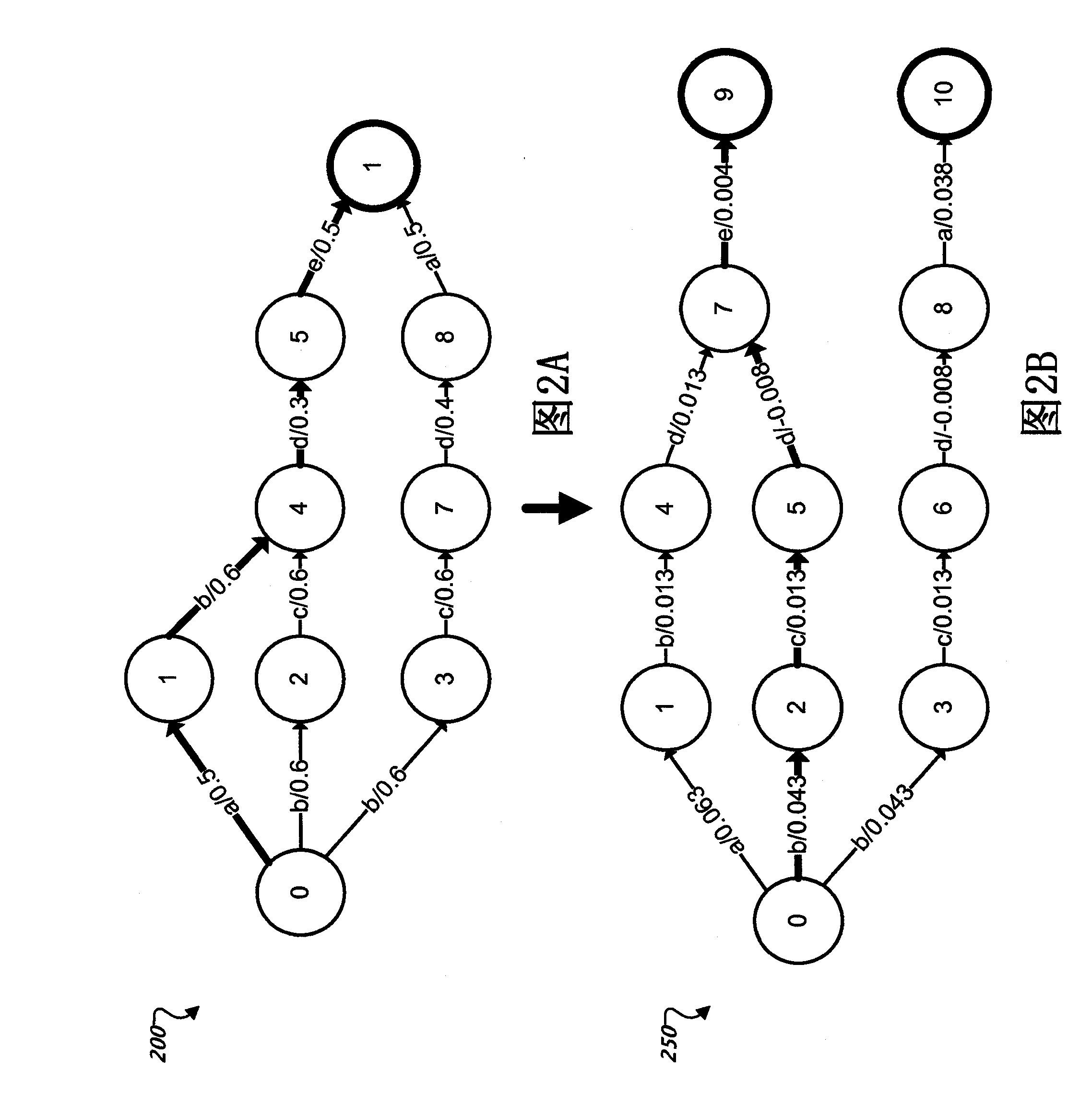
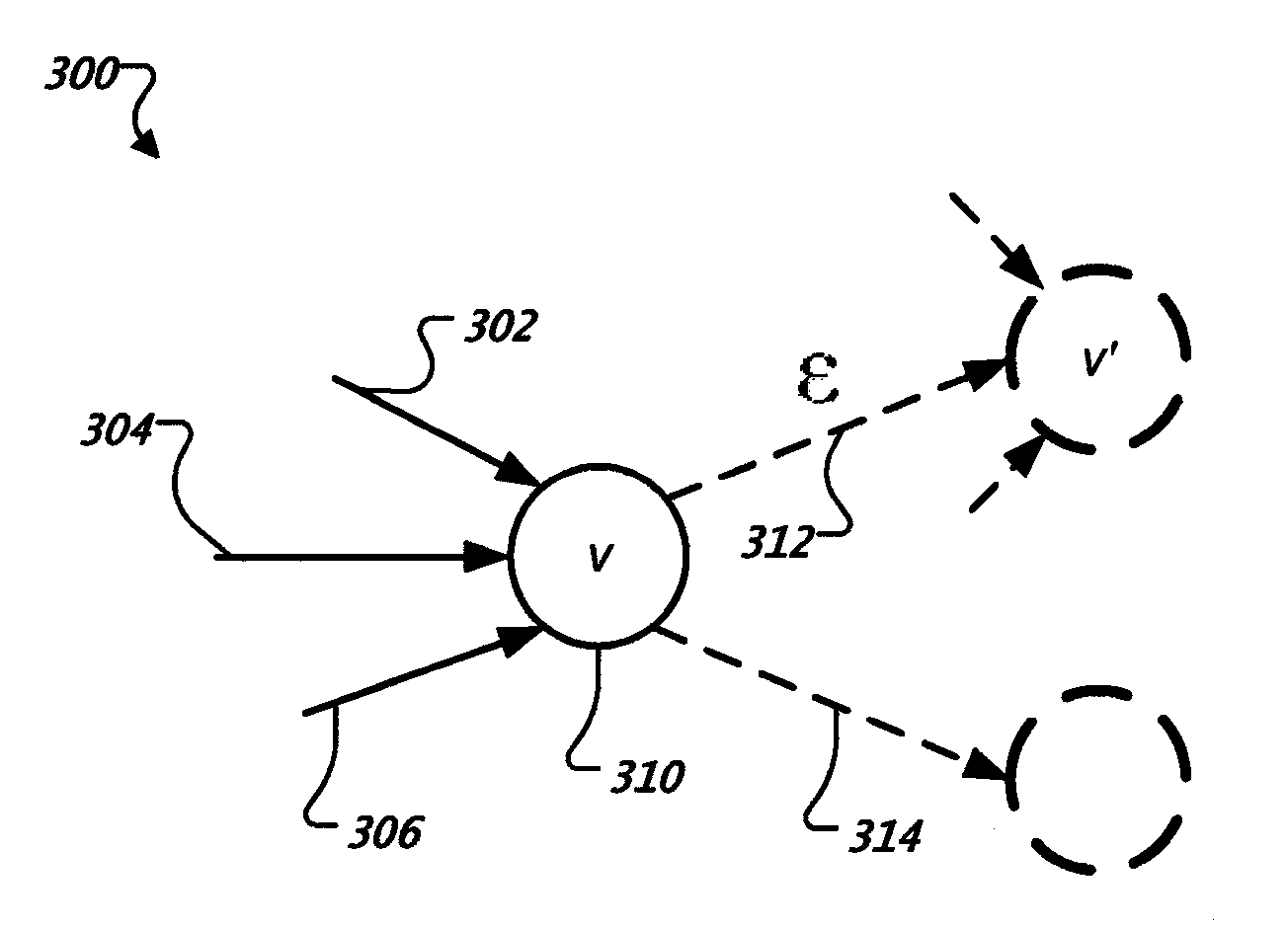
Optimizing parameters for machine translation
A technology based on users and times, applied in natural language translation, program control using stored programs, instruments, etc., can solve time-consuming and costly problems, achieve efficient running time, increase flexibility, and increase the number of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
[0125] Other implementations are possible. In particular, additional refinements can be performed to improve the performance of MERT (for lattices). For example, to prevent linear optimization techniques from getting stuck at poor local optima, MERT can explore additional starting points chosen randomly by sampling the parameter space. As another example, the range of weights for some or all feature functions can be limited by defining weight constraints. In particular, for the characteristic function h m The weight constraints for can be specified as the interval
[0126] R m =[l m , r m ], l m , r m ∈R∪{-∞,+∞}, which defines the feature function weight λ m The tolerance region from which to choose. If linear optimization is performed subject to weight constraints, γ is chosen such that:
[0127] l 1 M ≤ λ 1 M + γ · d 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com