Idle node assistance method for P2P (peer-to-peer) file transmission
A technology for idle nodes and file transmission, applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as network upload bandwidth bottlenecks, idle upload bandwidth and download bandwidth, small upload bandwidth, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
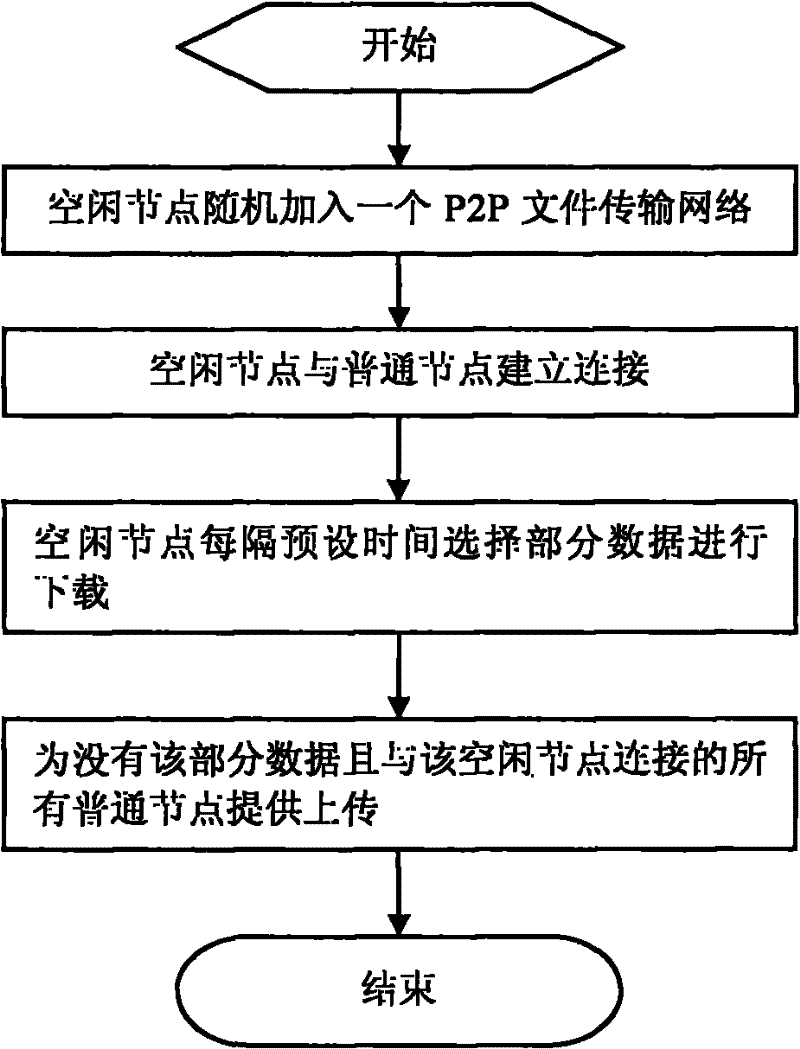
[0043] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the idle node selects a chunk for downloading and uploading.
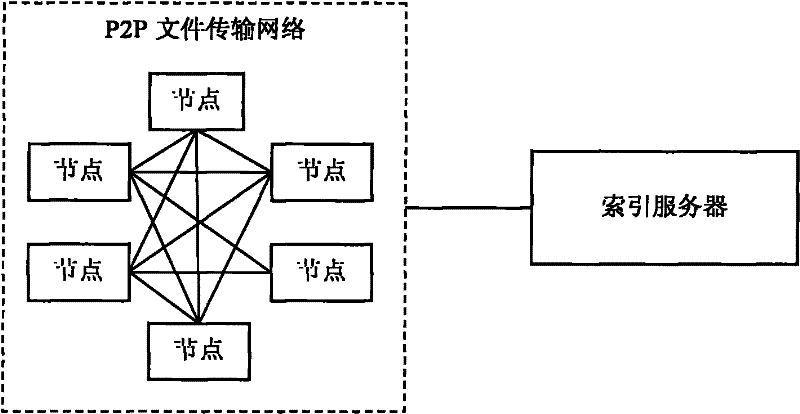
[0044] After an idle node establishes a connection with an ordinary node, a node list is used to record the information of all ordinary nodes connected to the idle node, and all ordinary nodes connected to the idle node are called the neighbor nodes of the idle node. And use a bitmap (bitmap) to record the situation that all the neighbor nodes of the idle node have chunks, and each neighbor node corresponds to a bitmap.
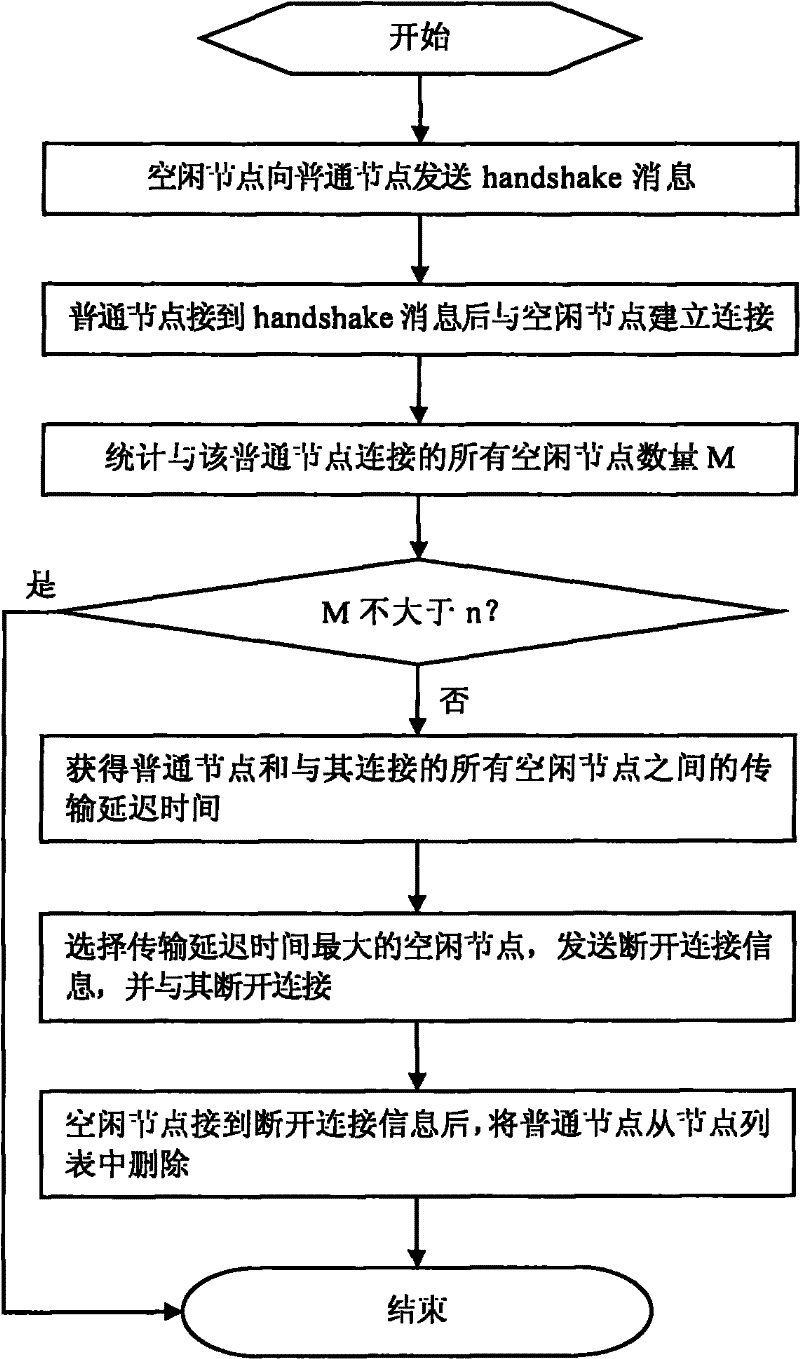
[0045] When the connection relationship between idle nodes and ordinary nodes changes, update the node list. For example, when an idle node receives a disconnection message sent by an ordinary node, it deletes the ordinary node from its node list, such as image 3 and Figure 4 shown. When the status of the chunk owned by the neighbor node of the idle node changes, the change information is sent to the idle node, and the idle node changes ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Such as Figure 6 As shown, in this embodiment, the idle node selects the last piece of a chunk for downloading and uploading. Since a piece is the smallest unit of data transmission between nodes, the nodes download the pieces in the chunk sequentially, so if a chunk is not recorded in the bitmap of a node, there must be no last piece of the chunk. The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0051] Every 10 seconds, each idle node performs a chunk selection. After receiving the request from the idle node, the normal node sends the last piece of the requested chunk to the idle node. After receiving the piece, the idle node directly sends the piece to the neighbor node that lacks the chunk by means of "push".
Embodiment 3
[0053] Such as Figure 7 As shown, in this embodiment, an idle node selects a piece for downloading and uploading.
[0054] After an idle node establishes a connection with an ordinary node, it uses a node list to record the information of each ordinary node connected to it, and all ordinary nodes connected to the idle node are called the neighbor nodes of the idle node. And use bitmap (bitmap) to record the data download situation of all neighbor nodes of this idle node, each neighbor node corresponds to a bitmap.
[0055] When the connection relationship between idle nodes and ordinary nodes changes, update the node list. When the status of the neighbor nodes of the idle node owning the piece changes, the change information is sent to the idle node, and the idle node changes the status of the neighbor node owning the piece.
[0056] Every 20-second period, each idle node performs a piece selection. From all the pieces that have not been downloaded yet, select a piece that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com