Method for choosing tasks by foresight
A technology for tasks and task groups, applied in the direction of multi-programming devices, etc., can solve the problems of increasing task scheduling problem scale, troublesome conflict identification and resolution rules, large problem scale, etc., achieving good versatility and flexibility, resolving conflict judgments With trade-offs, the effect of satisfying the time complexity of the algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
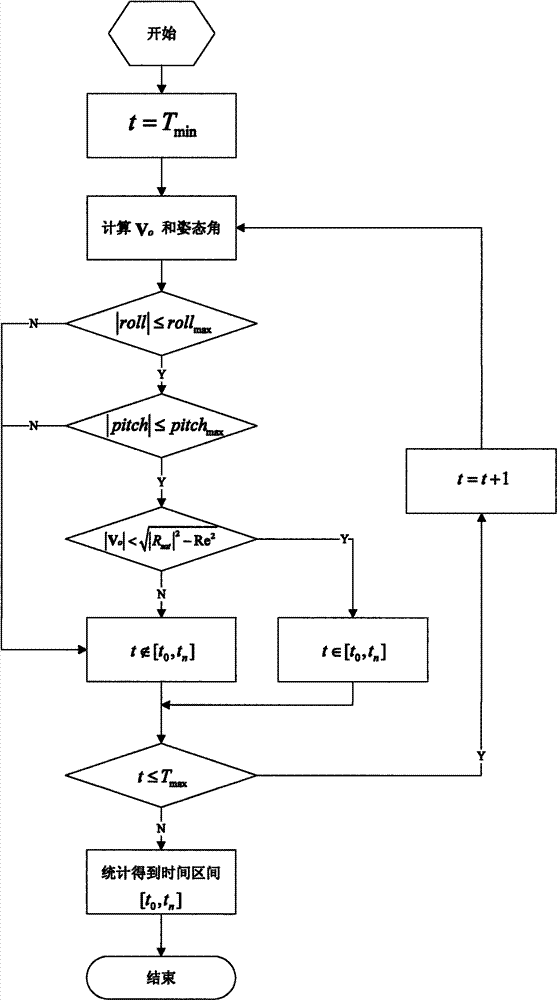
[0114] Consider a fast attitude maneuvering imaging satellite operating in a sun-synchronous circular orbit. At 00:00:00.000 UTC on July 26, 2009, the instantaneous root number is 7051.2km, the orbital inclination is 97.3087°, and the right ascension of the ascending node is 249.758°, latitude argument 0°. The satellite attitude maneuver range is ±45° in the pitch direction and roll direction, and the attitude control capability is 0° for 5s, 15° / 25s, 30° / 35s, and 45° for 5s.
[0115] The geographic latitude and longitude information of the target is shown in Table 1, and the longitude and latitude of the four vertices of each target correspond one by one in order.
[0116] Table 1 Target geographic longitude and latitude
[0117]
[0118]
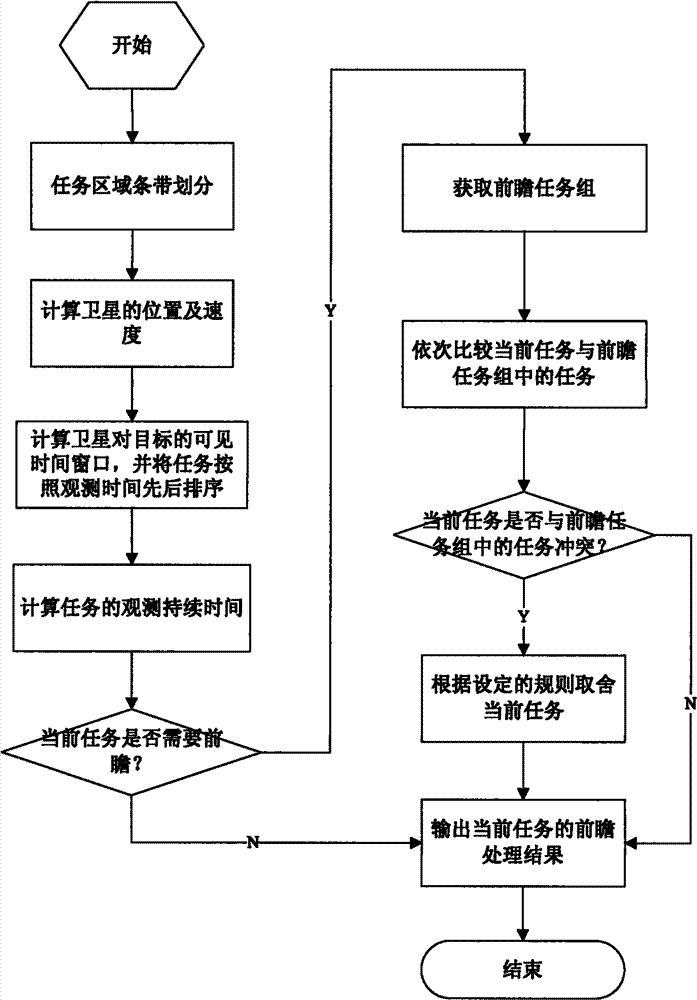
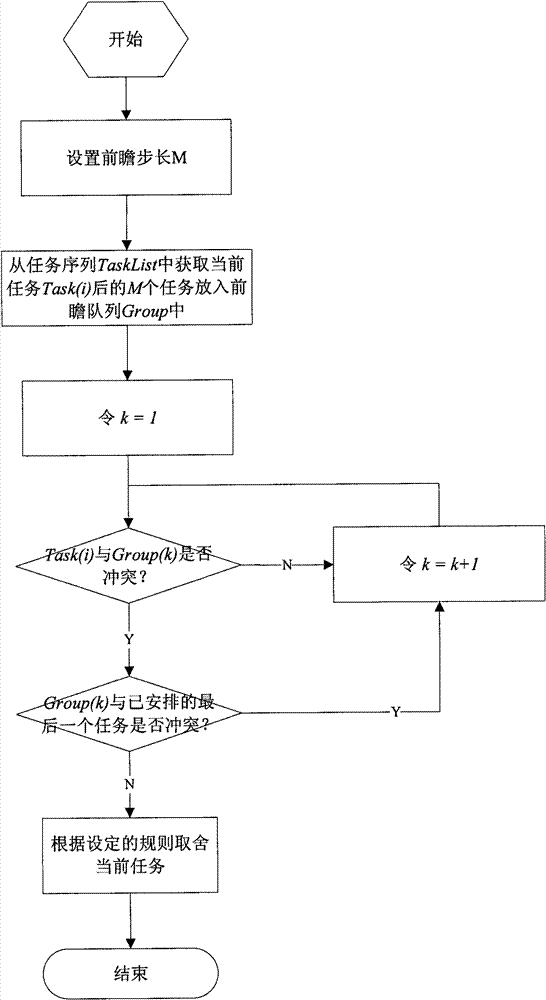
[0119] The steps of the method of choosing tasks through the look-ahead are as follows:
[0120] (1) Task area strip division
[0121] According to the camera width, the longitude and latitude of the mission area, and the satellit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com