Data transmission method and device in wireless network
A data transmission method and a wireless network technology, which are applied in the field of data transmission methods and devices, can solve the problems of user terminal interference served by micro base stations, large difference in transmission power between macro base stations and micro base stations, etc., so as to avoid interference and improve transmission performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
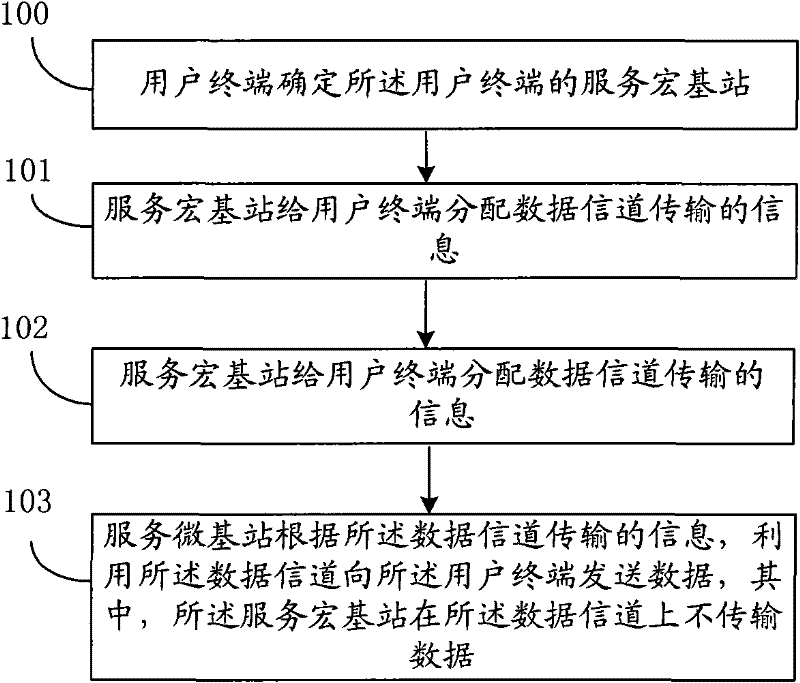
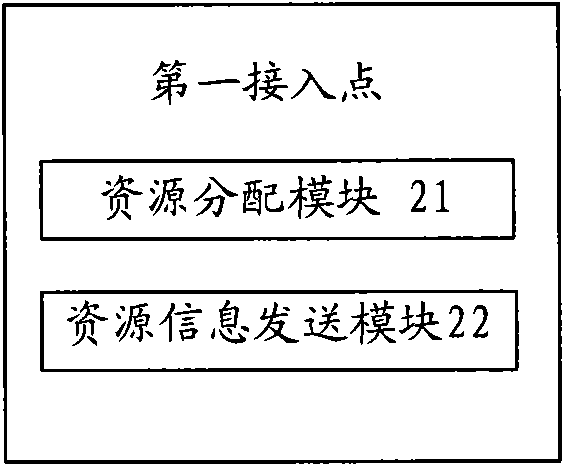
[0027] In the embodiment of the present invention, the first access point in the wireless network sends the information transmitted on the data channel allocated to the user terminal to the second access point, and the first access point does not transmit information on the data channel data.
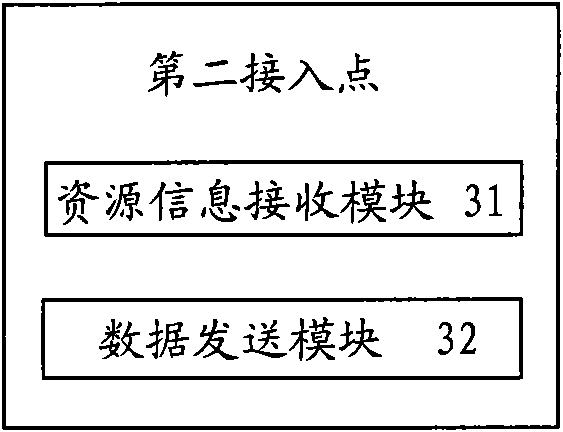
[0028] The second access point uses the data channel to send data to the user terminal according to the information transmitted by the data channel allocated to the user terminal.
[0029] In practical applications, the foregoing wireless network may be a heterogeneous network or a homogeneous network.
[0030] In practical applications, the first access point may be a macro base station, a micro base station, a home base station, a relay station, etc., and the second access point may be a macro base station, a micro base station, a home base station, a relay station, and the like.
[0031] In a practical application, the above user terminal may be an LTE user equipment or an LTE-A use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com