A hs-dsch capacity allocation method
A capacity allocation and user technology, applied in network traffic/resource management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as different quality of HS-DSCH shared channel air interface, different cache volume, different service signing rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] In order to make the purpose, technical means and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
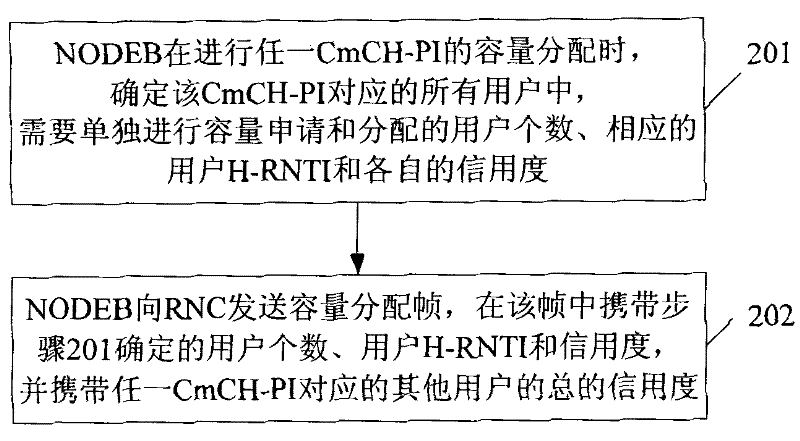
[0019] figure 2 It is a specific flowchart of the capacity allocation method in the present invention. like figure 2 As shown, the method includes:
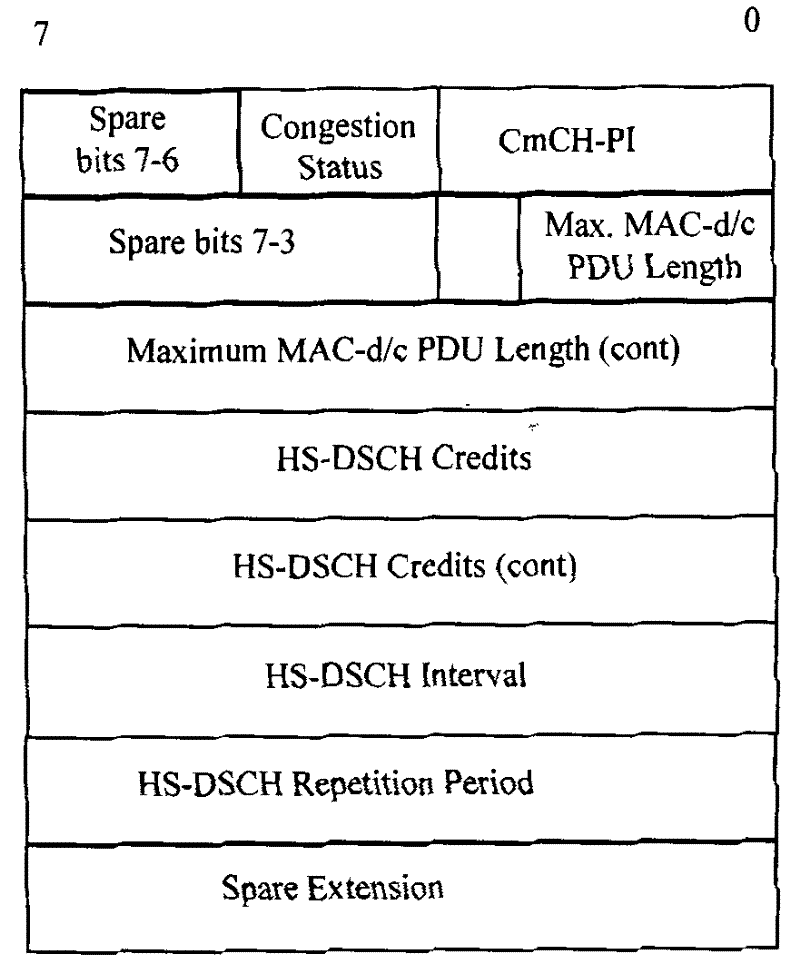
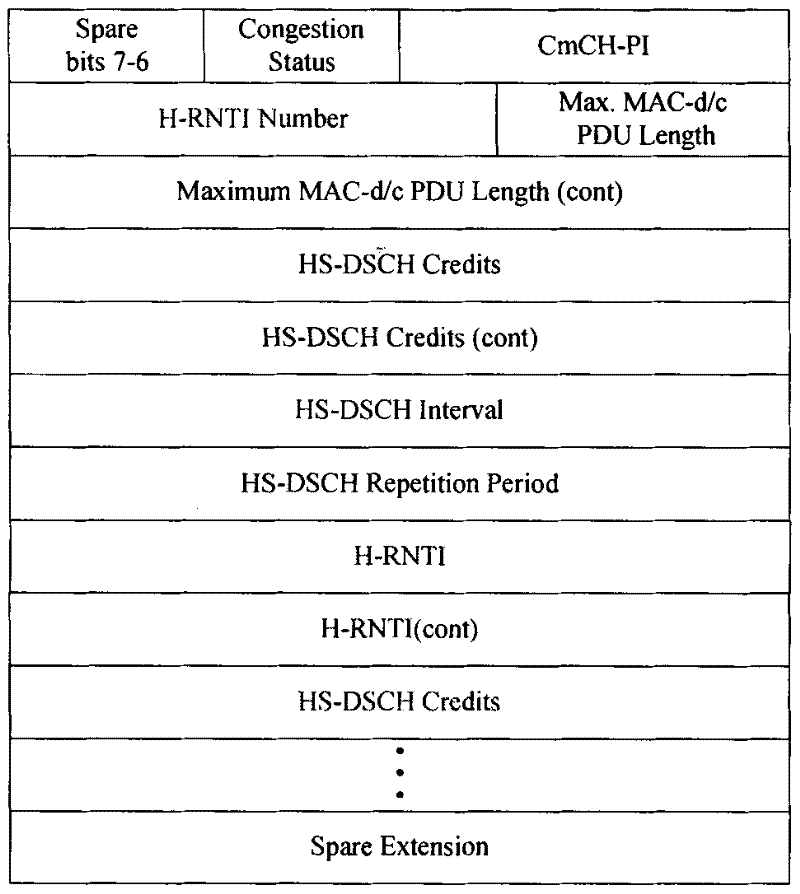
[0020] Step 201, when NODEB performs capacity allocation of any CmCH-PI, it determines the number of users that need to perform capacity allocation separately, the corresponding user identification (H-RNTI) and their respective credits among all users corresponding to the CmCH-PI .
[0021] As mentioned in the background technology above, when the air interface quality of a certain UE is not good or the downlink data of a certain UE has accumulated in the NODEB cache and reaches a certain threshold, the NODEB may want the RNC to reduce / stop the specific The downlink data transmission of the UE, instead of adoptin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com