Zooming lens, optical apparatus and method of manufacturing zooming lens
A zoom lens and focal length technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increased variation and inability to obtain optical performance, and achieve good optical performance, suppress variation, phantom and stray light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0084] A zoom lens according to a first embodiment of the present application is described below.
[0085] The zoom lens according to the first embodiment of the present application includes, in order from the object side along the optical axis, a first lens group having positive refractive power, a second lens group having negative refractive power, and a lens group having positive refractive power. Power of the third lens group. When zooming from the wide-angle end state to the telephoto end state, the distance between the first lens group and the second lens group increases, and the distance between the second lens group and the third lens group decreases. With this configuration, it becomes possible to realize an optical system capable of zooming, and at the same time suppress a change in distortion generated upon zooming.
[0086] In the zoom lens according to the first embodiment, the first lens group includes the positive lens A satisfying the following conditional exp...
example 1
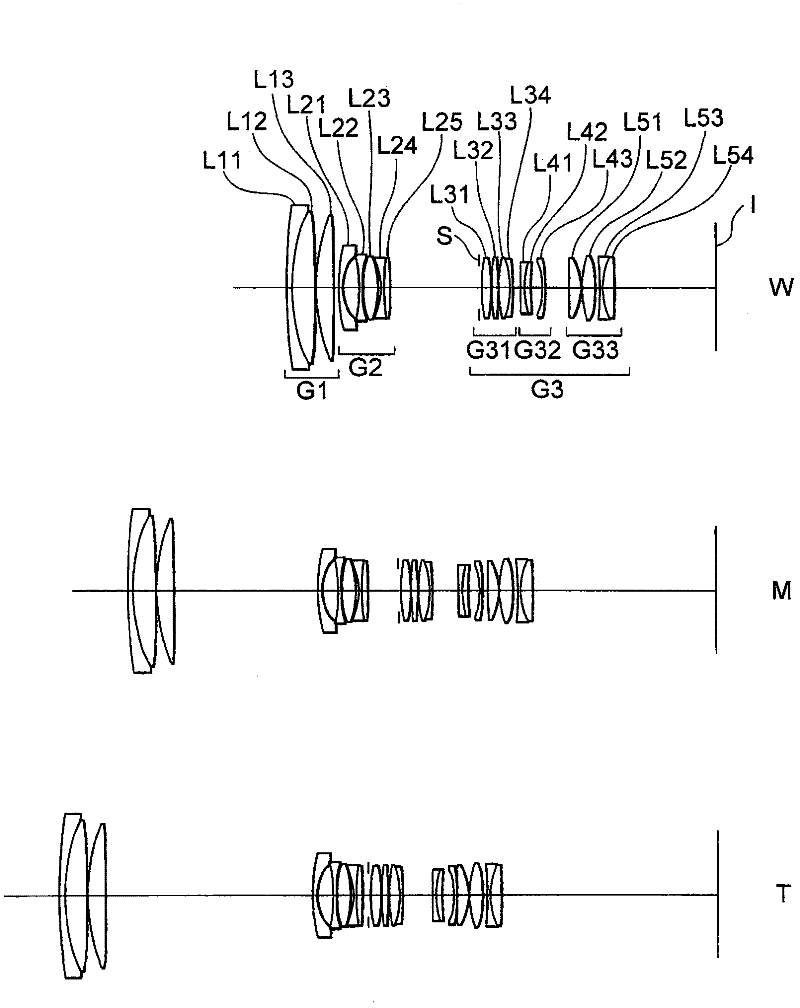
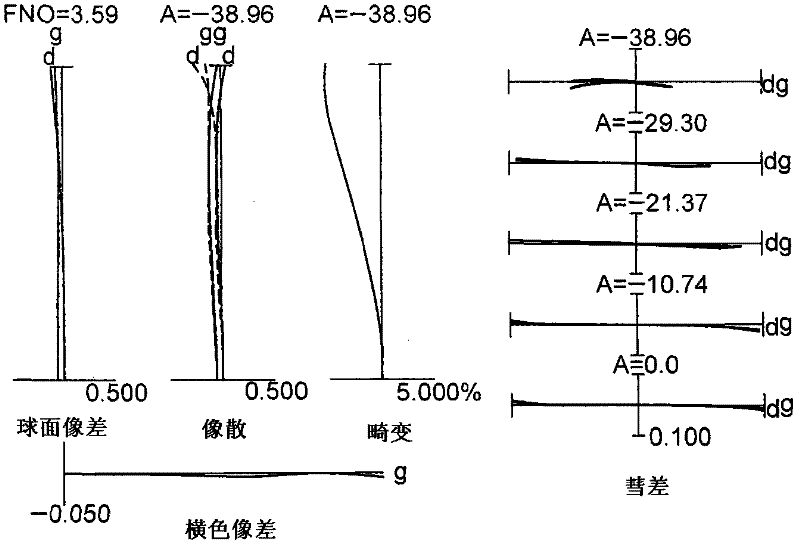
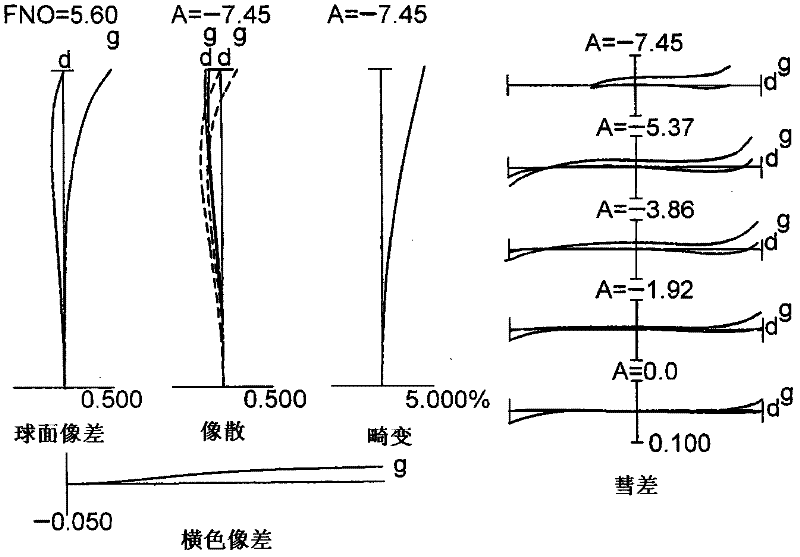
[0255] figure 1 is a sectional view showing the lens configuration of the zoom lens according to Example 1 of the first embodiment of the present application.
[0256] like figure 1 As shown in , the zoom lens according to Example 1 of the first embodiment is composed of, in order from the object side along the optical axis: a first lens group G1 having positive refractive power, a first lens group G1 having negative refractive power, The second lens group G2 with positive refractive power and the third lens group G3 with positive refractive power. The third lens group G3 is composed of, in order from the object side along the optical axis: a front lens group G31 having positive refractive power, an intermediate lens group G32 having negative refractive power, and a front lens group G32 having positive refractive power. Power of the rear lens group G33.
[0257] When zooming from the wide-angle end state to the telephoto end state, with respect to the image plane I, the fir...
example 2
[0287] Figure 4 is a sectional view showing the lens configuration of the zoom lens according to Example 2 of the first embodiment of the present application.
[0288] like Figure 4 As shown in , the zoom lens according to Example 2 of the first embodiment is composed of, in order from the object side along the optical axis: a first lens group G1 having positive refractive power, a first lens group G1 having negative refractive power, The second lens group G2 with positive refractive power and the third lens group G3 with positive refractive power. The third lens group G3 is composed of, in order from the object side along the optical axis, a front lens group G31 having positive refractive power and a rear lens group G32 having positive refractive power.
[0289] When zooming from the wide-angle end state to the telephoto end state, with respect to the image plane I, the first lens group G1 moves monotonously toward the object side, the second lens group G2 moves monotonic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com