In-situ steering wheel type robot base mechanism
A wheeled robot and in-situ steering technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and complexity, high synchronization requirements, large turning radius, etc., and achieve low cost and smooth trajectory Precise, dead angle reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
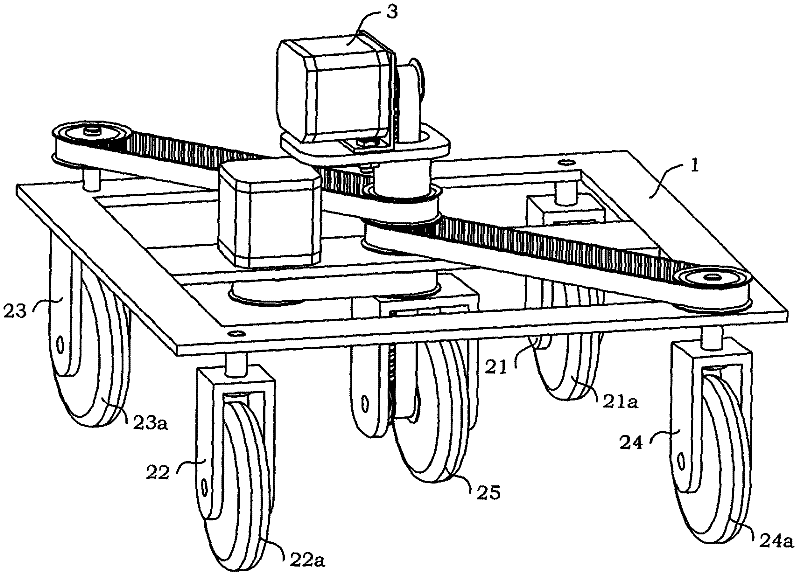
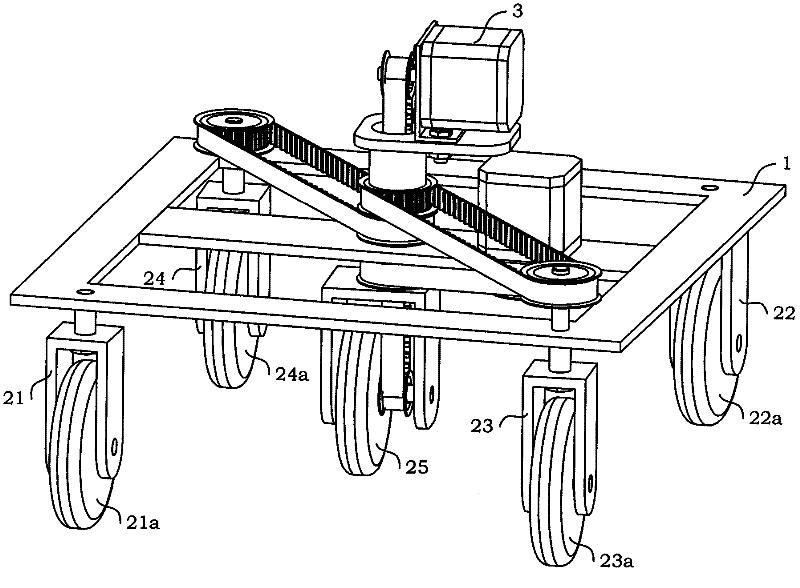
[0060] see figure 1 , Figure 1A As shown, a wheeled robot base mechanism with in-situ steering of the present invention includes three parts: a frame assembly 1, a wheel train assembly, and a steering and moving assembly 3, and the wheel train assembly is installed on the frame assembly 1 Below, the robot carrier is installed above the frame assembly 1. The steering and moving assembly 3 is placed inside the robot carrier.
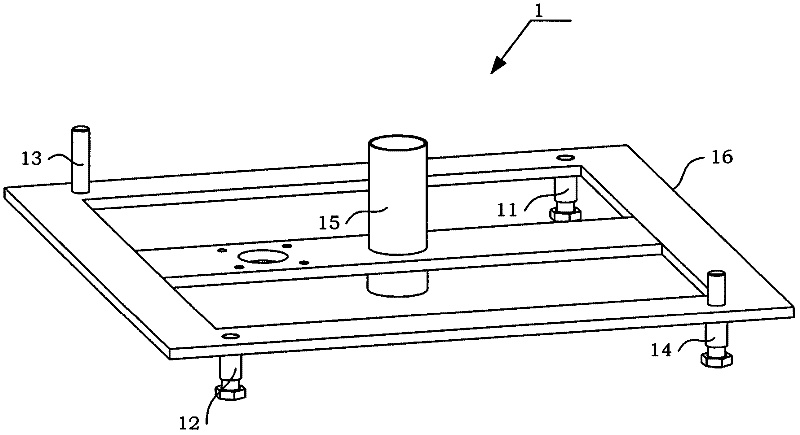
[0061] (1) Rack assembly 1
[0062] see figure 2 , Figure 2A As shown, the frame assembly 1 includes an A adapter 11 , a B adapter 12 , a C adapter 13 , a D adapter 14 , a steering shaft 15 and a quadrilateral frame 16 .
[0063] The middle part of quadrangular frame 16 is provided with middle beam 165, and this middle beam 165 is provided with central through hole 165a and motor shaft through hole 165b; E angular contact bearing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com